If we take the total number of orthopedists, approximately 70% of them specialize in knee and hip joints. 20% on the shoulder joints, and the remaining 10% on the elbows. That is, there are very few specialists who can not only pump out fluid from the cavity of the joint capsule, but also carry out the most complex surgical intervention. To find an expert with experience you need to try. We have such specialists in our arsenal, and as practice shows, their opinions and methods of treatment are positively assessed throughout the medical community.
A number of problems of the elbow joint, injuries and some diseases in the later stages are treated exclusively with surgery. There are several such treatment methods:
- Arthroplasty;
- Open repository;
- Stitching of ligaments;
- Endoprosthetics;
- Transposition.
There are two more types that relate to both therapeutic and diagnostic, one of them is puncture, i.e. fluid sampling, and the second arthroscopy - instrumental examination from the inside.
Arthroplasty
Similar effects are often carried out at the joints of the ends of bones. They represent the modeling of the joint to natural forms. If the patient complies with all the requirements of the rehabilitation medicine doctor, then the probability of a positive outcome is almost 100%.
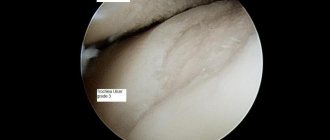
The result of the operation on x-ray.
Indications are fibrous and bone ankylosis. With this deviation, the joint partially or completely loses mobility due to pathological changes. The causes of destruction are often arthritis, trauma, and arthrosis. With multiple fragmentations of the elements included in the connection, reconstruction becomes impossible. In this case, the fragments are removed, and the missing part is filled with artificial or the patient’s own tissues.
The elbow joint is able to move normally and function only if all its components have natural sizes and shapes. The technique is aimed at performing precisely this task. Today they produce ready-made plates that cover the surface of the affected joint. They are made from medical alloys or polymers. Special pastes and mixtures are also used to coat the compound. These products penetrate into the pores and gaps and harden there.
Rehabilitation after elbow surgery
The difficulty of restoring the function of the elbow joint after injury or surgery is determined to a large extent by the complexity of its anatomical structure and special reactivity.
The increased reactivity of the elbow joint to external irritation can be partially explained by the peculiarities of its innervation.
The moment of onset of movement in the elbow joint is determined by the location of the fracture, its nature, the severity of reactive changes, the nature of the surgical intervention, the age factor and some others. However, it is necessary to strive for the earliest possible start of physical exercise , since with prolonged inactivity of the joint, secondary changes occur that persistently limit its mobility.
Movements in the limb begin as soon as the operating surgeon allows it. This usually happens in the next few days after surgery. The first exercises are aimed at the muscles of nearby joints - wrist and shoulder , as well as hand joints . These are exercises with slight muscle tension or relaxation, in easier starting positions, with help or self-help. If the postoperative period proceeds smoothly and without complications, after a few days the surgeon can allow movement in the joint (7-14 days after surgery). These periods increase if there were/are any difficulties (up to 21-28 days ).
Let us remind you that the issue of timing is always decided individually in each specific case .
The number of exercises and the frequency of their repetition gradually increases, the load is regulated by various other factors. Exercises for the healthy limb and for the back muscles continue to be included in the complex.
The elbow joint itself is developed, among other things, with a focus on the patient’s pain: it is important to remember that there should be no pain, since it can very quickly increase protective muscle tension around the joint and lead to persistent contractures.
In the early stages of rehabilitation, are not recommended due to its high reactivity: these procedures often lead to ossification of the tissues around the joint (the appearance of bone tissue fragments where they should not be), which, in turn, complicates and limits the possibilities of rehabilitation measures .
Over time, the complex of therapeutic exercises includes more and more exercises aimed at increasing the amplitude of active and passive movements directly in the elbow joint . Training complexes, for example, Primus BTE, help in this development. It allows you to develop all movements of the elbow joint : flexion, extension, supination, pronation. Since the elbow area is very important from the point of view of the functioning of the hand as a whole, this simulator makes it possible to restore all movements in the joints of the hand , including practicing everyday skills. The features of these simulators are accuracy and strict control over the load, its objective assessment in many respects. With their help, it becomes possible to constantly and clearly monitor any changes in the functioning of the joint and the dynamics of treatment as a whole, which allows timely making the necessary adjustments to the treatment process. The elbow joint , as, in fact, the most complex joint in a person, like no other, needs increased attention to its rehabilitation, and simulators are an excellent help for medical personnel in this.
Medical clothing wholesale
Reposition
Schematic representation of the procedure.
For fractures and dislocations, when it is impossible to set or restore the bone, reposition is performed. The operation is an internal restoration of the structure of the joint. To do this, an incision is made along the back surface of the extensor part of the arm, exposing the bones and their joints. Transverse channels are made on the fragment and on the inner surface. All components are assembled in their original position, a spoke is placed along it, which is secured with screws in the made channels. Tendon fibers, which are taken from the lateral sections of the triceps, wire, and other materials, can also be used as fastening. Fasteners are selected depending on the location of the fracture. The attachment process is called “osteosynthesis”. If the tendons were damaged during crushing, their restoration is carried out simultaneously with reposition.
Ligament restoration
Damage to this element is quite rare and relates more to sports. They can be partial or complete. In the first option, the entire course is treated with conservative methods and lasts for 2-3 weeks. During this period, the patient's limb is immobilized.
Elbow ligament injury
In case of a complete rupture, manipulations to fuse the ligaments are necessary. To do this, an incision is made on the back of the elbow, and the connective tissue is sutured in small sections.
Basic processes of the rehabilitation period
The recovery period begins immediately upon the patient's return to the ward after surgery.
From the first days, the rehabilitation doctor outlines the necessary training program and other physiotherapeutic procedures necessary to restore the motor functions of the elbow joint.
In some cases, a splint is placed on the limb to immobilize the arm, and an ice pack is also applied to reduce pain and swelling.
Endoprosthetics of the elbow joint does not require a long stay in the clinic after surgery. Usually, already on the second or third day, the patient is discharged for outpatient treatment, after removing the sutures and bandages.
Endoprosthetics
This technique is one of the most complex and at the same time effective. With its help, you can restore your limbs to their former mobility. Its essence is to replace a damaged part of the skeleton that cannot be restored or treated with an endoprosthesis made of neutral materials. Indications for this procedure are:
- Arthrosis and arthritis;
- Comminuted fractures;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- Dystrophic and atrophic processes;
- Dysplasia;
- False joint.
The prosthesis is implanted through an incision on the extensor side, fixed with cement or cementless and sutured. The rehabilitation period is 2-3 months, but movements of the replaced part are allowed within a month after suturing.
Transposition
It is performed for carpal tunnel syndrome. The disease develops due to increased pressure on the nerve passing through the elbow joint. It often occurs after bruises and is felt almost instantly: pain radiates to the forearm and hand, numbness appears on the inside of the limb and on the fingers. The pain intensifies when bending the elbow.
Pathology is diagnosed by palpation - a specialist finds pain points and determines the location of the damage. To confirm, electromyography and electroneuromyography can be performed, which examines the rate of arrival of nerve impulses. With carpal tunnel syndrome, the transmission rate is significantly reduced.
Treatment of the disease is permitted conservatively. In many cases, it is enough for the patient to exclude movements that cause him pain. If this is difficult, then it is possible to apply a special splint. If this method does not help, then transposition is performed.
This procedure involves moving the nerve to the front of the junction. This will avoid tension on the nerve and pain. To perform this, an incision is made in the area of the epicondyle, the nerve is removed from the articular canal and laid along the front side of the joint. Such operations are performed extremely rarely and only in situations where it is impossible to eliminate the disease by non-traumatic methods.
Diagnosis and treatment
There are two diagnostic methods that are also used for therapeutic purposes: puncture and arthroscopy.
Arthroscopy allows tissue examination without resorting to large incisions. To perform this procedure, a few small ones are enough, through which the arthroscope and instruments are inserted into the cavity. With such penetration, the specialist has the opportunity not only to study the condition of the patient’s bone and muscle materials, but also to remove damaged cartilaginous structures, inflamed synovial structures, restore cartilage, etc. Such targeted effects can shorten the rehabilitation period and reduce the area of damage to the integumentary tissue.
Indications:
- Cartilage lesions;
- Arthrosis;
- The presence of foreign bodies or fragments of bones and cartilage;
- Inflammation;
- Ligament ruptures;
- Arthritis;
- Joint instability.
The puncture is used to collect biomaterial for further research. This option may also be suitable for administering medications directly to the lesion site. At the same time, depending on the purpose of the procedure, tools are selected. If the process is performed for the sole purpose of research, then a syringe is used with a thick needle. It can reach 2 mm in diameter. This is necessary to prevent clogging of the needle tunnel with small particles. A thinner needle is used to administer drugs.
The puncture is performed in the following situations:
- Accumulation of lubricating fluid in the cavity;
- Collection of blood;
- Arthrosis;
- Degenerative processes;
- Inflammatory diseases.
Indications for arthroscopy:
Presence of free intra-articular bodies
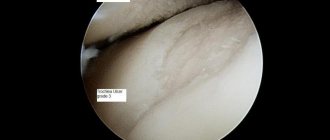
The problem may arise as a result of traumatic injury or chronic degenerative (destructive) processes. Such as: osteoarthritis, osteochondritis dissecans and others. As a result of the appearance of a free fragment of articular cartilage, periodic or permanent blockade of the joint occurs, accompanied by pain. The most effective method of treatment is arthroscopy, in which all detected fragments of cartilage tissue are removed or fixed if they are significant in size and viable tissue is preserved.
Exostoses
Pathological benign growths of bone or osteochondral tissue, which can occur as a result of inflammatory processes of bone and cartilage, chondromatosis, and abnormalities of the musculoskeletal system. In case of dysfunction, such growths are removed, while arthroscopically it is possible to perform the manipulation in full, as well as to prevent recurrence.
Synovitis
It is often a reason for arthroscopic diagnosis, especially when the process is chronic. The identified areas of altered synovial membrane are removed (synovectomy), and the articular cavity is sanitized.
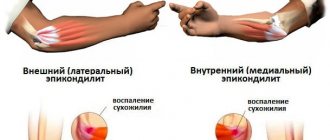
Lateral epicondylitis
A fairly common pathology, which has another name - “tennis elbow syndrome”, due to its prevalence among professional tennis players. Many methods of surgical treatment have been proposed, but in their comparative characteristics, arthroscopic release of the extensor carpi radialis brevis is the most gentle, effective and at the same time gives the least number of complications. However, a high level of specialist training (which the doctors of our clinic possess) is necessary.
Impingement syndrome
It can develop as a result of frequent injuries in a given localization, the formation of scar structures, chondromatosis, osteoarthritis and other pathologies. The function of the joint is disrupted to the point of blockage, and pain occurs. Arthroscopy involves excision of pathological growths and restoration of congruence (compliance) of the articular surfaces.