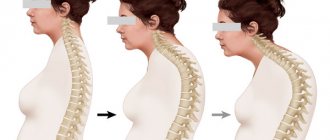
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the tissues of the spine, which not only leads to changes in shape, but also causes abrasion of intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies, as well as the surfaces of various joints.
During its development, the disease primarily negatively affects the bones and ligaments of the human body. Most domestic and foreign experts are inclined to believe that pain due to osteochondrosis of various parts of the spine is a common reason for people of all ages seeking medical help.
According to available statistics, most cases of diagnosing the disease occur in the lumbar region. This is due to the fact that the lower back bears the load of the entire upper part of the human body.
Types of osteochondrosis
Today, medical specialists usually distinguish four main types of spinal osteochondrosis, each of which has a name, symptoms and treatment corresponding to the location:
- lumbar (develops in the lumbar spine);
- cervical (develops in the cervical spine);
- thoracic (develops in the thoracic spine);
- widespread (affects two or more parts of the spine).
The localization of the disease in a certain place is due to its progression in particularly mobile areas that bear the greatest pressure.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Progressive dystrophic-degenerative damage to the intervertebral discs of 1-7 vertebrae, leading to disruption of normal blood supply and nerve conduction in areas innervated by the nerve roots of the cervical spine.
Possible complications include:
- formation of protrusion (a pathology of the spine in which the intervertebral disc protrudes into the spinal canal without rupture of the fibrous ring);
- compression of the spinal cord (even death);
- damage to the roots and the formation of spines on the vertebral bodies, with the probable manifestation of paresis and paralysis.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The most likely cause is previous injuries, but the disease occurs in people with different medical histories and is observed under conditions of constant load on the thoracic spine.
The most likely maltings include:
- myositis (inflammation of skeletal muscles), radiculitis (a complex of pain syndromes that occurs when the nerve endings of the spinal nerves are pinched or compressed) of the chest muscles;
- fracture, displacement of the chest bones;
- cancer diseases.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Loss of the ability of intervertebral discs to function normally in the lumbar spine.
Among the most dangerous complications, it is customary to highlight the development of:
- compressive vascular ischemia (circulatory disorders);
- compression myelopathy (spinal cord lesions);
- compression of the artery of the lumbar enlargement.
Both traditional and non-traditional methods can be used to treat any type of osteochondrosis. Self-medication is excluded. All procedures are prescribed only by the attending physician.
The duration of treatment is determined by the degree of neglect of the disease.
When does the disease appear?
Information about studies of the seasonal occurrence of exacerbations of problems with the spine, which were carried out by many researchers in various regions of Russia and employees of our medical institution in Moscow, can be seen in the diagrams.
Based on the assessment of the frequency of occurrence of exacerbations, we can conclude that most often the disease worries people in February-March and August-September, which many scientists explain by increased physical activity in people living in the city, during the planting period and during harvesting.
Therefore, doctors recommend equal stress on the body all year round, especially if there are problems with the spine. When a relatively healthy person has a tendency to develop pathologies of the spinal column, against the background of an already formed spinal syndrome, constant physical activity is extremely necessary.
Main symptoms
The localization of osteochondrosis largely determines its symptoms, which is directly related to protrusion of intervertebral discs and, as a consequence, pinching of blood vessels, which disrupts blood flow to nearby tissues and organs.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine
Lumbar osteochondrosis is the most common type. Due to the fact that the lower back acts as a shock absorber in most activities performed by a person, symptoms of this disease may include:
- aching type of pain in the lower back, intensifying when performing various types of exercises. Sharp pain may be observed, but this already indicates the formation of an intervertebral hernia;
- shooting or aching pain in the legs, resulting from pinching of the roots of the spinal cord;
- limited mobility caused by pain that accompanies any bodily movements.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Cervical osteochondrosis is not a rare case in modern medicine. It causes displacement of the vertebrae, which leads to pinching not only of nerve endings, but also of blood vessels, which causes various types of pain.
The main symptoms include:
- mild dizziness and increasing headaches are the most characteristic symptoms. Often the pain is constant, pressing in nature and is characterized by intensification with head movements that require the inclusion of the cervical spine in work;
- sharp shooting pain, felt even in the tips of the fingers;
- pain in the arms and chest. Sometimes patients may confuse this type of pain with heart pain, but unlike them, the unpleasant sensations accompanying osteochondrosis persist for several hours;
- numbness of the tongue and slight tingling in the fingertips.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Thoracic osteochondrosis is the rarest form, the main cause of which is scoliosis (spinal deformity). Due to the peculiarities of the location, it is quite difficult to diagnose this type of disease, however, among the probable symptoms are the following:
- girdle pain in the chest, aggravated by movement and bending;
- pain in the area of internal organs (heart, liver or gastrointestinal tract);
- feeling of numbness in the chest;
- disruption of the reproductive system.
Symptoms of common osteochondrosis
Due to the fact that common osteochondrosis is a combination of several forms of the disease, I also diagnose it by the combined symptoms characteristic of thoracic, cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis.
Signs of illness
The main symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis are initially caused by damage to the structure itself in the vertebrae (the so-called vertebral syndrome), in accordance with the area of damage called cervicalgia (cervical), dorsalgia (thoracic) and lumbodynia (lumbar), a large group of non-vertebral or extravertebral syndrome - neurodystrophic, neurovascular and muscular-tonic.
The clinical picture against the background of vertebrogenic pathology is caused not by changes in the discs, but by the level of involvement in the process of certain neurovascular formations that are located in the spinal canal. Many Russian and foreign authors claim that the leading role in the formation of spinal injuries is given to uneven muscle training.
For example, when flexors dominate over extensors, intervertebral joints can become displaced, leading to the development of subluxation. Infringement and damage to the nerve endings between the vertebrae can develop as a result of displacement or prolapse of intervertebral discs, which is manifested by protrusion or hernia in the intervertebral disc against the background of osteochondrosis, accompanied by local reactive changes.
In the spine affected by osteochondrosis, thanks to numerous nerve endings, pathological impulses are formed, which, in parallel with the negative effects of mechanical overload, leads to the appearance of muscle spasms. This causes the formation of compacted cords containing painful compacted areas, or trigger points.
Against the background of such trigger points, so-called myofascial pain, which causes the main severity of the disease in patients diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the spinal column.
Symptoms for diseases of the spine, due to their large number, are diverse, polymorphic, consisting of organic damage and modified functional states. Of course, it is worth noting that the division of painful conditions into organic and functional existing in medical practice is conditional.
Probable causes of osteochondrosis
Among the most likely causes of osteochondrosis are:
- hereditary factor (if one of the parents has osteochondrosis, the person automatically falls into the risk group, since the structure of the intervertebral cartilage is often inherited);
- high level of load, work associated with increased severity;
- static stay in the same position;
- diseases and injuries of the spine leading to curvature;
- lack or excess of vitamins and minerals;
- previous infectious diseases;
- congenital spinal defects;
- overweight;
- stress;
- hypothermia.
Degree stages of degenerative-dystrophic damage to spinal tissues
Each gradual stage of osteochondrosis is accompanied by symptomatic signs, as well as irritative-reflex syndromes (pain).
According to medical data, there are 4 gradual stages of disease progression:
Osteochondrosis 1st degree: initial (vertebral instability) - the initial stage, the causes of which are often displacement of the spinal disc or the formation of microcracks in the fibrous ring.
Degenerative-dystrophic transformation is accompanied by noticeable discomfort in the process of performing movements that involve the affected part of the spine.
Osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree: destruction of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral discs - aggravation of the situation and significant progression of the disease, leading to a reduction in the intervertebral spaces.
Pinching of the spinal nerves provokes pain even under conditions of minimal load on the spine.
Problems such as:
- disruption of blood flow to the spine;
- disruption of vascular function.
Osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree: rupture of the fibrous ring, accompanied by protrusion of the disc nuclei - a stage of direct deformation of the spine, often accompanied by the formation of an intervertebral hernia.
Osteochondrosis grade 4: bone overgrowth - the patient’s movements are limited, accompanied by pronounced pain. The ligaments of the spine become ossified.
The last degree of the disease is extremely dangerous for human health, since it is this that requires surgical intervention in order to remove the hernia and normalize the blood supply.
Regardless of the stage, treatment of spinal osteochondrosis remains possible, but it is worth noting that the longer osteochondrosis remains undetected, the more difficult it is to eliminate the resulting consequences of its progression.
Experts' opinion
The presence of certain morphological substrates is most often regarded “by default” as evidence of the irreversibility of pathology. Advances in manual therapy in patients with spinal problems have proven (V.L. Naminov, 1996) that this statement is not always correct.
Every specialist knows that functional damage in the spinal column is often a precursor to anatomical damage, significantly surpassing it in formation at a certain stage of pathology formation. Long-term or regular changes in functioning, for example, during the work of functionally blocked spinal-motor elements, or spastically shortened muscles, can cause their morphological restructuring.
The reflection of the complex interaction and functions of numerous vertebrae is its functional state, which represents a certain activity in certain areas and in the deep structure of the spinal column; moreover, at each level there is a different ratio in autonomic, motor and proprioceptive enhancement.
According to experts, the functional state as a whole is a systemic response of the body, which provides a combination of interacting simple structures and processes that contribute to achieving a solution to a specific problem.
Knowledge, timely detection and necessarily competent treatment of emerging painful changes, even in the process of developing stable morphological changes in the structure of the spinal motor elements of the spine, vascular and muscle tissue in people with problems in the spinal column, help to achieve a rapid weakening of the condition or final regeneration of the original functioning in initial volumes. If there is no treatment for osteochondrosis, the risk of formation and duration of relapse increases.
Diagnosis of spinal osteochondrosis
A neurologist diagnoses osteochondrosis. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a medical examination, which is based on various methods and principles for recognizing spinal diseases and making a clinical diagnosis.
Diagnostic steps:
- Taking an anamnesis (implies the study of the patient’s main complaints, clarifying the characteristics of the disease history).
- Physiological examination (includes assessment of the patient’s body position, determination of range of motion, palpation of deep and superficial layers of muscle tissue, as well as the use of a number of techniques to determine radicular tension).
- In-Depth Study
The following procedures may be prescribed as the main methods:
- radiography;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Lumbodynia
Lumbodynia occurs in three forms: acute (lumbago), subacute and chronic. Acute lumbodynia develops in a couple of minutes or hours, usually unexpectedly, during an awkward movement.
It is characterized by the appearance of stabbing pain deep in the integument, expanding with a feeling of burning or coldness in the lumbar region, and increased sweating.
The patient freezes in the position in which the attack caught him. Defensive posture can vary. A secondary symptom of lumbago is tonic remission of muscle tissue in the lower back with its tension, which is defined as a protective position.
The duration of acute lumbodynia is 5-6 days. The duration of the attack increases each time. The subacute or chronic course of lumbodynia is characterized by different symptoms.
In this case, initially a person feels cold, static tension, the pain syndrome develops after 1-2 days, is often predominant on one side of the lumbar region, and can increase during prolonged sitting, standing, and when bending the body.
There is limitation when bending forward, a decrease in motor activity is observed every day, the pain becomes constant, and increases with coughing or sneezing syndrome. Against the background of pain, an increase in skin temperature and changes in vegetative parameters are observed.
Subacute lumbodynia can last for several weeks or even months; the pain spreads to the area of the sacrum, buttocks, and legs.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Depending on the diagnosed stage of osteochondrosis, certain ways to combat it are selected. The earlier the disease is identified and diagnosed, the simpler and more accessible its treatment.
Often, treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out using conservative methods. However, everyone who has encountered the symptoms of the disease has a question: “Which doctor treats osteochondrosis?”
A specialist who deals with the elimination of spinal diseases and gives clinical recommendations for the treatment of osteochondrosis is called a vertebrologist.
To achieve a better result, a variety of complexes are used, including: massage, the use of medications, manual therapy, physiotherapy and, of course, exercise therapy.
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis
All drugs used in the treatment of osteochondrosis can be divided according to the type of effect. The following are often used as drug treatments:
- painkillers – help relieve acute pain;
- muscle relaxants – help eliminate muscle spasms;
- chondroprotectors – the action is aimed at restoring and improving the nutrition of intervertebral discs;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – relieve swelling;
- medications that improve metabolism;
- hormonal drugs - applicable in the absence of positive dynamics when taking drugs of another type;
- vitamin complexes – help improve well-being, restore nerve conduction.
Note that the greatest effectiveness in treating the disease is provided by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and chondroprotectors for osteochondrosis.
Pills
Often, in order to eliminate pain and treat, the doctor prefers to prescribe systemic drugs (medicines that enter the bloodstream and affect the functioning of all body systems) - tablets.
Simplicity and ease of use, as well as accessibility, are their main advantages.
The most effective include:
- Ketalgin/Ketanov (active ingredient – ketorolac);
- Dicloberl (active ingredient – diclofenac);
- Movalis (active ingredient – meloxicam);
- Nurofen (active ingredient – ibuprofen);
Injections
In order to quickly eliminate pain, NSAIDs are actively used in the form of injections, often intramuscular (the pain-relieving effect occurs within 10 minutes), in rare cases – intravenously (the analgesic effect occurs within 4 minutes).
In treatment it is customary to use drugs of two groups:
- non-selective (Dicloberl, Voltaren);
- selective (Arcoxia).
Among the most effective drugs, it is customary to highlight “Artradol” - an anti-inflammatory, analgesic agent, characterized by ease of absorption when administered intramuscularly and having an accumulating property in cartilage tissue.
Ointments and gels
Local drugs are used in treatment quite rarely, as they have a weak effect, unlike systemic drugs.
All kinds of ointments and gels have a local effect, which makes it possible to minimize the occurrence of side effects.
The most prescribed are:
- Voltaren emulgel, Diclak (active ingredient – diclofenac);
- Arthrocol, Ketonal (active ingredient – ketoprofen);
- Dolgit, Nurofen (active ingredient – ibuprofen);
- Indomethacin, Indovazin (active ingredient - indomethacin).
Plasters:
Another additional treatment for osteochondrosis is NSAID patches. Local action rarely causes adverse reactions.
It is important to remember that due to the peculiarities of local exposure, patches cannot replace full-fledged complex treatment.
The most popular means are:
- Voltaren;
- Diclobene;
- Ketotop.
In parallel with drug treatment, courses of physiotherapeutic procedures are used in accordance with the prescription of the attending physician.
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis
An excellent way to treat various types of diseases associated with dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system. It is actively used for the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis.
The main methods used:
- laser;
- ultrasound;
- magnetic vibrations.
All performed manipulations help to neutralize inflammation, which makes it possible to reduce the dosage of medications without losing the effectiveness of pain suppression.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis
Regardless of the location of osteochondrosis, physical therapy is the best means of treating it.
The method is based on the introduction of limited loads on the musculoskeletal system, which has a beneficial effect on the body and makes it possible to strengthen the back corset.
All exercises for osteochondrosis are performed under the supervision of an instructor or in strict compliance with his recommendations.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis can be used at any age, in the presence of various types of disease (the only exceptions are acute stages, serious spinal injuries), but only at the stage of remission.
Coccydynia syndrome
Coccydynia syndrome is characterized by pain syndrome mainly in the area of the sacrum and coccyx. A person complains of the appearance of pain in this area of a different nature: convulsive, disconnecting, dull burning.
There is irradiation of pain and paresthesia to the area of the lumbar region, the posterior femoral surface, which weaken in a standing position and increase when the person lies on his back. The symptoms are due to muscle-tonic remission and excitation of the corresponding endings in the fibrous formation. Coccydynia can be long-lasting and persistent.