Symptoms | Cervical instability in children| Cervical instability treatment
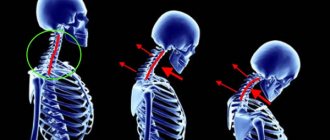
Instability of the cervical spine is a pathological excessive mobility of the vertebrae in the cervical spine, which occurs against the background of an impaired ratio of their articular surfaces and altered tone of the ligamentous-muscular frame.
Keeping the vertebrae in a certain position, as well as preventing the articular surface of one from sliding relative to the other, is formed by the ligaments and muscles that are located in this area.
Instability of the cervical spine in children can become the basis for the occurrence of not only the main symptoms of this process, but also contribute to the development of other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, such as osteochondrosis.
Instability of the cervical spine is a sign of displacement of the vertebrae and weakness of the ligamentous apparatus.
The main types of instability will be: degenerative, which often develops against the background of osteochondrosis, post-traumatic, postoperative and dysplastic. Instability of the cervical spine in children often occurs as a result of trauma, such as birth (excessive tension on the head).
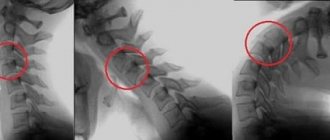
Very often, instability of the cervical spine can be hidden and is detected only during a random X-ray examination, for example, in osteochondrosis.
Symptoms
Pain in the neck and shoulder blades, muscle tension, limited mobility in the cervical spine, a feeling of displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, most likely you have instability of the cervical spine.
Symptoms may also include severe muscle spasms, discomfort or unpleasant sensations in the neck, decreased joint activity, lumbago and numbness in the limbs, headaches (vertebral artery symptom).
Instability of the cervical spine: symptoms are based on a state of increased muscle tone, impaired blood supply and excessive pathological mobility of the articular surfaces of the vertebrae.Sleep is disturbed, emotional lability, drowsiness, visual or hearing impairment, and gait disturbance appear.
A diagnosis has been made: “instability of the cervical spine”; treatment should be immediate and conservative.
Diagnostics
Back pain does not necessarily mean that it is a vertebral compression fracture. To correctly determine the cause of the ailment, a comprehensive examination is needed. The doctor at the Noosphere clinic will carefully examine, interview the patient and determine how dangerous the fracture is, if any. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis using the following diagnostic methods:
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
- Laboratory research
Cervical instability in children
Instability of the cervical spine in children is a manifestation of trauma, surgery or dysplastic processes in this area. Excessive load can provoke a spasm of the neck muscles and this will lead to displacement of the articular surfaces of the vertebrae relative to each other, which will lead to the formation of the condition “cervical instability”.
Treatment in children is carried out conservatively, the purpose of which is to relieve spasm and improve blood supply to the neck. Even at a young age, degenerative damage to the intervertebral joints can form, which will serve as a provocateur for the development of instability.
Contraindications
Spinal surgeries with metal structures cannot be performed if:
- local degradation of bone tissue, which is observed in osteoporosis and osteopenia;
- local inflammatory process;
- individual intolerance to the metal of the structure or other materials used for its production;
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- pregnancy;
- tumors or metastases in the spine.
However, each operation has its own contraindications and limitations. Therefore, only a neurosurgeon can say for sure which of them is acceptable and will give the best results in each specific case.
Cervical instability treatment
Instability of the cervical spine - treatment should include physiotherapy and massage methods. Physiotherapy is completely painless, effective and modern. Improving the nutrition of muscle fibers and their relaxation will lead to the elimination of the main symptoms of the disease that make everyday life difficult.
Taking medications and performing surgery on people diagnosed with cervical instability is an ineffective treatment, since the recovery period is very long, the effectiveness is low, and most importantly, this method is not applicable to everyone. The golden “pill” is an integrated approach that includes physiotherapy and massage methods.
Basic techniques for stabilizing spinal surgery
Today there are techniques for rigid and dynamic fixation of the spine. In the first case, the plates, screws and other metal structures used ensure complete immobilization of unstable vertebrae. This guarantees normalization of the patient’s condition, elimination of pain, neurological disorders and other symptoms. But if previously the patient’s physical capabilities were limited by pain and nerve conduction disorders, then after using rigid fixation systems, especially on a large number of vertebrae, they are limited by the implants themselves.
Dynamic fixation systems do not have such disadvantages. But they are more expensive and require more skill from the neurosurgeon during installation.
Modern spinal surgeries with metal structures can be performed open or percutaneous (percutaneous) method. These include:
- transpedicular fixation;
- transcutaneous stabilization;
- dynamic stabilization.
Each of them has its own indications and advantages. In certain situations, only one specific surgical tactic can lead to a positive outcome. Therefore, only a neurosurgeon can choose the correct surgical technique. To do this, he takes into account many factors, including the results of diagnostic procedures, the anatomical features of the patient, his overall health condition, age and a number of others.
Discharge from the hospital usually occurs on days 7–14.
Transpedicular fixation (TPF)
The transpedicular fixation technique has been used for about 50 years. The essence of the operation is to rigidly connect adjacent vertebrae to each other by screwing in special screws and connecting them together with springy rods. Indications for this type of surgical intervention are often:
- spinal fractures;
- vertebral displacement;
- progressive scoliosis;
- spinal canal stenosis.
Transpedicular fixation is performed from the posterior approach under general anesthesia. To ensure full control over the progress of the procedure, an image intensifier or CT is used. The neurosurgeon exposes the processes and body of the affected vertebra, finds the intersection of the articular process with the transverse one, and screws a titanium screw into this point. This manipulation is repeated on the opposite side of the spine and on all other affected segments.
Screws come in different shapes and sizes, which allows you to choose the best option for both the cervical, lumbar and thoracic spine. They are screwed exactly 80% deep into the bone tissue. There is a special hole in the screw head into which a metal rod is immersed, thereby connecting all pathologically altered vertebrae on both sides.
The result of the operation is the achievement of absolute immobilization of pathologically changed segments due to the strong fastening of two or more vertebrae. Over the course of 3–6 months, they fuse with each other and turn into a single bone fragment of the spine. Therefore, after the operation there is no possibility of making movements in the fixed segments.
This does not greatly affect the overall mobility of a person if the transpedicular system is installed on 2–3 vertebrae. In most cases, people notice virtually no changes and can walk normally and do everyday activities without experiencing discomfort or pre-existing symptoms.
But if it was necessary to install plates with screws on a larger number of vertebrae in one or more parts of the spine, this will lead to a more noticeable limitation of mobility, which cannot go unnoticed. As a result of multi-level fixation, the spine loses its former flexibility, so the patient will be able to perform some movements with a limited amplitude.
But in 10–15% of patients, six months or a year after the operation, the occurrence or worsening of osteochondrosis is observed in areas of the spine adjacent to the operated areas.
Design and features of modern systems for transpedicular fixation
One of the most common systems for immobile fixation of the spine is Ulrich Medical GmbH. It has original design features and is distinguished by ergonomics, safety and ease of installation.
The Ulrich system is effective when it is necessary to achieve decompression of nerves, eliminate deformation and instability of the spine. It is a set of titanium rods and screws that allow for quick and complete fusion of the vertebrae. "Ulrich" is designed for universal fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine and is characterized by high stabilizing properties, strength and the ability to withstand heavy loads.
The system rationally distributes the load on all metal elements and vertebrae, but its main feature is the 3D reduction instrumentation. It allows you to compare and reduce vertebrae in any order.
"Ulrich" does not require the use of transverse plates and makes it possible to screw in screws at an angle convenient for the neurosurgeon (variability range is 45°). A minimal incision is required to install it. This provides:
- minimal blood loss;
- careful treatment of vertebral and paravertebral tissues;
- almost complete absence of risks of injuring large blood vessels and spinal roots;
- simplicity and high speed of installation;
- rapid onset of improvement (pronounced positive changes in the patient’s condition are observed already in the early postoperative period);
- eliminating the need to wear an orthopedic corset in most cases.
Transpedicular fixation with installation of interbody endoprostheses
For osteochondrosis, the gold standard of neurosurgery is fixation of the unstable segment, total removal of the modified intervertebral disc and its replacement with an endoprosthesis. This combination allows you to eliminate compression of the spinal roots, pain and neurological disorders, as well as increase the functionality of the affected part of the spinal column. In this case, complications are observed in less than 1–2% of cases.
Interbody endoprostheses have been used in neurosurgery since 2004. Most experts agree that this is the best alternative to complete spinal fusion. Today there are the following types of intervertebral disc endoprostheses:
- DCI;
- M6;
- Bryan;
- SBSCharity;
- DePuy;
- ArcoMed.
The shock-absorbing and biomechanical abilities of intervertebral discs are best restored by endoprostheses in which simulators of the nucleus pulposus, close to natural in strength, elasticity and structure, are installed between metal end plates. These include M6 endoprostheses. They are available in different sizes and diameters, which allows you to choose the best option for intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical or lumbar spine.
The characteristics of the M6 implant are very similar to a natural disc. It is capable of independently moving along its axes, has 6 degrees of freedom and in many ways exceeds the compression and tension performance of a natural disk.
The design of the implant is identical to a natural disc. He has:
- An artificial core made of a viscoelastic polymer. It completely replicates the physiological center of rotation and guarantees normal axial compression.
- A polymer ring that is an analogue of the fibrous ring. But it is made from an elastic, high-molecular fibrous polymer that can withstand a load 15 times greater than steel.
- The shell is formed from polycarbonate urethane. It does not affect the biomechanical properties of the endoprosthesis, but eliminates the risk of soft tissue growing into it.
- Titanium end plates with different projection sizes.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia using special equipment. Its essence is decompression of the nerve roots, removal of osteophytes and fixation of the final structure with the endoprosthesis with titanium plates and screws.
Direct installation of the endoprosthesis involves the formation of special channels on the surface of the operated vertebra with a chisel. According to them, the M6 disc selected by size will simply enter the intervertebral space. Quality control of the procedure is carried out through the image intensifier.
As soon as the endoprosthesis is installed, the second stage of the operation begins - installation of a rigid stabilizing system. Since all structures have metal fragments, their condition is easy to monitor through the image intensifier.
Several intervertebral discs can be replaced at the same time. But their installation is carried out sequentially, moving from the most damaged vertebra to the least damaged.
Transcutaneous stabilization
Transcutaneous stabilization is one of the methods of percutaneous surgery, which involves rigid stabilization of the spinal motion segment by introducing a special kind of implant through a tiny soft tissue incision. As a rule, its dimensions do not exceed 1.5 cm. A surgical probe is inserted into it, through which, under the control of an image intensifier, the implant is immersed into the patient’s body and securely fixed to the bone structures.
This technique is characterized by minimal trauma. This allows it to be used not only to obtain a good result with an excellent cosmetic effect, but also to treat spinal pathologies in elderly people, as well as those who are severely weakened or have cancer. With transcutaneous stabilization, the back muscles are minimally injured. Therefore, intraoperative blood loss is insignificant, and recovery is rapid.
The technique is used for uncomplicated spinal fractures, segmental vertebral instability and in a number of other cases. In essence, it is a type of transpedicular fixation, but instead of one large incision, it involves making several small ones.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia; sometimes it is performed under epidural anesthesia. Incisions are made in the projection of the affected area of the spinal column on both sides. Through them, using special surgical equipment, fixing elements are inserted and mounted into the spine. All manipulations are carried out under the control of the image intensifier.
The stabilizing system itself, used for transcutaneous stabilization, consists of screw rods and extensions that act as supports for the screws.
Dynamic stabilization
The dynamic stabilization technique involves the implantation of dynamic (movable) implants of various types into the affected spinal motion segment, which allows it to be stabilized within physiological limits. An important advantage of this technique is the preservation of the normal biomechanics of the spinal motion segment, i.e., the natural range of mobility.
For dynamic stabilization, functional endoprostheses of intervertebral discs are used, as well as other structures that are installed mainly between the spinous processes of damaged vertebral bodies. Most often, the technique is used to eliminate disorders in the lumbosacral spine, in particular:
- sequestered hernias;
- foraminal stenosis;
- radiculopathy;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- posterior displacement of the vertebrae.
It is the dynamic fixation technique that they try to use as often as possible, since it allows one to achieve normal mobility and offers more prospects for a favorable outcome than transpedicular fixation.
This is due to the fact that with classical TPF, all fixed vertebrae grow together into a single whole. This creates significant preconditions for the occurrence or progression of existing degenerations in the vertebrae adjacent to the stabilized ones, the formation of a false joint or other negative consequences. The result of this is the resumption of pain, the development of neurological disorders, limitation of mobility and the formation of secondary deformities of the back, i.e., indications for performing a new operation on the spine with metal structures.
The dynamic stabilization technique eliminates such risks, since it brings the spine as close as possible to its natural biomechanics and allows you to correctly distribute the load across the entire spine.
To carry out dynamic stabilization, various types of metal structures are used:
- total intervertebral disc prostheses;
- prostheses for replacing the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc, installed inside the natural fibrous ring;
- facet joint replacement implants;
- dynamic transpedicular systems;
- implants for interspinous stabilization.
They are made from titanium, nitinol, polyamide, lavsan, thermoplastic polymers, and silicone. Neurosurgeons also have hybrid models, in which some of the structural elements are made of metal, and the other of high-molecular organic compounds. All modern implants are fully biocompatible and more or less close to natural elasticity indicators.
If the situation does not allow one to avoid spinal fusion, its combination with dynamic stabilization ensures uniform distribution of the load on the underlying or overlying spinal motion segment. This makes it possible to prevent or delay as much as possible their defeat by osteochondrosis.
Classification of the disease
It is customary to distinguish 4 main types of disease:
- Degenerative-dystrophic
- occurs due to impaired blood circulation of the intervertebral discs in the area of the upper section and leads to slow destruction of the segment (osteochondrosis is considered one of the main prerequisites for the occurrence of this subtype of pathology). - Post-traumatic
– a common variant associated with accidents and sports injuries. - Postoperative
– radical interventions to remove a segment of the vertebral arch (laminectomy). In some severe cases, secondary surgery may be required. - Dysplastic
- directly related to individual developmental anomalies and manifests itself in adolescence. As you get older, there is a noticeable deterioration in your health, especially if you have not sought medical help.
The intensity of the disease is characterized by two forms - obvious and hidden.
Obvious instability of the vertebrae of the neck manifests itself in the form of radicular syndrome, progressive myelopathy, cervical dyscalgia, vertebral nerve syndromes and vertebral artery compression. In the case of a latent form of the disease, blurred symptoms often lead to erroneous diagnoses and incorrectly chosen treatment options.
Numbness, or paresthesia, of the lower leg, from the ankle to the kneecap, is common. The pathology can affect the left leg, the right leg, as well as both limbs - each type of phenomenon has its own causes and treatment features. Read more in the article: “numbness of the leg from the knee to the foot.”
How children's school stability is restored
An integrated approach is required in the treatment of this type of pathology. You can often hear from a mother that the baby has undergone several sessions with an osteopath or, alternatively, a massage course. But that was all they had to do! A very frivolous approach to business.
The goal of treatment is not only to return the vertebrae to their intended places, opening the way for blood circulation, but also to make it as strong as possible, ensuring that the brain receives better nutrition, thereby accelerating its development. This is the only way to achieve the following:
- relieving your baby of migraines;
- improved learning ability;
- improvement of behavior.
All this is a long process. Moreover, treatment requires a whole complex of several procedures.
Osteopathy has a positive effect on the tone of the cervical muscles, which are located at great depths. A simple massage can only affect those muscles that are located on the surface. An osteopathic doctor uses manipulations to place the vertebrae in their naturally designated place. At the same time, it removes pressure on the arteries located in that area, thereby improving blood flow to the brain. How often the procedure should be performed should be determined by the osteopath. In most cases they are done weekly. After completing the next session, you need to exercise some caution for some time, namely, move as little as possible by running and jumping, and you should not tumble at all. It is not recommended for your child to attend physical education classes. It will be good if he wears Shants' collar for several hours a day. You should visit an osteopath from time to time for check-ups to be able to maintain the health of your spine.
Regular massage is also popular among patients with NSOP. But this type of procedure is categorically incompatible with osteopathy. It relaxes tense muscles while strengthening them. During the massage, metabolism and blood circulation improve there.
Physiotherapy procedures are not so rarely combined with massage. Electrophoresis is usually done with vasodilating drugs, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain becomes even better.
Treatment methods for children differ little from those for adults.
Exercise therapy . Perhaps the most important method for ridding a child of NSHOP. Naturally, first you need to use massage, physiotherapy and, at your choice, osteopathy or massage. However, without exercise therapy the result cannot be consolidated. Moreover: a child who has experienced such a pathology must do therapeutic exercises every day throughout his life so that the disease does not gradually return. So in childhood it is necessary to prevent NSHOP and unhealthy posture. Swimming in the pool is useful - it can increase the stability of the spine. Gymnastics and choreography also help a lot. In a word, such a person must strengthen and maintain the muscles of the neck, shoulders, arms and torso all his life.
Medicines . A neurologist can prescribe symptomatic medications to the baby: sedatives, vasodilators, nootropics, and so on. It is the pediatric neurologist who should lead the treatment. First of all, he will conduct an examination, after which, guided by the result, he will develop a treatment program. He will also observe the little patient. This is a matter for several years, but in order for him not to suffer as an adult from something that could be cured, he must get rid of the disease while still a child.
The baby’s brain must receive a sufficient amount of nutrients and microelements. It is necessary to contact a pediatric neurologist in a timely manner in order to be in time for examination and treatment. And then the baby will not learn from his own experience what headaches are. And if he manages to find out, he will quickly get rid of them.
Possible consequences and complications
In the first time after surgery, an increased temperature may be observed, as well as a sensation of the presence of a foreign object. This is often accompanied by pain of varying intensity and swelling of the soft tissues. This is not a sign of the development of complications and is a natural reaction of the body to surgical intervention.
Complications of the intervention may include:
- infectious-inflammatory process;
- muscle atrophy;
- degenerative changes in adjacent spinal motion segments;
- recurrence of segmental instability;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- paresis, paralysis;
- implant rejection.
The most striking sign of the development of complications is pain that does not decrease over time. Also, the undesirable consequences of spinal surgery with a metal structure may be indicated by the appearance of crunches and clicks in the back when moving.