Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 10.10.2014 Date of update: 12.11.2020
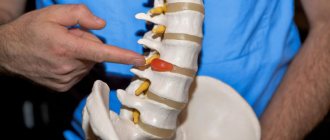
One of the serious diseases of the spine is the so-called cervical protrusion, when the intervertebral disc protrudes beyond its normal boundaries. This disease is considered very dangerous, since in the neck area there is a very thin and vulnerable spinal canal through which many nerve endings pass.
The negative impact of any external factors leads to the fact that the cervical discs lose their shock-absorbing ability and cease to compensate for the load on the spinal column. As a result, a person, without timely treatment, begins to experience severe and regular pain.
Causes
Malnutrition of the discs is associated with a change in the functioning of the tissues surrounding the spine, from which, and not through the vessels, the intervertebral discs receive the necessary nutrients. Accordingly, protrusion of the cervical vertebrae occurs due to metabolic disorders in the cervical spine. A serious role in this is played by the hereditary factor, which determines the structure of the spine, the composition of cartilage tissue, and the state of the circulatory system. Also among the causes of the disease are:
- disruption of internal organs;
- hormonal pathologies;
- metabolic disease;
- age-related changes;
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, rheumatism, scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis);
- incorrect posture;
- neck injuries;
- lack of physical activity;
- lack of nutritional intake of vitamins and minerals necessary for the structure of cartilage tissue.
Treatment methods for cervical disc protrusion
It is necessary to begin treatment of cervical protrusion in a timely manner, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his condition. The clinic’s doctors prescribe complex treatment, consisting exclusively of effective methods of oriental therapy:
- Herbal medicine – relieves inflammation, stabilizes metabolism, accelerating disc recovery
- Acupuncture - by influencing biologically active points, tissue healing is accelerated and blood circulation is stimulated
- Manual therapy - treats an ailment such as protrusion by reducing the load on the cervical spine and releasing compressed nerves and blood vessels.
- Pharmacopuncture. The essence of the method is to administer small doses of homeopathic medicines directly to the affected area to the patient, which allows activating metabolic processes and providing complete and deep tissue nutrition.
- PRP therapy is the latest method of stimulating regenerative processes. It is used to restore the functions of various organs after diseases and injuries, including to restore the function of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment of cervical protrusion at the Paramita clinic
Experienced doctors at the clinic will conduct the necessary diagnostic tests and select a comprehensive treatment that will make you feel better literally after the first procedures.
The specialists of our clinic are deservedly famous for their many years of experience and high qualifications. We treat cervical protrusion without the use of drugs or surgery, using only reliable and proven methods of oriental therapy. After completion of treatment, we give recommendations on prevention and maintaining your health in good shape.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
Symptoms
The spinal canal is narrow, so protrusion of the cervical spine, unlike protrusions in other parts of the spine, appears quite early. In this case, the patient experiences:
- pain in the neck and shoulders;
- stiffness when bending and turning the head;
- frequent headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances in the form of floaters and dark spots before the eyes;
- irritability;
- tingling in the hands, numbness and tremors in them;
- surges in blood pressure.
Exercises for cervical protrusion
Performing special exercises for cervical protrusion helps restore the shape and size of the vertebrae. You can do gymnastics for both treatment and prevention of the disease.
The greatest effect is obtained by performing the following exercises:
- We sit on a chair and place our palm on our forehead. We press our forehead into our palm, straining our neck muscles.
- We place our palm on the back of the head and press hard on it using the muscles of the neck.
- We lower our chin to our neck and turn our head in different directions.
- We tilt our head back and tilt it alternately to the left and right shoulder.
- We clasp our heads on both sides with our hands so that our palms are on our temples. We lightly squeeze the head and at the same time strain the neck muscles.
Therapeutic exercises can be harmful if used without the advice of a doctor. Our clinic specialists create an individual training plan for each patient, which gives better results.
Diagnostics
If the above symptoms occur, you should urgently visit a neurologist. Having suspected protrusion, he will refer the patient, first of all, to an x-ray. This simple and inexpensive examination will show whether there is a pathology, after which its examination is most effectively carried out using magnetic resonance imaging. It will provide comprehensive information about the size of the protrusion, the direction of the disc exit, the condition of the vertebrae and surrounding tissues. Myelography (x-ray examination using a contrast agent) and computed tomography are also considered informative methods. They are prescribed as needed as additional studies.
To identify the causes of the disease, you may also need to take a biochemical blood test, which will show the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and the degree of absorption of substances important for cartilage tissue. If you suspect hormonal diseases, you will have to do a separate blood test.
What happens when a disc protrudes?
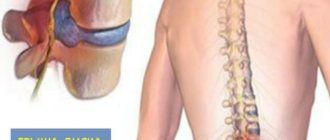
To understand what happens during protrusion, let’s look at how the intervertebral disc is structured. The gelatinous nucleus pulposus, the central part of the intervertebral cartilaginous disc, is surrounded by a fibrous ring consisting of fibrocartilaginous and connective tissue.
As a result of degenerative processes, the fibrous ring becomes thinner, loses elasticity, cracks appear in it, into which the nucleus pulposus begins to shift, a protrusion or protrusion is formed - this is disc protrusion. During protrusion , only the internal fibers of the fibrous ring are damaged, and the remaining external fibers form a mobile fragment of the intervertebral disc.
The resulting protrusion extends (falls out) into the spinal canal, resulting in irritation or pinching of the nerves and vessels located there. In addition to compression of the nerve, the stability of the spinal segment itself may be disrupted.
When there is rupture (damage to the outer fibers) of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc in combination with protrusion of a fragment of the nucleus pulposus, when its connection with the substance of the nucleus is not broken, prolapse (prolapse) of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal is formed, which is considered to be a true intervertebral hernia.
Treatment
- When treating protrusion in the neck area, it is important to immobilize this part of the spine, for which special fixing collars are used.
- Drug therapy helps relieve pain, inflammation and swelling. To improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors, drugs that stimulate blood circulation, and vitamins are prescribed.
- Massage, physiotherapy, and a special set of exercises play a big role in restoring the spine. They help improve nutrition of the intervertebral discs, relax and stretch the spine.
Drug treatment
Among the medications used to treat cervical disc protrusion, several drugs are used at once, as well as other methods of therapy. The combined effect gives the best result, so patients are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that can eliminate the painful symptoms of the pathology. Aseptic inflammation that develops during protrusion provokes pain and swelling, so NSAIDs are able to break the mechanism of the inflammatory reaction and relieve the patient from discomfort. Drugs for the treatment of protrusion of intervertebral discs of the cervical spine include Movalis, Diclofenac, Voltaren. For ease of use, various forms of medications are available - creams, ointments, tablets, injections.
- Glucocorticosteroids are drugs with hormones (Flosteron, Triamcinolone), which act on the principle of NSAIDs, only they have a faster effect, but cannot be used for a long time due to addiction and side effects, they are usually prescribed together with analgesics.
- Chondroprotectors are products for long-term use containing glucosamine and chondroitin that act as prophylaxis because they have a cumulative effect.
- B vitamins for the treatment of protrusion of intervertebral discs of the cervical spine are prescribed to improve the conduction of nerve impulses and are used as maintenance treatment, as well as for prevention.
Research shows that properly selected drug treatment and a set of exercises and physical therapy can get rid of protrusion at an early stage, as well as slow down further protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Treatment of cervical disc protrusion using a conservative method is the best solution rather than surgical intervention.
Prevention
You can avoid changes in the intervertebral discs by following simple rules:
- strengthen the neck muscles;
- avoid sudden movements;
- maintain correct posture;
- eat rationally, take additional vitamin and mineral complexes if necessary;
- control chronic diseases, avoiding complications.
Considering that protrusion occurs more often with age, doctors recommend that all people over 40 years old undergo regular preventive examinations of the spine.
Prevention of cervical protrusion
In order to reduce the likelihood of developing protrusion to a minimum, the following recommendations must be followed:
- do not lift heavy objects;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- monitor your posture, when working sedentarily, take breaks every hour and stretch your neck by performing special exercises;
- engage in physical exercise (swimming is especially useful for preventing cervical protrusion);
- fight obesity (extra pounds contribute to increased stress on the spine);
- Healthy food.
Types of protrusions
Depending on the location of the protrusion of the fibrous ring relative to the spinal column, lateral, posterolateral, central (median) and posterior protrusions are distinguished.
Lateral (side) protrusion
The term “lateral protrusion” means that the protrusion of the annulus fibrosus is located to the side (right or left) of the spinal column. In this case, the likelihood of pressure on the spinal cord roots is quite high. This type of protrusion occurs quite rarely (in 10% of cases) and is often asymptomatic until the protrusion puts pressure on nearby roots.
Posterolateral protrusion
The term means the location of the protrusion back and sideways in relation to the spinal column. With this location of the protrusion, there is a high probability of not only affecting the roots (as with lateral protrusions) on the right or left, but also on other structures of the spinal cord. Just like the lateral one, this protrusion can be asymptomatic until there is a physical impact on the nerve structures.
Central protrusion (median)
The term refers to the direction of the bulge towards the center of the spinal canal. With this arrangement there is a risk of impact on the spinal cord. As a rule, such protrusions are asymptomatic and rarely require treatment.
Posterior protrusion
The term means the direction of protrusion from the abdomen to the back. This location of the protrusion most often leads to a direct effect on the spinal structures and leads to pain syndromes, sensory disturbances, motor disorders, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Specialists
Tolkacheva Daria Evgenievna
Vladimir
Medical specialist
Galetsky Vladimir Stanislavovich
Bratsk
Deputy Director for Medical Activities, kinesiotherapist, orthopedic traumatologist.
Muravyova Irina Mikhailovna
Kinesiotherapist
PROTRUSION OF DISCS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE
The initial stage of the disease passes without any special manifestations. Over time, the protrusion leads to compression or pinching of nerve endings and nerve bundles. May cause compression of the spinal cord. These processes accompany:
- constant or paroxysmal pain syndrome. The pain is of a shooting nature, intensifies during laughter, sneezing, coughing, and jerky movements. May radiate to the pelvis, thighs, legs, heels;
- feeling of numbness in the legs;
- pallor or hyperemia of the skin of the lower extremities, feet, impaired sweating;
- weakness in the legs;
- staying in one position for a long time causes a nagging pain that disappears after changing position;
- burning sensation in the lower back;
- swelling of the legs and lumbar region;
- increasing pain with physical exertion, heavy lifting, or playing sports;
- urination disorder.
Degree of progression of protrusion
Conventionally, the degree of neglect of the disease can be conditionally attributed to one of three stages. Depending on how long the disease has progressed, treatment and rehabilitation are prescribed. Let's look at each of the stages.
First stage
At this stage, the fibrous ring, which is the shock absorption of the spine, begins to suffer from disturbances in its structure: cracks may form, the shape of the core may change, and so on. Patients with mild protrusion can be treated quickly and without further consequences.
Second phase
After this, the ring continues to deform. The core begins to protrude to a distance of approximately 3-4 millimeters. This leads to pressure on blood vessels and nerve endings that lie nearby. Patients at the second stage complain of lumbago in the spine and developing pain in the area where the ring was deformed.
Third stage
If the protrusion is not treated, the disease will move to the next stage. The ring begins to protrude to a distance of at least 5 millimeters, which leads to rupture of the core. The patient develops a hernia as a result.
Possible complications
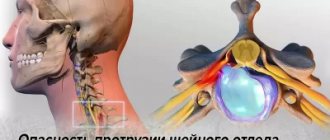
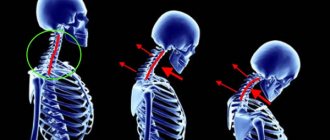
The cervical region of the back is very delicate, since it is made of the thinnest and most fragile vertebrae. But they are the ones who hold such a heavy construct on themselves - the head, and also make all our turns and movements of the head possible. For comparison, a person can live for a long time and unnoticed by himself with a disc protrusion in the lumbar region up to 4 mm in size. But this will not work with the cervical region: here a protrusion of even 1 mm can provoke a whole galaxy of the above neurological symptoms.
Dangerous consequences of unrecognized and untreated neck protrusion:
- Inflammation of a pinched nerve is the development of cervical radiculitis.
- Rupture of the disc shell, exit of the nucleus and formation of a hernia.
- Permanent paralysis of a certain area of the body (depending on the level of hernia formation).
It’s no wonder that paying close attention to your body and timely seeking help from a specialist will help you avoid many of the dangerous complications of neck protrusion.
Symptoms of cervical protrusion
As you know, problems begin when something gets out of control or beyond what is permitted. And protrusion of the neck discs is a textbook confirmation of this.
Protrusion of the fibrous ring of the disc to the limits of the axial skeleton of the spine is accompanied by irritation, and in advanced cases, pinching of the intervertebral nerves of the neck.
Irritated and pinched nerves cause symptoms such as:
- The pain is constant or transient (in the neck, shoulder girdle, upper limbs, palms).
- Numbness, paresthesia of the hands.
- Inability to painlessly rotate the neck, crunching and crackling when turning and bending.
- Unpleasant sensations in the back of the head, pressure, heaviness in the head.
The appearance of these symptoms is due to the area of innervation of the intervertebral nerves of the neck. For example, entrapment in the area of the C4 vertebra (dorsal roots) causes:
- neurological reactions of the facial nerves,
- ear and nose diseases,
- neurasthenia,
- headache.
Disorders of the C5 vertebra cause difficulty controlling swallowing.
With protrusions of the two lower discs (C6, C7) the following are possible:
- temporary paralysis of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs,
- arthritis,
- bursitis.
The intervertebral nerves of the neck penetrate with their branches the chin, part of the back of the head, neck, and the belt of the upper limbs. The nerve roots, leaving the spinal cord, pass through the intervertebral foramina in close proximity to the discs themselves. And if the latter protrude outward, they naturally come into contact with the nerves. And, as you know, it’s better not to interfere with the work of your nerves, otherwise you won’t end up in trouble!
The matter may get worse if the vertebral artery is pinched (or is periodically “touched” by a protruding disc) of the vertebral artery. It runs in the cervical region on both sides of the spinal column. Symptoms of a slightly different order arise here:
- “Jumps”, or persistent increase/decrease in blood pressure.
- Vegetative “storm”: nausea, dizziness, apathy, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes, lightheadedness.
- Behavioral disorders.
This group of symptoms characterizes oxygen starvation of the brain. Patients often complain of pain in the heart. This often confuses doctors because the root of the problem turns out to be pinched nerves in the neck.
Kinds
Depending on the location of the protrusion, three types of protrusion are distinguished. They are most often formed in one of three sections - cervical, thoracic, lumbar. This happens because these segments of the spine are characterized by the greatest mobility.
Cervical protrusion
Despite the rarity of the formation of protrusions in the cervical spine, we must not forget about the possibility of its occurrence in you. First of all, you need to pay attention to localized pain in the neck and shoulder area. The pain in this place is usually aching and sharp. As the disease progresses, the pain begins to increase. In addition, your hands may also begin to suffer.
Often, cervical protrusion leads to numbness, tingling of the skin, a noticeable loss of sensitivity of the skin, muscle weakness, “jumping” blood pressure, problems with coordination and dizziness.
The cervical region is where the brain begins and where the main blood vessels are located that provide blood flow to the brain. Therefore, deformation of the rings in this segment can lead to really serious health problems. The first signs of this are high fatigue. The neck often begins to become numb when sitting for a long time, it is uncomfortable to lie in bed (the pillow seems uncomfortable), the head is held only with great tension in the neck. These signs should alert you, after which you should immediately consult a doctor.
There are seven vertebrae in the cervical region, separated by IVDs. The main difference between this segment of the spine and others is mobility, high mobility thanks to the discs. Therefore, neck movements are easy for us, and the head is kept quite stable without additional problems in a healthy state.
Excessive mobility can lead to wear of the intervertebral discs and the appearance of a bulge. And this leads to pinching of nerve endings, roots, and also the spinal cord.
Another factor that makes cervical protrusion the most dangerous is the severity of detection without examination. Unfortunately, it is often discovered only after the ring has ruptured. During the progression of the disease, myelopathy, one of the types of chronic damage to the spinal cord, may develop. The syndrome is characterized by an irritating effect.
The main consequences of the pathology: hearing loss, loss of vision. Reflexes may disappear, and patients suffer from invincible muscle weakness. In the worst cases, paralysis of the entire body is possible.
Thoracic protrusion
It is rare to see protrusion of the intervertebral disc in this region. This is due to the relatively low mobility of the chest and spine in this segment. But they can still form. Why is this happening?
This can occur with general pain in the spine or incorrect diagnosis of a heart attack (the symptoms are quite similar). The disease most often manifests itself in the form of neuralgia in the intercostal space with varying strength. Pain is accompanied by muscle weakness and noticeable stiffness in the chest and back.
Not only pain can become an important signal about the development of thoracic protrusion: thus, another flag should be discomfort that appears when sitting or standing. Also, an eternal, persistent feeling of fatigue in the back muscles, a negative effect on the spine in the form of irritation of local places. Unpleasant sensations in the thoracic region. The body uses these signals to tell you that the IVD is in poor condition.
Let's highlight the main symptoms of the development of pathology, which indicate the need for treatment of spinal protrusion in the thoracic region. You should never give them little importance, everything is important. So the list is like this:
- the middle of the back suffers from constant pain;
- numbness and lumbago appear in the chest and abdomen;
- intercostal pain;
- the tone of the abdominal muscles noticeably decreases;
- stiffness in the back.
This variant of the pathology becomes dangerous for the internal organs of the body. First of all, the kidneys and liver come under fire, which can lead to permanent diseases, pathologies and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The pain can become chronic and intense.
Lumbar protrusion
The most defenseless section of the spine, which is most often susceptible to protrusion formations, is the lumbar and lumbosacral sections. This occurs due to the large number of loads on this area, the greatest amplitude in movements and mobility. With age, protrusions can only get worse. Intervertebral discs noticeably wear out over time, especially under the influence of provoking factors. In this case, the characteristic features are pain in this region, which spreads to the lower limbs and significantly complicates coordination, up to the loss of the ability to move the legs.
There are other markers that need to be considered for the possible formation of a bulge. This is tension and aching pain in the lumbar region before going to bed (the syndrome is relieved by lying down), lack of comfort in a sitting position. It is difficult for patients to spend at least a few minutes without changing their position; sitting without leaning on the back of a chair becomes difficult. These and other signs indicate deeply developed protrusions that need to be treated urgently. Don't delay this, especially if you have the following symptoms:
- pain in the central part of the lower back, which spreads horizontally and covers the entire lower part of the torso;
- there is noticeable stiffness in the affected area;
- radiculitis develops;
- the muscle frame in the legs noticeably weakens, especially in the thighs and calves;
- constant feeling of numbness in the toes;
- tingling feet;
- from time to time the process of urination is disrupted, the body’s false urge to urinate appears;
- leg reflexes noticeably decrease and disappear;
- the body is difficult to rotate along the vertical axis;
- when sitting, the lower back suffers from severe pain;
- the body reacts sharply to changing weather conditions.
In the future, lack of treatment leads to paralysis of the lower limbs. Don't delay going to the doctor.