How to treat protrusion L4 – L5
For therapy for lumbar protrusion to be effective, it is necessary to exclude all provoking factors - avoid heavy lifting, monotonous sedentary work, jumping and sudden movements.
Treatment includes medications, physical therapy and surgery. The absence of timely measures to combat pathology will lead to the formation of a herniated disc in the spine.
Medications
Medicines for disc protrusion are designed to eliminate pain, relieve swelling and inflammation, and reduce spastic contraction of skeletal muscles. After the acute condition is relieved, the doctor may recommend medications that help restore cartilage tissue, improve blood circulation and nerve conduction.
Relieving pain spasms and inflammation
To eliminate pain and spasm of skeletal muscles, the following medications are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Movalis. These medications help relieve pain and inflammation in the affected area. It can be used internally in the form of tablets, externally in the form of ointments and gels, and also as injections intravenously and intramuscularly. Contraindication for use is gastric ulcer.
- Tricyclic antidepressants - Amitriptyline, Saroten. This group is effectively used in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome with lesions of the joints and spine.
- Muscle relaxants – Tizanidine, Sirdalud, Mydocalm. A group of medications can relieve muscle spasms, reduce pain and restore the normal position of the vertebrae.
Regenerating
To improve the condition of intervertebral disc tissue, the drug complex also includes chondroprotectors - Glucosamine-Chondroitin, Dona, Alflutop, Teraflex. These products allow you to restore cartilage and promote its nutrition. Thanks to this treatment, it is possible to reduce the intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compounds.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of protrusion of the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae is carried out in the following cases:
- with severe pain that cannot be relieved with conservative methods;
- in case of dysfunction of the pelvic organs – fecal and urinary incontinence.
During the operation, the doctor excises the protruding part of the intervertebral disc and thus eliminates compression of the nerve trunks. Surgical intervention is performed in no more than 10% of all cases of protrusion.
Minimally invasive surgical methods
To eliminate pain and restore function during protrusions, minimally invasive surgical techniques are used:
- Blockade is the introduction of non-narcotic analgesics into the disc area. The procedure helps relieve pain, swelling and inflammation at the site of the lesion.
- Hydroplasty is the most physiological method of surgical treatment. A liquid is injected into the area of protrusion, which washes out the destroyed core and fills the resulting cavity. With this method, the clinical manifestations of the disease disappear very quickly.
- Laser burning of protrusion. This method is effective in the early stages of the disease, when the nucleus has the consistency of a gel and has not yet had time to ossify.
- Cold plasma nucleoplasty – evaporation of part of the disk using a special ionized liquid. As a result, the pressure in the cavity between the vertebrae decreases, and the fibrous membrane stretches less.
Physiotherapy
In the complex treatment of L4–L5 disc protrusion, hardware methods are widely used. The most effective are:
- Phonophoresis is the effect of ultrasonic waves on the lesion. The procedure helps relieve pain and inflammation.
- Laser therapy is a light treatment method. With the help of the beam, blood circulation in soft tissues is improved, the quality of cartilage is restored, pain, swelling and inflammation go away.
- UHF is a method of therapy in which special electrodes are pinned onto the affected area. Under the influence of current, the tissues warm up, which promotes the resorption of swelling and inflammation.
- Electrophoresis is a method of exposure in which a medicinal substance is delivered to the diseased area using weak electrical currents.
- Magnetotherapy is the effect of magnetic fields on the spine, which eliminates muscle spasm and promotes the restoration of cartilage tissue.
Massage and exercise therapy
Dosed physical activity and massage help strengthen the muscle corset, stimulate tissue nutrition and blood circulation, and help reduce swelling and inflammation. Regular exercise therapy will help prevent the formation of a hernia. An approximate set of exercises is shown in this video.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=hUqY-p79kq8
Prevention of posterior protrusion
In most cases, posterior diffuse protrusion requires surgical intervention to prevent the development of hernial formations. Posterior protrusion poses a significant danger to human life and health.
Therefore, along with conservative and surgical treatment methods, experts recommend disease prevention, which consists of the following actions:
- maintaining an active lifestyle, which includes exercise therapy;
- maintaining a proper balanced diet;
- abstinence from bad habits (smoking, alcohol, etc.);
- timely correction of excess weight;
- avoidance of stressful situations.
Posterior protrusion is a pathology that can bind a person to bed at any age. But with timely treatment and effective prevention, in 80% of cases, complications of the disease can be successfully avoided without resorting to traumatic surgical treatments.
Symptoms and diagnosis of pathology
Diffuse protrusion is characterized by typical signs that allow you to independently diagnose the disease.
Main symptoms:
- Pain syndrome in the lumbar region.
- Stiffness of the spine.
- Numbness of the limbs and buttocks.
- "Goosebumps" in the lumbar region.
- The muscles have lost their elasticity.
At the first stage of the disease, the pain is clearly localized and appears from muscle contraction. With increased compression of the nerve endings, immobilization may occur, and this is typical for an intervertebral hernia. Compression syndrome can cause inflammation in the tissues, which also causes pain.
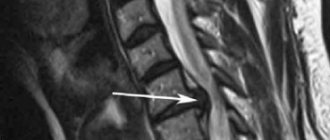
At the first symptoms you need to visit a neurologist. The specialist, having studied the symptoms, will prescribe the necessary tests. In this case, X-rays, CT and MRI are used. These methods allow you to obtain the most reliable information. With their help, the degree of damage to the spine and the location of the protrusion are determined. In order for the diagnosis to be complete, it is better to carry it out comprehensively.
For example, a CT scan provides less information than an MRI. She cannot determine whether the deformity affects the spinal canal of the brain and is even often mistaken in the size of the protrusion.
Magnetic resonance examination, although more complex, provides comprehensive information about the pathology. MRI detects inflammation, the presence of various changes and the presence of other spinal diseases.
If the diagnosis is made in a timely manner, then the treatment will be successful.
You can learn about how protrusions appear and are treated in each part of the spine in the following articles:
- The reasons for the appearance of intervertebral disc protrusion in the neck are described on the page https://spinatitana.com/pozvonochnik/drugie-zabolevaniya/protruziya/protruziya-shejnogo-otdela.html
- About the symptoms and treatment of protrusion of the thoracic spine in the next article
- You can learn more about the diagnosis and treatment of L5-S1 disc protrusion here
- What is a C5-C6 disc protrusion in the cervical spine?
Symptoms of posterior disc protrusions
As a rule, posterior disc protrusions occur without pronounced symptoms in the initial stages, which is fraught with serious consequences in the future.
Protrusion is an early alarm bell indicating the start of the formation of an intervertebral hernia.
Many patients still do not understand how to correctly interpret the symptoms of a disease that has no obvious signs.
The first obvious symptoms will appear only when the disease reaches nearby nerve endings, but even in this situation the pain can be quite mild.
Signs of exacerbation of posterior protrusion
Doctors specializing in the treatment of posterior protrusion of the spine identify several main signs by which one can suspect the presence of an insidious disease:
- Difficulty getting out of bed after a night's sleep or a long day's rest, expressed by stiffness of movement.
- Dull aching pain with the slightest physical activity, which is caused by protrusion of the nerve roots.
- The appearance of reddened areas of the skin in the area where the pathology is localized, which is explained by impaired blood flow.
- Severe pelvic organ disorders
- Weakening of the muscle corset and loss of muscle elasticity in the protrusion zone.
- Radiating pain in the lumbar spine.
Each patient has his own individual symptoms of dorsal protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Signs of pathology directly depend on the form and stage of the disease, and a person’s pain sensitivity.
Concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system further complicate the diagnosis of protrusion.
Brief description of the pathology and the main stages of its development
At its core, circular disc protrusion can be briefly described in one word – “protrusion”. The intervertebral disc with its contents protrudes beyond the line of the spine. The protrusion occurs in a circular pattern, and its dimensions can vary from 3 mm to 12 mm. The protrusion may vary in different parts of the disc, but not more than 1 mm.
We advise you to study - Which doctor treats scoliosisIn most cases, the disease takes a chronic form. If a patient neglects therapeutic procedures and does not promptly seek help from a medical organization, advanced stages of pathology lead to the person losing his ability to work and becoming disabled.
In the process of pathology development, doctors distinguish three main stages:
- A crack appears in the structure of the fibrous ring. Because of this, the structure of the intervertebral disc begins to change. Intense sudden pain at the site of pathology indicates that circular disc protrusion is developing.
- The disc protrudes, but the size of the protrusion is small (up to 0.3 cm). Localization of pain occurs where cartilage tissue and bone are subject to deformation. Referred pain may occur.
- Increasing the size of the protrusion. The fibrous ring is in danger of rupture (subsequently developing a hernia). The intensity of pain increases. At the stage of hernia formation, the patient experiences acute severe pain and numbness of the limbs.
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out using computer or magnetic resonance imaging. The methods of radiography and ultrasound examination of the spine to detect protrusions of intervertebral discs show low efficiency, and therefore are practically not used.
In case of timely detection of pathology, conservative therapy methods are effective - according to statistics, in such situations, surgical intervention is required only in 10% of cases.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Affected discs may not cause any clinical manifestations, but more often present with pain. It happens that intervertebral disc protrusion is not diagnosed immediately, as patients come with vague pain in the hips, knees or legs. Although it is theoretically possible for a hernia to appear in any part of the spine, in practice, as a rule, patients are faced with damage to the intervertebral discs in the cervical and lumbar regions. The onset of protrusion formation can be acute, due to injury or sudden movement, or develop slowly, progressively, without visible external causes.
Symptoms of intervertebral disc protrusion may vary depending on the location of the hernia and the type of soft tissue that is affected by it. They can range from a pain-free existence, where a bulging disc is the only change, to severe and unrelenting pain in the neck or lower back that radiates to adjacent areas. Other symptoms may include sensory changes such as numbness, tingling, or a crawling sensation; Muscle weakness, paralysis, and changes in reflexes may occur.
For example, in the case of a disc protrusion in the lumbar region, the patient may experience pain along the outer or back surface of the leg, a feeling of “muscle spasm,” numbness or tingling in these areas.
Damage to the nerves in the lumbosacral region can lead to loss of bowel and bladder control, as well as sexual dysfunction (cauda equina syndrome).
After the appearance of protrusions of the cervical intervertebral discs, pain occurs, localized in the neck and sometimes in the arms. Typically, symptoms are experienced on only one side of the body.
If the bulge is very large in shape and volume, pressure on the spinal cord can cause pain on both sides of the body, often with serious consequences, which can lead to permanent nerve damage or paralysis.
Protrusions can cause secondary changes in the spine, such as:
- intervertebral disc herniation - rupture of the fibrous ring.
- Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal cord canal, which leads to compression of the spinal cord and the nerve roots emerging from it. Stenosis can also be the result of thickening of the ligaments, the presence of posterior marginal growths, and other reasons.
- Osteoarthritis of the intervertebral joints is the result of wear and tear of the articular cartilage in the intervertebral joints. In this case, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, which changes the relationship of the articular surfaces to each other, as well as the mechanics of the joint itself.
Types and clinical manifestations
Lumbar protrusion is a degenerative change in cartilage tissue that can develop into a hernia.
The term protrusion of the intervertebral disc means the formation of a protrusion without compromising the integrity of the fibers of the fibrous ring. The pathological process is divided into several types according to certain criteria. Depending on the level of damage, there are:
- Changes at the l2-l3 level - the pathological process develops in the upper part of the lumbar spine with damage to the cartilaginous disc between the 2nd and 3rd vertebrae.
- Protrusion l3-l4 – the upper part of the lumbar spine is affected, a protrusion forms in the disc between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae.
- Lesion l4-l5 is the most common type of protrusion, which affects the intervertebral disc located between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae.
- Protrusion l5-s1 - changes affect the intervertebral disc, localized between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae. The pathological process often leads to disruption of the functional state of the pelvic organs.
Conventionally, damage to the intervertebral discs of the upper, middle and lower parts of the lumbar spine is distinguished, which determines the clinical picture of the pathological process.
Protrusions are differentiated depending on the location of the disc protrusion.
Depending on the location of the protrusion in the intervertebral disc itself, several types of protrusion are distinguished:
- Circular – changes affect the entire disc circumference, as a result of which compression of the spinal cord root in the area of exit from the spinal canal is not excluded.
- Dorsal disc protrusion l4-l5 - protrusion is localized in front of the cartilaginous disc between the vertebrae in the midline behind. With pronounced dimensions of the dorsal formation, the risk of compression of the spinal cord substance increases, followed by muscle paresis and a pronounced impairment of the functional state of all pelvic organs.
- Median or central - the protrusion is localized along the medial or midline of the intervertebral disc in front, which leads to disorders that largely affect the spine.
- Diffuse protrusion of the l4-l5 disc, in which the localization of changes cannot be clearly established.
- Lateral or paramedian - changes are localized along the lateral surface of the intervertebral disc, which is often accompanied by the development of an inflammatory reaction of surrounding tissues and compression of the spinal cord root.
Lumbar protrusion can affect the functions of the pelvic organs.
There are several main clinical symptoms that appear when intervertebral discs are damaged.
- Pain in the lumbar region, which has different localization. Most often it occurs in the area of vertebrae l4-5, somewhat less often - l3-4. The severity of pain depends on the size of the formation. It usually worsens after exercise.
- Irradiation of pain - compression of the substance or root of the spinal cord leads to pain radiating to the right or left leg, thigh, mainly along the back surface to the knee or lower to the foot. Irradiation can be left-sided or right-sided. As a result of radiculopathy, the buttock and leg hurt down to the foot on the left or right.
- A decrease in muscle strength is a sign of a disturbance in the transmission of impulses along the motor nerve fibers of the substance of the spinal cord or its roots. Complete blockade leads to the development of paralysis on the affected side. When the substance of the spinal cord is severely compressed, movement disturbance affects both legs. The symptom is often provoked by circular protrusion of the disc of the l4-l5 vertebrae. At the same time, the fifth vertebra is deformed.
- Decreased skin sensitivity - when the conduction of impulses along motor nerve fibers is disrupted, which is called discoradicular syndrome, numbness develops. It affects the lumbar region, lower limb on one or both sides.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs is an unfavorable sign indicating severe compression of the spinal cord substance. Accompanied by difficulty in defecation and urination. Men experience problems with erection, women experience changes in their menstrual cycle.
Types of dorsal protrusion
Depending on the location of the intervertebral disc protrusion, doctors classify the pathology into several types.
Posterior median protrusions: types, causes
The median part of the spine often suffers more than other areas due to increased load and large range of motion. In addition, the situation is aggravated by age-related degenerative processes.
Doctors classify several types of median protrusion according to the following characteristics:
- Middle. The pathology is localized in the back of the disc and protrudes towards the spinal cord.
- Central. The damaged area bulges towards the center of the canals.
- Rear. The protrusion is directed towards the center of the spinal canal.
In fact, the classification of pathology (middle, central, posterior) describes the same disease, which is slightly different in symptoms. In all forms of the disease, the patient will have to face similar symptoms - pain of varying intensity, stiffness of movement, numbness of the limbs, dizziness and other symptoms.
Posterior median protrusions are fraught with the development of paralysis of the limbs in the absence of qualified treatment.
Paramedian protrusion: causes, features
Due to some features of the protrusion of the degenerative nucleus of the intervertebral disc, doctors distinguish a special type of protrusion - paramedian. Posterior protrusions of intervertebral discs can be right or left-sided.
Protrusions are classified according to the uniformity of protrusion:
- uneven disc protrusion;
- uniform bulging of the disc towards the center of the spine.
Among the main causes of pathology, doctors especially highlight a sedentary lifestyle, incorrect posture and poor development of the back muscles.
Localization of pathologies and typical symptoms of lumbar hernias
The intensity of symptoms may be associated with the primary disease that caused the hernia in the lumbar region. Education can be triggered by:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Congenital anomalies;
- Microelement imbalance that disrupts the nutrition of the intervertebral space;
- Improper drinking regime (dehydration);
Each part of the spine is responsible for a specific muscle
- Obesity;
- Problems with blood vessels;
- Great physical activity;
- Spinal injuries.
When problems associated with protrusion of the intervertebral disc occur, symptoms manifest themselves in the form of lumbar pain, radiculitis, general weakness of the body, and numbness of the lower extremities. Severe forms of the disease may be accompanied by a disorder of the urinary system. In case of pathological processes associated with the development of intervertebral disc herniation l3-l4, l4-l5, l4-s1, l5-s1, the patient will be observed by a neurosurgeon. The disease requires constant monitoring of the condition and timely treatment. The disease manifests itself in different ways, the severity of symptoms is associated with the localization of the pathology, that is, the location of the damage.
Disc herniation l3-l4
This is a rare type of disc herniation. Damage to nerve fibers l3, l4 is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, in the groin area, and inside the thigh. The sensitivity of the outer surface of the thigh is impaired, numbness, a slight burning sensation, and the appearance of “goosebumps” on the skin are possible.
Intervertebral hernia l4-l5
The most common type of hernia. Disks l4, l5 bear the maximum load. When the nerve is compressed, the patient feels pain in the first toe and foot. The sensitivity of these organs decreases and movement is limited.
Hernial formations l5-s1
This type of hernia is diagnosed frequently. The s1 nerve is compressed, causing weakness of the fingers, muscle pain, and numbness on the outer surface of the foot. A typical symptom is the inability to rise on the toes. Damage to the l4, l5, s1 nerve roots, which are part of the sciatic nerve, is usually characterized by pain in the thigh, foot and lower leg. It is difficult for the patient to bend his leg and move his fingers. The foot becomes cold, sometimes due to muscle atrophy it is difficult for the patient to control its movement.
We advise you to study - Treatment of back painWhat is (dorsal) posterior protrusion?
Posterior protrusion is a serious and dangerous disease associated with protrusion of the intervertebral disc towards the axis of the spinal canal. With pathology, patients are often diagnosed with inflammation and pinched nerve roots, which risks leading to the formation of an intervertebral hernia.
The pathology is accompanied by a pronounced pain syndrome, and in the absence of qualified treatment, it can cause the development of disease of the spinal nerves.
Unlike other forms of protrusion, the pathology of the dorsal zone is characterized by repeated and uneven protrusion of the discs, which negatively affects the functioning of vital internal organs.
Types of semicirculatory deformities
Local protrusions of cartilage tissue, depending on the direction, can be divided into these types of protrusions.
Lateral (side)
Disc deformity occurs to the left or right of the spinal column. This variety more often than others leads to the development, where the compression of the vertebrae is the strongest.
But if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis for such a bulge is favorable.
Posterior (dorsal)
The bulging of the disc cartilage occurs inside the spinal canal, compressing the spinal cord and the nerve processes extending from it.
Dorsal semicircular protrusion is considered the most dangerous, because compression of the spinal tissue and the roots extending from it often leads to dysfunction of organs or limbs and causes various neurological symptoms.
Unfortunately, this type of pathology can only be detected at an early stage, and therapy begins when the form is already advanced. Dorsal changes are most often subject to surgical treatment.
By location
Protrusions according to location are divided into:
- Cervical. The most dangerous due to the narrowness of the spinal canal in this section, and due to the fact that many important vessels feeding the brain are located in the neck.
- Breasts. This variety is less common than others, since the thoracic region is less mobile and less frequently exposed to motor stress.
- Lumbar. Due to the high load on the vertebrae, this type of protrusion is diagnosed in most patients.
Is it possible to be cured?
Unfortunately, destructive phenomena in cartilage tissue, once they have occurred, cannot be restored.
Those who believe the advertising and pay a lot of money for the opportunity to be completely cured will remain disappointed with the result, receiving only temporary relief.
So is there really no hope? Not everything is so sad: osteochondrosis and its more advanced forms (disc protrusions) cannot be completely cured, but you can stop the development of the disease for a long time and partially restore the pathologically altered disc with the help of:
- regular performance, selected by a doctor;
- lifestyle changes and giving up bad habits.
It seems incredible, but it is rarely used for therapeutic purposes, mainly to relieve pain.
Forecast
The outcome of the disease in the early stages is favorable. Maybe:
- Slowing down or completely stopping deforming changes in the disc.
- . This is not always possible, but the “younger” and smaller the deformity, the greater the likelihood of reduction.
But when forecasting you should consider:
- Location. Cervical pathologies are less amenable to treatment and complications most often arise with them.
- Direction. Lateral protrusion is much easier to treat and preventive procedures.
But if timely treatment is neglected, semicircular disc protrusions with signs of discodural conflict may occur, during which the following may be observed:
- Severe pain syndrome, almost unresponsive to drug therapy.
- Impairment, up to complete loss, of sensitivity and motor functions.
Is the diagnosis of semicircular disc protrusion scary? No more than anyone else reporting spinal problems.
There is no need to panic, looking for expensive miracle drugs and looking for a miracle doctor. There is no such thing. The disease cannot be cured, but you can learn to live with it.
If you want to get more information and similar exercises for the spine and joints from Alexandra Bonina, check out the materials on the links below.
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
Stages of development
Like any disease, protrusion does not develop simultaneously. There are pathological stages that occur in stages.
Table. Stages of development of protrusions
| Stage | Characteristics |
| Initial | Sometimes there is an asymptomatic course, but usually the patient already at this stage experiences paroxysmal pain that goes away on its own, without any medical intervention. During this stage, the annulus fibrosus loses its elasticity. It is not subject to destruction, only microcracks appear on the surface. Identification of violations in most cases occurs during a preventive medical examination or at the stage of diagnosing other diseases. |
| Second | The main events of this period are the beginning of displacement of the fibrous ring. It protrudes (due to which the disc protrudes) is still insignificant, literally by one or two millimeters. If the pain of the initial stage is localized, then the second stage is characterized by migrating pain. The complexity of the second stage is higher than the initial one, but when the pathology is diagnosed at this stage, the disease is not considered dangerous and can be cured even without the use of medications. An exception is the protrusion of the vertebrae L4 -L5, during which the displacement of the fibrous ring occurs faster, can reach three millimeters and spreads in several directions at once |
| Third | There is a maximum protrusion reaching five millimeters. To the previous symptoms is added an increase in pain to the point of unbearable, numbness of the lower parts of the body, and the occurrence of an inflammatory process that begins due to increased pressure of the fibrous ring on nearby nerve endings. At this stage, complex therapy is required, including medication, physiotherapy and corrective methods. |
Stages of spinal hernia and top and side views
Clinical picture
This type of lumbar protrusion is the main one, in which the nervous system is affected: both individual nerve roots and their bundle (“cauda equina”). Posterior protrusion is recognized by the location of pain - on the side and back of the thigh; it can spread to the foot.
The pain initially manifests itself in attacks after a long stay in one position or heavy loads. It is difficult for a person to move, and the functions of the pelvic organs are impaired.
Due to pinched nerves, the following develop:
- intervertebral hernia;
- leg paralysis;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
Dorsal disc protrusion l5-s1 is treated with manual therapy at the initial stage, painkillers; in severe cases, surgery is required.
Symptoms
L5-s1 disc protrusion may initially be asymptomatic: the bulging disc does not come into contact with the nerve roots and does not affect them in any way. Erased symptoms do not draw the patient’s attention to themselves.
When the bulging disc has reached the nerve endings, it manifests itself through:
- periodic or constant pain that radiates to the hips, buttocks, reaching the heels;
- discomfort and stiffness of movement;
- loss of sensitivity in the affected area of the back (feeling of “pins and needles”, tingling, etc.);
- soreness of the lateral and front part of the thigh, big toe;
- pain in the lower back, especially when lifting a straight leg.
We advise you to study - What you need to know about x-rays of the spine?
Causes
Protrusion is characterized by gradual formation. The disease manifests itself due to:
- improper or inadequate nutrition (deficiency of vitamins, minerals and amino acids), due to which the disc loses its elasticity and density;
- injuries;
- physical inactivity;
- concomitant vertebral diseases: osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, osteoporosis;
- hypothermia;
- age (from 50 years or more).
Signs of the disease depending on the type
The occurrence of protrusion does not depend on the gender or age of a person. Of course, physiological aging is a significant factor in the occurrence of disc displacement and deformation, but various pathologies can also influence these processes.
To prescribe the correct treatment, the doctor must know what type of disease it is. In the existing classification, dorsal and medial protrusions are considered the most dangerous and unpredictable.
With this pathology, the disc nucleus protrudes, which puts pressure on the spinal canal and provokes neurological manifestations.
Dorsal protrusion is a posterior displacement of the center of the disc, that is, its nucleus. This type of disease provokes severe pain, as parts of the spinal canal and nerve fibers of the spinal cord are compressed.
If the l4l5 vertebral segments are damaged, the following signs of the disease appear:
- pain in the lumbar region, which can radiate to the buttocks, legs, thighs;
- movements are constrained;
- some areas of the body may lose sensation;
- toes become numb and tingling;
- There is a disruption in the functioning of some organs that are affected by pinched nerves.
Most protrusions provoke pain, but it varies. It all depends on which part the displacement occurred. Protrusion of the l5 s1 disc causes pain not only at the site of the lesion, but also in the occipital part and intercostal region.
Damage to the muscular corset in the lumbar region leads to the fact that the muscles begin to weaken, as a result of which the nerves of the sacral plexus suffer.
The main symptoms of this condition include:
- pain in the shoulders and arms, numbness in the fingers;
- headaches that become more intense during movement;
- sudden changes in blood pressure.
Such signs cannot be classified as special, so they are often confused with symptoms of other ailments or with fatigue. Not a single patient could have guessed that spinal disc displacement was occurring in his body, which often leads to treatment for the wrong disease.
Another type of disc protrusion is foraminal protrusion. The displacement occurs in the area of the intervertebral (foraminal) foramen and the 5th lumbar root. The condition is accompanied by pain in the outer thighs, radiating to the lower leg area.
The medial type of protrusion causes a particular danger to human health, since its direction is the central part of the spinal canal. This type of disease is divided into several types:
- Median protrusion requires urgent treatment; complications such as loss of sensation in the legs are possible.
- Posterior protrusion - protrusion is localized in the back of the spine.
- Another type of protrusion is circular displacement, when the bulging of the disc contents is distributed evenly in a circle. This is the most common type of disease and is detected in 80% of all cases of protrusions.
The size of the protrusion varies from 2 to 12 mm, and there is no particular difference in size between the protruding parts in different areas.
Circular protrusion has a protracted course, and if left untreated, it leads to the development of an intervertebral hernia.
De2p7HJ3Sxk
What is the treatment for dorsal diffuse disc protrusion?
Dorsal diffuse protrusion usually occurs in the lumbar region, although it can be diagnosed on any part of the spine. The lower back receives more physical activity, so it is here that the vertebrae and intervertebral discs are more often exposed to various disorders.
In itself, this condition is almost not dangerous, but there are some caveats. Firstly, the concept of diffuse protrusion means damage to up to 50% of the intervertebral disc tissue. Accordingly, the resulting bulge is quite large. Secondly, “dorsal” is a characteristic of the direction of disc deformation, meaning “backwards”. That is, at this stage of the development of the disease, pressure on the spinal canal may already be noted.
If the bulging disc is so large that it affects not only the spinal cord, but also the nerve roots, the patient often notices severe pain. With diffuse protrusion, a damaged disc sometimes infringes on two roots at once, simultaneously affecting the spinal cord - this often results in a whole series of unpleasant consequences.
Symptoms and probable consequences of the disease
The degree and direction of disc deformation largely determines the symptoms of the disease. Among the first signs, mild but long-lasting pain in the lower back is most often noted, which can intensify over time and then become paroxysmal. After intense physical activity or, conversely, prolonged immobility in the same position, an exacerbation of symptoms may occur. Patients sometimes feel a crunch or click in the area where the disease is located, and after this the pain is felt much more intense.
In the acute period of the disease, pain may be felt even when coughing or taking a deep breath. If treatment is not started during this period, the pain may spread to the legs, even to the very toes, accompanied by some neurological manifestations.
But no matter how unpleasant these symptoms are, they are reversible. If treatment is started in time, the development of the disease can be controlled and even stopped. If treatment for disc protrusion is not started in a timely manner, then sooner or later it will develop into a herniated disc, and this always means serious unpleasant consequences for the health of the spine.
In addition to the various pain manifestations observed with intervertebral herniation, functional impairment may also occur. A destroyed intervertebral disc will put pressure not only on the bases of the nerves, but also on the spinal cord, and sometimes until it is irreversibly damaged.
Based on the fact that this pathology is most often localized in the lower back, the consequences can be associated with this particular part of the spine. Compression of the spinal cord can lead to serious problems such as urinary incontinence, leg paresis and other consequences of sensory impairment. In the future, this may result in loss of ability to work and subsequent disability.
What methods are used to treat disc protrusion?
The success of treating this disease depends almost entirely on the timeliness of its onset. The earlier the problem was identified and solved, the easier and sooner the result is achieved. If detected early, protrusion can be treated quite simply, without surgery.
If at the time of diagnosis the patient already complains of pain and neurological changes, then treatment should begin with control of physical activity and medication aimed at pain relief and inflammation relief. At the same time, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, which are also involved in alleviating the patient’s condition by relieving pain and improving blood circulation in the area where the disease is located.
Further treatment consists of three components, used in combination: diet, massage, physical therapy. Diet control makes it possible to provide the body with all the necessary nutrients, along with limiting the consumption of foods that provoke the development of osteochondrosis and other deposits in the vertebrae and joints. Massage returns the necessary balance to the back muscles - relaxes those that are overstrained and normalizes the state of those that are too relaxed. And finally, exercise therapy is the main component of treatment. It improves metabolism and provides the necessary, carefully adjusted load on the spine.
Surgical treatment of the disease will not be necessary at this stage, but if you miss the moment of development of a hernia from a protrusion, surgery will be inevitable.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment methods
L5 s1 disc protrusion must be treated. This will avoid the development of complications, among which the most serious is disability. In addition, timely treatment will significantly improve the quality of life, eliminating constant pain and other manifestations of pathology. The therapeutic process includes several areas:
- Taking medications;
- Massage courses;
- Carrying out acupuncture;
- Manual therapy;
- Physical therapy classes;
- Reflexology.
In addition to the main methods of influence, there are general recommendations, the observance of which is also mandatory. These include:
- Avoiding heavy stress on the back;
- Limiting stress factors;
- Quality food.
The list of medicines includes the use of:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Analgesics;
- Muscle relaxants;
- Vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Immunostimulants.
At the recovery stage after the main treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out. Among them, the most effective is considered to be:
- Magnetic therapy;
- Electrophoresis;
- Myostimulation.
The indication for this will be not only severe pain, but also the involvement of internal organs in the pathological process. Among the effective methods of surgical intervention are hydroplasty, laser vaporization, and microdiscectomy.
Protrusion of the l5 s1 disc creates many problems for its owner. Constant pain, including headaches, disrupts the usual way of life. Deterioration in health negatively affects the performance of professional duties, even if they are not related to physical activity. Timely diagnosis and treatment will allow you to restore lost or weakened functions and significantly improve your life in general.
L5-S1 protrusion is a protrusion of the intervertebral disc between the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae. This is the most frequently and dangerously affected area of the spine.
Dr. Ignatiev’s clinic treats L5-S1 disc protrusion using non-surgical methods. Reception is by appointment.
According to statistics, lesions of the L5-S1 disc are the most common among all lesions of the lumbar region; this pathology can be found in almost 45-50% of cases of all lumbar protrusions. In 10-11% of cases, a combination of lesions of L5-S1 and L4-L5 (less often L3-L4) occurs. In almost 40% of cases, there are concomitant diseases: anthespondylolisthesis, retrospondylolisthesis, disc herniation, uncoarthrosis, spondyloarthrosis, etc. In almost all cases, the disease occurs against the background of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine (osteochondrosis).
Protrusion of the L5-S1 intervertebral disc can cause entrapment of the right and left roots of the fifth lumbar and first sacral nerve roots, as well as the bundle of nerve fibers (cauda equina) in the spinal canal.
Factors provoking the development of the disease
Posterior protrusion of intervertebral discs is diagnosed by doctors much more often than other types of pathology.
Dorsal protrusion has a systematic effect on the spinal canals. In this case, pain occurs only when the disease has already reached nearby nerve endings.
The annulus fibrosus is closely surrounded by a cartilage core. As a result of degenerative processes, connective and cartilaginous tissue loses its density and elasticity, which contributes to displacement and protrusion of the nucleus. This is the posterior – dorsal protrusion of the discs.
Traumatologists and neurologists note that the most common causes of protrusion of intervertebral discs towards the spinal canal are:
- shocks and mechanical injuries of the spine;
- the presence of a focal inflammatory process;
- problems with blood flow, rapid blood clotting (thrombosis);
- degenerative changes in cartilage tissue;
- genetic predisposition and abnormalities of intrauterine development of the fetus.
The most common protrusions of discs located in the cervical spine (C3-C5). These areas of the spine are responsible for the correct functioning of the neck, head, arms and chest.
Determination of disease development factors
Dangerous posterior protrusions of intervertebral discs can affect a person at any age, especially if the patient has a history of trauma and osteochondrosis.
For a detailed diagnosis of the disease and determination of the causes of the pathology, the localization of protrusion of intervertebral discs, the following diagnostic methods are recommended to the patient:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
- X-ray examination.
- Injection of a contrast agent into the intervertebral space.
- Ultrasound examination.
- Visual examination and palpation of venous systems.
Each of the methods allows you to obtain reliable results, thanks to which the doctor will determine the factors that provoked the disease and will be able to prescribe effective treatment and prevention methods.
Risk factors, causes
Hernias between the L4 and L5 vertebrae, in which the intervertebral disc partially extends beyond the established physiological space, can occur due to:
- unsuccessful falls, blows, which resulted in displacement of the lumbar vertebrae;
- intense physical activity, during which the patient lifted and carried heavy objects, sharply bent over, bent, jumped, turned;
- dystrophic processes developing in the tissues of intervertebral discs;
- a sedentary lifestyle, in which the spinal column is bent, skeletal muscles atrophy, and osteochondrosis develops;
- inflammatory processes that have developed as a result of the activation of viral and bacterial infections.
Very often, the exit of the intervertebral disc into the foraminal opening is provoked by lifting heavy objects. The space between the lumbar vertebrae L4 and L5 suffers mainly, since they bear the greatest load.
Risk factors for the development of pathology include:
- inadequate living conditions;
- hard work;
- low mobility;
- overweight;
- professional sports.
Under the influence of these factors, protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the foraminal opening may begin.