Why does range of motion become limited?
Traumatic injuries
The symptom is almost always observed with injuries, in most cases it is temporary and disappears after healing. The more severe the traumatic injury, the more limited the range of motion. The following conditions are the cause:
- Injury.
Movements are moderately or slightly limited, support is maintained. - Ligament damage.
When stretched, the restrictions resemble a bruise; when they are torn and ruptured, there is an almost complete lack of mobility due to pain. - Fractures.
The symptom is pronounced, with intra-articular and periarticular injuries, it is caused not only by pain, but also by the loss of congruence of the articular surfaces. - Dislocations.
There is no movement, springy resistance is noted.
Amplitude limitations are also observed in wounds, burns, frostbite, caused by pain, tissue damage. With tendon injuries, certain movements (flexion, extension, and, less commonly, abduction and adduction) become impossible due to a violation of the integrity of the structure that pulls the limb segment in the desired direction.
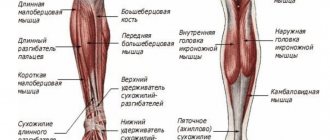
In the knee joint, the symptom may be associated with damage to the menisci. Along with a painful decrease in mobility, this injury is characterized by blockades - temporary fixation of the joint in a forced position due to pinching of the torn meniscus between the articular surfaces. Accompanied by sharp pain, it is eliminated immediately after reduction.
Purulent processes
Temporary limitation of limb mobility due to pain is observed in most purulent lesions of bones and soft tissues. It is more pronounced with intra-articular and periarticular localization of the process and a significant volume of damage. It is detected in the following pathologies:
- purulent arthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- phlegmon;
- abscess;
- felon.
Consequences of injuries, infectious processes
A persistent limitation in the range of motion is observed after injuries to bones, joints, soft tissues, and some purulent diseases. The following types of contractures are distinguished:
- Arthrogenic.
Formed as a result of purulent arthritis, after intra-articular fractures, especially unreduced ones. - Dermatogenic, myogenic, desmogenic.
They are provoked by extensive scars after burns, large lacerations and bruises. Occurs as a result of phlegmon and abscesses. - Ischemic.
They develop as a result of disturbances in the local blood supply during fractures. They are more often diagnosed in children with injuries to the humerus and forearm bones.
In addition, after prolonged fixation of a limb due to injuries or purulent processes, immobilization contractures can form. In some patients, in the long term, the cause of amplitude limitation is myositis ossificans.
Limitation of range of motion
Joint diseases
The range of motion decreases in inflammatory and degenerative diseases, secondary joint damage:
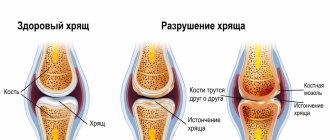
- Arthrosis.
Movements are limited slowly, gradually. The process is observed in the final stages of the disease, several years or even decades after the appearance of the first signs of arthrosis. Contractures can occur in any joint and are of greatest clinical significance in coxarthrosis and gonarthrosis. - Arthritis.
With reactive arthritis, the symptom appears for a short period of time. In gouty, rheumatoid, psoriatic, and other chronic arthritis, the function of the joints is gradually impaired, ranging from mild contractures to ankylosis. - Arthropathy.
Most arthropathy occurs without a decrease in range of motion. A persistent decrease in amplitude can be observed with diabetic arthropathy, HIV infection, Kawasaki syndrome, and Reiter's syndrome. - Synovitis.
Caused by injuries, exacerbations of chronic joint diseases. The symptom is mildly expressed, movements are restored after puncture and the disappearance of inflammatory phenomena. - Tuberculosis of the joints.
Restriction of movement in tuberculosis is initially gentle. Subsequently it turns into persistent pain, and with significant destruction of the joint - into arthrogenic contracture.
Soft tissue lesions
Most often, significant limitations in the range of motion are determined with glenohumeral periarthritis, which combines a group of diseases of the periarticular tissues of the shoulder joint. They are provoked by the following pathologies:
- adhesive capsulitis;
- shoulder bursitis;
- impingement syndrome;
- calcific tendinitis;
- rotator cuff syndrome;
- biceps tendonitis.
Limitations of movement in other joints may be caused by enthesopathy, tendonitis, and tendovaginitis. Usually mildly expressed, aggravated during the period of exacerbation. Persistent restriction of flexion of the ring, and less commonly, other fingers is observed with Dupuytren's contracture. With de Quervain's disease, movement of the thumb is limited due to pain, but persistent contractures do not form.
Diseases of the nerves and spine
The causes of the development of joint contractures are the following pathological conditions:
- encephalitis of various etiologies;
- ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke;
- severe traumatic brain injury;
- cerebral palsy;
- spinal circulatory disorders;
- spinal cord injuries;
- neoplasms of the brain and spinal cord;
- traumatic injuries of peripheral nerves.
Less persistent decreases in the range of motion in the joints of the limbs, caused by compression and inflammation of the nervous tissue, are observed with neuritis and neuropathies. The mobility of the spine is temporarily limited during exacerbation of diseases such as:
- osteochondrosis;
- disc protrusion and herniation;
- radiculitis;
- spondylosis;
- spondyloarthrosis.
Hereditary diseases
Limitation of range of motion develops due to lesions of the skeleton and soft tissues and is detected in the following cases:
- Mucopolysaccharidoses.
Contractures form first in the shoulder and elbow joints, then in the joints of the lower extremities. The spine becomes bent and its mobility also decreases. - Ollier's disease.
There is a shortening or change in the shape of one or more segments. The cause of contractures is periarticular deformation; the number of affected joints ranges from 1 to dozens. Damage to the small joints of the hands is especially severe. - Primary myopathies.
Contractures form in the later stages of the disease and are a consequence of limited active movements. Observed in juvenile Erb myopathy, pseudohypertrophic Duchenne myopathy, and other forms.
Osteochondropathies and other aseptic necrosis
Limitations in range of motion are found in some osteochondropathy in children and adolescents. Particularly pronounced in Perthes disease. At the height of the disease, the range of motion in the affected hip joint decreases. When a mushroom-shaped femoral head develops, the symptom may persist to some extent throughout life, and worsens with the development of secondary deforming arthrosis.
Aseptic necrosis in adults includes lesions of the femoral head and Kienböck's disease. The course is less favorable than in childhood. Limitation of mobility appears at the stage of bone destruction; complete recovery is rarely observed even with adequate timely treatment. In patients with osteochondritis dissecans, there are no persistent contractures; when a section of bone is separated, repeated blockades occur.
Developmental anomalies
Limitations in the range of motion arise primarily due to underdevelopment or disruption of the configuration of articular surfaces, soft tissue defects, and changes in the relationships between bone structures. The following are considered as etiological factors:
- congenital hip dislocation;
- hip dysplasia;
- varus deformity of the hip;
- congenital dislocation of the patella;
- congenital dislocation of the leg.
Other diseases
Along with the conditions listed above, the following pathologies can become the reasons for limiting the amplitude of movements:
- Foot deformities
: cauda equina, calcaneal foot, clubfoot, hallux valgus and hammertoes with transverse flatfoot. - Endemic diseases
: Kashin-Beck disease. - Mental disorders
: hysteria.
Causes
Predisposing factors for the development of joint pain:
- mature and old age (over 40 and especially over 60 years);
- hereditary predisposition;
- congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system;
- intense physical activity or its complete absence;
- overweight;
- injuries and fractures.
Reference! Joint pain is often found in people who do not eat properly and are deficient in calcium, manganese, phosphorus, boron, zinc and silicon.
Problems with joints can arise against the background of disorders in other organs and systems. For example, pain in the hand or knees may be associated with slowed blood flow and impaired regeneration of cartilage tissue.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diseases that cause amplitude limitation is carried out by orthopedic traumatologists. According to indications, patients are referred to a surgeon, rheumatologist, neurologist, and other specialists. The examination program includes a survey, external examination and a number of diagnostic procedures:
- Measuring range of motion
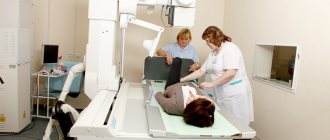
. It is part of the physical examination and plays an important role in assessing the severity and nature of the disorders. Includes determining the volume of active and passive movements, calculating the severity of restrictions, taking into account the norms for various joints. - Radiography.
It is performed for most pathologies with the exception of wounds, burns, and superficial frostbite. Allows you to detect signs of fracture, dislocation, inflammation, degeneration, and clarify the cause of persistent limitation of movements. - Ultrasound
. Sonography is used to study the condition of soft tissues in case of damage to the extremities, to assess the condition of the vessels of the spinal cord and brain in case of circulatory disorders. - Other visualization techniques
. For a detailed study of the state of hard structures, a CT scan is prescribed, and for the study of soft tissues, an MRI is prescribed. The methods are widely used in the study of joints, spine, and brain. - Electrophysiological studies
. Indicated for patients with neurological disorders. Electromyography, electroneurography, and evoked potential studies may be performed. - Lab tests
. They are produced to confirm the inflammatory process, determine microflora, and identify specific markers of rheumatic diseases.
Physiotherapy
Pathologies
In addition to the well-known arthritis and arthrosis, there are dozens of pathologies, which can only be detected and differentiated by a specialist with a medical education and extensive experience. The Kuntsevo Medical Center employs expert-level orthopedists and traumatologists, and has installed advanced equipment that makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, determine the extent of the lesion and choose the optimal treatment regimen.
The most common joint pathologies include:
- arthritis (mono- or polyarthritis);
- gout;
- osteoarthritis;
- arthrosis;
- bursitis;
- fibromyalgia;
- osteoporosis.
The diseases have common symptoms, so differential diagnosis plays a key role in making a diagnosis.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
Persistent restrictions develop gradually and are not subject to self-treatment. If there is a sudden decrease in range of motion, rest is required. Patients with traumatic injuries to the limb are given a splint and an analgesic. In case of exacerbation of chronic degenerative diseases, anti-inflammatory and local analgesics are effective. Deterioration of the general condition, sharp pain, significant swelling are indications for immediate consultation with a specialist.
Conservative therapy
The treatment tactics for transient disorders are determined by the nature of the underlying pathology. In case of injuries, fractures are repositioned, dislocations are reduced, and immobilization is performed. For synovitis, a puncture is performed. According to indications, the blockade is removed. Depending on the cause of the disease, antibiotics, NSAIDs, and other medications are prescribed. Non-drug methods are used. For persistent amplitude limitations, the following methods are used:
- Physiotherapy.
Includes passive and active exercises, muscle relaxation complexes. At the initial stages of treatment or in parallel with exercise therapy, mechanotherapy is carried out. - Physiotherapy.
For minor contractures, diadynamic currents and medicinal electrophoresis are prescribed. With a more pronounced limitation of the amplitude of movements, applications of ozokerite and paraffin are effective. Massage is recommended for patients. - Stage dressings
. An arm or leg is sequentially fixed in several positions, which increases the range of movements and improves the functions of the limb.
What is joint pain?
A joint is a complex movable complex located at the junction of bones, the movement of which is possible thanks to muscles and tendons. If at least one of these formations causes discomfort (crunching, clicking, pulling, aching, burning), the condition is called joint pain.
Reference! According to statistics, 50% of the population over 40 years of age may complain of joint pain.
The Kuntsevo Medical Center specializes in the treatment of various joint pathologies src=»https://kuncevoclinic-ok.ru/upload/medialibrary/09e/09e9d40d4c386e0d8c0f82bbf7697f0a.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»400″ height=»323″[/img]
Lifestyle recommendations
Further recommendations are determined by the attending physician on an individual basis. Normalization of nutrition, weight loss to normal levels, giving up bad habits, regular walks in the fresh air and protection from injury are mandatory.
To maintain healthy joints, vitamin complexes or a course of special medications (chondroprotectors) may be prescribed. If pathological symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Joint pain is not uncommon today. People put them under a lot of stress every day. To get rid of discomfort and lead a normal life, you need to immediately visit a specialist, establish the cause and begin timely treatment.