The foot is one of the main parts of the body's support. Its area is about 1% of the entire body surface. However, it bears the main load, equal to the mass of the human body. The foot performs several functions: shock-absorbing, supporting, balancing. Under the influence of certain factors, its arch is subject to deformation, and a disease such as flat feet develops. As a result, the sole loses its shock-absorbing properties, which is accompanied by unpleasant complications.
Flat feet - what is it?
The human foot consists of 26 bones. They are connected to each other by joints and ligaments, the movement of which is controlled by tendons and muscles. In a healthy person, the foot has 2 arches: transverse and longitudinal. They are located in the area of the base of the toes and the inner edge of the sole. When walking, a person does not fully rest on the foot. As a rule, three points are involved: the heel bone, the area at the base of the little finger and the big toe. If the ligaments and muscles of the foot weaken, its shape begins to change. It gradually becomes flat. When walking, a person is forced to rest his sole on the surface. As a result, shock-absorbing properties deteriorate and flat feet develop. A photo of the leg deformity is presented in this article.
The arches function like springs or levers, providing comfortable movement with minimal consequences for the body. Damage to this link entails disruption of the entire system. The body, as we know, is a single whole. Any changes in the operation of one system necessarily affect the functioning of the other. Flat feet can lead to damage to the hip and knee joints and spinal deformation. If the foot cannot cope with its functions, they move to structures located above. The spine, knee and hip joints are not adapted to such a load, so they quickly fail.
Can flat feet be treated with insoles?
Flat feet in the initial stages, without accompanying foot deformities and without arthrosis of the joints, can be cured with the help of insoles or orthopedic shoes. Insoles should only be made to order for a specific person. They are worn at least 5-6 hours a day. The course of treatment lasts from 2 to 4 years or more. The desired result is achieved in 60% of patients. The rest show improvement, but the disease is not completely cured.
Important conditions for the effectiveness of insoles:
- ideal conformity to the topography of the plantar surface of the foot;
- the absence of areas of increased pressure on the foot, which over time can lead to structural changes in soft tissue structures;
- creating conditions for training the muscles of the arch when walking.
Custom insoles affect the degree of muscle tension, joint position, and tendon tension. They also have an effect on proprioceptive sensitivity and contribute to better control of the dynamics of the human body. Good insoles not only relieve symptoms and correct foot deformities, but also improve posture and form a correct gait.
Classification of the disease
The foot has two arches. Therefore, it is quite reasonable to distinguish between the forms of the disease - longitudinal and transverse flatfoot. The symptoms and treatment of each are discussed below. There is also a mixed (combined) version of the disease.
Classification of the disease by type also provides for the separation of acquired and congenital flat feet. The first case is extremely rare and is the result of abnormal fetal development. Acquired flat feet can appear at any age. It, in turn, is divided into several subspecies:
- static (occurs due to decreased muscle tone);
- rachitic (as a result of vitamin D deficiency in the body, the muscle system is weakened);
- paralytic (develops against the background of polio);
- traumatic (appears as a result of injuries and bone fractures).
How do orthotics and inserts help eliminate the disease?
The use of insoles and liners is an opportunity to correct flat feet at home, since these therapeutic and prophylactic products:
- support the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system;
- stimulate blood circulation;
- help to recover from injury;
- reduce pain in the joints and muscles of the legs;
- prevent damage during sports;
- correctly distribute the load when walking, which is especially important for older people, pregnant women, and overweight people;
- reduce the load on the ankle, hip, knee joints and spine.
For the longitudinal type of the disease, insoles allow:
- improve foot shock absorption;
- reduce the load on the spine and leg joints when walking;
- reduce pain and fatigue.
With a transverse type of pathology:
- reduce the likelihood of swelling;
- prevent calluses and corns;
- maintain proper foot clearance;
- allow you to place your foot correctly;
- reduce pain.
Symptoms of flat feet
What signs should you pay attention to in order to prevent flat feet in time? Symptoms of this disease appear gradually. Its very first sign is considered to be severe pain in the legs at the end of a working day. By evening, the soles and legs swell and cramps appear. It becomes difficult for women to walk in heels. Due to the enlargement of the foot, you have to give up your old shoes and buy new ones, but in a larger size. Gradually, the pain syndrome spreads higher, moving to the knee and hip joints. Such signs characterize not only flat feet. Symptoms of a similar nature are observed with varicose veins. But treatment for this disease requires something completely different.
To reassure yourself, you can do a simple test at home. To do this, lubricate the soles of your feet with a dye (for example, brilliant green or iodine). Then leave an imprint on a piece of paper so that the load on your feet is even. After this, draw a line parallel to the plantar notch from the heel to the toes. Place a perpendicular line at the deepest part to the outer edge of the foot. If the imprint of the narrow part of the sole occupies at least half of the first line drawn perpendicularly, you have flat feet. A photo of an example circuit is presented below.
Making insoles
Making insoles
- custom size;
- reconstruction of the arch of the foot;
- energy-saving depreciation;
- optimal thermoregulation.
Methods for planning the production of insoles are mechanical and computer. Although mechanical methods were historically the first, today the computer method is increasingly used in modern clinics.
The mechanical method involves obtaining a cast of the foot. In the future, orthoses are made on its basis. However, the technique has one huge drawback: it does not take into account the load on the foot when walking. The impression is taken in a static body position. However, when walking, areas of overload shift, and in different ways for different people. The cut is adjusted subjectively, based on the patient’s feelings, not on objective measurements.
The computer method is more accurate. Pedobarography is performed using a special apparatus. Many parameters are assessed: the position of the direction of the patient’s center of body mass, his movement when walking. There are 5 zones of greatest load on the plantar surface:
- finger;
- metatarsal (metatarsophalangeal joints, rollover axis);
- medial middle region;
- lateral medial region;
- the heel area, which is the axial support.
Based on the results, the structure of the integral load graphs is assessed. A model of the insole for manufacturing is formed. After its production, the orthosis is adjusted to the patient, based not on his sensations, but on the data of pedobarography and photoplantometry.
The use of individual insoles allows obtaining positive treatment results after 1.5 years in 85% of patients. Their pain and muscle fatigue when walking decrease or disappear. Measurements show an increase in arch height. Further treatment can be carried out using other insoles. The examination and orthoses are made again, as the configuration of the foot changes. In a few years, in this way, a person can completely recover from flat feet, after which the need for further use of insoles will disappear.
Causes of the pathological process
Flat feet is a serious disease characterized by foot deformity. In ordinary life, no one pays attention to this defect. It is worth knowing the characteristics of the disease in order to take timely measures to correct it. The causes of the disease can be both external and internal. Considering the rhythm of life of a modern person and the disdainful attitude towards one’s own wardrobe, sometimes flat feet have a mixed etiology. Even everyone's favorite sneakers can cause foot deformation. Why? The sole of the sneakers is equipped with excellent shock absorption. They take on the entire load, fixing the heel. As a result, the muscles relax, creating all the conditions for the development of a problem such as flat feet. What flat feet are and how they arise is now clear.
Returning to the internal causes of the disease, it is worth noting a number of provoking factors. First of all, this is the presence of concomitant ailments. Among them, rheumatoid arthritis takes pride of place. It affects not only the cartilage, but also the ligaments that are responsible for supporting the foot. Injuries and mechanical damage to the leg also contribute to the development of foot defects.
Exposure to external factors can be easily prevented if you take care of your own health and carefully choose your shoes. The exogenous causes of flat feet include the following:
- excessive physical activity;
- insufficient activity due to work;
- hormonal disorders, pregnancy;
- incorrectly selected shoes.
Therapeutic and preventive insoles
Purpose and features of preventive insoles
Ready-made orthopedic insoles, which can be purchased at a pharmacy or store, support the arch of the foot. The arches may not withstand heavy physical exertion, pregnancy, sudden weight gain, in old age, or in people who are weakened due to another disease. To prevent flat feet from developing in these cases, preventive supportive insoles are needed.
Properties and purpose of therapeutic insoles
Such products are intended for those who have already been diagnosed with certain foot problems. After an accurate medical diagnosis, such products are manufactured individually. The foot contains 20 joints and 28 bones. When walking, this part of the leg performs a pushing function and maintains balance. Due to trauma, abnormal development, and other problems, the coordination of the various parts of this complex system is disrupted. As a result, pain appears, adaptive reactions occur, and a painful reaction of the body as a whole may occur. The task of the insole in this case is not only to support the arches, but also to compensate for pathology and prevent serious general disorders.
Longitudinal flatfoot
With this form of the disease, an increase in the length of the foot occurs against the background of lowering of the longitudinal arch. As a result, the sole is in complete contact with the floor. The main sign of deformation is a reduction in the gap between the inner edge of the foot and the floor surface itself. Patients with this diagnosis develop clubfoot over time.
There are three degrees of longitudinal flatfoot:
- At the first stage of development of the disease, there is no visible deformation. Discomfort in the legs appears after prolonged exercise. Pain occurs when pressure is applied.
- The second degree is characterized by a change in the arch of the foot. Painful discomfort intensifies and spreads to the ankles and legs. The muscles gradually lose their elasticity.
- The third degree of the disease is characterized by pronounced deformation of the foot. Painful sensations in the legs do not go away even in the evening. Discomfort appears in the lower back, and productivity decreases. It is difficult for a person diagnosed with third-degree longitudinal flatfoot to walk in ordinary shoes.
treat flat feet
treat flat feet
- plantography - obtaining foot prints with subsequent decoding;
- radiography – to visualize the bones of the foot;
- podometry – change in the nature of walking;
- computer pedobarometry is the most accurate method that measures pressure during standing and walking on different parts of the foot (allows you to ideally select orthopedic insoles).
In conservative treatment, the most important role is played by the use of orthopedic insoles or shoes. At stage 1 of flat feet, patients can buy ready-made insoles. However, they do not take into account the individual configuration of the foot, and therefore have only a symptomatic and not a corrective effect. Pre-made insoles relieve pain, but over time they can further weaken the muscles. Therefore, the disease can progress with their use.
The best option is individually selected and custom-made insoles. They not only reduce symptoms, but also help eliminate foot deformities.
Transverse flatfoot
With this form of the disease, the length of the foot decreases, the big toe deviates, and the middle toe becomes deformed. It takes on a hammer-like appearance. A small lump appears at the base of the first finger.
There are three degrees of transverse flatfoot. Their differences are due to the angle of deviation of the big toe.
- The first degree is mild transverse flatfoot. Symptoms of the disease appear as it progresses. The deviation of the thumb does not exceed 20 degrees. After physical activity, painful discomfort appears. On the foot, calluses are clearly visible in the area of 2-4 toes.
- With the second degree, the deviation angle is already 35 degrees. When under load, a burning sensation occurs in the sole area, and the corns increase in size.
- The third degree of the disease is characterized by constant pain. The deflection angle exceeds 35 degrees. Some patients develop bursitis. This is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the periarticular bursa.
Mixed flatfoot is considered separately. We have already discussed what longitudinal and transverse flatfoot are, and this pathology is accompanied by symptoms that are characteristic of both types. The manifestation of signs of a mixed form is distinguished by a greater degree of their severity.
Symptoms and stages of combined flatfoot
With the development of longitudinal-transverse flatfoot, there are signs characteristic of flattening of both the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot. Therefore, patients may experience:
- rapid fatigue of the legs, which ultimately leads to general fatigue up to the development of chronic fatigue syndrome;
- aching pain in the area of the arches, heel, upper part of the foot, increasing after prolonged standing, walking, physical activity or at the end of the working day;
- pain in the muscles of the lower extremities and lower back, which tend to appear during movement, as well as standing, and go away after a long rest;
- flattening (widening) of the foot, which causes difficulties when selecting shoes;
- swelling of the legs;
- coarsening and thickening of the skin in the area of the transverse arch of the foot and especially the big toe, followed by the formation of painful corns and calluses;
- tension in the calf muscles;
- heavier gait;
- valgus deformity of the 1st toe or Hallux valgus with the formation of a bump at its base, and subsequently deformation of the 2nd and 3rd toes with their acquiring a hammer-like shape.
In the vast majority of cases, pathological changes are present simultaneously in both feet. Unilateral combined flatfoot is usually observed only after injury.
In general, the course of the disease can be divided into 3 stages, each of which is characterized by its own manifestations. As the foot deformity progresses, the intensity of the symptoms increases, and externally noticeable changes occur. Thus, at stage 1, there is a weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the foot, although it still retains its normal shape. At the same time, after a long walk or at the end of the working day, aching pain, a burning sensation and fatigue in the legs begin to appear, which disappear after rest. Sometimes you may notice subtle changes in your gait, causing it to become less flexible.
At the 2nd stage of combined flatfoot, you can already notice the flattening of the arches of the feet with the naked eye. As a result, it expands, becomes flattened, and a protrusion forms at the base of the thumb. This is accompanied by the appearance of constant pain, which becomes increasingly stronger. In this case, the pain already spreads along the ankle joint, covers the lower leg and may be present in the knee. Therefore, the gait undergoes noticeable changes, and clubfoot also occurs.
At the 3rd stage of longitudinal-transverse flatfoot, the deformation of the foot becomes pronounced. This leads to damage and the occurrence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joints of the legs, i.e., the development of arthrosis. The spine, in particular the intervertebral discs, also suffers greatly. This can lead not only to the development of osteochondrosis, but also to the formation of intervertebral hernias, as well as curvature of the spine. Pain in the legs is constantly present and becomes very severe. Headaches often occur. All this together leads to a sharp decrease in performance, since it is difficult for the patient to move even short distances.
What is the difference between flat feet in children?
The foot of a child under five years of age is a fragile structure that is in the process of formation. Therefore, parents have a great responsibility. They must prevent the disease, recognize it in a timely manner and begin treatment.
Children rarely talk about health problems. Even if they try to hint, parents do not pay attention to them. Children lead an active lifestyle and are in constant motion, which is usually accompanied by fatigue. But there are certain points that parents should pay attention to:
- flattening of the arches of the feet;
- unevenly worn shoes;
- child's complaints of pain in the legs after outdoor games.
If your child’s gait has changed or he or she begins to move less, you should consult an orthopedic doctor. An experienced specialist can recognize flat feet at an early stage. The symptoms and treatment of this disease in children are practically no different from those in adults. Its only feature is the reversibility of the pathological process. The gradual maturation of the child is accompanied by a natural recovery from the disease. The foot is formed before the age of 13. During this period, it is necessary to focus on physical activity (running, walking). As a result, the muscles will begin to develop harmoniously, and the foot will acquire the correct shape.
Causes
Taking into account statistical data, the pathology is congenital in approximately 3% of all identified cases of the disease. Flat feet can occur at any age due to a variety of reasons. Flattening of the arches can be caused by:
- excess body weight;
- pregnancy;
- heavy physical activity;
- wearing uncomfortable, tight shoes, their incorrect selection for sports activities, which can also cause injury;
- a sedentary lifestyle with a lack of stress on muscle tissue, which contributes to its weakening and the inability to maintain the correct position of the foot;
- work that requires you to constantly stand on your feet;
- diseases of the joints and connective tissue, leading to foot deformation;
- potassium deficiency and disturbance of its metabolism;
- limb injuries.
The cause can also be diseases of the central nervous system, in which sensitivity and movement in the legs are impaired or completely disappear. But shoes still take the leading position among all risk factors. This is confirmed by the fact that women suffer from flat feet much more often than men. Wearing shoes with a heel higher than 4 cm is already a threat to the foot, and the higher it is, the greater the likelihood of developing foot deformity and its complications.
When wearing heels, the center of gravity shifts, the angle of inclination in the ankle increases, which overloads the forefoot. Due to such a load, the transverse arch begins to change, which ultimately leads to flat feet. But not only heels are dangerous, but also shoes with completely flat soles, especially for children when the period of formation of the foot has not yet completed. To eliminate this risk factor, adults need to wear shoes with a heel height of no more than 3-4 cm, and children - 1-1.5 cm.
Medical examination
Flat feet in adults and children can be determined based on the clinical symptoms of the disease. To assess the extent of the pathological process, a serious examination of the patient is required. It includes several points. This:
- Plantography allows you to determine the severity of the pathological process using prints. To do this, a solution of methylene blue is applied to the feet. Then make prints on a blank sheet of paper. Plantography provides approximate data on the condition of the arches of the feet.
- The Friedland podometry method allows you to estimate the percentage of foot height to its length.
- The clinical method is based on the construction of a special triangle. Its base is equal to the distance from the head of the metatarsal bone to the tubercle of the heel. The vertex of the triangle is located in the center. The first leg reaches the highest point of the heel tubercle, the second - to the head of the metatarsus. Normally, the height of the arch should not exceed 60 cm.
- The X-ray method is also based on constructing a triangle, but in this case the angle at the apex is measured. This parameter should not exceed 130 degrees.
Based on the examination results, the orthopedic surgeon can confirm the diagnosis and make recommendations for treatment.
Do people with flat feet join the army? This question worries many young men who have reached adulthood. If a conscript is diagnosed with a 1st or 2nd degree foot deformity, he is required to serve in the armed forces. In case of longitudinal or transverse flatfoot of the 3rd degree, the young man is exempt from the army. He is given a military ID from Fr.
treat flat feet
treat flat feet
You can often find orthopedic insoles and shoes on the Internet, orthopedic salons, pharmacies and medical equipment stores. They are much cheaper than those performed individually and do not require preliminary diagnostics. You can start using these insoles immediately after purchase. Sellers help you choose them, taking into account the degree and type of flat feet.
The only problem is that such insoles do not treat flat feet. In them, a person can feel more comfortable, pain and fatigue in the leg muscles are reduced. But such treatment is only symptomatic. Purchasing ready-made insoles always creates areas of increased pressure on the foot. In addition, the arch muscles are not trained. On the contrary, they are unloaded and gradually atrophy.
The relief of the vast majority of mass-produced insoles does not at all correspond to the relief of the foot of an individual person. It does not take into account the characteristics of walking.
Thus, store-bought insoles are unlikely to be a good treatment, since flat feet in adults cannot be cured with their help. Even minor positive changes are unlikely. The disease will progress more quickly with regular use of these medical products.
Principles of treatment
Many people do not pay attention to flat feet and ignore the first symptoms. In fact, this is a rather serious and rapidly developing pathology that is practically untreatable. It can be completely cured only in childhood, when the foot is not yet fully formed. In adults, therapy is aimed at slowing the development of the disease and preventing complications. Treatment of the pathological process is complex. The patient's muscles are strengthened, pain is eliminated, and progressive longitudinal/transverse flatfoot is stopped. The symptoms and treatment of these types of disease are practically the same. Now let's look in more detail at modern methods of therapy.
Medicines in combination with physical therapy help eliminate pain. Patients are prescribed systemic analgesics (Ibuprofen, Aspirin), as well as ointments for topical use (Dolgit, Voltaren).
The basis of therapy is therapeutic exercises. A set of exercises is selected by an orthopedist taking into account the stage of the disease and the patient’s age. A foot massage has a good healing effect. Regular procedures help normalize blood circulation and increase muscle tone. Unfortunately, all of the above treatment methods are effective only at the initial stage of the disease. For severe foot deformities, only one option helps - surgery.
Treatment of this disease in children requires a different approach. Most often, young patients are diagnosed with longitudinal flatfoot (all parents should know that such deformity cannot be ignored). The pathology is highly treatable if detected early. The child's bones, ligaments and muscles are susceptible to conservative therapy. Exercise therapy and massage have a positive therapeutic effect. If a child has congenital flat feet, they begin to be treated from the very first days of life. For this purpose, special bandages and splints are used.
Types of flat feet
There are three types of disease according to the location of the vaults:
- Transverse flatfoot – characterized by a shortened, lowered transverse arch and an enlarged anterior part.
- Longitudinal flatfoot - here the length is increased and the longitudinal bend is decreased. Most often, this type of pathology affects people aged 15–26 years.
- Longitudinal-transverse flatfoot (combined). This type is the most difficult because it causes serious consequences for the musculoskeletal system due to rapid wear and tear. In this case, the disease leads to postural deformation and problems associated with the spine:
- radiculitis;
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia.
Degenerative changes and inflammation also occur in the joints (osteoarthritis, arthrosis, coxarthrosis).
The consequences of flat feet are inextricably linked with:
- lameness, the cause of which lies in the poor functioning of the venous vessels in the calf muscles;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- varicose veins;
- formation of heel spurs;
- impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system.
If a patient has flat feet, accompanied by varicose veins, diabetes, or a tendency to heart problems, then there is a high probability of trophic ulcers appearing on the legs, feet and pelvis. In addition, pathological swelling of the tissues often occurs.
Why is flat feet dangerous?
The human body works as a whole. There are not only anatomical, but also functional connections between all organs. With flat feet, a shift in the center of gravity occurs. To maintain balance, a person is forced to constantly deviate in the opposite direction. Over time, the deformation increases, and the back becomes noticeably rounded. Poor posture and flat feet have similar causes of development. This is weakness of connective tissue, muscles, and obesity. In a healthy person, the arch of the foot acts as a shock absorber. With flat feet it is lost. As a result, increased stress is placed on the spinal column and knees. This leads to even more severe curvature of posture, scoliosis.
Foot deformity can provoke the development of other specific complications, including:
- ingrown nails;
- curvature of fingers;
- heel spurs;
- dystrophic changes in the legs;
- clubfoot.
In children with this diagnosis, the shock absorption of the foot is also impaired. As a result, the vibration of the body when moving is transmitted to the legs and spine. Constant irritation of the joints leads to inflammation, and arthrosis develops. The effect of flat feet on the spine is reflected in its curvature. The child constantly suffers from pain in his legs and head, his ability to work and his performance at school decreases.
Preparation for surgical treatment
After identifying indications for surgery, patients are prescribed a comprehensive preoperative study. This allows not only to detect possible contraindications, but also to correctly plan surgical intervention, detect potential causes of complications and take measures to prevent their occurrence. Thus, as part of preoperative preparation, patients will need to provide the following results:
- UAC and OAM;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- test for HIV and syphilis;
- tests for hepatitis B and C;
- ECG;
- fluorography performed no later than a year ago;
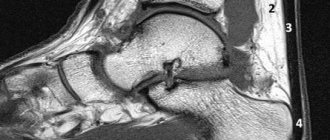
- MRI, CT or X-ray of the feet;
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities.
During the consultation, the orthopedic surgeon will definitely find out what medications the patient is taking on an ongoing basis and will recommend stopping the use of anticoagulants and a number of other medications in advance. You should also stop drinking alcohol 2 weeks before surgery.
Prevention of disease in children and adults
To prevent the development of flat feet, it should be periodically prevented. First of all, doctors recommend paying attention to shoes. Today, in almost every store you can buy special orthopedic shoes and insoles. The range of similar children's products is amazing in its diversity. Do not forget that shoes and insoles cannot correct foot deformation. They only prevent its development.
To strengthen muscles, it is useful to do contrast baths. It is necessary to alternately dip your feet in basins with cold and hot water. In addition, regular consumption of vitamins in their natural form (A, E, C, D) and microelements (including copper, selenium, calcium) helps strengthen muscles.
Prevention of flat feet in children can begin with increasing physical activity. Martial arts, skiing and horse riding are considered beneficial. In summer you can walk barefoot on mown grass and pebbles. Such daily walks have a positive effect on the motor skills of the small muscles of the foot.
Diagnostics
If you suspect that you have flat feet, you should consult an orthopedist. Initially, the doctor will definitely conduct a survey of the patient and find out what complaints he has about the condition of the feet and health in general, clarify the features of work and rest, etc. After this, he conducts an examination, during which he will evaluate not only the condition of the foot, but also the shoes. In doing so, he will pay attention to:
- the nature of the wear of the sole (normally the outer part should wear out more);
- the color of the skin of the feet (normally it should be pale pink, pallor and, conversely, a rich red color of the skin indicates circulatory problems);
- coarsening of the skin of the feet, the presence of corns, calluses;
- features of foot placement, when a person stands straight with his feet close to each other;
- the presence of deviations of the feet inward or outward;
- the presence of hallux valgus, i.e. the formation of a so-called lump at its base, which can be swollen and painful;
- flat feet;
- difficulty maintaining balance when squatting;
- gait changes.
Based on these data, the orthopedist can already diagnose flat feet and determine its type. But to determine the degree of deformation, obtain initial data for the manufacture of individual orthopedic devices and determine the most effective treatment tactics, additional examinations are required. Therefore, all patients, including children, who have signs of combined flatfoot, are prescribed:
- Computer plantography is a modern diagnostic method that allows you to obtain images of the plantar part of the foot under load. It means that the patient stands on a special instrument panel in a position that is comfortable for him. At the same time, he should evenly distribute the load on both feet. The results are assessed in accordance with the norms characteristic of each age. Children have physiological flat feet, which goes away as they grow older and develop the musculo-ligamentous system.
- Podometry is a method for diagnosing flat feet, in which the Friedland index of the longitudinal and transverse arches of the feet is determined. Normally, the longitudinal arch index is 29-31%. Lower scores indicate flat feet. The transverse index of the arch is normally no more than 40%.
- Podography is a diagnostic method that makes it possible to study the biomechanics of walking and movement patterns. To carry it out, special equipment is required, which is not available in all medical institutions. But with its help you can accurately determine all the features of gait. It allows you to study the phases of the heel roll, as well as obtain an accurate coefficient of gait rhythm.
- X-ray method gives an accurate understanding of the peculiarities of the position of the bones of the foot. This allows you to determine the degree of flatfoot, and subsequently monitor the dynamics of changes. It is from X-rays that you can accurately determine the height of the arch of the foot, intermetatarsal angles, the angle of the longitudinal arch of the foot, etc.
Sometimes electromyography is additionally performed, with the help of which the condition of the muscles of the lower extremities is assessed.
Methods for diagnosing flat feet
Diagnosis of flat feet is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist. The degree of flatfoot is determined using instrumental research methods.
Plantography
Plantography is the determination of flat feet based on the imprint of the plantar surface of the foot obtained using special equipment (plantograph).
Radiography
To diagnose flat feet, radiography of the foot is used. This research method makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and determine the degree of flat feet.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Symptoms
Signs of flat feet depend on the severity. In the early stages of development, symptoms are mild, patients do not feel discomfort. If there is no heavy physical activity, the development of the disease can drag on for years without much impact on well-being or ability to work. But still, upon detailed questioning, patients notice a number of symptoms that are usually not paid much attention to:
- increased fatigue of the legs during prolonged walking and standing;
- aching pain in the feet at the end of the day;
- slight swelling of the feet;
- tightness of the calf muscles;
- problems with choosing shoes;
- the appearance of rough skin (corns) in the area of the thumb.
With flat feet, there are a number of external signs: the inside of the shoe wears out quickly, the foot increases in size, so you have to buy larger shoes. Even high-quality shoes that previously fit become uncomfortable, so a person is forced to purchase more spacious ones.
As the disease progresses, all of these signs become more pronounced. The main symptom is pain, most often it is noted in the foot, calf muscles, and under the knee. In later stages, pain appears in the joints of the limb, sacral, and lumbar spine. It does not appear spontaneously, but gradually, and increases taking into account the load on the body. It is especially pronounced towards the end of the working day if a person has been walking and standing for a long time.
Treatment of flat feet
Flat feet are treated conservatively, surgically, which is decided individually taking into account:
- age of the patient;
- degree of disease and its progression;
- presence of complications;
- mobility restrictions.
Regardless of the chosen method of treatment, one cannot count on a quick result, since the disease is difficult to correct. It takes time, patience from the patient and concentration of his energy on treatment. The effectiveness of therapy is higher in children, since their arches are still forming and are easier to influence.
Conservative therapy
This type of therapy is aimed at reducing the rate of disease progression, preventing complications, maximizing relief from negative symptoms and includes a number of measures.
Massotherapy
The essence of the technique is to influence ligaments, biologically active zones, muscles in order to increase blood flow, improve metabolic processes, get rid of fatigue in the legs, and normalize muscle tone. Therapeutic massage is prescribed at any stage of flat feet; it is especially effective in the early stages of the development of pathology. The procedure must be performed by a specialist, but self-massage at home is allowed. In addition, it is necessary to use mats, massage rollers, balls and other special devices.
When flat feet are detected in children, it is recommended to walk barefoot as much as possible on various uneven surfaces: stones, sand, grass. If this is not possible, walk on a massage mat. Walking on different types of convexities affects multiple biologically active points, which the foot is very rich in. Massage mats are used not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for preventive purposes.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Effective for all stages of flat feet, especially for pain and impaired joint mobility. Physiotherapy is used only in complex treatment. Her goal:
- reduce inflammatory processes;
- relieve pain;
- improve blood circulation;
- normalize muscle tone;
- strengthen the vaults.
Physiotherapy procedures include electrophoresis with medications, phonophoresis, and magnetic therapy. Shock wave therapy deserves special attention. It has a beneficial effect on cartilage and bone tissue, destroys salt deposits without having a damaging effect on healthy cells.
Exercise therapy
Regular, long-term and properly selected exercises show high effectiveness in the initial stages of the disease, especially in combination with other methods of conservative therapy. Physical therapy is prescribed to all patients. Effect of exercise therapy:
- improved blood circulation;
- strengthening muscle tissue and ligaments;
- formation of correct arches;
- improvement of gait and foot placement.
A set of exercises is selected for each patient, taking into account the severity of the disease, age, concomitant pathologies and other nuances. The first classes should be conducted by a specialist so that the patient can master the correct technique for performing the exercises; in the future, the person can practice independently at home.
It is better to perform exercises in the morning; you need to do them before the muscles become tired, and increase the load gradually. Swimming has a positive effect on the entire musculoskeletal system. Regular exercises have a positive effect not only on the condition of the foot, they become an excellent prevention of spinal curvature and osteochondrosis. By strengthening the back muscles, the spine will receive additional support.
Orthopedic insoles
Properly selected shoes and orthotics significantly improve the quality of life. It allows you to correct structural changes in the foot, evenly distribute the load on the foot in order to remove overload from other parts of the musculoskeletal system. Custom orthopedic insoles are especially necessary:
- athletes;
- pregnant women;
- persons who experience heavy stress on their legs due to a certain type of activity: sellers, hairdressers, surgeons.
Insoles correct incorrect foot position relatively quickly and painlessly. They perform a passive correction - they relieve many of the unpleasant symptoms of flat feet, but do not improve the condition of the muscles. Insoles should not be used as the only method of treating the disease; it must be complemented by other methods. General functions of orthopedic insoles:
- improvement of the general condition of the patient;
- support of arches in normal position;
- improvement of blood circulation in the extremities;
- reduction of fatigue, pain, heaviness in the legs;
- reducing the likelihood of complications;
- increasing stability during any physical activity.
Wearing orthotics not only makes life easier, but also stops the further progression of the disease.
Surgery for flat feet
If conservative therapy does not produce results, the disease progresses, complications develop, in such situations the issue of surgical treatment of flat feet is decided. In the final stages of transverse, longitudinal and combined flatfoot, this is the only way to improve the patient’s quality of life.
There are about 500 methods of surgical treatment, all of them can be divided into three groups:
- on soft tissues;
- on the bones;
- combined.
Most often, operations are used to move tendons in order to tighten and correct the position of bones and form a normal arch. Often, an osteotomy is performed, in which surgeons make an artificial bone fracture in order to later move the bone fragments into the desired position.
In very rare cases, arthrodesis is performed. This is an operation in which the articular surfaces of certain bones are fused with special clamps to ensure their immobility. Often, combined flatfoot is combined with hallux valgus - the formation of a protruding tubercle (bone, bump on the foot) in the area of the big toe. During surgical treatment, this callus is additionally removed, since it also negatively affects the functionality of the foot.
Classification of flat feet
According to the nature of the changes in the arches, transverse, longitudinal and combined flat feet are distinguished. In the latter case, flattening of both the transverse and longitudinal arches is observed. Taking into account the reason that caused the pathology, the following types of flat feet are distinguished:
- rickets – applies to children with rickets. During the period of intensive growth, the supply of minerals to the bone tissue is disrupted, it weakens and becomes more pliable. This is reflected in the foot as deformation due to the heaviness of the child’s weight;
- traumatic – the result of injuries: bone fractures, damage to joints, tissues of the arch;
- paralytic – associated with paralysis of the muscles of the arch;
- static – the result of heavy loads that the muscular-ligamentous apparatus cannot cope with;
- congenital – occurs against the background of congenital malformations of the elements of the foot.
Taking into account changes in the bone frame, height and angles of the arch, 3 degrees of longitudinal flatfoot are distinguished:
- The bones of the foot are not changed, the arch angle is up to 140 °, the height is 3.5-2.5 cm.
- The talus is characterized by shortening and increased prominence of its neck. Arch angle up to 155°, height 2.4-1.7 cm.
- A large protrusion appears on the heel bone, the heel moves outward, the foot turns inward, and the big toe is retracted outward.
Normal indicators are considered to be an arch angle of 125-130°, height 3.9-3.6 cm.
Transverse flatfoot has 4 degrees, which takes into account the angle between the first and second metatarsal bones and the angle of deviation of the big toe. Normally, these indicators are less than 9 and less than 14, respectively. The higher the indicators, the higher the degree of transverse flatfoot. There are primary and secondary flat feet. The first occurs as an independent disease, the second - as a result of other pathologies.