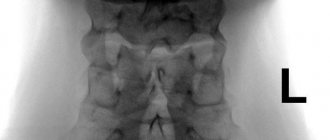
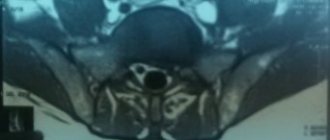
Schmorl's hernia is a disease in which the intervertebral disc protrudes not in the horizontal plane, but in the vertical, and presses through the vertebral body. Its bone structure is destroyed and pressed vertically - up or down, the cartilage tissue of the disc fills the resulting cavity.
Diagnosis by MRI.
The pathology is often hereditary and develops mainly in adolescent children and the elderly due to degenerative processes in the structures of the spinal column.
What is Schmorl's hernia
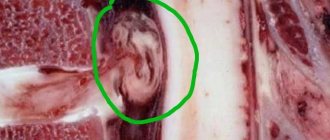
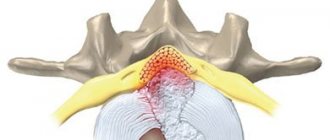
The intervertebral disc consists of cartilage tissue. A Schmorl's hernia occurs when the cartilage tissue of the disc begins to press on the surface of the vertebra. His bone tissue “falls” inward under pressure, resulting in a microscopic compression fracture. The resulting cavity in the vertebral body is overgrown with cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc after some time.
This is a generally painless process as the disc goes inside the vertebra and does not protrude beyond it, so the nerve endings, arteries and spinal cord are not affected. Painful symptoms appear with the development and enlargement of cartilaginous protrusion, as a result of which the intervertebral disc almost completely falls into the body of the overlying or underlying vertebra, the space between the vertebrae decreases, and compression of the nerve roots and sometimes the blood vessels of the spinal column occurs.
A Schmorl's hernia is also called a Schmorl's nodule or a vertical hernia. Its description was made by the scientist Christian Schmorl in 1927. This pathology was named after him.
According to recent studies, the disease occurs in approximately 75% of older people. Rapidly progressive bulges increase the likelihood of a vertebral compression fracture by approximately 10%.
Types of pathology
Depending on the number of nodes and the location of pathological formations, Schmorl's hernias are classified into several types. Below are the main ones.
Table. The main types of Schmorl's hernia.
| Type of disease | Description |
| Intracorporeal | Accompanied by damage to the spongy structures of the adjacent vertebra by the intervertebral disc. It is considered one of the most common types of the disease. |
| Rear and front | The pathological process leads to disruption of the dynamics and statics of the spine, which causes specific symptoms. |
| Intravertebral | Another type of disease, which is accompanied by displacement of the elastic lining of the vertebrae. |
| Lateral and central | A negative process in the intervertebral disc is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms, so the diagnosis of this type of Schmorl nodes occurs by chance. |
| Single and multiple | They are accompanied by damage to one intervertebral disc and, accordingly, several at once. According to statistics, most often people encounter single Schmorl nodes. |
Schmorl's hernia in the picture
Note! Sometimes the affected area of the spine, if not properly treated, can lose its mobility, as a result of which, under the influence of increased stress on the joints, the risk of a vertebral break or fracture increases. In rare cases, this leads to the development of arthrosis of the intervertebral joint.
Locations of Schmorl's hernia
Schmorl's hernias form in different parts of the spine. The patient’s symptoms and well-being depend on the location of the protrusion.
Lumbar
Vertical protrusions of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar region appear more often than in others, since this part of the spine bears the heaviest load. Most cases are diagnosed in elderly patients.
As the pathology progresses, back pain occurs in the lumbar region. Such localization of the hernia is dangerous due to a serious complication - a compression fracture of the spine due to provoking factors.
Thoracic region
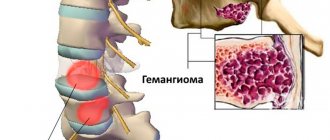
This is the main place where Schmorl's hernias occur. More often, the pathology develops in adolescence and causes complications. The child develops scoliosis and other degenerative diseases of the spinal column.
Damage to the thoracic region.
In the initial stages, with small sizes, it does not cause painful manifestations. As it progresses, the tissue of the vertebrae becomes thinner, the cartilage grows, begins to touch the structures of the spinal column, and the risk of developing neurological disorders increases.
Cervical region
Schmorl's nodes in the cervical spine are dangerous due to compression of the vertebral artery, which goes to the brain and supplies it. This occurs with significant destruction of the vertebral structure and proliferation of intervertebral cartilage. The patient experiences dizziness, headaches, and the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, which is dangerous for the development of a stroke.
Multiple Schmorl's hernias
According to the number of foci, vertical hernial protrusions can be single or multiple. With multiple pathologies, cartilage enters the bone tissue of the vertebral body in several places simultaneously, the disc becomes diamond-shaped, and protrusions appear on both sides.
Multiple nodules are diagnosed in approximately 70% of cases. They cause chronic pain, which intensifies if the patient is forced to constantly be in one position - standing or sitting.
Causes
The main condition for the development of Schmorl's hernia is hereditary predisposition. Factors that provoke its appearance and further progression:
- rapid growth in adolescence - bone structures develop unevenly, the skeleton forms more slowly than soft tissues, voids appear in the spongy body of the vertebrae;
- old age – degenerative processes begin, accompanied by a decrease in tissue elasticity and bone strength (osteoporosis);
- spinal injury resulting in deformation of the intervertebral disc;
- calcium deficiency in the body;
- excessive physical activity, professional sports, regular weight lifting.
Symptoms of the disease
Schmorl's hernia forms gradually and until a certain point does not touch adjacent arteries and nerve roots. Therefore, for a long time, Schmorl's hernia does not cause any symptoms.
Pain in the back may gradually appear in the following cases:
- prolonged physical activity;
- lifting heavy things;
- long static stay in a standing or sitting position;
- hit in the back or chest.
As the protrusion progresses and its size increases, the following symptoms occur:
- soreness, tingling in the back muscles;
- limited mobility in the thoracic spine;
- inability to sit for a long time without back support;
- numbness of the limbs;
- dizziness, headaches.
Treatment methods for Schmorl's hernia
If small hernial protrusions are identified that do not cause pain or discomfort, therapy is not needed. The patient is given recommendations regarding maintaining a healthy lifestyle, good nutrition, and moderate physical activity. Periodic examinations are necessary to monitor the progression of the hernia.
If the nodules grow and cause pain, complex treatment is indicated, which includes:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy;
- physical therapy.
If complications occur, advanced stages of Schmorl's nodules, or their combination with horizontal hernias, surgery may be performed.
Drug therapy
The peculiarity of drug treatment for vertical hernias is that there are no drugs that could completely cure or eliminate protrusions. The goal of therapy is to relieve pain and restore damaged tissue. After a course of taking medications, pain may reappear when exposed to provoking factors.
What is prescribed to the patient:
- Ointments and gels for topical use with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects - Diclofenac, Voltaren.
- Chondroprotectors – promote the regeneration of damaged tissues. These are the drugs Chondroitin, Teraflex.
- Muscle relaxants – relieve muscle spasms, which cause pain. Mydocalm and Baclofen are prescribed.
- Vitamin complexes - prescribed to saturate tissues with necessary substances and strengthen bone strength.
- Preparations with calcium and vitamin D.
Physiotherapy for Schmorl's hernia
Physiotherapeutic techniques for vertical hernial protrusions are aimed at improving blood supply and lymph flow in the vertebral structures, relieving inflammation and eliminating congestive processes. The following physiotherapy methods are prescribed:
- Electrophoresis. This is the introduction of drugs locally into the lesion using an electric field created by the device.
- Phonophoresis. It involves the introduction of active medicinal substances into the affected tissues using ultrasound.
- Magnetotherapy. This is the effect on the tissue of the hernial protrusion by a magnetic field.
- Electrical stimulation. The technique is aimed at stimulating blood flow and metabolic processes with weak discharges of electric current.
Physiotherapeutic techniques, like drug therapy, cannot completely get rid of a hernia. But their use in combination with other treatment methods improves the patient’s condition to stable remission.
Hardware traction
Spinal traction, or traction, is performed using special simulators. The method allows you to increase the distance between the vertebrae by stretching muscle fibers and ligaments, in the process strengthening the back muscles.
The procedure is carried out under strict supervision by a doctor who determines the load. Poor technique or excessive load can cause complications.
Good results are obtained by one of the modern proprietary methods - the combined use of underwater traction with underwater light therapy of the spine. Involves simultaneous exposure to infrared light and traction using bandages in water.
Reflexology
One of the methods of reflexology is acupuncture. This is the insertion of thin metal sterile needles into biological points. The duration of the session is about 30 – 40 minutes.
Acupuncture reduces disc pressure on the vertebrae, relieves pain, vascular spasms, and stops degenerative processes in bone tissue. However, according to the principles of evidence-based medicine, acupuncture does not have proven effectiveness.
Massage
The purpose of therapeutic massage for Schmorl's nodules is to relieve well-being and eliminate pain and fatigue in the back. The procedures restore metabolism in the structures of the spinal column, improve overall blood flow and lymph movement.
Diet therapy
A special diet is not required when the vertebrae are pressed through cartilage tissue. There are general recommendations:
- Weight control. Excess body weight puts additional stress on the spine, and lack of weight weakens the muscle corset.
- Balanced diet. Your daily diet should contain fruits and vegetables to provide the body with essential nutrients.
It is necessary to eat foods containing:
- Calcium – dairy and fermented milk products.
- Magnesium – spinach, beans, seeds.
- Phosphorus – fish, seafood.
- Manganese – algae, eggs, chicken fillet.
The patient should give up alcoholic beverages and nicotine, this will improve blood supply and tissue nutrition.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is an obligatory component of complex therapy for Schmorl’s hernia. A set of exercises is compiled by a physiotherapist, taking into account the location of the hernial protrusion, its size and the presence of symptoms.
Objectives of exercise therapy:
- strengthen the muscle corset;
- relieve spasms and tension from the spine.
An important condition is that the exercises must be performed regularly. If pain or discomfort occurs, use should be discontinued.
Manual therapy
When performing manual therapy, and especially with elements of stretching, as with traction therapy, negative pressure is created in the spine. This affects the hernia, causing the cartilage tissue to return to its original position.
With the correct technique, the blood supply to all structures of the spine improves and pain is relieved.
Orthopedic corset
If frequent pain attacks occur with Schmorl's nodules, patients are prescribed to wear an orthopedic corset. It fixes the back, which relieves stress on the spine, eliminates pain, and minimizes the risk of developing neurological symptoms.
An orthopedic corset is indicated for those who, due to their activities, are forced to remain in one position for a long time - sitting or standing.
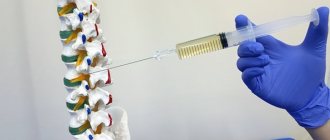
Surgery for Schmorl's hernia
There is often no need for surgical intervention for Schmorl's hernia. The operation is prescribed for severe destruction of the vertebrae, large protrusions, or combination with a horizontal hernia, which causes compression of the spinal cord.
The following methods are used:
- Laser vaporization. Under the influence of laser radiation, excess fluid is evaporated from the intervertebral disc. The nucleus pulposus in the middle of the disc becomes smaller, reducing pressure on the affected vertebra.
- Radical surgical treatment is indicated for very large hernias. During the operation, the disc is completely removed and replaced with an implant.
- The most common type of intervention on the vertebrae after repair of a hernia is percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty. Yes, there is no hernia, and it is not growing, but there is a cavity left in the vertebra, which impairs its strength. A large cavity is fraught with a vertebral fracture. Therefore, it is filled with special bone cement, turning it into a single monolith.
Diagnostics
After a person consults a doctor (vertebrologist, neurologist, surgeon or therapist), he goes through several diagnostic stages. The first stage includes collecting anamnesis, that is, a thorough questioning of the patient, collecting information about his state of health and the presence of allergic reactions to certain medications. After this, a detailed examination of the problem area of the body and palpation is carried out.
By palpating the vertebrae, a specialist can feel the extent of the damage and determine the location of the nodes. To make sure of the diagnosis and accurately determine the type of nodes, the doctor prescribes one of the instrumental diagnostic methods. These methods include:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - a technique based on electromagnetic radiation that penetrates various tissues of the body and displays a ready-made three-dimensional image of bone structures on the monitor.
- CT (computed tomography) is a method based on recording the difference in attenuation of X-ray radiation in various tissues of the body. The tomography machine scans the spine in just 5-10 minutes, after which the finished data is transferred to the computer.
- Radiography – imaging of bone tissue is carried out in closed capsules using a small dose of x-ray radiation.
In medical practice, X-rays or CT scans are most often used to accurately determine the location of the pathological process. This is due to the fact that X-ray radiation is better suited for detailing bone structures
No ads 2
Possible complications
A small Schmorl's hernia does not cause symptoms and is not dangerous to health or life. But with progression and lack of treatment it gives complications:
- complete disc depression and dysfunction;
- development of horizontal intervertebral hernia;
- thinning of the vertebrae;
- arthrosis, spondyloarthrosis;
- spinal cord canal stenosis;
- compression fracture of the spine (when Schmorl's hernia is localized in the lumbar spine);
To avoid the development of complications, it is better to treat Schmorl’s hernia in clinics in the Czech Republic. The methods and integrated approach used there will significantly improve physical well-being, increase performance and quality of life.
Surgery
In rare cases, doctors are forced to resort to surgical treatment of Schmorl nodes. The main indications for the operation include:
- large and numerous pathological formations, the presence of which creates a serious threat of damage to the vertebrae;
- diagnosing an intervertebral hernia that compresses the patient’s nerve roots or spinal cord;
- vertebral fracture.
Surgery
During surgery, the doctor performs resection (removal) of the nodes, after which the bones are rebuilt and the intervertebral disc is gradually restored. To speed up the rehabilitation process after surgery, you must follow all doctor’s orders. As a rule, the patient is prescribed a special diet, which consists of daily consumption of foods that are healthy for bones and cartilage tissue.
Prices for postoperative bandages
Forecast
The asymptomatic course of the disease does not have a negative impact on a person’s activity and well-being. Pain syndrome requires complex treatment, combining drug therapy and physiotherapy. This will stabilize the condition and lead to remission.
In the absence of therapy, the protrusion progresses, acquires large sizes, and begins to compress important structures of the spinal canal. This is dangerous by the development of complications up to complete paralysis, that is, immobilization of the patient.
Prevention measures
Any physical activity that puts stress on the back and is performed regularly or too vigorously can cause the development of a vertical hernia of the spine.
To prevent the formation of a hernial protrusion or to prevent complications with already diagnosed Schmorl's nodules, preventive measures should be followed. It is necessary to exclude excessive physical activity on the spinal column, especially during its growth (in adolescence), control body weight so that additional stress is not placed on the spine, and do not lift heavy objects. It is important to observe moderation when engaging in strength sports.
Why is it dangerous?
As a rule, Schmorl's nodes do not pose any danger to the patient's health, since the affected intervertebral discs return to their original position on their own over time. Bone tissue is strengthened, and cartilage tissue takes on its natural appearance. But this does not mean that this disease can be ignored and no therapeutic measures can be taken.
In patients who have previously had to deal with such a disease, mobility at the site of the hernia decreases, which causes the load on the intervertebral joints to increase. In addition, if the size of the hernia has increased to a certain point, the risk of vertebral damage during physical activity increases significantly. This is due to weakening of the vertebral body.