HOW SPINAL DISC PROTRUSION OCCURS
Protrusion of intervertebral discs is provoked by degenerative transformations in the spinal column, which can begin after 20 years. The speed of the process is affected by the natural atrophy of the vessels that supply the intervertebral discs with useful microelements. Subsequently, they receive the necessary elements only through hyaline cartilage. More than 90% of cases of protrusions are observed in people over 45 years of age. After 60 years, all persons have protrusions in one or another part of the spine.
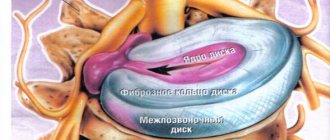
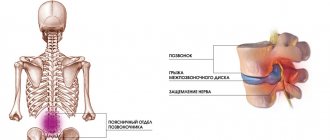
The axial impact on the spine when the body is in a vertical position increases every year. This provokes ruptures of the membranes of the fibrous ring. Body tissues, including fibrous plates, lose water and become less elastic. The combination of these processes leads to thinning of the disc. A decrease in its height leads to the advancement of the nucleus pulposus towards the rupture of the fibrous ring. A cartilaginous ring begins to extend beyond the boundaries of the vertebra. Disc protrusion is formed.
The following reasons can lead to degenerative transformations in intervertebral structures:
- hypodynamic lifestyle;
- pathological posture;
- spinal injuries;
- disproportionate physical activity;
- metabolic disorders leading to obesity;
- elderly age.
Causes and negative factors
The main cause of circular protrusion is degenerative processes in the disc, which lead to weakness of the fibrous ring and loss of its former elasticity. Negative factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- Maintaining a sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity leads to deterioration of blood supply to the spinal tissues. The problem is aggravated by weakness of the spinal muscles. The pressure on the disc increases, which leads to its deformation.
- Incorrect posture. In terms of the development of protrusion, kyphosis, scoliosis and lordosis are dangerous.
- Previous injuries to the spinal column. Not only fractures and bruises are dangerous, but also regular microdamages.
- Hereditary predisposition to diseases of the spinal column.
- Excessive loads. The formation of protrusion is caused by lifting heavy objects and spending a long time in an uncomfortable position.
- Diseases associated with metabolic disorders. This includes diabetes mellitus, endocrine pathologies, and hyperthyroidism.
- Serious errors in nutrition. Deficiency of calcium and vitamin D is especially dangerous in this regard.
- Aging of the body. With age, the condition of all elements of the spinal column worsens.
The impetus for the development of circular protrusion is often osteochondrosis of the spine and osteoporosis of bone tissue.
STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT
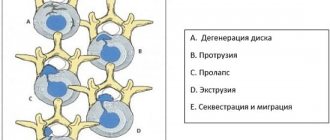
The degeneration process is quite long. Disc protrusion forms through several stages:
1. Stage I - changes affect up to 70% of the intervertebral structure. The disc is flattened, inelastic, and tears form in the fibrous ring. The nucleus pulposus gradually shifts to the area with the least resistance. The patient complains of local pain and mild muscle spasms.
2. Stage II - actual protrusion. The nucleus pulposus is significantly shifted, the fibrous membranes are stretched to 2-3 mm. In the area of damage there is intense pain and loss of sensitivity. The pain extends below the protrusion zone.
3. Stage III - the last before complete rupture of the fibrous ring and the formation of an intervertebral hernia. The filling of the disk protrudes greatly. The pain is intense, radiates to various parts of the body, and neurological symptoms are observed.
Treatment methods and their effectiveness
For lumbar protrusions, conservative and surgical therapy is recommended. In some cases, a conservative approach helps to effectively combat exacerbations and relapses of pathology. The main purpose of non-invasive tactics:
- relieve pain and inflammation, create favorable conditions for nerve roots;
- improve blood circulation, metabolism, nutrition delivery to a weakened area;
- prevent the progression of disc destruction and ensure the prevention of recurrence of protrusion symptoms;
- increase mobility of the diseased area;
- prevent the development of muscle atrophy (back, lower extremities);
- to prevent as much as possible from degenerating the protrusion into a true hernia (unfortunately, in practice, sooner or later this outcome of the disease usually occurs in most patients).
For conservative treatment to truly be beneficial, it must comprehensively and competently take into account all the criteria of the underlying pathology, concomitant diseases and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Therefore, it is ideal that only a highly competent doctor observing the patient can plan it. So, what is included in the basic range of non-invasive treatment and are its methods effective?
- The use of medications is the effect of drugs on a disease. Among the medications used are: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (if necessary in the acute phase) - Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac; stimulators of metabolism and regeneration of cartilage tissue - Chondromix, Rumolon; vitamins and dietary supplements based on B vitamins and calcium. All medications act symptomatically and prophylactically. For minor protrusions, chondroprotectors and mineral-vitamin formulations in combination with other mandatory treatment tactics still work well, preventing the destructive pathogenesis from progressing. And in isolated cases, they can completely restore the disc if it is deformed by no more than 1 mm. Formations larger than 1 mm are only prevented from progression by these drugs, but not for everyone and not always. Painkillers of any group have no effect on reducing the volume of protrusion; they can only “extinguish” painful symptoms.
- Physical therapy is the leading type of conservative recovery for the patient. Tactics involve the daily use of moderately gentle but effective physical training techniques. Exercise therapy relieves the pathological area from excessive tension, locally and generally increases the endurance and plasticity of the musculoskeletal system, produces a tonic effect, and improves the synthesis of the main metabolites of the disc. In addition, due to proper gymnastics, the vertebrae and joints are straightened, thereby increasing the intervertebral space and freeing the nerve roots from the clamp. The effectiveness of the exercise therapy method has been proven. Of course, a complete cure will not take place, such is the nature of the pathology, but keeping protrusion under control is quite possible. However, the value of the exercises will be negated by the unauthorized use of exercises, the recommendations of which the patient received not from the first person (his own specialist), but from second parties (friends, consultants from thematic Internet sites, etc.).
- Physiotherapeutic procedures – stabilization of well-being with an optimally selected set of physical sessions. A selection of physiotherapy may consist of several procedures in one treatment and rehabilitation program. For example, from electrophoresis, shock wave treatment, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, balneo- and mud therapy, etc. Physiotherapy can significantly improve the patient’s well-being and lead to a long-term stop in the further development of pathology. Its effectiveness is especially noted for protrusions of mild and moderate severity, not complicated by neurological deficit. Unfortunately, a lumbosacral lesion of this form cannot be regressed and eliminated forever.
- Massage procedures are auxiliary treatment with special non-traumatic massage techniques. Massage locally stimulates lymphatic drainage, blood circulation, and metabolic processes. Thanks to its action, muscle tone, reflexes and sensitivity are corrected, locomotor and support strength of the lumbosacral segments are improved. The level of effectiveness is similar to physiotherapy. Massage for certain types of displacements may be completely contraindicated. Therefore, it is forbidden to contact him without the consent of the treating doctor. If the doctor approves such medical care for your diagnosis, it should be done exclusively in a medical facility with the best specialized massage therapist. Otherwise, you run the risk of serious consequences. And this is instability of the spine, an increase in the degree of disc prolapse, critical infringement and death of nerves, the development of prolapses at other levels, etc.
Methods of physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and massage can be put into practice only in the absence of signs of inflammation and pain, that is, without relapses. Initially, during the acute period, the patient is treated with medications, wearing an orthopedic bandage and ensuring maximum rest for the lower back. Only after the acute phase has been completely suppressed are the sound methods used.
Clinical experience shows that 5%-10% of patients with protrusions require surgical treatment. As a rule, minimally invasive puncture technologies of neurosurgery from the nucleoplasty profile are used. Further about the indications, features and effectiveness of minimally invasive procedures.
MAIN SYMPTOMS
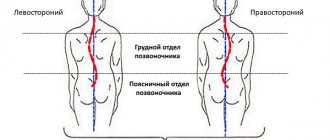
The clinical picture of intervertebral disc protrusion depends on the location of the damage and the degree of protrusion. If the protrusion is noted in the direction from the spine to the abdomen (anterior and anterolateral protrusion), painful symptoms may be absent. Posterior or posterolateral protrusion is observed when protruding towards the back. In the early stages, the damage does not have a clear clinical picture. Over time, symptoms of irritation of the spinal roots are recorded - severe pain of a radiating nature, sensory disturbances in the innervation zone.
Types of protrusion
Classification occurs according to the location of the anomaly, as well as the direction of displacement of the disc, since it is the direction of its bulging part that most often plays the most significant role in the manifestation of the symptoms of the disease and the degree of its danger and possible complications.
The most common types of intervertebral disc protrusions are:
- Dorsal - protrusion, in which protrusion of the fibrous ring occurs from the front, inner side of the spinal column. This pathology is more difficult to correct than protrusion of the disc ring on the back, outer side of the spine; Dorsal protrusion has several forms: diffuse, circular, foraminal and extraforaminal, median. The most dangerous type of protrusion is dorsal diffuse protrusion.
- Diffuse disc protrusion. This form of the disease is characterized by uneven bulging of the disc on different sides of the spine and an increased risk of pinching nerve endings.
- Circular protrusion. The disc bulges equally from different sides, and the vertebrae are deprived of shock absorption.
- Foraminal protrusion. In this extremely dangerous form of the disease, the bulging of the disc is directed towards the intervertebral canal and the spinal root and directly affects the nerve structure.
- Ventral disc protrusion. In this form, disc protrusion occurs without affecting the nerve fibers, and such a disease is not clinically detected.
- Median protrusion. This form of protrusion is characterized by prolapse of part of the fibrous ring directed towards the center of the spinal canal. The development of the anomaly depends on the part of the spine.
- Paramedian disc protrusion. For this anomaly, a characteristic feature will be a bulging part directed towards the center of the spinal canal and at the same time slightly to the side.
PROTRUSION OF DISCS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE
The initial stage of the disease passes without any special manifestations. Over time, the protrusion leads to compression or pinching of nerve endings and nerve bundles. May cause compression of the spinal cord. These processes accompany:
- constant or paroxysmal pain syndrome. The pain is of a shooting nature, intensifies during laughter, sneezing, coughing, and jerky movements. May radiate to the pelvis, thighs, legs, heels;
- feeling of numbness in the legs;
- pallor or hyperemia of the skin of the lower extremities, feet, impaired sweating;
- weakness in the legs;
- staying in one position for a long time causes a nagging pain that disappears after changing position;
- burning sensation in the lower back;
- swelling of the legs and lumbar region;
- increasing pain with physical exertion, heavy lifting, or playing sports;
- urination disorder.
What is posterior circular protrusion (circular-dorsal protrusion)?
Posterior circular protrusions of the discs are directed towards the back. If the deformation is significant, then the likelihood of damage to the spinal tissue increases.
The main danger of this pathology is that it is asymptomatic for a long time. The disease makes itself felt after it begins to have a mechanical effect on the nerve fibers.
Violation of the innervation of internal organs leads to changes in their functioning. Damage to the spinal cord can lead to paralysis.
A hernia formed due to posterior circular protrusion is difficult to treat. Surgery is associated with a high risk of complications.
PROTRUSION OF DISCS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
Cervical disc protrusion may present as symptoms that are mistaken for signs of other neurological diseases. Characteristic manifestations of cervical disc damage are:
- pain in the neck area of a pulling, aching or shooting nature;
- painful sensations radiate to the shoulder, shoulder blade, and fingers;
- shooting pain in the back of the head;
- feeling of numbness, burning, or tingling in the hands;
- decreased strength in the hands;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- restrictions on turning and tilting the head.
Recovery prognosis
In most cases, circular protrusion can be cured even without the use of surgical methods . But for this it is necessary to promptly identify the degenerative processes that have started in the intervertebral discs. If you experience recurring back pain from time to time, contact a specialist immediately.
He will help identify the disease, determine the causes of its development and prescribe the necessary treatment. 90% of patients successfully overcome the disease without the help of surgeons , following only the recommendations of the specialist observing them and revising their lifestyle.
DIAGNOSTICS
A presumptive diagnosis is established by a neurologist based on the patient’s complaints. Upon examination, areas of impaired sensitivity, decreased muscle tone, decreased or loss of reflexes are determined.
To confirm the presence of disc protrusion, hardware diagnostic methods are prescribed:
1. X-ray of the spine. The examination can determine indirect signs of protrusion - changes in the height of the discs, provides information about the curvature of the spine, and injuries to the vertebrae.
2. CT scan records the protrusion of the membranes beyond the vertebra. The edges on the protrusion side are always smaller than those at the base.
3. MRI provides a complete diagnostic description. Indicates the exact location of the damage, the direction and size of the protrusion, and the condition of the spinal cord canal.
Treatment
Exercise therapy
Treatment of intervertebral disc protrusion is possible only by spinal correction . It is performed through regular physical therapy exercises.
Exercise therapy is aimed not only at correcting the spinal column, but also at strengthening the muscular corset that surrounds and supports it. Since weak muscles also often cause the development of protrusion and contribute to the aggravation of the situation with already developed disc deformation, their strengthening plays an extremely important role. Strengthening the muscle corset is also extremely necessary to prevent further development of protrusion or its recurrence.
A set of therapeutic exercises should be prescribed by a specialist in each individual case - they will be different for each patient. An individually selected exercise program will help return all elements of the spinal column to the anatomically correct position, in possible cases, contribute to the restoration of intervertebral discs, or contribute to a maximum delay in the further progression of circular protrusion.
Video: “Exercises for lower back pain”
Massage and manual therapy
Did you know that...
Next fact
The exercise therapy complex must be supplemented with massage and manual therapy. In addition to the exercise therapy complex, the patient must be prescribed the use of manual therapy.
A specialist performing massage is able to influence the deep subcutaneous layers, restore and strengthen muscles, correct the spinal column and return displaced vertebrae and intervertebral discs to their place.
Also, patients with protrusion are recommended to visit a physiotherapy room . To speed up treatment, as well as for the purpose of rehabilitation, the following may be prescribed: paraffin therapy, hardware DDT (diadynamic action of current).
Patients with circular protrusion may be prescribed water or dry traction of the spinal column . Its purpose is to return all elements of the spine to an anatomically correct position.
Drug treatment
To eliminate the symptoms that appear with advanced protrusion, the patient may be prescribed a course of non-steroidal drugs - NSAIDs . They have not only an anti-inflammatory effect, but also an analgesic effect.
Non-steroidal drugs can be prescribed in the form of: intramuscular injections, ointments, creams, gels. Most often prescribed : Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Naproxen. These drugs also help get rid of swelling that can occur in the soft tissues located above the location of the protrusion.
Sometimes, in cases of advanced foraminal or dorsal protrusion, surgical treatment can be used .
But such a need arises only in 10% of cases.
Causes of the disease
Most often, the trigger for protrusion is osteochondrosis. But it can also occur with an insufficiently active lifestyle and metabolic disorders. This is due to the fact that the intervertebral disc is nourished by the diffusion of substances into it from surrounding tissues due to the lack of blood vessels. When this mechanism is disrupted, “starvation” and destruction of disc tissue occurs.
The risk group includes people involved in heavy physical labor and athletes. Hereditary features of the development of the spine and frequent infectious diseases also cause protrusion.
Methods for diagnosing intervertebral disc pathology
If any of the above symptoms occur, patients are advised to immediately make an appointment with a chiropractor, neurologist or vertebrologist. At the first appointment, the doctor will conduct a thorough interview and examination of the patient, perform a series of neurological tests that will help to accurately determine the cause of pain in the lumbar region and other abnormalities.
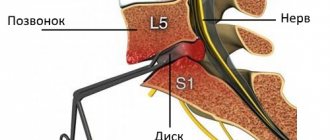
A typical sign of L3-L4 protrusion is the appearance or intensification of pain when trying to lift a straight leg.
Often, these data are enough for an experienced specialist to suspect the presence of a protrusion or hernia of L3-L4. But making a final diagnosis, as well as developing the most appropriate treatment tactics for a particular patient, is possible only on the basis of the results of instrumental diagnostic methods.
The main method used to detect protrusions, hernias and other diseases of the spine is MRI or magnetic resonance imaging. With its help, you can thoroughly and in great detail study the features of the soft tissues of the spine and notice the slightest changes in the discs at the earliest stages of development. Therefore, MRI can detect even the smallest protrusions, the size of which does not exceed a millimeter.
The method also makes it possible to detect nerve damage, inflammation in the soft tissues surrounding the spine, their swelling and many other features, knowledge of the presence of which will help develop the most effective treatment tactics.
Patients may also be prescribed other diagnostic methods, in particular:
- X-ray;
- CT;
- electromyography;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (if any disturbances occur in their functioning);
If you have previously had any spinal tests, it is recommended to take their results to your first consultation with a doctor. This will make it possible, if not to refuse to conduct new studies, then at least to provide the specialist with data on the dynamics of progression of L3-L4 protrusion.
In our clinic, you can also learn in more detail about the composition of your body and the state of the vascular system, which is involved in the blood supply to internal organs, skeletal muscles, and the brain. Our experienced doctors will explain the data obtained to you in detail. Bioimpendansometry calculates the ratio of fat, muscle, bone and skeletal mass, total fluid in the body, and basal metabolic rate. The intensity of recommended physical activity depends on the state of muscle mass. Metabolic processes, in turn, affect the body's ability to recover. Based on the indicators of active cell mass, one can judge the level of physical activity and nutritional balance. This simple and quick test helps us identify disturbances in the endocrine system and take the necessary measures. In addition, it is also very important for us to know the condition of blood vessels for the prevention of diseases such as heart attacks, hypertension, heart failure, diabetes and much more. Angioscan allows you to determine such important indicators as the biological age of blood vessels, their stiffness, stress index (which indicates heart rate), and blood oxygen saturation. Such screening will be useful for men and women over 30, athletes, those undergoing long-term and severe treatment, as well as everyone who monitors their health.
In this case, body composition analysis gives us information that adipose tissue predominates in the body, and the bone-muscle component is in relative deficiency. These data will help the rehabilitation doctor competently draw up a physical activity plan, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.