The lower back is the most overloaded part of the spinal column. As a result of the influence of certain provoking factors, intervertebral hernias often form in this area. These formations tend to increase. Their formation is accompanied by severe symptoms. As the disease progresses, the intensity of symptoms increases. Getting rid of this disease completely is quite problematic, especially if it is in the later stages of development. Treatment of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine is carried out using conservative or radical methods.
Lumbar intervertebral hernia - what is it?
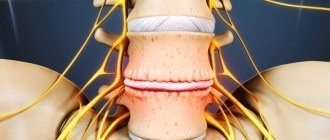
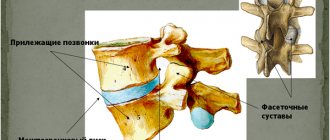
The intervertebral (intervertebral) disc is a shock-absorbing device, which is a fibrocartilaginous ring, inside of which there is an elastic pulpous nucleus pulposus. Intervertebral (intervertebral) hernia is a disease in which, under the influence of various factors, the fibrous ring ruptures, the nucleus pulposus exits the spinal column, and it compresses the spinal cord or spinal nerve roots.
The incidence of this pathology has increased significantly in recent years and amounts to 150 people per 100 thousand population. Most often, a hernia develops in the lumbar spine, since it is this section that bears the greatest load.
There are 5 vertebrae in the lumbar region (L1 – L5), they are the largest, and the discs between them reach 4 cm in diameter and 7 mm in height. Hernias usually develop between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae or between the 5th lumbar and first sacral vertebrae (L4-L5 - 25%, L5-S1 - 42%). Between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae, hernias occur only in 10% of cases. The disease code according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) is M51.
Lumbar disc herniations often develop in young and middle age due to various diseases, injuries and physical activity. In old age, the elasticity of the nucleus pulposus decreases and it is much less likely to extend beyond the lumbar intervertebral disc. But this does not mean that older people do not have lumbar hernias at all.
It is better to treat a lumbar hernia in the initial stages, so when the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. But even in advanced cases, experienced specialists will be able to help the patient.
Reasons for formation
The main reasons for the formation of intervertebral hernia are:
- increased load on the disk;
- disk power failure;
- disc asymmetry due to incorrect position of the overlying and underlying vertebrae.
Most often, a hernia is formed due to osteochondrosis, a disease characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. As a result of this process, the core tissue extends into the area of the annulus fibrosus. The disc ceases to fully perform its functions, and the vertebra, which is located above, shifts in relation to the lower one. The result of dystrophic changes is the formation of a hernia with disruption of the integrity of the fibrous ring and compression of the nerves by the nucleus pulposus, and in severe cases, the spinal cord.
Factors that may contribute to the formation of a herniated disc include:
- lifting weights;
- constant exposure to vibration;
- improperly distributed load on the spinal column during curvature;
- obesity;
- previous spinal injuries.
The risk of developing intervertebral hernias is higher in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Those who subject their bodies to increased physical stress, such as professional athletes, are also at risk.
Causes of lumbar disc herniation
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region develops under the influence of various factors that injure and disrupt the nutrition of the cartilaginous structures of the spine. These factors include:
- Degenerative-dystrophic (metabolic) disorders in the spine - osteochondrosis; disruption of the blood supply to the discs leads to their flattening, cracking and hernia formation. Such disorders also occur in young people with a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- Injuries and diseases of the spine that disrupt tissue nutrition, change the shape and position of the vertebrae, and injure discs.
- High physical activity, constant vibration, prolonged standing or sitting. Professional risk groups: loaders, heavyweight athletes, drivers, cooks, hairdressers, office workers, etc.
- Sedentary lifestyle – undeveloped back muscles do not support the spine; A lumbar hernia can develop when lifting small weights or turning the body poorly;
- Excess weight increases the load on the spine, which leads to metabolic disorders and microtraumas.
- Poor posture – the vertebrae become curved, which is an additional injury to the discs.
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region develops under the influence of various factors
Psychosomatics
Sometimes the cause of the disease is mental trauma. Lumbar hernias are most often associated with unresolved financial problems, the desire to improve one’s financial situation in the absence of opportunities. It turns out to be a vicious circle. At the same time, nerve connections are destroyed, blood circulation in the lower back is disrupted, tension in the back muscles is maintained, which leads to the destruction of the discs.
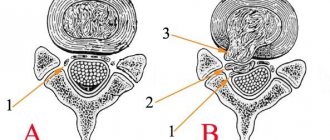
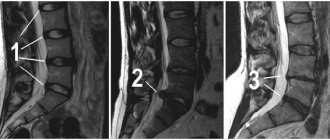
What doctors will see
The two main projections of the procedure allow you to see the vertebral arch and spinous processes. Regardless of the degree of development of the hernial tumor, the image will definitely show the following nuances:
- Distance between disks.
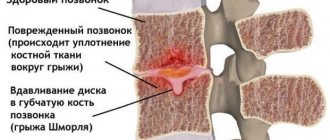
- distinct contouring of each of the vertebrae: the slightest irregularities in the outlines can become a signal. For example, with a Schmorl's hernia, a peculiar concavity of the vertebra is present, and if additional processes are detected, osteochondrosis is diagnosed.
- Bone density level. Bones fixed in one place are particularly brightly colored in the image.
At first glance, all this is quite enough to make the correct diagnosis. In reality, it turns out completely differently. All these are indirect signs of a vertebral hernia; in fact, it will not be possible to consider a serious pathology. But at the same time, one should not underestimate the effectiveness of X-ray examination as part of the general identification of back problems.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine
The disease begins slowly, in most cases asymptomatic or with minimal symptoms. The starting factor (trigger) can be any sudden movement or lifting of weight, leading to acute pain.
First signs
The initial symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation can be so subtle that not everyone pays attention to them. But if you listen to your body, you will notice:
- a feeling of fatigue in the lower back when sitting or standing for a long time;
- sensory disturbance - numbness of the skin or a crawling sensation in the lumbar region, groin, lower extremities;
- the appearance of transient lower back pain;
- weakness in the legs, gait disturbance.
Obvious symptoms
In some patients, the obvious symptoms of lumbar intervertebral hernia are periodic and moderate, while in others they are pronounced and constant. Symptoms of the disease are associated with compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerve roots. Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- Local pain syndrome. Pain in the lumbar region can have different duration and character. There are sharp, weak, aching, pressing, burning pains, permanent or transient. They intensify with physical stress, sudden turns of the body, etc.
- Radicular pain associated with pinched spinal nerve roots. When different lumbar discs are affected, the pain will have different localization:
- L1-L2, L2-L3
- hernias are very rare; manifested by pain and loss of sensitivity on the inner and front surface of the thigh; early symptoms of pelvic organ dysfunction may appear; - L3-L4
- pain spreads along the front and inner surface of the thigh, moving to the lower leg and inner ankle; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in this area; - L4-L5
- pain spreads from the upper gluteal region to the outer thighs and lower legs, extends to the rear and 1 - 3 toes; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in the same areas; - L5-S1
- pain moves from the middle of the buttock along the back and outer surfaces of the thigh and lower leg, radiates to the heel, and then along the outer edge of the foot to the 4th - 5th toes; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in the same areas. - Symptoms associated with compression of motor nerves - muscle weakness, fatigue when walking, gait disturbance.
- Symptoms associated with compression of the autonomic (innervating internal organs, walls of blood vessels, sweat glands) nerves - pallor and sweating of certain areas of the skin, the appearance of vascular spots on it.
At different stages of lumbar intervertebral hernia, different symptoms appear
Dangerous symptoms of lumbar hernia
The most dangerous symptoms are the consequences of compression of the spinal cord - paresis and paralysis, dysfunction of the pelvic organs - fecal and urinary incontinence, reproductive dysfunction.
If such symptoms appear, even if they are transient, you should immediately seek medical help.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine in men
In addition to the general manifestations of the disease, which are characteristic of men and women, men may experience symptoms of reproductive dysfunction. This is due to impaired blood circulation and innervation in the pelvic organs and is manifested by erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation.
In advanced diseases, spermatogenesis – the synthesis and maturation of sperm – may also be affected. The number of sperm decreases, they become less mobile, often incapable of fertilization - infertility occurs. But with adequate treatment, restoration of reproductive function is possible in most cases.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine in women
Poor circulation in the pelvis cannot but affect women's health. Depending on the type of hernia and its size, the following symptoms may appear:
- menstrual irregularities and, as a consequence, infertility;
- frequent inflammatory processes of the genital organs, as a result of which adhesions are formed in them, preventing conception and pregnancy;
- difficulties during pregnancy and childbirth.
But all this can be restored if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his instructions. A lumbar hernia is not an obstacle to the birth of a child, but requires mandatory pregnancy planning with a preliminary course of treatment and constant monitoring during pregnancy by an obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist at the antenatal clinic. Delivery is most often carried out by caesarean section.
Kinds
All hernias can be divided into anterior and posterior (dorsal). The former are rare and have a very favorable prognosis, while the latter pose a danger to a person’s physical capabilities because they fall into the lumen of the spinal canal. Depending on their location they are divided into:
- central (median) – located in the central part of the spinal canal, so they can provoke the appearance of pain, both on the right side of the body and on the left;
- paramedian - formed on the left or right side relative to the central axis of the spine, therefore causing the appearance of characteristic symptoms on the corresponding side of the body;
- circular - the entire posterior surface of the disc protrudes, which leads to filling of the entire spinal canal and the development of severe neurological symptoms, as well as severe pain;
- foraminal - a hernia forms in the area of very narrow openings of the spine formed by the vertebral body and articular processes, and causes burning, excruciating pain.
Depending on the size of the hernia they are divided into:
- small – the size of the protrusion does not exceed 5 mm;
- medium – the hernia reaches 5–7 mm;
- large - the formation increases to 8 mm or more.
But, unlike popular belief, the size of the intervertebral hernia is not strictly related to the severity of the observed symptoms. Even very large hernias can exist for a long time completely asymptomatically and are discovered by chance, while small ones can so infringe on the spinal root that not only severe pain syndrome occurs, but also serious disruptions in the organ innervated by it. Therefore, treatment tactics for each patient are chosen to a greater extent in accordance with the severity of complaints, rather than the size of the formation.
Why is lumbar hernia dangerous?
The danger of a lumbar hernia is that in the initial stages it occurs with minimal symptoms, and then can instantly manifest itself in severe pain and dysfunction of various organs.
Paying close attention to your health will allow you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and prevent the progression of the disease.
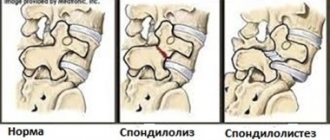
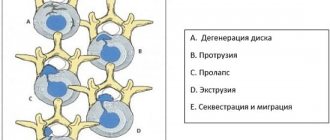
Stages of lumbar hernia
There are several stages during the course of the disease:
- Initial – the lumbar discs change and become thinner. Symptoms: tired and aching lower back, goosebumps.
- Protrusion is cracking of the disc in the lumbar region and displacement towards the nucleus pulposus. At this stage, the pain intensifies, and short-term radicular pain may occur due to disc displacement. Patients tolerate this condition differently: for some, the pain is not too intense and is transient; for others, debilitating local and acute radicular pain due to a herniated spine sharply reduces the quality of life.
- Rupture of the lumbar disc, protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord. All characteristic manifestations of a vertebral hernia appear.
- Sequestration is the separation of individual segments (sequestra) from the nucleus pulposus and their penetration into the spinal canal. Symptoms of irritation and compression of the spinal cord appear: paresis, paralysis, fecal and urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction.
By size, lumbar hernias are divided into small (1 - 6 mm), medium (6 - 8 mm), large (more than 9 mm).
Possible complications
Symptoms of lumbar intervertebral hernia increase rapidly
In the absence of adequate treatment, a lumbar hernia can have serious consequences:
- sudden onset of severe pain in the lumbar region (lumbago) or along the sciatic nerve (sciatica); monstrous pain cannot be relieved using home methods;
- paresis and paralysis – partial or complete immobilization;
- neurological symptoms such as sensory disturbances such as “saddle block” on the inner thighs, perineum and lower buttocks due to compression of sensory nerve fibers; a dangerous symptom, a signal that the disease has progressed;
- dysfunction of the pelvis and genital organs of men and women due to injury to the cauda equina, a bundle of spinal nerves extending from the end of the spinal cord.
Even if one of these symptoms appears briefly, you should immediately seek medical help. If this is not done, the symptoms will quickly increase and the consequences in the form of complications will not keep you waiting. Helping such a patient will not be easy.
What to do during an exacerbation
In some patients, lumbar hernia occurs for a long time without significant symptoms. Periodically, symptoms either disappear completely (remission) or increase (exacerbation). A peculiarity of this course is that with each exacerbation the condition of the fibrous ring worsens. One fine day, instead of a slight exacerbation, paralysis or severe, knocking down pain may suddenly occur.
To prevent this from happening, a lumbar hernia should be treated regularly under the supervision of a doctor, trying to prevent an exacerbation or begin to treat an aggravated disease as early as possible.
Pros and cons of the study
The advantages of diagnosing a hernia using X-ray equipment are the following:
- X-ray is a quick way to study a spinal disorder;
- X-ray imaging of a spinal hernia is considered a simple, safe and accessible procedure for all patients, which shows even the smallest deviations in the back;
- when performing an x-ray, the doctor evaluates the bone structure of the vertebral discs, the density and thickness of the various cortical layers;
- In the X-ray image, the neurologist sees fluid accumulation and various deformations of the vertebral discs.
Moreover, x-rays of the lumbar spinal region are used in the diagnosis of various ailments of the spine, and it is the primary examination of the patient.
The only disadvantage of X-rays is that X-ray rays have a negative effect on the human body.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
Types of lumbar intervertebral hernias
Lumbar hernias have a certain direction. Based on the direction in which the protrusion occurs, lumbar hernias are divided into the following types:
- Posterior (dorsal)
– in the lumbar region this is a common type of hernia:- median (median)
- can be very large, compressing the spinal cord; - mid-lateral (paramedian)
- causes pinching of two roots - at this and the following levels; These are not very large, but painful hernias. - Foramial
- spread to the hole from which the roots of the spinal nerves emerge, always accompanied by severe pain. - Lateral (lateral)
- causes pinching of the root at a given level, but less severe than foramial ones. - Anterior (ventral)
- the protrusion goes in the opposite direction from the spinal cord; are often asymptomatic; are rare in the lumbar region. - Schmorl's hernia (vertical)
- a protrusion penetrates into a higher or lower located vertebra. It is asymptomatic, but can sometimes cause vertebral destruction.
Diffuse (widespread)
– a type of hernia with a protrusion extending over half the circumference of the disc. Sequestrated are lumbar hernias in which part of the hernial protrusion separates and enters the spinal canal.
Read the full classification in our article “Types of spinal hernias.”
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Operation
Radical intervention is used when it is necessary to free the spinal cord and nerves from the pressure of protruding tissues. The most popular methods are:
- Endoscopy is an operation through an incision in the spine using a probe. A camera and instruments are inserted through a small hole, and displaced tissue is removed.
- Disc endoprosthetics. Damaged elements are removed. A prosthetic structure is installed in their place.
- Percutaneous discectomy. Access is made through a puncture, the deformed core is removed and replaced with a special compound.
- Laser reconstruction – the hernia is removed by evaporating moisture from the tissue.
Pain due to lumbar hernia of the spine
Types of pain with a hernia of the lumbar spine:
- Lumbago (lumbago) is the occurrence of acute, sudden pain in the lumbar region associated with some physical movement that causes displacement of the intervertebral disc. At the same time, an instant protective spasm of the back muscles occurs, increasing the pain. Signs of a hernia of the lumbar spine, complicated by lumbago: the patient freezes in the position in which the pain occurred. The attack can last from several minutes to a day and pass as suddenly as it began or decrease under the influence of drug therapy. The cause of lumbago is most often caused by heavy lifting or a sharp turn of the body, so it is more common in men in young and middle age.
- Sciatica (lumbosacral radiculitis) is a sudden infringement of the lumbar roots of the spinal nerves. The continuation of the roots is the sciatic nerve, located in the buttock and posterior surface of the lower limb. The main symptom of a herniated disc in the lumbosacral region, complicated by sciatica, is the appearance of a burning unilateral pain in the leg along the sciatic nerve.
- Constant or recurring pain in the lower back of a very different nature and intensity: aching, twitching, sharp, burning, etc. mainly due to irritation of nerve endings.
How to relieve pain
If the lumbago started suddenly, you need to:
- stop moving or take a position that helps reduce pain;
- ask others to call an ambulance;
- if possible, take any painkiller (analgin, diclofenac, paracetamol, etc.);
- apply anesthetic ointment (Voltaren, Fastum-gel) to the lower back;
- if possible, lie on the floor on your back, bend your knees and place a pillow under your knees.
Emergency medical assistance:
- treatment begins with the intramuscular injection of any pain reliever from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - diclofenac, nimesulide, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, etc.;
- at the same time, a medicine is administered that relieves spasms of the lumbar muscles (muscle relaxant), for example, Mydocalm;
- Neuromultivitis (B vitamins), enhances the analgesic effect of other medications;
- if the pain is not relieved, treatment is continued by performing a paravertebral block: a solution of novocaine or lidocaine is injected subcutaneously into the exit site of the spinal roots;
- if this does not help, treatment is continued in a hospital setting, an epidural block is performed: an anesthetic is injected into the epidural space, located between the hard shell of the spinal cord and the vertebrae.
How does a hernia manifest?
At the very beginning of the development of the pathological process, the patient does not feel serious pain, symptoms are few. The more tissue protrudes, the more the patient feels it. There are three groups of symptoms for intervertebral hernia:
- The main symptom of a herniated disc is pain. At first it is not sharp, may be aching, and go away with a change in body position. The more serious the stage of the process, the stronger the pain. Shooting sensations appear, it is painful for the patient to turn the body, the sensations intensify with physical activity.
- Spinal syndrome. Constant pain causes spasms in the lower back muscles. The patient cannot move fully and is forced to tilt the body in order to relieve some of the load and reduce pain.
- Damage and death of nerve roots due to constant compression. The compression that occurs due to tissue protrusion constantly affects the nerve fibers. This disrupts blood flow, their functions, and later death occurs altogether. The manifestations of this process are: weakness, decreased tone, loss of sensitivity, the appearance of body asymmetry, decreased sensitivity and tone of the skin.
If the protrusion occurs in the posterior direction, any physical work is highly likely to cause severe compression and paralysis.
Diagnosis of lumbar hernia
To prescribe the correct treatment, the patient needs to undergo an examination and establish a final diagnosis. For this purpose, the doctor examines the patient and prescribes the following instrumental studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an ideal method for identifying lumbar hernia, allowing you to see soft tissues - discs;
- Computed tomography (CT) – allows you to examine the condition of the bone tissues of the spine and, based on indirect signs, determine the presence of a hernial protrusion;
- X-ray of the spine in two projections - a hernia can be detected only by indirect signs.
Without an examination, it is impossible to diagnose an intervertebral hernia and prescribe full treatment. You should not sit at home and wait for complications; consult a doctor as early as possible.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
Contraindications
Not all patients with spinal hernia can undergo an X-ray examination. Radiation during such a diagnosis of the back is considered insignificant, however, there are conditions of patients in which the body is very sensitive to radiation exposure. In such cases, x-rays cannot be performed.
Thus, the doctor does not refer a patient with a hernia for a similar diagnosis in the following situations:
- in case of serious condition of the patient;
- if a person has a pneumothorax (air appears in the pleura);
- for any internal bleeding. In this case, the hernia on the x-ray will only worsen and the pain will become stronger;
- if the patient is pregnant (especially 1st trimester).
In the above cases, the neurologist sends the patient to the safest diagnostic methods: MRI, ultrasound (ultrasound), etc.
Treatment of lumbar spinal hernia
Complete treatment for lumbar disc herniation should be selected by a doctor individually based on an examination of the patient and his examination data. Complex therapy includes:
- drug treatment, including using folk remedies;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- hirudotherapy courses;
- massage and manual therapy sessions;
- taping;
- reflexology courses;
- psychotherapy courses;
- therapeutic exercises.
If there is no effect from conservative treatment, the issue of performing a surgical operation is decided.
Drug treatment and folk remedies
The choice of drugs for drug treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the intensity of the pain syndrome. If the pain syndrome is severe, the patient is hospitalized, given pain blockades, and given injections of painkillers from the NSAID group. Sometimes glucocorticoid hormones (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) are prescribed to relieve inflammation and swelling.
If the patient’s condition allows treatment on an outpatient basis, the same painkillers can be administered to him either in the form of injections or prescribed orally in tablets or capsules. Treatment is continued with the prescription of pain-relieving ointments: diclofenac (Voltaren, Diclofenac), ketoprofen (Bystrumgel, Ketonal, Fastum gel), nimesulide (Nise), etc.
To relieve muscle tension, muscle relaxants are prescribed at this stage of treatment. The most famous of them is Mydocalm, available in tablets. For severe spasms of the lumbar muscles, the combined drug Mydocalm with lidocaine is prescribed intramuscularly.
Treatment also includes the prescription of B vitamins, which have a neuroprotective effect and enhance the analgesic effect (Neuromultivit, Milgamma).
To improve tissue nutrition, the comprehensive treatment plan includes vasodilators (pentoxifylline) and agents that improve metabolic processes in cartilage tissue (chondroprotectors) - Donu, Sustilak, Teraflex. These drugs are administered in the form of injections, taken orally in the form of tablets or externally in the form of ointments and gels: Chondroxide, Chondroitin, Theraflex. To strengthen bone tissue, it is recommended to enrich your diet with dishes prepared on the basis of gelatin.
Sometimes folk remedies are included in drug treatment, as a result of which the drug load is partially removed. All folk remedies must be prescribed by a doctor. For example, you can use this recipe at home:
- take a tablespoon of honey and flour, add a teaspoon of chopped fresh horseradish leaves, make a cake and apply it to the sore spot for an hour before going to bed; After the procedure, wipe the skin with a napkin and wrap your lower back with a woolen cloth overnight. Treatment can be carried out every other day.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Only if there is no effect from physiotherapeutic treatment, surgery is performed.
During exacerbations of the disease, electrophoresis with anesthetic medicinal solutions is prescribed to relieve pain. Treatment also includes courses of laser therapy, magnetic therapy and other procedures.
Read more about electrophoresis as a treatment method here.
After the pain subsides, courses of treatment with shockwave therapy (shock wave therapy) are prescribed to eliminate muscle spasms, improve blood circulation and restore the cartilage tissue of the discs.
Hirudotherapy
Treatment with leeches may also be helpful. Their saliva is rich in unique substances that have the following effects:
- vasodilation, improved tissue nutrition;
- anesthesia;
- resorption of segments of the nucleus pulposus trapped in the spinal canal.
Treatment is carried out in a course, the number of procedures and intervals between them is prescribed by the doctor.
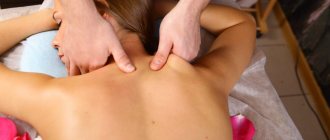
Massage treatment and manual therapy
Already after the first massage sessions, lower back pain is significantly reduced
Massage is prescribed after the pain subsides. It is very important that the massage therapist is certified as a specialist in medical massage and knows how to properly carry out procedures for lumbar hernia. Massage improves blood circulation, relaxes the back muscles and restores their strength, and activates metabolism.
Manual therapy courses are conducted by a manual therapist. He sets the hernia with his hands, restores the correct position of the vertebrae, and eliminates pinched tissue. An experienced manual therapist can relieve severe lower back pain in the first session.
Taping – treatment with muscle fixation
A modern method of treatment in which adhesive tape (tape) is applied to the lower back to fix the muscles. This leads to complete elimination of tension, pain, restoration of muscle strength, improvement of blood circulation and lymph outflow. When applied correctly, taping is a great help for lumbago and radiculitis.
Reflexology courses
Reflexology (RT) is an ancient Chinese method of treatment by influencing acupuncture points (AP) located on the human body in the projection of the channels (meridians) of the movement of Chi energy. AT are reflexively connected with all organs and systems of the body. For treatment, a reflexologist selects an individual recipe for each patient (a set of points and methods of influencing them).
This method of treating lumbar spinal hernia is effective; pain is eliminated or significantly reduced already in the first session. RT courses help patients return to normal life.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
In recent years, the percentage of patients with vertebral hernias caused by psychosomatic disorders has increased significantly. A psychotherapist or psychologist helps such patients identify the true causes of the disease and eliminate them, thus preventing further destruction of the intervertebral discs and a decrease in quality of life.
Which doctor should I contact?
Spinal diseases are treated by vertebrologists and neurologists, who often also work as chiropractors. They should be contacted if the slightest of the above-described deviations occurs. They are also the ones who interpret MRI, CT and X-ray images.
But due to their own workload, and often laziness, when symptoms of hernias and, in particular, back pain occur, people delay seeing a doctor. Painkillers in the form of tablets or ointments are often used on their own. But they only temporarily eliminate the symptom that is key to the disease.
This allows you to continue to lead your usual lifestyle, but has a negative impact on the prognosis, as the protrusion continues to increase. Therefore, over time, the pain syndrome intensifies, then neurological disorders in the form of numbness of the limbs or even paralysis join it, and internal organs corresponding to the level of damage also suffer.
Often in such situations people say that they are “falling apart.” And the reason lies in the intervertebral hernia. Therefore, in order to prevent this from happening, you should consult a doctor if the slightest manifestations of the disease appear. This specialist will be able to choose the right treatment tactics and assess the prospects for conservative therapy. Indeed, in advanced cases, the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
Prolonged ignoring of the problem can lead to the development of severe complications, including:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- disorders of the pelvic organs, up to loss of control over urination and defecation, as well as persistent erectile dysfunction;
- complete paralysis of the limbs.
Therefore, we recommend not to delay and contact a vertebrologist, chiropractor or neurologist as early as possible. Otherwise, conservative therapy will not bring results and the patient will have to muster the courage, as well as material resources, to perform a neurosurgical operation. Moreover, no neurosurgeon can give a 100% guarantee that it will be effective.
The specialist will prescribe the necessary studies, based on the results of which he will select the correct treatment tactics, taking into account the nature of the existing changes, the size of the hernia, its location and the clinical picture.
Exercise therapy for lumbar hernia
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy, therapeutic gymnastics) is always part of the complex treatment of lumbar spinal hernia. The initial set of exercises for daily training is introduced immediately after severe pain subsides. Therapeutic effects of exercise therapy:
- back muscle tension is eliminated;
- blood circulation and lymphatic drainage improves;
- metabolism and tissue restoration are activated;
- The mobility of the spinal column is restored.
Exercises for rehabilitation treatment
Recommended exercises for lumbar disc herniation:
- lie on your back on a hard surface, arms along your body; Slowly tense the muscles of the back, lower back and buttocks 10 times, fix the body in this position for 5 seconds, then quickly relax; repeat 10 times; after a week of training, gradually increase the fixation time and the number of approaches;
- from a supine position, raise your back, lower back and pelvis and remain in this position for 5 seconds, then return to the starting position and relax; repeat 10 times; after a week of training, gradually increase the time of lifting and tension and the number of approaches;
- while lying on your back, bend one leg at the knee, pull it to your chest (as far as possible without pain), then extend it and repeat the exercise with the other leg; gradually increase the number of painless approaches.
What not to do:
- running, jumping and walking quickly - this will lead to shaking and progression of the hernia;
- perform exercises with dumbbells and any other weights - this creates additional pressure on the spine;
- perform exercises with sharp turns and twisting of the torso;
- pull yourself up on the bar - the weight of your own body will injure the spine;
- ride a bicycle, drive for a long time
For severe pain, you need to lie on your back on a hard surface with your knees slightly bent; You can’t do gymnastics; after the pain begins to subside, you can begin to perform light exercises under pain control: as soon as it increases, the exercise should be interrupted.
It is best if a set of special exercises for exercise is agreed upon in consultation with a doctor and the first classes are carried out under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor. If the exercises take place without pain, subsequent exercises can be carried out at home, gradually increasing their intensity.
Read more about treatment methods in our article “Treatment of lumbar hernia without surgery.”
We use non-surgical hernia treatment techniques
Read more about our unique technique
Diet
Proper nutrition for a herniated disc is an element of complex treatment. The diet therapy method is aimed at maintaining the patient’s well-being and optimal weight.
It is important to choose a diet rich in vitamins and microelements. Food should be varied, you should eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, fish, and whole grains. A sufficient amount of protein must also be supplied to the body. Glycosaminoglycans, which are part of cartilage tissue and prevent its destruction, are found in products of animal origin: beef, poultry, and sea fish. Therefore, vegetarianism is not recommended for intervertebral hernia.
However, you shouldn’t get carried away with meat dishes, especially fatty, fried and spicy ones. Every person should remember that obesity is one of the factors that provokes the onset and progression of the disease.
So, we talked about how to cure a herniated disc and what the danger is if you ignore this disease. If you experience back pain, you should not rely on painkillers and put off seeing a doctor for a long time, because the key to the success of treatment is its timely start.
Did you like the article? Add the site to your browser bookmarks
Surgical treatment of lumbar hernia
Indications for surgical treatment of lumbar spinal hernia:
- severe pain that cannot be relieved by painkillers, blockades and physiotherapeutic methods;
- motor disorders - paresis and paralysis;
- progressive sensory impairment of the “saddle block” type;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
The type of surgical intervention is chosen by the doctor together with the patient. Currently, there are several types of operations when the disc, disc core, and vertebral arches are removed in different ways with the possible subsequent installation of an implant.
Neurologists believe that conservative treatment of lumbar disc herniation is more effective. But there are situations when surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
Principle of the method
When passing through different tissues of the body, X-rays are absorbed with different strengths. Thus, bones and spinal hernia on x-rays delay such radiation more strongly, and muscle structures and various organs - less. Therefore, on a computer monitor, the doctor sees an x-ray image, which shows the outlines of different parts of the body, first of all, bones.
X-rays were first used to diagnose various ailments in 1895. In the 19th century, 1 x-ray of the hand was taken. Over the past century, application methods have improved significantly, and the resolution of X-rays has also increased.
Doctors have not performed such fluoroscopy for a long time, during which the doctor saw a picture of the patient’s body on a special fluorescent screen. Today, more promising and accurate diagnostic methods are often used: computer tomography (CT), MRI.
However, today radiography is still considered indispensable in the diagnosis of spinal and other joint ailments, because it is an almost free procedure and has a high diagnostic value.
Approach to the treatment of the disease in the Moscow clinic "Paramita"
Our clinic uses all known methods of treating lumbar hernias. The peculiarity of our specialists’ approach to the treatment of these diseases is the combination of standard and latest Western techniques with traditional Eastern techniques proven over thousands of years, aimed at restoring balance in all organs and systems, which leads to the elimination of pathology.
We make sure to carefully examine our patients using oriental techniques and modern instrumental studies. We do not have a standard treatment plan; the doctor selects an individual combination of various techniques for each patient.
The specialists at the Paramita clinic know how to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine. All our patients get rid of pain in the shortest possible time, and then return to the clinic for regular maintenance treatment and forget about their problems forever. Detailed information about treatment can be found on our website.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Can an X-ray of the spine show a hernia? Yes maybe. However, the patient needs to carefully prepare for such an examination. In such a situation, a person performs the following actions:
- cleanses the intestines with a regular enema. After all, intestinal gases attach to each other and do not transmit x-rays. As a result, the overall picture of the hernia is blurred.
- A few days before the x-ray, he follows a specific diet. For example, a person refuses various gas-forming foods (cabbage, carrots, milk, peas, etc.).
- After meals, he drinks tablets such as Festal, Mezim, and activated charcoal.
- He does not eat anything in the morning before the hernia x-ray.
Before performing an x-ray, the doctor asks the patient if she is pregnant, since such a procedure negatively affects the development and growth of the intrauterine fetus.
If an x-ray of the hernia is urgently needed, the doctor covers the pregnant woman’s stomach with a special leaded apron.
FAQ
Is it possible to give birth?
A lumbar hernia is not an absolute contraindication for pregnancy. But it all depends on its type, size and existing complications. In any case, a woman must first undergo treatment and then plan a pregnancy.
Is it possible to do yoga?
Yes, with the permission of your doctor, you need to start doing the exercises under the supervision of an instructor.
How to sleep with a herniated lumbar spine?
You need to sleep on a hard surface with an orthopedic pillow, which allows you to relieve the spine during sleep. You can sleep on your back with a pillow under your knees, or on your side with a pillow under your back to maintain your chosen position.
Is it possible to run with a lumbar disc herniation?
Running is shaking, which is undesirable with a hernia. It's better to go swimming.
A herniated lumbar spine is not a death sentence. With regular maintenance treatment, you can lead an active life with this disease and forget about pain. Clinic "Paramita" is waiting for its patients!
Literature:
- Tsivyan Ya.L., Burukhin A.A.: Pathology of the degenerating intervertebral disc. Novosibirsk: Science. Sib. department, 1988.
- Technique and principles of surgical treatment of diseases and injuries of the spine / A.V. Baskov, I.A. Borshchenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 136 p. : ill.
- Kambin P. (Editor) Arthroscopic and Endoscopic Spinal Surgery Text and Atlas, Second Edition, Humana Press, Totowa, NJ.
- Regan J editors. Endoscopic Spine Surgery and Instrumentation. New York: Thieme Medical Publisher; 2004. p. 48-55.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 07/29/2020 Date of update: 03/16/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.75 / 5 (4)
When examination is not advisable
Performing radiography is impractical and even dangerous if:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- Nervous disorders;
- The patient's serious condition;
- Obesity;
- Oncology;
- Inability to track the dynamics of the disease;
- High radiation dose in old devices.
In general, it should be noted that the radiographic method has a number of advantages, including simplicity and accessibility, low cost, quick results, and painlessness. The disadvantages include the difficulty for a doctor to accurately establish a diagnosis without additional information.
SOURCE: https://diagnostinfo.ru/rentgenografiya/kosti-i-sustavy/pokazyvaet-li-rentgen-gryizhu-pozvonochnika.html https://lechisustavv.ru/diagnostika/4505-gryizhi-pozvonochnika-pokazhet-li-rentgen .html https://ortocure.ru/pozvonochnik/gryzha/pokazhet-li-rentgen-gryzhu.html