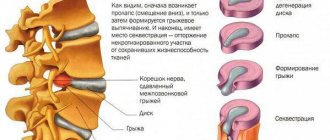
Dorsal disc protrusion is a condition in which a damaged spinal disc, having lost the amount of fluid it needs to function, falls outside the vertebral body.
“Dorsal” protrusion is called because the disc protrudes dorsally, i.e. posteriorly, to the side where the spinal canal with the dura mater, spinal cord and spinal nerves is located. Protrusion is the process of destruction of the intervertebral disc and is the initial stage of development of a herniated disc.
Dorsal disc protrusion - what is it?
There are a large number of factors leading to the destruction of the intervertebral discs of the spine, but no matter what the reason or combination of reasons is the cause of the destruction, there is always a fairly typical algorithm for the damage and destruction of the intervertebral disc.
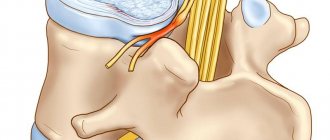
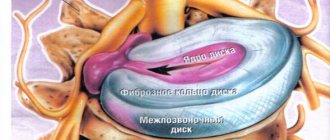
First of all, cracking of the outer shell of the disc (fibrous ring) occurs, as well as a parallel progressive loss of fluid from the central pulpous nucleus of the disc, without which the disc is not able to perform its functions.
The result of the disc losing fluid from the nucleus pulposus is a decrease in its shock-absorbing properties and it is squeezed out. Thus, a protrusion is formed directed towards the spinal canal area.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of intervertebral disc protrusion
The occurrence of protrusions depends on a number of circumstances, ranging from preventable causes (for example, injury, inadequate physical activity, improper lifting and moving objects) to inevitable (genetics, aging).
In addition to degenerative processes in the spine (osteochondrosis), there are other predisposing factors, such as:
- constitutional weakness of the ligaments,
- congenital pathology of the spine;
- incorrect posture during work;
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- falls on the buttocks, legs, injuries, weightlifting;
- bending, torsion of the spine;
- weakness of the abdominal muscles and muscles that support correct posture.
These and other reasons can lead to protrusion of the annulus fibrosus, usually on the posterior side, where the annulus fibrosus is thinner, up to rupture of the nucleus pulposus and the formation of a prolapse (hernia) into the epidural space of the spinal canal with the appearance of symptoms of compression of nerve tissue.
Mechanism of occurrence
In the lumbar and cervical spine, the pulpous nuclei of the intervertebral discs (if you look at the spine from the side) are not located strictly in the middle, but are shifted somewhat posteriorly in order to create the correct physiological curves in the spine - cervical and lumbar lordosis.
That is why, when the height of the disc decreases, which occurs when it is destroyed, part of the disc with the nucleus begins to be squeezed out mainly posteriorly, i.e. dorsally.
This condition is provoked by particular inclined positions of the torso (working “inclined”) or head (working at a computer).
Straightening the physiological curves in the cervical and lumbar spine is also of great importance, which very often happens with osteochondrosis.
In the thoracic spine, where the nuclei pulposus are somewhat displaced anteriorly, dorsal protrusions are much less common.
What it is?
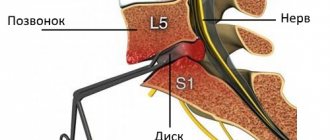
The diagnosis of “protrusion of the L5-S1 intervertebral disc” indicates damage to the lumbar region , namely the fifth (last) lumbar vertebra and the first sacral vertebra. Essentially, this is an extension of the intervertebral disc beyond the boundaries of the spinal column, which, if left untreated, can develop into a hernia.
Clinical picture
The first symptoms of protrusion may appear at a young age (16-19 years) . At first, lower back pain is mild, unobtrusive and intensifies with physical activity. The next stage is the appearance of a sharp, pronounced pain syndrome.
Anything can trigger an attack: lifting weights, working out in the gym, staying in one position for a long time (for example, while sleeping or working). Such attacks may be accompanied by a characteristic crunch in the lower back.
Protrusion in the lumbosacral region may be accompanied by a crunch in the back
If no action is taken at this stage, the pain will intensify, smoothly flowing from the lower back to the legs and buttocks. The patient may experience characteristic tingling, numbness, muscle weakness and other unpleasant symptoms. In addition, difficulties arise when laughing, coughing, and walking.
Degrees and classification
In its development, protrusion of the L5-S1 intervertebral disc goes through three stages:
- First stage . It is characterized by the appearance of small cracks in the fibrous ring, which leads to a change in the design of the disc itself. This is the very beginning of the disease, when the ring can collapse by about two-thirds. A characteristic symptom of the first stage is acute outbreaks of local pain.
- Second stage . Accompanied by protrusion of the disc by 2 or 3 mm. The pain becomes radiating, the patient feels serious discomfort in the area of the damaged disc. At this stage, protrusion can be cured without surgery or medication. It is enough to change your lifestyle, do physical therapy and find a good massage therapist.
- Third stage . It is characterized by increased disc protrusion and precedes the rupture of the fibrous ring and the appearance of an intervertebral hernia. At this stage, a person is faced with acute radiating pain, minor neuralgic disorders (numbness of the limbs, etc.).
It is important to understand that the treatment of protrusion depends not only on what stage it is at, but also on its type.
Scientists have found that L5-S1 protrusion, located in the lumbar spine, may be:
- circular;
- dorsal (posterior);
- median;
- diffuse;
- foraminal;
- paramedian.
Note! The most dangerous are median and posterior protrusions.
Prevalence, who suffers most often, significance
According to statistics, lesions of the L5-S1 disc are the most common lesions of the lumbar region (this pathology occurs in 45-50% of patients with diagnosed lumbar protrusions). In 10-11% of patients there is a combination of lesions of L4-L5 and L5-S1 (less often L3-L4 and L5-S1) .
Sometimes there may be a combination of displacement of the intervertebral discs L4-L5 and L5-S1
In almost 40% of cases, concomitant diseases are observed, such as anthespondylolisthesis, disc herniation, spondyloarthrosis, retrospondylolisthesis, uncoarthrosis, etc. In the vast majority of cases, the disease develops against the background of osteochondrosis and other degenerative changes in the spinal column.
If previously the disease occurred mainly in older people, today the diagnosis of “protrusion” is also given to young people (including teenagers).
Symptoms
Symptoms of dorsal protrusions depend on the direction of extrusion of the protrusion.
- If the protrusion is directed strictly posteriorly , then it causes muscle tension, irritating the posterior longitudinal ligament running along the edge of the vertebra. With loads, heavy lifting, or working in a forced position of the torso, already formed muscle tension can increase many times and manifest itself as pain. Depending on the degree of disc destruction, pain can be strong or weak, be present for a long time after the exercise itself, or pass quickly.
- If the protrusion is shifted slightly to the side from the central line , then the extruded intervertebral disc is close to the nerve emerging from the spinal cord. In this case, with the development of inflammation or swelling, the dorsal protrusion will take part in irritation and/or compression of the nerve, causing pain that will not only be located at the site of inflammation, but also spread to the periphery (to the shoulder, arm, buttock, thigh or leg). In this case, the pain can be quite severe and long-lasting, and it will be difficult to distinguish it from a progressive herniated disc.
Classification
There are several types of pathology characterized by a posterior orientation. It is worth considering the features of each of them in order to understand what the presence of the disease can lead to.
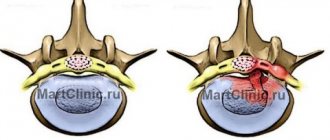
Posterior median protrusion
Posterior median disc protrusions are among the most dangerous. They are directed towards the middle of the spinal cord canal, so an increase in protrusion can lead to compression of the spinal cord. This, in turn, is fraught with serious consequences for the patient’s health.
Posterior diffuse protrusion
This name for the pathology means that the intervertebral disc protrudes backwards, but only a small part of it is affected. As a rule, the damage to the structural element is 25-50%. The doctor identifies such a disease using methods of visualizing the structures of the spinal column, after which he immediately prescribes treatment that can return the damaged disc to its place.
Anteroposterior protrusion
Anterior-posterior protrusion is characterized by the presence of protrusions in both directions. This can make the disease more difficult to treat.
Posterior median protrusion
This protrusion is located in the back of the disc and tends to the central part of the spinal cord or cauda equina. Can lead to significant pinching of nerve tissue and severe pain.
Diagnostics
Dorsal protrusion can be objectively diagnosed only with an MRI or computed tomography examination. Radiographs do not show posterior protrusions.
On Rg images, dorsal disc protrusions can be judged only on the basis of indirect signs.
Since it is very difficult to distinguish a dorsal protrusion from a formed spinal hernia based on complaints and symptoms, all patients who first complain of pain in the spine must undergo an MRI examination, this will allow identifying the protrusion at an early stage of development, which means timely treatment aimed at curing it. .
Treatment options
Posterior diffuse protrusion of intervertebral discs or another type of this pathology is usually treated with a conservative method. The doctor prescribes medications aimed at:
- pain relief;
- relieving the inflammatory process;
- improving blood supply to tissues in the affected area;
- relieving swelling - as a rule, these are diuretics;
- myorelaxation - relaxation of spasmed muscles near the location of the protrusion;
- restoration of cartilage tissue - chondroprotectors;
- restoration of the necessary balance of minerals and vitamins in the body.
In addition, the doctor refers the patient to massage, physiotherapy, and also informs about the need to engage in physical therapy.
Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening muscles and the body as a whole, restoring ease of movement, as well as improving blood circulation in the body. Additionally, you can use traditional medicine methods. However, remember that none of them can cure posterior median protrusion, so you should not rely on such methods alone.
Surgical treatment of protrusion is indicated in rare cases: if the patient has advanced the disease and has not gone to the clinic for a long time, despite obvious manifestations. However, posterior diffuse protrusion can also be cured surgically using minimally invasive methods.
Treatment of dorsal disc protrusion
Correct treatment of dorsal disc protrusion in its tactics usually differs little from the treatment of intervertebral disc herniation.
Since the main problem in the development of dorsal (i.e., posterior) disc protrusion is damage to the posterior parts of the intervertebral disc with its extrusion into the spinal canal, the main basic treatment must necessarily be aimed at this particular damage. For proper treatment of dorsal protrusion of the spine, it is first necessary to carry out a “preparatory” stage of treatment, the task of which is to remove pain, the inflammatory process, relieve increased muscle tone, swelling, eliminate the lack of blood supply to the spinal tissues in the disease areas, after which the main, “restorative” stage treatment. The task of the “restorative” stage of treatment is to heal damage to the outer fibrous ring of the disc and restore the nucleus pulposus of the disc, without which the intervertebral disc will not be able to fulfill its shock-absorbing properties and, in this case, will still remain squeezed out.
The method of treatment of dorsal protrusions used in the clinical diagnostic Center of Dr. Yavid takes into account not only all the symptoms of the disease, but also all the reasons leading to its appearance.
The most innovative and effective technique used at Dr. Yavid’s clinic today is the “revitalizing” technique, aimed not only at relieving symptoms, but also at permanently restoring damaged intervertebral disc tissue.
Sign up and come see us! We help!
Types of dorsal protrusions
Depending on the area of protrusion of the intervertebral disc, dorsal protrusion is divided into diffuse and circular. Diffuse dorsal protrusion of the disc is accompanied by the release of cartilage tissue in different places, and the protrusions can have different sizes. This pathology is considered the most dangerous, since in case of complications an extensive inflammatory process can develop. Circular protrusion develops evenly throughout the cartilaginous disc. It is more common than other protrusions, develops without pain symptoms and does not cause concern in patients.
Prevention
The main problem of prevention for posterior disc protrusions is maintaining proper muscle tone and posture. This may involve playing sports, therapeutic exercises or yoga.
This is especially important if the patient has a curvature of the spine (scoliosis). It is advisable to avoid prolonged positions with the torso tilted forward and the head tilted forward, since it is these loads that primarily provoke the formation of posterior disc protrusions.
If you experience even minimal complaints from the back, lower back or neck, you should definitely consult a doctor who specializes in spine diseases. The sooner protrusion is diagnosed and the sooner treatment is started, the more effective and quick the treatment result will be.
Clinical symptoms of paramedian disc protrusion L5-S1
Paramedian protrusion of the L5-S1 disc produces severe neurological symptoms. The clinical picture develops acutely. When the disc bulges into the lumen of the spinal canal, numbness of certain parts of the body and a decrease in muscle strength of the lower extremities are observed. Various paresthesias appear.
The clinical picture of left-sided paramedian disc protrusion is based on damage to the lower limb on the same side. Complaints of severe weakness in the left leg are accompanied by a decrease in the intensity of tendon reflexes.
Left-sided paramedian protrusion of the L5-S1 disc is relatively rare in the form of a certain load distribution algorithm in right-handed individuals. The risk of developing pathologies on the left side increases in left-handed people.
Right-sided paramedian disc protrusion is a more common location of pathological bulging of the annulus fibrosus. The right leg is mainly affected; with prolonged progression, muscle tissue wasting is observed. At the initial stage, acute lumbargia syndrome occurs. This is an acute pain in the lumbar region, which in the form of lumbago can spread to the buttock area and upper thigh. Increased pain is associated with body movements.
Diagnosis is carried out by a vertebrologist or neurologist. If characteristic symptoms appear, you should contact these doctors. Unfortunately, the local physician in the city clinic does not have sufficient professional competence to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Causes
In order to correctly prescribe treatment for spinal disc protrusion, it is necessary to correctly determine the cause of the pathology. They can be very different:
- age-related changes in the tissues of the spine, as a manifestation of osteochondrosis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- different types of spinal curvature;
- spinal column deformities resulting from injury;
- a number of congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system;
- acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of spinal tissue;
- excessive mechanical and physical overload of the spine;
- improper distribution of the load on the spine, which occurs as a result of various diseases.