Diffuse herniation of the intervertebral disc is one of the types of hernias in which the integrity of the fibrous ring is not compromised, but uneven displacement of the disc is observed. The difference from other types of hernias is the absence of a hernial sac and the presence of a bulge similar to a hernia. It is worth noting that with this disease the disc is partially affected - however, if the process is started and is more than 50%, it can lead to rupture of the annulus fibrosus.
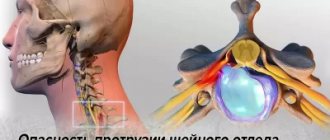
The most dangerous subtype of this pathology is posterior diffuse disc herniation, which is directed inside the spinal canal and can lead to compression of the spinal cord and spinal nerves, especially with the simultaneous presence of stenosis and narrowing of the spinal canal.
If you are diagnosed with diffuse disc herniation and want to know what it is, read this article. It provides all the necessary information about the dangers, symptoms, as well as diagnosis and treatment of this disease at the CELT clinic.
Depending on the type of operation and category of complexity from 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
Included in the price:
surgery, anesthesia, dressings, medications, food and hospital stay, observation by a surgeon in the postoperative period.
40-60 minutes
(duration of operation)
2-3 days in hospital
Indications
- persistent and severe symptoms of compression of the spinal nerves by a herniated disc, not amenable to conservative therapy
- the patient's desire to get rid of pain
Contraindications
- chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation
- acute inflammatory processes in the body
Clinical manifestations of diffuse hernias
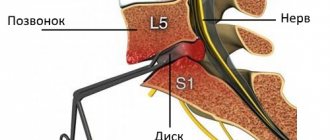
The most common is diffuse L4-L5 disc herniation, along with diffuse L5-S1 disc herniation. This is due to the fact that the lumbar region bears the greatest load.
It is worth noting that in the stage of formation of a dorsal hernia, symptoms are practically not manifested, so patients often seek medical help much later, when treating the disease is much more difficult. Clinical manifestations of diffuse hernias are as follows:
- the appearance of pain of a different nature, from pulling to stabbing;
- radiating pain to other parts of the body in the limbs, arms, legs;
- decreased sensitivity, and often its loss;
- decreased muscle tone in those parts of the body for which the nerves compressed by the hernia are responsible for the innervation.
If the lumbosacral region is affected, pain symptoms are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the sphincters of the rectum and bladder.
If the hernia is located in the thoracic or cervical region, the following may occur:
- blood pressure surges;
- pain in the heart area;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- headache.
Advanced forms are characterized by paralysis of the upper/lower limbs.
How does dorsal disc protrusion occur?
Intervertebral discs are elastic “pads” between the vertebrae.
They absorb the load on the spine, making it strong and flexible at the same time. Each disc consists of a dense shell - the fibrous ring, and a semi-liquid “filling” of the ring - the nucleus pulposus. With metabolic disorders and increased physical activity, the condition of the intervertebral discs worsens. They become fragile, lose elasticity, and their height decreases. As a result, cracks appear in the fibrous ring under pressure, and the nucleus begins to shift within them. As a result, the disc protrudes into the spinal canal. With dorsal protrusion, the disc protrudes toward the spinal canal, spinal cord, and nerve roots.
Disc protrusion most often occurs in the lumbar region, less often in the cervical or thoracic regions.
Treatment of diffuse hernia
Treatment of diffuse hernia is carried out by conservative and surgical methods. The latter, as a rule, are used only if there are indications for this, or if conservative treatment has not achieved the desired effect.
Conservative treatment involves taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and performing a number of physical procedures. Epidural blocks are often used and provide excellent pain relief that lasts from six weeks to six months. They also have a therapeutic purpose, allowing them to relieve swelling and inflammation, and often allow them to completely avoid surgery.
Surgical treatment at the CELT clinic is carried out using endoscopic intervention technology and involves a minimal incision no more than one and a half centimeters long. The operations last no more than 40–60 minutes and are accompanied by minimal blood loss and risks to the patient’s health. They always bring the desired result and allow their patients to return to their normal lifestyle within two weeks!
Risk factors and causes
It is worth highlighting a number of factors that significantly increase the risk of developing protrusion:
- inactive lifestyle;
- excessive physical activity;
- hereditary factors;
- weakened muscles;
- improper exercise;
- elderly age.
In addition, there are a number of other reasons that can lead to protrusion:
- incorrect posture;
- various types of injuries;
- overweight;
- metabolic disorder;
- sedentary work;
- circulatory disorders;
- diseases of the spinal column, which include lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis.
Consequences
Did you know that...
Next fact
If the patient does not receive timely medical care for developing protrusion, a significant deterioration in health is possible :
- increased pain syndrome;
- the appearance of intervertebral hernia;
- Due to increased compression of the spinal cord and its roots, paresis and paralysis may develop as the hernia enlarges.
Treatment of bulging vertebral discs
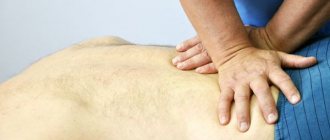
Treatment of bulging vertebral discs is possible only with the help of manual therapy in combination with therapeutic exercises. Pharmacological remedies against this disease are completely powerless. By using them you are only wasting your time and wasting your money.
Treatment should always begin with several procedures of traction traction of the spinal column. due to this, pressure is removed from the intervertebral discs, they straighten and the process of tissue regeneration of the fibrous ring starts.
Then the doctor develops an individual course of therapy, which may include:
- massage and osteopathy to increase the elasticity of all soft tissues and enhance the processes of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the lesion;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy to restore muscle tone and strengthen the spinal frame;
- reflexology – to launch tissue regeneration processes using the hidden reserves of the human body;
- physiotherapy, laser treatment and much more.
If you need a safe and effective course of treatment for bulging discs, make an initial free appointment with a spine specialist at our manual therapy clinic. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe individual treatment.
Diagnosis of intervertebral disc protrusions
If you experience back pain in the lumbar region, neck, sensory disturbances in the limbs and other symptoms described above, you should consult a neurologist and undergo an examination.
To diagnose degenerative changes in the spine, the doctor usually finds out the presence of typical painful symptoms, concomitant rheumatic diseases, sensory and motor disorders, and deterioration of reflex activity. In addition, MRI plays a decisive role in forming an objective diagnosis.
Causes of protrusion
Natural aging processes lead to discs losing their elasticity due to decreased collagen production, changes in hormonal levels, and slower restoration processes in tissues. At an early age, protrusion occurs if a person ruins his health with his own hands, getting carried away by bad habits, including addiction to alcohol and tobacco. In addition, low physical activity causes a slowdown in blood circulation in the back, which in turn leads to a weakening of the muscular skeleton.
Additional factors influencing the susceptibility of intervertebral discs to protrusions are:
- excessive exhausting physical activity, which creates microtraumas of cartilage, reduces the ability of the spine to absorb the load when walking and running;
- spinal abnormalities, whether congenital or acquired;
- pathologies of organs responsible for the production of hormones, causing diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism.
Separately, there are spinal injuries that result in displacement of the intervertebral discs with further protrusion, which over time turns into a hernia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dorsal protrusions depend on the direction of extrusion of the protrusion.
- If the protrusion is directed strictly posteriorly , then it causes muscle tension, irritating the posterior longitudinal ligament running along the edge of the vertebra. With loads, heavy lifting, or working in a forced position of the torso, already formed muscle tension can increase many times and manifest itself as pain. Depending on the degree of disc destruction, pain can be strong or weak, be present for a long time after the exercise itself, or pass quickly.
- If the protrusion is shifted slightly to the side from the central line , then the extruded intervertebral disc is close to the nerve emerging from the spinal cord. In this case, with the development of inflammation or swelling, the dorsal protrusion will take part in irritation and/or compression of the nerve, causing pain that will not only be located at the site of inflammation, but also spread to the periphery (to the shoulder, arm, buttock, thigh or leg). In this case, the pain can be quite severe and long-lasting, and it will be difficult to distinguish it from a progressive herniated disc.
Diagnostics
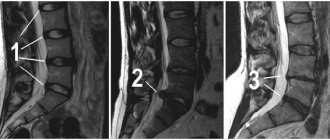
Dorsal protrusion can be objectively diagnosed only with an MRI or computed tomography examination. Radiographs do not show posterior protrusions.
On Rg images, dorsal disc protrusions can be judged only on the basis of indirect signs.
Since it is very difficult to distinguish a dorsal protrusion from a formed spinal hernia based on complaints and symptoms, all patients who first complain of pain in the spine must undergo an MRI examination, this will allow identifying the protrusion at an early stage of development, which means timely treatment aimed at curing it. .
Treatment
After establishing an accurate diagnosis and in the absence of objective contraindications, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment, including medication and physical therapy to prevent further protrusion of the substance.
General therapy for protrusion usually includes:
- physical therapy;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- swimming;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis.
The doctor also usually recommends physical rest and avoiding stress on the spine. Patients benefit from wearing an orthopedic corset.
Drugs
The use of medications in the treatment of protrusion allows:
Drugs for protrusion help eliminate symptoms and eliminate spasms;- remove inflammatory processes;
- promote the regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue.
Most often, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Ibuprofen) and non-narcotic analgesics (Pentalgin, Tempalgin). Muscle relaxants, immunostimulants, and vitamin and mineral complexes may also be prescribed.
In order to improve cerebral circulation, Cavinton may be prescribed.
To restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotective therapy is prescribed using injections of chondroitin sulfate, the course of therapy with which is 25 injections administered every other day.
Surgery
The need for surgical intervention arises in the final stages of protrusion , when the irreversible nature of the degenerative changes becomes obvious. In general, such methods are used extremely rarely, only in 10% of cases.
Exercise therapy and massage
In the early stages of detecting protrusion, physical therapy exercises are very useful. It allows you to strengthen muscles, reduce the likelihood of deterioration of the condition, and eliminate increased pain. A set of exercises must be prescribed by a specialist. Classes can take place either under his supervision or independently with careful observation of sensations.
also benefit from swimming, light fitness, and yoga . Active sports, running, and bodybuilding should be excluded.
During physical therapy exercises, sharp bends and turns should be avoided.
Massage procedures are useful as an aid. They allow you to relieve peripheral inflammation of soft tissues and reduce pain. Massage will help improve muscle tone.
Treatment at home
Self-treatment for protrusion is extremely undesirable. Only a specialist can correctly select a therapeutic complex.
At the same time, to relieve suffering and reduce pain, decoctions and tinctures of medicinal herbs, compresses and rubbing may be recommended :
- garlic compress, which is prepared from 300 g of chopped garlic, which needs to be poured with 200 ml of vodka and left in a warm place for 10 days, then moistened with gauze in it and applied to the sore area for no more than 30 minutes;
- Decoctions of wormwood, Kalanchoe, oil extracts of St. John's wort and birch leaves are also suitable for preparing compresses.
Prevention
You can avoid disc protrusion by following simple rules of prevention. Preventive measures for protrusion include:
- timely correction of posture;
- prevention of osteochondrosis and other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- regular exercise;
- eating foods rich in calcium;
- maintaining proper weight;
- use of an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- taking preventive massage courses.
Protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs
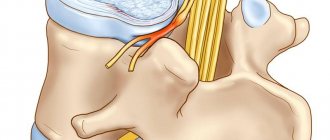
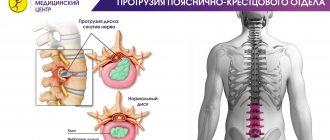
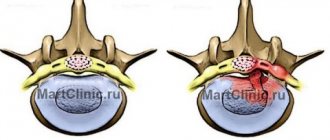
The protrusion process begins with a point bulging of the ring: a protrusion from 1 to 8 mm is formed from its fibrous plates. At the same time, the internal structure of the fibrous ring has already been destroyed, and, most likely, significantly - by the time protrusion appears, usually more than half of the outer shell of the disc is cracked and has lost its functionality. But the outer, stronger layer of the disk still holds the core.
In the scientific literature, especially foreign, a herniated disc is considered to be a localized displacement of part of the disc (nucleus pulposus, cartilage, collagen rings in various combinations) outside the intervertebral disc space, generally speaking, both when the fibrous ring is ruptured (prolapse) and when the integrity of the outer, more durable layers of the fibrous ring (protrusion). In popular scientific literature and in everyday life, a hernia is most often understood as prolapse - loss of the internal tissues of the ring through a rupture of its outer shell.
Thus, protrusion in a simplified view is the initial stage of the formation of a hernia, but at the same time it can lead to consequences no less serious than a developed disc herniation. In the diagram you can see that the main threat is not so much the rupture of the fibrous ring, and not the bulge of the disc itself, but its size and location in relation to the nerve roots and spinal cord, compression of which will inevitably lead to the occurrence of pain and other consequences.
Not every protrusion causes concern and threatens health, just as not every protrusion will inevitably turn into prolapse. But the presence of protrusions of any type and size in the intervertebral discs indicates the development of degenerative processes in the spine and should be an incentive to begin timely treatment of osteochondrosis in order to avoid severe stages of the disease and complex surgical intervention.
How is protrusion diagnosed?
Some cases can be diagnosed already at the initial appointment, when the doctor understands the source of the problem based on the patient’s complaints and the collected medical history. In other situations, additional examination is carried out:
- X-ray. This type of study of the condition of bone tissue is the most accessible, because such installations are available even in the smallest and most undeveloped cities. This is a primitive option for diagnosing fractures, dislocations and thinning of the intervertebral space.
- CT and MRI. In this way, you can obtain maximum information about the condition of the discs, their elasticity, body thickness and the integrity of the fibrous ring.
- Palpation. The specialist may additionally conduct a manual examination of the spine.