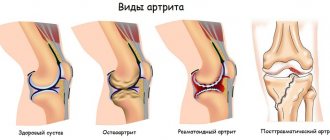
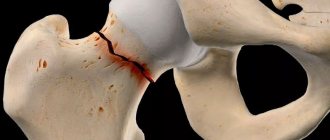
Post-traumatic arthrosis of the knee joint is a very common disease that can be encountered by a person of any age and social status. Even those who lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor their health are not immune from it. After all, it is a direct consequence of a knee injury, which can be obtained under certain circumstances even when falling from your own height. At the same time, the disease is dangerous because, if left untreated, it tends to progress and lead to severe limitations in movement, even to the point of disability.
Development mechanism
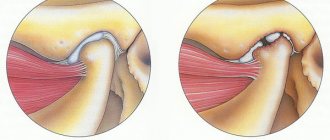
Due to injury, a disruption occurs in the structure of articular or cartilage tissues. The bones change position in relation to each other and can no longer move safely. Cartilage ceases to perform a shock-absorbing function and becomes deformed, and a lack of synovial fluid develops in the joints. Competent treatment can stop this process.
Sometimes therapy for post-traumatic arthrosis may be needed after surgery. During surgery, soft tissues and muscles are damaged, scars form on them, which makes proper nutrition of the joints impossible. This leads to inflammation and then to degenerative phenomena.
The disease most often affects the knees, which bear the maximum dynamic load. A synovial fluid prosthesis of the knee joint or complex therapy can help solve the problem. Representatives of certain professions, such as massage therapist, painter, tennis player, are also at risk. Their degenerative phenomena manifest themselves due to regular injury to the elbow joints.
Older people are most susceptible to post-traumatic arthrosis
Diagnostics
If signs of arthrosis of the knee joint develop after an injury, you should contact an orthopedic traumatologist. The diagnosis is established based on the medical history, taking into account the nature of the injury suffered, as well as the patient’s symptoms and the results of instrumental research methods.
As a rule, the doctor initially interviews the patient about the nature of the complaints, the characteristics of pain, and other disturbing manifestations of the disease. After this, he examines the sore knee for any deformity or limitations in mobility. In most cases, these data are sufficient to suggest with a high degree of probability the presence of post-traumatic arthrosis. But for an accurate assessment of the degree of degenerative-dystrophic changes and the consequences of injury, instrumental examinations are necessarily prescribed. These may include:
- X-ray of the knee joint - the resulting images assess the condition of the joint area, the presence of signs of its flattening and deformation, narrowing of the joint space, the presence of osteophytes (sharp bone protrusions), cysts, etc.;
- CT scan – is prescribed if X-rays do not provide the necessary information or it is necessary to assess the condition of the knee joint with greater accuracy;
- MRI – required to study soft tissue structures, which include the cartilaginous components of the joint;
- arthroscopy - is prescribed in difficult cases and allows not only to visually assess the condition of cartilage, ligaments, menisci, articular surfaces of bones, but also to immediately carry out therapeutic actions to remove torn off and irreparable fragments of cartilage, etc.
Symptoms of post-traumatic arthrosis
At the initial stage, a person may not be aware of the problem and turn a blind eye to fatigue in the limbs, mild pain, and slight crunching. Symptoms often appear in the morning, but their intensity increases over time. Pain syndrome manifests itself even without physical activity.
At later stages of post-traumatic osteoarthritis, when intra-articular injection of synovial fluid prostheses is relevant, the outlines of the bones change, bone growths, growths or fusions are formed. The joint loses full motor activity.
Post-traumatic arthrosis can appear after 5-7 years
General clinical recommendations
Those who have had acute or suffer from chronic post-traumatic arthritis should adhere to the following recommendations:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, alternate between activity and rest, regulate sleep;
- eat well; monitor your weight;
- eliminate heavy physical activity and stress;
- treat all acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- regularly perform therapeutic exercises, go swimming; conduct massage courses several times a year; walk more in the fresh air;
- as prescribed by the attending physician, conduct courses of anti-relapse treatment.
Prevention
To prevent post-traumatic arthritis, you need to improve your health, harden yourself, avoid risky traumatic situations, as well as permanent injury to a joint. It is especially important to comply with all these conditions for people already suffering from chronic arthritis - additional trauma can worsen its course.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Characteristic symptoms as the disease progresses:
- joint crunch during movement, especially after waking up in the morning;
- if the disease affects the ankle, the limb may twist;
- aching pain of increasing intensity, especially after a long stay in a static position or after physical activity;
- in advanced cases, when it is definitely impossible to do without the best synovial fluid prostheses, the pain intensifies at night, the skin over the joint swells and turns red.
Post-traumatic arthrosis most often affects the knee joint
How to diagnose in the early stages?
Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable. The use of so-called folk remedies can lead to the fact that the most favorable moment for starting treatment will be missed and complex surgical intervention will be required.
Medical assistance is necessary, since without it disability may occur. This is especially true if there is a violation of the integrity of the cartilage of the spine, hip joint or knee.
Treatment of the disease begins with diagnosis. An orthopedic doctor will examine the patient, collect a detailed medical history, perform x-rays, perform ultrasound and MRI of the joint, send synovial fluid for analysis, etc.
The final diagnosis is associated with the analysis of x-rays, CT or MRI results. From them one can judge at what stage the disease process is and what is the current state of the cartilage and surrounding soft tissues.
The first stage on x-ray looks like a narrowed space (cracks) of the joint. The cartilage is compacted. There is no disruption of its structure yet.
The second stage manifests itself as deformation of the bones that form the joint. Its cavity is significantly modified and greatly reduced. The process of development of pathology has already been significantly advanced.
During the third stage, the joint space practically closes. The appearance of the joint is significantly different from the norm, and growths are noted everywhere on the bones. The limb is deprived of normal mobility.
Treatment of post-traumatic arthrosis
The principles of treating osteoarthritis caused by mechanical trauma are the same as any other. It is impossible to completely cure the disease: therapy is aimed at reducing pain, restoring the lack of synovial fluid in the joint, and preventing further deformation of the joint structures.
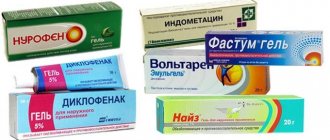
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain.
- Antispasmodics are prescribed for muscle spasms.
- Chondroprotectors and biostimulants are needed to restore processes in cartilage.
- In cases of severe inflammation, steroid hormones, such as corticosteroids, are indicated.
- Treatment of arthrosis is supplemented with massage and paraffin therapy, exercise therapy, and various physiotherapeutic techniques.
How to help joints maintain their physical shape? An arthrologist and rehabilitation methodologist tells us what safe exercises can be done at home or in the office:
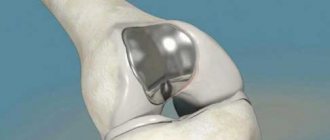
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to cope with post-traumatic arthrosis conservatively. If the injury has led to serious anatomical disorders, muscles and ligaments are damaged, and articular structures are significantly destroyed, endoprosthetics is prescribed.
In some cases, the problem can be solved with a course of intra-articular injections of the synovial fluid substitute, the Noltrex endoprosthesis. The drug is injected into the joint capsule, where it is evenly distributed on the damaged surfaces of the cartilage, moves them apart and stops painful friction.
This course of several injections relieves pain and returns normal mobility for a year or a year and a half. The main thing during this period is to avoid re-injury, otherwise any therapy becomes meaningless.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Is it possible to get disability?
Yes, if there is a persistent limitation of joint function.
Which doctor treats you?
Acute arthritis - a traumatologist or surgeon, chronic - a rheumatologist.
Can children develop post-traumatic arthritis?
Maybe.
What prognosis do doctors usually give?
Depends on the severity of the injury and the timeliness of medical care. In acute arthritis, the prognosis is generally favorable. Chronic progression can also be stopped at any stage.
Post-traumatic arthritis requires careful attention to your health and timely administration of adequate treatment. Our medical center can help you!
Literature:
- Karateev A.E., Barskova V.G. Criteria for choosing a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Handbook of a practical doctor, 2007.- T. 5.- No. 5.- P. 13-17
- Kramer WC, Hendricks KJ, Wang J. Pathogenetic mechanisms of posttraumatic osteoarthritis: opportunities for early intervention Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2011; 4(4): 285-298.
- Lieberthal J, Sambamurthy N, Scanzello CR. Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23: 1825-1834.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 03/12/2021 Date of update: 03/15/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (3)
How to treat osteoarthritis?
The best way to get rid of osteoarthritis is to see a doctor early.
First, a conservative treatment method is used. With advanced deforming arthrosis of the joints, the pain becomes so unbearable that it is necessary to resort to intra- and periarticular blockades, and injections of steroid drugs are performed. In this case, after blocking severe pain, joint replacement surgery is indicated.
At the onset of the disease, the use of medications is used. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- chondroprotectors,
- analgesics,
- local anesthetics,
- anti-inflammatory drugs,
- hyaluronic acid,
- means that stimulate blood circulation,
- vasodilators,
- minerals and vitamins.
Warming or cooling compresses with special medications, mud and paraffin, and liquid nitrogen are used externally.
Treatment of deforming osteoarthritis should be comprehensive. In addition to the use of medications, it is necessary to prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, joint massage, therapeutic exercises and dosed physical activity, a special diet, spa treatment, etc.
Treatment with a magnetic field, ultrasound and laser, electrical myostimulation, and electrophoresis can have a positive effect. Swimming can be of great benefit.
Treatment of deforming arthrosis is carried out in courses. After a certain period they repeat. Therapy is carried out until the pain completely disappears and significant improvements appear.
It should be remembered that deforming arthrosis alternates with periods of exacerbation and subsidence of the main symptoms. Therefore, during remission, the patient must be constantly monitored by the attending physician, since relief can only be temporary.