Home / Articles / TMJ arthritis: how to treat it?
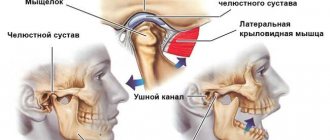
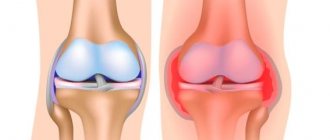
When talking, eating, laughing, a joint called the temporomandibular joint works. This joint is located in front of the ear and is a movable connection of the head of the lower jaw with the ellipsoidal fossa of the temporal bone of the skull. Like any other joint in the human body, the TMJ can also experience inflammation, the advanced form of which is called TMJ arthritis. What are the symptoms of this disease and how to treat it – we will look at it in our article.
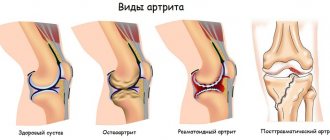
Symptoms and treatment of TMJ arthritis depending on its type
Arthritis of the temporomandibular joint is a very serious disease, the consequences of which can lead to irreversible changes in the joint. These consequences, in turn, greatly spoil a person’s life and significantly change his appearance (asymmetry of facial features appears). The first step in treating TMJ arthritis should be to see a doctor immediately.
Treatment begins with identifying the duration of the process and the type of inflammation.
| View | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Chronic arthritis of the TMJ | - nagging or aching pain in the joint, intensifying when moving the jaw; - difficult to open your mouth in the morning; - strong crunching sound when opening the mouth; — no visual changes are observed in the joint area (redness, swelling); - pain when feeling the joint and when pressing the chin forward and upward. | - if there is no exacerbation, you can massage the masticatory muscles; — hirudotherapy; — physiotherapy (ultrasound and electrophoresis with iodine and bee venom preparations); - myogymnastics. |
| Acute TMJ arthritis | - the main symptom is a sharp pain in the joint area, radiating to the tongue, back of the head, temple, ear, which intensifies when trying to open the mouth or move the jaw; - when you try to open your mouth by at least 5 mm, the lower jaw moves to the painful side; - swelling of soft tissues in the joint area; - pain when palpated; - hyperemia of the skin; - feeling of fullness in the jaw. | - dentist treats; — treatment includes a set of measures: 1. complete rest of the joint by applying a sling-shaped bandage to the head and lower jaw; 2. a plate is installed between the teeth, which separates the teeth; 3. All food should be ground almost to a liquid state. All events last at least 2 days. |
| Infectious arthritis of the TMJ | - at the initial stage, a feeling of discomfort in the joint; - increased pain when opening the mouth and chewing food for a long time. If there is no treatment, the process develops into a purulent form: - temperature rise to 38 degrees; - lack of appetite and sleep; - general weakness and malaise; - sharp pain in the joint when moving the lower jaw and opening the mouth; - hyperemia, swelling and pain when pressing the skin in the ear area. | - rest in the joint and lower jaw (sometimes with the help of a sling bandage); - taking broad-spectrum antibiotics with antihistamines; - compresses with dimexide; — physiotherapy (dry heat, UHF, electrophoresis). Treatment of the purulent form should be accompanied by opening the foci of infection in the joint. |
| Traumatic arthritis of the TMJ | - sharp pain in the joint at the time of injury with subsequent limitation of any movements of the lower jaw; - sometimes there is a rupture of the ligamentous apparatus and hemorrhage into the joint, which can lead to ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint. | - applying a cold compress immediately after an injury to reduce the accumulation of blood in the joint; - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; - it is possible to use analgesics to reduce pain; — physical therapy is indicated when pain symptoms subside (UHF, paraffin and mud therapy). |
| Rheumatoid arthritis TMJ | - begins in acute form; - severe throbbing and local pain in the joint, which intensifies with movement of the lower jaw, can radiate to the back of the head, ear, tongue, temple; - if treatment is not timely, the mouth opening is limited by 3-5 mm; - hyperemia and swelling of soft tissues in the ear area; - pain in the articular head upon palpation. | - treatment is carried out jointly with a rheumatologist; - antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed; — sanitation of the oral cavity; — bite alignment is performed using various methods. |
Development factors
In infectious arthritis, pathogens affect the joint in several ways:
- contact (for otitis, osteomyelitis, furunculosis of the external organs of hearing, etc.);
- direct (infection enters the joint due to puncture of the TMJ, fracture of the movable jaw, injury, etc.);
- hematogenous (for sore throat, tuberculosis, measles, diphtheria and other infectious diseases).
The reactive form of arthritis is observed with chlamydia, rubella, viral hepatitis and other infections. Rheumatoid arthritis can spread to other joints. An acute traumatic form of pathology can develop due to mechanical damage to the joints.
Pathology of the temporomandibular joint
Other symptoms may indicate the presence of TMJ pathology:
— pain in the shoulders (shoulder blades) and back due to increased muscle tension (spasm) (so-called myofascial pain syndrome);
- dizziness, disorientation, sometimes confusion;
- increased sensitivity to light (photophobia);
- ringing in the ears.
Pathology of the temporomandibular joint is often accompanied by a depressive state. This results in poor sleep and inability to get a good night's sleep. Sometimes constant pain in the TMJ area contributes to this. In some cases, pain only makes depression worse.
Prognosis and prevention
Due to the seriousness of the pathology, it is recommended to immediately visit the clinic at the first problems and symptoms indicating the presence of negative changes in the structure of the jaw. Proper treatment can prevent the development of bone ankylosis, which can only be eliminated through surgery. Preventive measures recommended by experts include compliance with standard hygiene procedures, periodic sanitation of the oral cavity and timely treatment of infectious diseases.
Treatment of temporomandibular joint arthritis with traditional medicine
If it is impossible to get an appointment with a doctor or the initial stage of the disease, traditional medicine recommends applying compresses and rubbing externally.
- Mix the beaten egg yolk with a teaspoon of turpentine and a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar. Rub the mixture into the sore joint.
- Squeeze the juice of grated black radish through cheesecloth, mix it with ¾ tbsp. honey, 1 tbsp. l. salt and 100 g of vodka. Rub the resulting mixture into the sore joint, then wrap it in something warm.
Traditional healers also have remedies for internal use in the treatment of TMJ arthritis.
- Displace 2 tbsp. buckthorn bark with 2 tsp. fennel fruits, 2 tsp. dandelion roots and 2 tsp. mint leaves. Pour the resulting mixture into 0.5 liters of water and simmer over low heat for 15 minutes. Take 2 tbsp before meals once a day.
- Pour 1 cup of boiling water over lingonberry leaves (20 g) and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Drink 1 tbsp decoction. l. 4 times a day.
Before using folk remedies in the treatment of TMJ arthritis, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
What are the causes of arthritis of the jaw?
Nowadays, this disease rarely occurs due to bacterial or viral exposure. However, in not so distant times, when oral hygiene products were not as high quality as they are now, this happened often. Nowadays, arthritis of the jaw more often occurs as a result of injury to the jaw joint. This also often happens due to inflammation of the organs adjacent to the jaw joints. In particular, diseases such as osteitis, otitis and phlegmon can cause jaw arthritis. It is extremely rare that it occurs due to blood diseases.
Diagnostic measures
Why does the upper jaw hurt?
Who treats temporomandibular joint arthritis? The problem requires consultation with specialists of several profiles: dentist, phthisiatrician, rheumatologist, otolaryngologist, traumatologist, infectious disease specialist.
To determine the extent of damage to the joint and the characteristics of the course of the disease, the patient is prescribed an x-ray. The method is suitable for identifying dystrophic changes in bone structures, but does not visualize soft tissues.
X-ray examination is complemented by CT, which differentiates different areas of affected soft tissue. The procedure is advisable only with high resolution capabilities of the device.
Ultrasound helps detect fluid in the joint field. The only disadvantage of the study is the impossibility of establishing the exact cause of the problem and a detailed study of individual fragments of soft tissue.
An accurate method for determining the disease is MRI diagnostics. The scan reveals the extent of the problem, the presence of synovial fluid in the joint and other important points. The only drawback of the procedure is the price and duration.
It is important to differentiate arthritis from other problems with similar symptoms: inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, arthropathy, acute otitis media. For this purpose, patients are prescribed PCR analysis and ELISA diagnostics.
No ads 2
Physiotherapeutic methods
In the treatment of arthritis of the maxillofacial joint, various physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect. But they should be used only after acute periods have been eliminated.
Physiotherapeutic methods from the table below are usually used.
| View | Description |
| Massage | It has a positive effect on microcirculation processes; it also activates blood flow abilities. Due to this procedure, there is an acceleration of the flow of nutrients and vitamins into the cartilage tissue, and the properties of its plasticity and mobility are restored. |
| Using Ultrasound | Ultrasound relieves spasms and prevents congestion. All this leads to the elimination of swelling and inflammation. |
| Laser exposure | Treatment using laser radiation helps eliminate inflammatory processes. During therapeutic therapy, joint mobility is restored, and active removal of calcium salt deposits is observed. It also eliminates swelling and cramps. |
| Mud applications | They increase lymph circulation and have a positive effect on trophism. When using them, the patient experiences restoration of the jaw in a fairly short time. |
Features of the disease
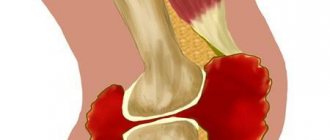
Arthritis of the jaw joint most often manifests itself unilaterally and occurs in people prone to inflammation of the articular apparatus. In the initial stages of development, the problem manifests itself as inflammation of the joint capsule and the soft tissues that surround it. As the pathology develops, the inflammatory process spreads to cartilaginous tissue, provoking degenerative changes in them. Severe forms of arthritis occur with damage to muscle tissue and ankylosis.
When arthritis of the jaw develops, bone destruction occurs
Causes of pathology
Due to a number of negative factors, the jaw structures cease to function normally. Because of this, a person experiences difficulty chewing food and speaking.
The causes of the pathological condition include:
- mechanical damage to the jaw when opening the mouth;
- severe infectious diseases (mumps, otitis media);
- illiterate treatment of bacterial and viral pathologies;
- hypothermia;
- osteomyelitis;
- chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- autoimmune diseases – lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- carious teeth in the oral cavity.
You should know! Among the main causes of jaw arthritis are the penetration of an infectious agent into the joint tissue.
Manifestation of jaw arthritis
In this case, the disease causes a feeling of pressure on the jaw joint or both joints. Later it becomes impossible to fully open the mouth. As the disease further develops, the patient's body temperature can rise to 39 degrees. Often at this stage even intoxication occurs.
The affected joint or both joints become very painful and swollen. The mucous membrane around the joints becomes inflamed. Then the pain intensifies and begins to radiate to the ears and temples. Bursts of pain are felt even when walking or tilting the head.
Classification
Depending on the source that provokes the development of arthritis of the temporofacial joint, the pathological process is divided into the following types:
- traumatic. Causes include severe blows or bruises to the joint, and x-rays may not immediately reveal the presence of the disease. Constant grinding of teeth and malocclusion provokes the development of an inflammatory process;
- infectious. This form is provoked by pathogens that spread through the bloodstream. Bacteria can enter the body due to various infectious diseases - acute respiratory infections, influenza, otitis media, purulent mumps, tonsillitis, carious lesions;
- autoimmune. Arthritis of this type develops as a result of gout, lupus erythematosus, and rheumatism. With a long course of the pathological process in this form, the body produces specific protective immune cells, which gradually, together with the pathological formations, begin to gradually destroy healthy tissue, including joints.
Photo: Before and after
Arthritis of the maxillofacial joint is a dangerous disease. It is important to determine its presence at an early stage, this will help prevent serious complications and pathologies. To do this, you need to study all its symptoms and features, which will help identify the presence of pathology.