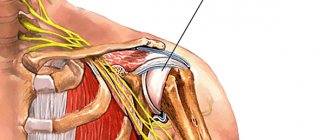
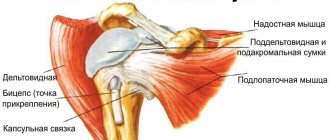
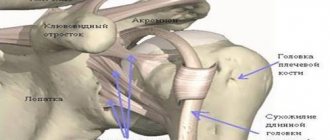
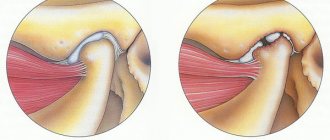
The human shoulder anatomically consists of two joints - the first, acromioclavicular, connects the clavicle and scapula, the second, scapulothoracic, connects the humerus and scapula. Quite often, many of us have to deal with specific pain in the shoulder joint, since it is one of the most mobile. The cause of such pain can be an inflammatory disease - arthritis of the shoulder joint, which can affect both joints or each of them separately.
ICD-10 code: (M13.9) - Arthritis, unspecified.
Types of Shoulder Arthritis
This disease, depending on the source of occurrence and symptoms, is divided into three types:
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the shoulder (ICD-10 code: M05.8, 06.0). The cause can be the slightest infection that could enter the body as a complication of another disease, such as flu or tonsillitis. Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by symmetry. This means that if the joints of one shoulder are affected, the other will be affected as well. It can occur in anyone, regardless of age.
- Osteoarthritis of the shoulder (ICD-10 code: M19.0, M19.1, M19.2). A disease that develops mainly in people over 50 years of age as a result of wear and tear of the joint tissue. It can also occur at a younger age with neglect of the joints.
- Post-traumatic arthritis of the shoulder (ICD-10 code: M84.1). The most common case of arthritis is the shoulder joint. Occurs as a result of injuries, cracks in the articular cartilage or damage to the tendons.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Inflammation of the shoulder joint occurs in three main forms: osteoarthritis, post-traumatic and rheumatoid arthritis. Each form has its own characteristic features, symptoms, locations and causes of development.
The main reasons for the development of the disease may be:
various injuries and infectious diseases;- allergic reactions;
- excessive loads;
- systematic hypothermia of the joint;
- aging of the tissues of the shoulder joint and their wear and tear as a result of age-related changes.
If in the early stages of the disease there is no adequate treatment for arthritis of the shoulder joint, its synovial membrane begins to become inflamed. During the course of degenerative transformation, the smooth surface of the bone is destroyed.
Symptoms of shoulder arthritis
The main symptom that makes people see a doctor is pain. Even if you manage to tolerate it at first, then gradually, depending on the degree of deformation of the joint, it will intensify more and more. The pain appears with movement, but in later stages it will begin to be felt at rest, perhaps even interfering with sleep. Treating the disease at such stages becomes more difficult.
In addition to pain, inflammation will be accompanied by an increase in temperature of both the affected area and the entire body. As a result, you may feel stiff, tired and weak. In this case, light gymnastics is recommended. Swelling may also form around the inflamed joint.
The joint is capable of pinching the nerves that control the movement of the arm, which is why coordination is likely to be impaired. For the same reason, problems with grasping movements may arise.
Shoulder arthrosis symptoms
Pain is the most common symptom accompanying arthrosis. The pain associated with osteoarthritis can range from long-lasting, mild soreness to periods of severe, sharp shoulder pain. Painful sensations always increase as the activity of the arm increases and progressively intensify. Depending on which joint has undergone arthrosis, pain may be felt in different parts of the shoulder. If the acromonio-clavicular joint is affected, the top or front of the shoulder will hurt. If the shoulder joint is affected, pain is felt in the center or behind the shoulder. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis experience pain in both areas, with increased discomfort experienced during changing weather conditions. Symptoms of arthrosis may also include limited movement, joint stiffness, and difficulty with movements such as lifting or extending the arm. Mechanical symptoms such as clicking or crunching noises may also be present. As the disease progresses, any movement of the shoulder causes pain and does not go away even at night, creating difficulty sleeping.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment, it is very important to make sure that the disease is present and to identify its type and nature.
During the medical examination, the following factors are determined:
- looking for signs of injury to ligaments, muscles or tendons;
- painful transfer of touches in the problem area;
- range of active and passive movements;
- amyotrophy;
- crunching in the joint when moving;
- pain during exercise.
X-rays indicate thinning of the joints, deformation of the bones, and the formation of osteophytes (bone growths) on them. If the pain was relieved with an intra-articular injection of local anesthetic, this is evidence of the correctness of the diagnosis.
Shoulder arthritis treatment
Conservative
There are a variety of conservative treatment options for shoulder arthritis. Many patients live with the symptoms of arthritis, taking medications to reduce inflammation and pain and taking cortisone shots to help reduce the unpleasant symptoms of the disease. Physical therapy exercises can also help maintain the ability to move your arm. When symptoms of shoulder arthritis become chronic and it becomes apparent that the disease is progressing, surgical correction becomes necessary.
Surgical
Treatment methods depend on each specific case. The cause of the disease, the intensity of the symptoms, the degree of damage to the shoulder joint and age are taken into account. In the early stages of the disease, shoulder arthritis can be controlled and treated using arthroscopic techniques. During the procedure, the surgeon trims the inflamed synovium and removes fragments of destroyed cartilage. In this case, arthroscopy will not cure arthrosis, but will help delay more serious treatment methods and relieve many unpleasant symptoms.
Find out more about treating shoulder arthrosis
Treatment of shoulder arthritis
If similar symptoms are detected, you should not take risks and consult a doctor for examination. Prescribed tests and x-rays will help determine the disease, its type and level of development. After this, it is necessary to prescribe appropriate therapy that can cure the body.
Drug treatment
Treatment with drugs is prescribed by a doctor after a full examination and an accurate determination of the type of arthritis. The course of drug treatment includes a whole series of medications prescribed for each individual:
- to combat pain in the periarticular area, analgesics are used;
- Steroid injections are prescribed to relieve inflammation and reduce pain;
- Non-steroidal drugs such as voltaren, movalis, ibuprofen, etc. may also be included;
- There are also modern means that can, in some situations, stop the process of joint deformation - chondoprotectors.
It is important to remember that any of the above remedies can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, otherwise they can even worsen the condition.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy has a good effect on blood circulation, improves metabolism in the body, relieves pain and reduces inflammation. It is prescribed depending on the type of arthritis. You should not undergo physiotherapeutic treatment unless absolutely necessary.
Surgery
It is necessary to treat arthritis of the shoulder joint with this method only in acute forms of the disease, only when all other methods are powerless. This procedure is called arthroplasty and involves the complete replacement of a damaged joint with an endoprosthesis. If the cartilage tissue is preserved and can be restored, only the humoral head is replaced.
In order not to wait until surgical intervention is needed, it is important to conduct a timely examination and undergo the necessary treatment in the early stages. You should not put it off, since arthritis of the shoulder joint is not a disease that can go away on its own.
Symptoms
Symptoms of arthritis of the shoulder joint can be very diverse, but all patients with this disease experience systematic chronic pain in the shoulder. In the early stages of the disease, pain may be barely present and cause virtually no discomfort to the patient. As arthritis progresses, the intensity of pain begins to increase, intensifying at night and causing insomnia.
In severe stages of shoulder joint deformity, pain can be unbearable and acute. They also tend to intensify when weather conditions change. When the scapulothoracic joint is damaged, the pain is radiated to the shoulder area, mainly to its back. As for acromioclavicular arthritis, in this case the pain will be localized in the front of the shoulder.
What can you do when you are sick?
In addition to taking medications, it is important to independently do everything possible for a speedy recovery:
- rest, do not strain damaged joints too much;
- do muscle exercises every morning;
- apply warming compresses;
- follow a diet;
- saturate your body with vitamins.
Exercises for arthritis of the shoulder joint play a really important role, because thanks to them the joint is developed and the feeling of stiffness is reduced. You should do exercises in moderation and not more than the prescribed norm, as overload can have a negative impact.
Watch your weight, create a diet and eat only healthy foods containing vitamins and minerals. Include dairy products, meat, jellied meat, and fruits in your diet. Do not overuse very fatty foods. Also consume sea fish and flaxseed oil, which contain omega-3 fatty acids.
Vladimir Konovalov. Shoulder arthritis
Shoulder arthritis and arthrosis: main causes of disease
Shoulder arthritis: has the nature of an acute disease that accompanies damage to the cartilaginous surface of the joint. Symptoms may go away without medical intervention, but can develop into arthrosis, a chronic form of the disease.
Osteoarthritis : This degenerative condition of the shoulder is usually the result of wear and tear because the smooth outer surface (articular cartilage) has been completely worn away. Osteoarthritis usually affects people over 50 years of age. As a rule, it also affects the acromonial-clavicular joint (although not always) and is quite often found in the glenohumeral bursa, damaging the ligaments of the joint (rotator cuff).
Rheumatoid arthritis : This arthritis can appear at any age and can affect any joint in the body. For example, in addition to affecting the shoulder, signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may appear in the knees and elbows. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune joint disease, an inflamed condition of the joint capsule.
Post-traumatic arthrosis : develops after injuries such as a fracture or dislocation of the shoulder. This type of arthrosis can also develop in the glenohumeral bursa after chronic rotator cuff disease (or damage).