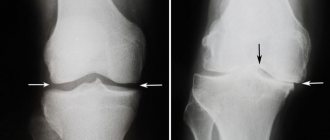
Many people experience pain in the knee joint. Unpleasant sensations can appear both after heavy physical work and after a long walk, and sometimes due to unstable weather. This condition causes a lot of inconvenience and interferes with daily work. There comes a time when a person is forced to undergo examination. Sometimes a regular x-ray is not enough, and an ultrasound cannot detect minor changes.
This diagnostic method does not provide a complete picture of the course of the pathology. Insufficient information on the obtained images is the reason for making an incorrect diagnosis. In such cases, doctors prescribe an MRI of the knee joint.
Description of the procedure
Tomography of the knee joint is a new direction in the field of radiology diagnostics. The study allows you to obtain a high-quality image of the examined part of the body or organ. MRI is a relatively new technique, but has already gained a good reputation during this time. Ten years ago, it was possible to undergo examination only in reputable clinics. Now this method is available even to residents of the provinces.
Scanning is used both for examining adults and very young children. The diagnostic principle boils down to the effect of a magnetic field on the human body. This process results in highly accurate images. Now developers of MRI machines have begun to change the flow of radiofrequency pulses. This made it possible to improve the quality of the images. Despite the high cost, diagnostics are in demand.
MRI with contrast
Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee is performed with additional contrast enhancement in cases where there is a suspicion of the presence of neoplasms or vascular pathologies. Thanks to contrast, the quality of images is improved and the diagnostic information is increased.
Contrast agents are injected into a vein in the elbow area immediately before the start of the diagnosis. This process feels similar to drawing venous blood. For most patients, this does not cause discomfort or side effects. The substance is independently eliminated from the body within one day.
Features of the study
Not all patients are aware that each tomograph provides for a specific range of examinations. An experienced radiologist always knows the pathological and normal anatomy, because this helps to avoid a number of diagnostic errors.
The examination of the knee joint is carried out under the influence of a powerful magnetic field. This is what allows you to obtain high-quality and most accurate images. It is simply impossible to create such conditions in open tomographs. MRI on such cases does not always pay off. Such devices have low power, which is why they are much inferior to closed devices. Patients are not always informed of such nuances. People often choose open devices because they inspire more confidence and do not cause fear.
Advantages of the MRI method
Diagnosis using MRI can identify many different joint pathologies. Doctors speak very highly of this research method for making a correct diagnosis.
Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging in examining the knee joint:
- high information content and accuracy due to the fact that it is possible to obtain high-quality images of all joint tissues;
- the list of contraindications is very limited, no specific preparation for the study is required;
- images obtained using MRI are highly clear and can be printed or transmitted electronically;
- high safety of the technique: MRI is allowed even for children, because the impact of the harmful field is minimal;
- MRI, in comparison with other diagnostic methods, provides the most complete, accurate and detailed picture of what is happening in the part of the body being examined and is the best tool for making a correct diagnosis regarding the knee joint;
- this is a completely non-invasive and non-surgical method, which eliminates the risk of infection, and also makes it possible to examine any part of the body;
- the duration of the study is not too long, results are obtained within half an hour;
- Diagnosis is absolutely painless.
MRI or ultrasound of the knee
In some cases, the doctor refers the patient not to an MRI, but to an ultrasound. Only a specialist can decide which is better in each specific situation - MRI or ultrasound of the knee. However, ultrasound diagnostics of the knee joint has a main drawback - insufficient accuracy. This makes it difficult to establish a correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound is often performed to examine internal organs. MRI is prescribed to detect bone pathology. Ultrasound diagnostics is non-invasive and safe, which cannot be said about MRI: a magnetic field is created during scanning, which is why this diagnostic method has contraindications. MRI of the knee is strictly prohibited for some patients.
The availability of such methods is an important point: everyone can pay for ultrasound, but not everyone can pay for MRI. From the above, a logical conclusion suggests itself: only a doctor can make a decision about undergoing an MRI or ultrasound of the knee, based on their medical history.
Indications for tomography
MRI of the knee is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- to examine the severity of injuries received;
- against the background of progressive degenerative changes in the joint;
- to determine the degree of bone damage when other diagnostic methods do not provide a complete picture;
- for chronic diseases of the knee joint;
- if the patient complains of pain in the knee area, identify the cause of the occurrence, which did not work out;
- due to decreased joint mobility;
- to determine the causes of blood and fluid accumulation in the joint;
- to determine tumor processes and metastases;
- before preparing for surgery;
- to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Contrasting
MRI, like X-ray computed tomography, is often performed with the introduction of contrast. Contrasting takes additional time, in addition, you need to find out if there are any contraindications, for example, allergic reactions to contrast agents. Even when the documents prepared by the attending physician indicate the absence of allergic reactions, the procedural personnel are required to verbally interview the patient. Although time is lost, modern medical centers provide the maximum level of health safety.
The introduction of a magnetic contrast agent prolongs the study by about 15-20 minutes. In preparation for an MRI, medical personnel evaluate how a person tolerates a contrast agent, whether rashes characteristic of allergies appear, and doctors also ask about the sensations that the patient experiences.
In some cases, MRI is almost always associated with contrast (distal arms and legs), so the time spent on contrast preparation should be added to the time period of the examination itself. But when a patient is being prepared for an abdominal examination or a brain procedure, contrast is usually not needed, and the diagnostician gets the job done faster.
What does the study show?
An MRI of the knee allows you to look at the knee structure in great detail. The image shows the condition of the tissues and bones. A simple method of comparing images of a healthy knee and a diseased one will allow the doctor to make a diagnosis without any problems.
In the images you can see:
- Condition of the bones. Tomography allows us to identify degenerative changes, consequences and severity of injuries.
- Cartilage. Doctors can assess the degree of wear and tear of the cartilage tissue;
- Tendons and ligaments. The knee consists of muscles, tendons, blood vessels, and a calyx. In the pictures you can see tears, stretching and decreased elasticity.
- Meniscus. The two menisci of the knee joint are often torn due to injury. Such injuries can only be seen on tomography.
Interpretation of MRI results
The results of diagnosing the knee joint using magnetic resonance imaging provide doctors with high-quality information for making a diagnosis. An X-ray examination can only see changes in bone tissue, while an MRI allows us to examine the condition of the soft tissues of the joint.
An MRI clearly shows the meniscus, muscles and ligaments of the knee joint, cartilage, as well as fluid in the tendon bursa. The images show blood vessels and nerves, visualize vascular pathologies and atherosclerotic narrowings. Using MRI, you can detect a tumor: its location, size, appearance and spread to other tissues.
We recommend
Anti-wrinkle facial massage: 10 effective techniques Read more
The result of tomography of the knee joint allows you to see it in a three-dimensional projection, as well as in sections along different planes, which allows doctors to thoroughly examine all tissues and structures for abnormalities. MRI images are provided in printed or electronic form with recording on digital media at the request of the patient.
MRI is an accurate tool for detecting arthrosis of the knee joint. Only in 10–15% of cases are inaccuracies possible, which are most often associated with low qualifications or inattention of the doctor deciphering the results. That is why the diagnosis must be made based on several diagnostic methods.
Most often, patients with a problem in the meniscus of the knee joint are referred for an MRI. In MRI images, the meniscus is visible as a dark stripe, and its injuries and structural changes are visible as a white background. Examination of this knee joint structure does not require the use of contrast. Most often, changes in the meniscus on MRI are visible in people with large body weight, as there is constant pressure and increased load on it.
Unfortunately, damage to the knee joint ligaments is less visualized on MRI than changes in the structure of the meniscus. This is due to the fact that tendons are made up of small parts, which makes them difficult to study.
Contraindications
It is not always possible to conduct an MRI of the knee joint due to the patient having certain indications, which include:
- metal implants present in the patient’s body;
- tattoos made using metal chips;
- early stages of pregnancy;
- patient obesity;
- mental illness;
- tremor of the limbs;
- serious condition of the patient.
There is a special list of restrictions on the use of a contrast amplifier:
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- diabetes;
- contrast agent intolerance.
Separately, I would like to dwell on some restrictions. Early pregnancy is the period when any negative influence from the outside can cause the birth of a baby with severe defects. Given this, doctors do not prescribe MRI to pregnant women. Over long periods of time, scanning is only permissible if there is a vital need for it.
In exceptional cases, MRI of the knee with contrast can be performed for nursing mothers. In this case, you will need to transfer the baby to artificial feeding for 2 days. This is done in order to avoid the negative effects of contrast on the body of a fragile child.
For seriously ill patients, MRI of the knee joint can be performed only after the condition has stabilized and the patient’s life is not in danger. In such cases, diagnosis of the joint can be carried out after the patient’s condition has normalized or there are vital indications. People with claustrophobia can be examined using an open-type apparatus, or resort to the use of sedatives as prescribed by a doctor.
The use of a contrast enhancer is unacceptable for patients with liver and kidney dysfunction. The chemical will not be able to naturally leave the body quickly enough, causing severe toxicity.
What does the equipment look like?
There are two main types of MRI – standard closed and open. A classic magnetic resonance imaging scanner looks like a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a circular magnet. The patient lies on a movable table that moves into a tube with a magnet.
Some MRI scanners, called short-circuit systems, are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround the person. Some newer MRI machines have a larger opening, which is more comfortable for larger patients or those with claustrophobia. Other MRI machines are open only on the sides (open MRI). Open magnetic tomographs are especially useful for examining larger patients or those with claustrophobia. Newer open MRI machines provide very high-quality images for many types of diseases. Older open MRI devices may not provide the same image quality. However, some diseases cannot be diagnosed using open MRI. The computer workstation that processes the image information is located in a separate room from the scanner.
Which specialist should I contact?
An oncologist, orthopedist or traumatologist can prescribe a referral for a scan. The doctor conducts a visual examination and inquires about complaints. A specialist may make such a decision for a number of reasons:
- significant knee injuries;
- decreased mobility;
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- degenerative changes.
Based on the referral received, each patient can count on undergoing a tomography free of charge. However, you usually have to wait a long time for your turn. Because of this, patients choose paid clinics. There is no need to provide referrals to private centers. All you need to do is make an appointment and come at the appointed time for the examination.
Examination in a modern clinic
When undergoing an MRI in our clinic, you can count on the high professionalism of our staff. The staff quickly resolves issues that arise during the study, reduces the duration of the procedure to a minimum without compromising quality.
As a result, MRI makes it possible to quickly identify injuries and acute illnesses and allows one to obtain valuable information in an urgent manner, for example, when transporting a patient by ambulance.
We employ experienced diagnosticians who take the most informative images. An official medical report is issued in digital and written form. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Preparing for an MRI of the knee
No preparation is required before undergoing an MRI. This is a huge advantage for many patients. The patient must follow the recommendations of specialists:
- Provide the radiologist with complete information about your health status. Women of childbearing age need to make sure that there is no pregnancy.
- Those patients who will undergo an MRI of the knee joint with contrast should insist on an allergy test. Clinics with a solid reputation usually do it for free.
- If an MRI is performed on a child, it is better to carry out the diagnosis under anesthesia - children cannot remain motionless for a long time.
- On the day of the examination, it is better not to use cosmetics, because... it causes image distortion.
- You need to bring the results of previous studies to the tomography.
- 6-8 hours before the start of the examination you need to refuse food and water. This is done to prevent nausea.
- Immediately before entering the office, you must remove any metal objects from your body, as well as jewelry. You will have to leave all personal belongings outside the office that could interfere with the scanner’s operation.
Procedure
Diagnosis of the knee joint is carried out in a special room where a tomograph is located. Scanning can be carried out either on closed devices or on open devices. The choice depends on the patient’s preferences and specialist recommendations.
An MRI of the knee joint is quite simple:
- The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, asking him about his health.
- Then the patient changes into hospital clothes and is escorted to the room with the tomograph.
- The medical staff suggests taking a horizontal position on a retractable table. The limbs are secured with straps. This is done to prevent involuntary movements.
- If the scan will be performed using contrast, the patient will be given the drug intravenously.
- At the final stage, the table moves into the tunnel, and the medical staff leaves the office. The scanning progress is monitored through a special window.
Communication with the patient is maintained via a microphone. In case of deterioration of health, the patient will be able to report this. Usually tomography does not cause any complications, because the examination is safe and painless.
Excessively suspicious patients may experience dizziness and nausea due to overexertion. It is better to report this condition to a radiologist. In case of emergency, the specialist can stop the study. Such cases are rare. To avoid such situations, it is better to take a sedative before entering the office.
How is an MRI of joints performed?
The patient lies face up on the retractable tomograph table; to ensure a static position, the body is fixed using bolsters and holding devices. If necessary, the limbs are given the desired position, which will determine the degree of dysfunction of the joint.
Headphones provide protection from the noise of the operating device, communication with the patient is maintained using an intercom, and a panic button is provided. During the procedure, medical personnel are positioned behind the partition. This measure allows you to avoid exposure to extraneous electromagnetic pulses on the tomograph.
MRI procedure: scanning on a closed tomograph
The table with the subject is rolled into the tunnel of the apparatus that generates the induction field. Scanning is carried out in the axial, sagittal and frontal planes.
The contrast procedure takes place in two stages. First, a series of native images are taken, then the study is suspended and the patient is injected with a gadolinium solution. They continue filming.
Intravenous injection is carried out using a catheter connected to an automatic device. Bolus enhancement allows contrast to be delivered at a constant rate. A solution of gadolinium salts penetrates the bloodstream and interstitial (intercellular) space, “staining” the tissue and visualizing changes in the structure of the formation being studied.
Getting the result
The scanning duration is from 30 to 40 minutes. During this time, the subject is stationary in the inside of the tomograph. Even minor movements of the limbs can cause severe distortion of images. You need to remember this.
As soon as the device stops working, the table leaves the scanner, the person is freed from the fastenings, and he can immediately leave the office. Meanwhile, the doctor begins to decipher the received images and prepare a report. This usually takes no more than an hour. In rare cases, a specialist will need a little more time.
The patient can wait for the conclusion at the medical center, or he can go home and go about his business. In this case, the results will be sent to him by email shortly. With the obtained images, you must contact the doctor who has written a referral for an MRI. The doctor will evaluate the results and prescribe the correct treatment.
Where can I get an MRI of the knee?
Knee pain affects quality of life. However, this is not a verdict yet. Modern examination methods make it possible to identify the cause of pain in the shortest possible time. Based on the conclusion received, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment that will help get rid of the disease. The choice of diagnostic method is the task of a specialist. Only a doctor can decide which is better: X-ray, MRI or ultrasound of the knee, because only a specialist is competent to make such appointments.
You can choose a clinic to undergo an MRI of the knee joint using the free service piter-mrt.ru. The site presents many medical clinics with ratings, available equipment and qualifications of specialists. You don’t have to spend a lot of time selecting a medical center, because a convenient search and filtering system based on the necessary parameters makes your search easier.
Another advantage of the portal is that everyone who signs up for an MRI through the site receives a discount on scanning the knee joint. If difficulties still arise during selection, you can call the operator. The specialist will find answers to your questions and will also help you make a preliminary appointment for a tomography. Remember that timely diagnosis is the key to good health in the future.
Decoding
The results of the tomography will be black and white images in three-dimensional format. They are deciphered by a radiologist. He carefully evaluates the anatomical features of the patient’s knee structure and notes all the anomalies found in his conclusion. The conclusion, together with MRI images printed on film or recorded on electronic media, is handed over to the person being examined. The decryption procedure takes on average 40-60 minutes. In complex and controversial cases, doctors are sometimes forced to resort to a second independent opinion. This is a situation where the patient’s images are additionally assessed by a radiologist of the highest category and expresses his independent opinion on the accuracy of the diagnosis. With the tomography data, the subject must make an appointment with his or her attending physician. It is he who, summing up all the data on the medical history, the results of analyzes and tests, makes the final diagnosis and proposes a treatment strategy.
An example of MRI decoding of the knee joint
On a series of MRIs of the right knee joint, the relationships in the joint are not disturbed.
In the area of the upper inversion and lateral pockets, an accumulation of effusion is determined in the joint cavity. The synovial membrane is hypertrophied. In the anterolateral sections, at the pre- and infrapatellar level, areas of edema of the subcutaneous fatty tissue are determined.
The patella is in the middle position. MR signal from the subchondral parts of the patella without pathological changes. The ligaments holding the patella are not changed. Hoff's fat body has a homogeneous structure. The patellar ligament has a homogeneous structure, the area of the tibial tuberosity is not changed.
The cartilaginous covering of the condyles of the femur and tibia is unevenly thinned, the articular cavity is moderately narrowed, and is more pronounced in the medial part of the joint. The bone contour of the condyles of the femur and tibia is not deformed. In the postero-central internal sections of the medial condyle of the tibia, a local area of cyst-like restructuring is identified subcortically, without pathological changes from adjacent trabecular sections. Small antero- and posterolateral marginal bone growths of the condyles of the femur and tibia are identified.
The anterior cruciate ligament is defined throughout its entire length, its structure is heterogeneous, the contour of the ligament is clear, and its overall integrity is preserved. Extrusion of the medial meniscus and an increase in the intensity of the MR signal from the posterior horn of the meniscus, with signs of damage, are determined. The intensity of the MR signal from the lateral meniscus, posterior cruciate and collateral ligaments is not changed, their integrity is not compromised.
In the posteromedial thigh, in the area of the intermuscular space of the medial head of the gastrocnemius and semimembranosus muscles, a cystic expansion of the mucous bursa is noted.
Conclusion:
MRI signs of grade 2 deforming arthrosis of the right knee joint; damage to the posterior horn of the medial meniscus; degenerative changes of the anterior cruciate ligament. Synovitis. Baker's cyst.