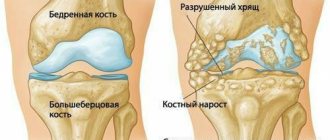
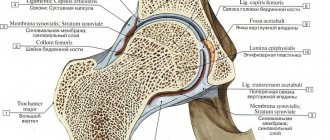
The hip joint is formed by the upper part of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. This powerful joint bears the main load during any physical activity, ensuring normal functioning. Playing a key role in human motor activity, the hip joint is especially susceptible to damage and disease.
The most accurate and informative instrumental method for diagnosing the condition of the pelvis is MRI. The action is based on the passage of electromagnetic radiation and radio frequency waves through the human body. As a result of interaction with protons contained in the tissues of the area under study, a signal is formed that is picked up by the sensors of the MRI machine. The information obtained is converted into layer-by-layer images, which make it possible to construct a three-dimensional 3D model of the articular parts of the pelvis.
The study provides information about the slightest changes occurring in the joint tissues, allowing for an accurate diagnosis of existing diseases. The photographs can be used to examine and evaluate in detail the condition of the cartilaginous covering of the articular surfaces, the joint capsule, ligaments and tendons, and the muscular system. The method identifies inflammatory, degenerative, and oncological processes and allows us to clarify the diagnosis in more than 95% of cases.
In what cases is ultrasound of the hip joints prescribed?
Diagnostics can be prescribed by a traumatologist, surgeon or orthopedist. Typically, ultrasound examination of the hip joints is indicated in the following cases:
- Limited mobility, difficulty getting out of bed after sleep;
- The appearance of stiffness when moving;
- Painful sensations;
- Suspicion of a dislocation or dislocations in the past;
- Change in skin color in the hip joint area;
- The appearance of a distinct crunch in the joint during physical activity;
- Frequent muscle spasms in the buttocks and thighs;
- Different lengths of the lower limbs.
Indications for MRI of the hip joint
The study is carried out after performing simpler and more accessible methods - ultrasound, x-ray. MRI of the hip allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis in complex cases, determine the cause of symptoms that cannot be treated, and differentiate diseases. In addition, MRI is actively used in surgery before surgery. Information about the internal location of anatomical structures and painful areas is necessary to determine the stages and plan of the operation.
As a rule, an MRI of the hip joint is prescribed if the patient has the following pathologies:
- prolonged pain in the pelvic area, the cause of which is difficult to establish using other research methods;
- acute pain that occurs when moving;
- injuries - hip dislocation, bruise, fracture, rupture of muscles, ligaments;
- swelling of the periarticular area, stiffness of movement, crunching, decreased mobility;
- congenital diseases - dysplasia, dislocation of the hip joint, skeletal development abnormalities;
- suspicion of an oncological process;
- control of the course of chronic rheumatic, degenerative, inflammatory diseases.
If you experience unusual, painful symptoms in the pelvic area, you should consult a doctor or get yourself diagnosed. MRI of the hip joint allows you to detect diseases at the beginning of their development, which determines the success of treatment.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound of the hip joints
Today, there are many different diagnostic procedures, such as x-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Of course, these studies provide more detailed information, but such methods have a higher cost. Ultrasound examination, in turn, is cheaper, completely safe and allows you to identify pathological processes even in the early stages. In addition, the diagnostic result can be obtained within 10 minutes after the end of the examination.
Let's look at a few more benefits:
- The procedure is non-invasive;
- It is painless;
- It is also possible to study the condition of the blood vessels in the area under study.
How is the procedure carried out?
The patient removes clothing below the waist (except underwear) and lies down on the couch. Diagnosis is made using a sensor, with which the doctor reads information about the condition and density of bone, cartilage and soft structures. To obtain a complete clinical picture, the doctor uses several access options.
Anterior approach
The ultrasound doctor asks the person to lie on his back, and a small cushion is placed under the femoral surface. This position helps to better examine the structural elements of the hip joint. By observing the image on the screen, the specialist receives information about the condition of the ilium, femoral head, ligaments, muscles and lymph nodes of the groin.
Rear access
For such an examination, the specialist asks the patient to lie on his side and bend his knees slightly closer to his chest. During the study, it is possible to identify the functioning and characteristics of the sciatic nerve, obtain information about the surface of hyaline cartilage, and examine the superficial and internal structure of muscle fibers in the gluteal region.
Medial access
The person lies on his back, bends the lower limb and moves it to the side. This position allows for a detailed examination of the pelvic flexor muscles and articular ligaments if a pathological process is suspected.
Lateral access
The person lies on his side, and the specialist asks him to rotate his hip inward. In this position, the protruding elements of the tibia and the trochanteric bursa are clearly visualized.
On average, this manipulation lasts no more than 30-40 minutes. The patient is given the results of the examination; in some cases, additional images are attached so that the doctor can independently assess the clinical picture.
MRI of the hip joint with contrast
To diagnose some groups of diseases, a more detailed image of pathological structures is necessary. In such cases, according to the doctor’s decision, during the examination, a contrast agent is injected into the patient’s vein, the main active component of which is the metal gadolinium. Possessing paramagnetic properties, the drugs enhance the signal from the tissues being studied, resulting in an image with a higher resolution.
Contrast enhancement is performed if an oncological process, inflammatory diseases, abscess, or vascular pathologies of the pelvic area are suspected.
Decoding the results
An orthopedist, surgeon, or orthopedic surgeon can interpret the results. The research protocol usually contains the following information:
- the presence of pathological processes, a detailed description of the deviation.
- congenital or acquired changes inside the joint;
- condition of ligaments and nerve bundles;
- increase in the thickness of the joint capsule;
- functioning of adjacent muscles;
- features of cartilaginous structures;
- the amount of synovial fluid inside the joint.
- the presence of neoplasms, if any, their shape, structure, size and individual characteristics;
- information about the ilium, labrum and femoral head;
- metastasis of nearby tissues;
- presence of hematomas.
Please note that the result of an ultrasound examination is not a basis for making a diagnosis. If any inconsistencies or pronounced pathological processes are detected, it is additionally necessary to perform a computed tomography scan and pass various tests for laboratory research. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary (for example, if the doctor suspects a malignancy). The final diagnosis and necessary treatment are prescribed only after additional studies.
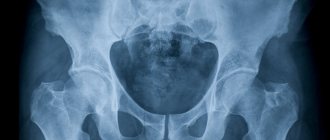
Normal hip joints according to ultrasound
If the patient does not have various pathological processes, the protocol indicates that the hip joints have a clear and smooth surface, without deformations and bone growths. The joint capsules should have folds and branches; their structure is normally hypoechoic.
The following information is also usually indicated:
Right joint:
The bony part of the acetabulum is normal. No major changes. Rectangular bony protrusion. The overlap of the cartilaginous part of the roof of the femoral head is sufficient. The limbus is projected laterally from the femoral head, is presented, and has a normal angle of inclination. The head of the femur in the acetabulum is located correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is less than 60 degrees. Angle b is greater than 55 degrees.
Left joint:
the roof of the acetabulum is moderately flattened, without structural changes. The femoral head is centered correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is more than 60 degrees. Angle b is more than 55 degrees. The angular parameters of the joint are not changed. When performing functional tests, the joint is stable.
Please note that these indicators may vary depending on age - deviations from them do not always indicate the presence of diseases or some problems.
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint with osteopathic methods
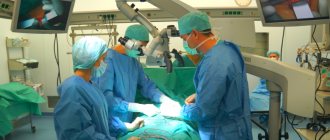
There are several methods for treating arthrosis of the joint, including the most drastic - surgery. But the most effective methods are osteopathic methods. Especially if they are correctly combined with physiotherapy and physical therapy.
In osteopathy, treatment of arthrosis disorders of the hip joints is carried out in several stages:
- relief of pain. Effective complex treatment (using physiotherapy and exercise therapy) will be impossible if the patient experiences pain. Manual osteopathic techniques make it possible to achieve complete and long-term pain relief in the hip joint area, even in particularly severe cases - with pinched nerve processes;
- treatment of the underlying causes of the disease. With arthrosis of the pelvic joint, the main cause is disorders of the circulatory and metabolic systems. The influence of an osteopath is aimed at normalizing blood flow not only in the damaged area, but throughout the entire body. Depending on the stage of the disease and the condition of the joint, restoring blood circulation may require a different amount of time (sessions). During treatment, a specialist may advise limiting the mobility of the joint, reducing the load on it, recommending movement with a crutch or cane;
- restoration of the body. Proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. The diet should be adjusted by a specialist so that it includes a set of all necessary microelements, vitamins and nutrients in their natural form (that is, in food, and not in the form of medicines). Nutrition must necessarily contain chondroprotective substances - compounds that help restore cartilage tissue and provide it with the necessary elements for recovery. The natural chondroprotector is the bone cerebellum, cartilage, gelatin, so during the treatment period it is recommended to include jellied meat, jellies, and jelly in the diet;
- treatment of complications. In many cases, arthrosis of the hip joint is accompanied by various complications - inflammatory processes, injuries and muscle tears, diseases of internal organs. After the body receives a powerful impulse and all the necessary components for healing the joint, the osteopath will help ensure that the restoration work also affects other damaged organs.
Often, when treating arthrosis (and immediately after it), a specialist prescribes exercise therapy (physical therapy) for the patient. This approach is explained by the natural desire to strengthen the body as a whole, but without the danger of injuring or overloading the pelvic area. Strengthening the muscles helps them hold the femoral neck more tightly in the joint capsule, which means the likelihood of dislocation and other injury is reduced.
How to protect your joints
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a disease that is quite difficult to cure in its later stages. Traditional medicine practically does not diagnose it in the early stages. But preventive methods can reduce the risk of the disease or delay the age of onset of its first symptoms:
- physical exercise. You shouldn’t give them up at all, but periods of work and activity should be alternated with periods of rest. To fully restore the body, it needs relaxation of the muscles around the joints, which improves blood flow and promotes the supply of oxygen and nutrients;
- weight control. It is excess weight that often causes strain on joints, which affects their wear and increases the risk of injury. In case of problems, a specialist will help you adjust your weight. Usually, introducing fiber into the diet in the form of vegetables and fruits, cereals, and cereals is quite effective. Intake of fatty and sweet foods should be reduced as much as possible, but not to the detriment of your own body;
- nutrition. With food, your body should receive all the building elements and nutrients it needs. Only in this case will tissue restoration proceed normally. For the health of cartilage, products that contain a concentrated decoction of cartilage tissue are important - jellied meat, brawn, rich fish or meat broth, etc. It is also necessary to include foods to maintain bone health in the diet - milk, eggs, nuts;
- movement. Just as excess physical activity and hard work lead to joint diseases, lack of movement can also cause them. Loads must be strictly standardized. Sports such as running, walking, and swimming are especially useful.
Prevention is always more effective than treatment for arthrosis, so try to lead a healthy lifestyle and you will avoid this disease. Of course, we should not forget about another important aspect - regular examinations by a specialist.
What pathologies can be identified
Most often, during an ultrasound examination of the hip joints, the following diseases are detected:
- Arthrosis (it develops as a result of congenital dislocation of the hip, a disturbance in the circulatory system, or as a result of a fracture of the femoral neck);
- Arthritis (may occur due to infection of joint joints by pathogens);
- Synovitis, which is characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation inside the joint;
- Necrosis of bone tissue (can occur due to frequent fractures, dislocations, bruises);
- Tears and spasms of muscle fibers;
- Swelling of the joint.
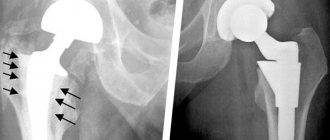
The hip joints are most susceptible to various pathological processes. Diseases can be either congenital or acquired. If you visit a medical facility as soon as the first symptoms appear, you can hope for a favorable outcome and complete recovery. Otherwise, your doctor may recommend surgery.
Treatment method
In order to properly structure the treatment process, professionals need to develop an integrated approach to solving the problem. First of all, pain and inflammation are eliminated, for which a certain group of drugs is often used. In addition, physiotherapy is used. Patients who suffer from pain in the hip joint are prescribed the correct diet and physical activity. In restoring motor ability and eliminating pain of the mobile joint, the correct behavior of the patient himself plays a very important role, from whom he is required to comply with the doctor’s instructions and the correct treatment regimen.
By contacting our clinic, you can receive qualified assistance. The use of high-quality modern treatment methods allows our specialists to reduce pain and inflammation. We work with patients using an individual approach - for us, each case is unique and requires the most careful consideration. Since the hip joint is a complex mechanism in the human body, we pay special attention to diagnosing its condition and the causes of pain. With us you can always count on receiving qualified treatment, as well as affordable prices and special conditions for different groups of patients.