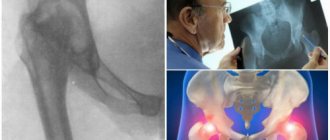
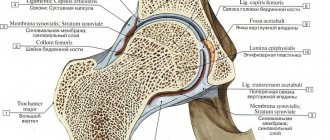
X-rays of the hip joint are now useful not only in older patients in whom osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis of the joint is suspected, but also in younger patients.
Young people often come to the radiologist's office without osteoarthritis, but (unless there is a clearly defined problem) they are examined for femoroacetabular impingement or hip dysplasia.
A simple x-ray can evaluate both a normal and a dysplastic hip joint, or those with signs of damage.
In addition, pathological processes such as osteoarthritis, infections or tumors may be detected.
What is x-ray diagnostics
X-ray diagnostics is based on special X-rays that the device emits. Soft tissues allow them to pass through, while hard tissues absorb them, which is why in the picture the former are painted dark, and the latter light. Bone tissue is most clearly visible in the photographs, so the method is used to examine the condition of bones and joints. The results are provided on paper or digital media and saved on the computer’s hard drive.
Today you can get an X-ray image on digital media
How is it carried out?
X-rays are performed without preparation. The patient is positioned on a special table. The groin area is protected from irradiation with a lead apron. For children, protection is applied to the eye and thyroid area, while in infants, only the area being examined, such as a limb, is left exposed.
The doctor takes a picture in one or several projections. To make them clear, you need to remain motionless. The specialist independently determines the optimal projection depending on the segment being studied: straight, lateral or a combined option.
If the patient is overweight, the image may not be clear
Preparation
- If you need to have an x-ray of your hip joint, no special preparation is usually required, but it is still worth paying attention to certain points.
- Since the area of interest is quite close to the intestine, its contents may affect image quality. In particular, this concerns the process of gas formation. To remove intestinal contents, it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the evening before the test and the next morning. The patient can also take any laxative before the procedure.
- If radiography is performed with a contrast agent, it is necessary to conduct a test in advance to determine an allergic reaction. The procedure is carried out if the result is negative.
Is it dangerous
X-rays are often prescribed not only at the diagnostic stage, but also during the treatment of arthrosis of the knee, hip or other joint. Many fear that radiation will harm the body and trigger irreversible processes in it, for example, the degeneration of cells into malignant ones, and weaken the already weak immunity of an elderly person. Is it possible to take x-rays often?
The harm from radiation on modern devices is minimal if all safety rules are followed. The dose of radiation is comparable to that which we receive daily from television or while flying on an airplane. Therefore, you should not refuse the examination if the doctor insists. The main thing is to take precautions.
How dangerous is x-ray and who is strictly contraindicated to undergo this examination? The answers are in the video below:
Restrictions
X-rays are not performed on children under three months of age, who are prescribed an ultrasound if necessary. Doctors also do not recommend excessively irradiating infants in the pelvic area, as this can lead to infertility, blood disease, and a tumor process in the future. Children are examined strictly according to indications and in a standardized manner, no more than once every six months.
X-rays are not performed on pregnant women to avoid negative effects on the fetus. It is also contraindicated in people with metal prosthetics or implants in the area being examined and in people with schizophrenia (and other mental disorders) who are unable to remain still. Other people, including older people, can undergo the examination.
Contraindications
Digital X-ray is a method with a safe level of radiation exposure, which we receive from radiation from household appliances and mobile technologies. However, x-rays of the pelvic area are contraindicated:
- Pregnant women (at any stage) – the normal development of the fetus may be disrupted.
- Children under the age of 15, when active growth and skeletal formation are underway.
- When referring women of childbearing age for an X-ray examination, the attending physician is obliged to clarify the time of the last menstruation before prescribing the examination. All studies in the abdomen and pelvis must be carried out in the first ten days of the menstrual cycle.
An exception may be made at the discretion of the physician for emergency reasons. Also, the advisability of x-rays may be questionable for people with significant excess weight, which can reduce the information content of the procedure.
What does an ankle x-ray show?
The ankle suffers very often, since the feet take on the maximum load when walking upright. X-rays of this joint are usually taken in three projections, with or without load: lateral, oblique, and x-ray of the heel bone. Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis and assess the condition of soft tissues, CT or MRI are additionally prescribed.
X-ray allows you to diagnose:
- injuries;
- ankle arthrosis;
- arthritis, synovitis, gout;
- congenital anatomical disorders;
- osteophytes – heel spurs;
- flat feet;
- metabolic disorders, etc.
X-ray image shows the condition of the foot bones well
Interpretation of the radiograph
Patients at the NEARMEDIC clinic receive an x-ray 20 minutes after the examination. The x-ray technician prepares a protocol that describes all the abnormalities he finds, but the final analysis and diagnosis remain with the specialized doctor.
When analyzing the finished image, the following indicators are important:
- Wiberg angles (about 30 is normal), neck-shaft angle (115-140 is normal), inclination of the entrance to the acetabulum (indicator 31-42 is acceptable);
- the width of the symphysis and the changes that have occurred in it;
- width of the sacroiliac joint;
- debris rotation;
- width of the joint space in the hip joint;
- deformation of the femoral heads;
- number and location of fragments during a fracture;
- displacement of bones, fragments along the length/width;
After identifying an injury or pathology, the doctor decides on the need for additional diagnostics; in this case, a computed tomography scan is prescribed for a more detailed study and clarification of the diagnosis. The advantage of CT over pelvic x-ray is that it monitors small tears and changes (up to 5 mm). CT results are useful for surgical planning.
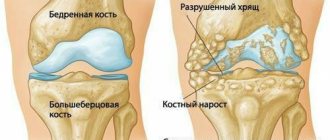
How informative is a knee x-ray?
In the case of the knee, this examination is prescribed for any damage and injury, pain at rest and movement. Other indications include swelling, changes in skin color, deformities and limited mobility, symptoms that often accompany arthrosis.
X-rays of the knee have the greatest diagnostic value for injuries - bone cracks, fractures, dislocations and subluxations of joints. He diagnoses condyle fractures, meniscus and patella injuries, and hemorrhages in the knee joint. The method allows you to examine the joint and adjacent areas - fibula, femur and tibia. With its help, you can identify arthrosis, arthritis and osteoporosis, and then continue the examination with other methods.
MRI is often used along with X-rays to diagnose the knee joint.
Comparison with MRI and ultrasound
Sometimes ultrasound is used to diagnose joint pathology. The studies are diametrically opposed, since radiography helps to identify bone pathologies, while ultrasound helps to identify soft tissue diseases.
X-rays look at the anatomical structure, while ultrasound reveals functional deficits, such as insufficient or excessive amounts of intra-articular fluid. Often, for the most complete picture of the disease, a joint appointment of studies is required.
Tomographic examination is a relatively new method, compared to conventional x-rays, which is much more informative. The main advantage of X-rays compared to MRI is its general availability, since the machines are present in every hospital, and its low cost, since MRI is much more expensive.
MRI
In what cases is a hip x-ray prescribed?
The hip joints are one of the most complex joints in the body. The patient is sent for an x-ray if he experiences discomfort when moving and has limited mobility. If the joint is painful or deformed, as well as after any injury.
Using radiography, you can identify the following diseases and pathologies:
- congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip joint;
- acquired dislocations and fractures (relevant for older people suffering from coxarthrosis);
- primary tumors, metastases of cancer of another location;
- osteoporosis, necrosis of the head of the femur;
- inflammation in the joint;
- arthrosis and other pathological changes.
Unlike other areas, before an x-ray of the hip joint, the patient may be advised to do a cleansing enema or take a laxative the day before. This is done to ensure that there are no shadows in the image due to a full intestine.
X-ray of the hip joint allows diagnosing coxarthrosis
Features of x-ray of the upper extremities
X-rays of the elbow are also prescribed after injuries - severe bruises, dislocations, fractures - or if various pathologies are suspected. It allows you to obtain information about the joint space and its narrowing, about the condition of the ends of the bones of the humerus and forearm. The specialist also receives data about the areas adjacent to the elbow joint, which facilitates diagnosis. After all, the cause of pain is not always arthrosis of the elbow, arthritis or bursitis: it often has a spreading nature and a completely different source.
Shoulder pain often occurs against the background of neurological and vascular diseases, but the cause may also be shoulder arthrosis, as well as systemic inflammatory diseases of the shoulder joint. X-rays are mainly prescribed if a dislocation or fracture is suspected. The image also shows adjacent formations - the collarbones and shoulder blades. It is also informative for arthrosis and arthritis, necrosis of the humeral heads, tendonitis and other diseases.
Osteoarthritis of the upper extremities is often discovered by chance on an X-ray
X-ray is a simple, quick, painless diagnostic method that provides information about the condition of bones and joints. When arthrosis is detected, additional instrumental methods are often prescribed to examine the deep structures of soft tissues and study the condition of the cartilage. However, MRI and CT scans are expensive and not always necessary. Therefore, if the orthopedist insists on an x-ray, you should not refuse.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
We draw your attention to the schedule of technological breaks in the CT and X-ray rooms.
If you are looking for where you can quickly, efficiently and effectively do an X-ray examination of the pelvis, come to a multidisciplinary medical center in St. Petersburg. The center operates an emergency room equipped with a modern Italian X-ray diagnostic device Clinomat, which allows for complete diagnostics in the shortest possible time, studying images in various processing modes¸ which is especially important, given the specifics of the emergency room. Experienced and sensitive doctors at the Medical Center will carefully examine you, take an x-ray of the hip joint, identify the disease,, if necessary, refer you to a specialist and prescribe a course of treatment and recovery.
A person is designed in such a way that the hip joint is involved in the process of walking and sitting and plays an important role in the implementation of these functions. Injuries, pathologies and diseases of this joint can lead to serious consequences and even disability. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose the disease in the early stages and begin treatment in time. X-ray of the pelvis in this case will be the primary and most informative method of obtaining data on the condition of the upper thigh, ischium, pubic bone, and hard tissues of the pelvis.