| Name of service | Price | |
| R-graphy of the knee (one) joint in 3 projections (3 images) | 1600 | rub. |
| R-study of the knee (one) joint in 2 projections (2 pictures) | 1000 | rub. |
X-ray of the knee is one of the frequent examinations at the International Center for Health Protection. You can take an X-ray of the knee joint quickly and accurately; prices are indicated in the price list on the website. Patients of the medical center sign up for examination at a convenient time and day.
X-rays of the knee joint are usually used for traumatic injuries:
- dislocations and subluxations;
- cracks and fractures of bones;
- ligamentous injuries;
- hemorrhages in the joint;
- injuries of the meniscus, condyles, patella.
Indications for x-rays of the knee joint include diseases such as gonarthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, secondary lesions due to syphilis and tuberculosis, and knee tumors.
The patient is referred for radiography if the following complaints occur:
- suspected injuries and damage to the articular-ligamentous apparatus;
- swelling of the knee, pain at rest and with movement, redness and swelling of the skin;
- joint deformity;
- limitation of mobility.
The procedure is contraindicated for pregnant women and persons with metal implants in the examination area.
Preparing for the blood donation procedure
A number of tests are done on an empty stomach. For example, biochemical (glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, etc.) and serological tests (syphilis, hepatitis B), hormones (TSH, parathyroid hormone), etc. “Fasting” is when at least 8 hours pass between the last meal and taking blood (preferably at least 12 hours). Juice, tea, coffee, especially with sugar, are also food, so you will have to be patient. You can drink water.
Strictly on an empty stomach (after a 12-hour fast) you should donate blood to determine lipid profile parameters: cholesterol, HDL, LDL, triglycerides.
If you have to take a general blood test, your last meal should be no later than 1 hour before donating blood. Breakfast may consist of unsweetened tea, unsweetened porridge without butter and milk, and an apple.
It is advisable to exclude fatty, fried and alcohol from the diet 1 - 2 days before the examination. If there was a feast the day before, reschedule the laboratory test for 1-2 days. Avoid smoking an hour before blood collection.
The content of many blood tests is subject to daily fluctuations, so for some studies blood should be taken strictly at a certain time of day. So, blood tests for some hormones (TSH and parathyroid hormone), as well as for iron, are given only before 10 am.
When donating venous blood, it is necessary to exclude factors that influence the research results: physical stress (running, lifting weights), emotional arousal. Therefore, before the procedure you should rest for 10-15 minutes in the waiting room and calm down.
Blood is taken for analysis before starting to take medications (for example, antibacterial and chemotherapy) or no earlier than 10 to 14 days after their discontinuation. The exception is when they want to study the concentration of drugs in the blood (for example, valproic acid, anticonvulsants). If you are taking medications, be sure to tell your doctor about this.
Blood should not be donated after X-rays, rectal examinations, or physical therapy procedures.
During hormonal studies in women of reproductive age (from approximately 12 to 13 years of age and before the onset of menopause), the results are influenced by physiological factors associated with the stage of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, when preparing for examination for the hormones FSH, LH, prolactin, estriol, estradiol, progesterone, the phase of the cycle should be indicated. When conducting a test for sex hormones, strictly adhere to the recommendations of your doctor about the day of the menstrual cycle on which you need to donate blood.
When performing tests for the presence of infections, it should be taken into account that depending on the period of infection and the state of the immune system, any patient may have a negative result. But, nevertheless, a negative result does not completely exclude infection. In doubtful cases, re-analysis is recommended.
Different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement. To ensure that the assessment of your results is correct and the results are acceptable, do the tests in the same laboratory, at the same time. Comparison of such studies will be more correct.
Knee-joint
The knee joint is formed by the convex articular surfaces of the femur (1) and tibia (2). The articular ends of these bones are covered with strong and elastic cartilage (3), and the joint cavity is filled with slippery synovial fluid (4), which reduces friction, softens shock and transfers some nutrients. The convex articular surfaces of the bones are articulated with each other using two biconcave menisci - internal and external (5). The knee joint is very mobile, so nature has provided it with strong medial (6), lateral (7), cruciate (8) ligaments. The joint is protected in front by the patella (9), which also serves to articulate the muscles and ligaments of the thigh and lower leg.
The structure of the knee joint. (1) femur, (2) tibia, (3) elastic cartilage, (4) synovial fluid, (5) menisci - internal and external, ligaments: (6) medial, (7) lateral, (8) cruciate, (9) patella.
The knee joint usually responds well to treatment, except in cases of significant destruction of the joint tissue. It is important not only to relieve inflammation and pain, but to pay attention to blood circulation in the joint, ensuring its nutrition, and proper muscle function. We often find meniscal damage due to a lack of cooperative work of the knee stabilizer muscles. Read more about treatment at the Echinacea Clinic...
Typical knee problems
Injury to the meniscus, ligaments, and joint hemorrhage . When there is a bruise or violent movement in the knee joint, the menisci and ligaments of the knee joint are often torn and the joint cavity fills with blood. The situation requires clarification using radiography, MR imaging or endoscopy of the joint. After the acute effects of the injury have subsided, we are ready to provide you with a course of rehabilitation treatment. Read more…
Meniscus and cruciate ligament rupture
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint and gradual degeneration of the meniscus can appear with prolonged overload of the joint (sports, excess weight, occupational stress, scoliosis, joint instability). The volume of fluid in the joint decreases, the cartilage becomes thinner and tears, hence pain and limited mobility in the joint. The diagnosis is easy to establish by examination and MRI. Read more…
On the left is a normal joint. On the right is osteoarthritis.
Inflammation of the knee joint (arthritis, gonarthritis) occurs with damaged menisci, arthrosis, joint overload and with such serious rheumatic diseases as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, articular psoriasis, reactive arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus. For proper treatment, it is necessary to accurately find the cause of the inflammation. and we do this with the help of modern laboratory research. Read more…
Preparing for the urine donation procedure
Urine for general analysis is collected in a container.
On the eve of the test, it is recommended not to eat vegetables and fruits that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots, etc.), and not to take diuretics. Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the genitals. Women are not recommended to take a urine test during menstruation.
Collect approximately 50 ml of morning urine in a container (with a yellow lid). To properly conduct the study, during the first morning urination, release a small amount of urine (the first 1 - 2 seconds) into the toilet, and then, without interrupting urination, place a urine collection container into which to collect approximately 50 ml of urine.
Immediately after collecting urine, close the container tightly with a screw cap.
If it is not possible to immediately deliver urine to the laboratory, then the container with urine should be stored at a temperature of +2...+8°C.
Collection of 24-hour urine for biochemical analysis
Urine is collected over the course of a day. The first portion of urine in the morning is removed. All subsequent portions of urine excreted during the day, night and the morning portion of the next day are collected in one container, which is stored in the refrigerator (+4...+8°C) during the entire collection time (this is a necessary condition, since at room temperature it is significantly glucose levels decrease). After completing urine collection, accurately measure the contents of the container, be sure to mix it and immediately pour it into a small jar (no more than 5 ml). Bring this jar to the laboratory for testing. You don't need to bring all your urine. On the referral form you need to indicate the daily volume of urine (diuresis) in milliliters, for example: “Diuresis 1250 ml”, also write down the patient’s height and weight.
Remember that only the attending physician, who has the opportunity to observe the patient’s condition and explain the need to prescribe certain tests, can draw up an optimal laboratory examination program and evaluate the test results.
Indications
X-rays of the hip joints are performed to identify pathological processes in the joint itself and adjacent tissues. Such processes include:
- Dislocation of the hip joint in adults is a fairly rare occurrence, because the joint is protected by a powerful muscular frame. Can only occur with very strong traumatic exposure. Characterized by pain both when walking and at rest, swelling at the site of injury
- Dislocation of the hip joint in children can occur due to a fall or other traumatic impact. Similar symptoms as in adults.
- Femoral neck fracture is the most common injury. Basically, it prevails in older people. Associated with osteoporosis and decreased bone strength. It is marked by pain both when walking and at rest, swelling at the site of injury, and extensive hematoma. An X-ray of the hip joint will show the fracture line in the femoral neck, as well as the displacement of the fragments. It is performed both in one (direct) projection and in two (direct and axial with abduction of the affected hip, in order to identify a more accurate location of the fragments).
- Congenital dislocation of the hip or Dysplasia of the hip joint (hip joints) is a pathological development of the joint, leading to dislocation of the head of the femur. Typically, x-rays are taken of both hip joints for comparison and diagnosis. It is recommended to produce it from 3 months of age. It is performed both in one (direct) projection and in two (direct and axial, or, as it is also called, according to Launstein) to measure the range of hip movement and select a more accurate treatment regimen.
- Arthrosis, coxarthrosis, deforming arthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease that occurs mainly in middle-aged and elderly people. They happen in one joint or in both. For diagnosis, radiography of the hip joints along with the pelvic bones is mainly performed.
- Hip arthroplasty is the installation of an artificial prosthesis in place of the joint. It is done in one (direct) projection or in two (direct and axial, or, as it is also called, according to Launstein) to visualize the condition of the femoral neck and select a more accurate operation scheme.
Rules for preparing a patient for ultrasound examinations
Preparation for ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity, kidneys, bladder
Preparation for ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity and kidneys involves the exclusion of certain foods. A few days before the test, you should limit your consumption of foods that cause excessive gas formation, because they can distort the resulting ultrasound image. On the day of the examination, it is better to come on an empty stomach. If you go for an ultrasound after lunch, eat an easily digestible breakfast.
You should not smoke immediately before the test because smoke may distort the images.
An hour or an hour and a half before entering the diagnostic doctor’s office, drink still mineral water or tea (1 liter), since a full bladder is required during the examination (you should feel the urge).
Improper preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys can lead to distorted results. In this case, the doctor may reschedule the test for another day.
Factors influencing ultrasound of the peritoneal area:
Preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys includes taking laxatives the day before the diagnosis. For the study to be plausible, doctors recommend cleansing the intestines and getting rid of flatulence using medications available in pharmacies. This makes the research easier.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys in adults implies that the patient must fulfill certain conditions so that the image of the organs obtained on the monitor screen is readable. If food, liquid and gas accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract, then some organs, as a rule, cannot be visualized.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, kidneys, and bladder includes using fluid as an acoustic window. You should also keep in mind that you need to drink slowly so as not to swallow too much air, since the space it creates makes it difficult to read the image from the device screen.
Preparation for ultrasound examination Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys during pregnancy
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys in pregnant women does not differ from the preparation of the rest of the category of patients.
On the eve of the examination, you should not eat raw fruits and vegetables, especially legumes. Avoid heavy meals. Eat a light dinner in small portions. You should not eat anything 6 hours before the test.
If the test is performed in the morning, it is better to come on an empty stomach.
If the study time falls on or after lunchtime, you can have a light snack.
Preparation for ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvis in women
Pelvic ultrasound in women is performed transabdominally (through the anterior abdominal wall) and transvaginally (through the vagina).
During transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs, the bladder should be full. To do this, before the procedure, it is recommended to drink at least 1.5 liters of still water (BUT not juice!) and not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the examination.
For transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) of the pelvic organs, no special preparation is required; this study is also used to determine pregnancy in the early stages. The study is carried out with the bladder and intestines emptied.
Preparation for ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the prostate gland
Ultrasound of the prostate gland can be performed in two ways:
through the skin of the anterior abdominal wall and transrectally (the sensor is inserted through the anus) way.
Preparation for an ultrasound examination of the prostate, which is planned to be performed through the abdominal wall:
The patient needs to drink about half a liter of plain still water an hour before the test, and then not urinate. Alternatively, you can deliberately avoid urinating 2 hours before the procedure.
Preparation for ultrasound examination of the prostate, which is planned to be performed transrectally (trusound):
When preparing, two conditions must be met:
A few hours before the test, you need to cleanse your intestines. For this, the best option is to perform a cleansing enema in a volume of about 1.5 liters of cool water. To cleanse the intestines, you can also use microenemas such as Microlax or insert a glycerin suppository into the rectum.
Fill your bladder. You must come to the examination in advance, at least half an hour in advance, taking with you a liter container of still water, fruit juice or tea. When you arrive, start drinking this liquid. As soon as you feel the urge to urinate, you need to tell the doctor conducting the study so that he can call you into the office.
Preparation for ultrasound examination of the bladder
Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder is similar to preparing for a TRUS of the prostate, but it needs to start a day before the study. To do this, in the morning of the day before the test, you need to drink about 2 tablespoons of castor oil.
Then eat all day in such a way as to prevent the formation of gases in the intestines, as they will interfere with a good view of the bladder.
It is not recommended to eat: meat and offal, legumes, carbonated drinks and sweets.
You can eat: vegetables and fruits, nuts and seeds, black bread and grain crispbreads, drink only herbal or natural teas, that is, juices squeezed in a juicer.
Next, you need to do an enema, or micro-enema, or use a glycerin suppository to empty the bowel. Then you need to take with you a container of one and a half liters of still water.
You should start drinking liquid 30–40 minutes before the test, and stop filling your bladder when you feel the need to urinate (it is not necessary to drink the entire volume for this). You need to drink little by little, slowly, as a full bladder with very stretched walls will distort the picture of the disease.
Preparation for ultrasound examination of the breast
No special preparation is required before prescribing a breast ultrasound. Every woman can drink, eat, and take medications (by notifying the specialist in advance). In order to properly prepare, you need to know some points: the procedure is prescribed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (5 - 14 days of the cycle from the beginning of menstruation).
Shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is a movable connection of the humerus (1) with the scapula (2) and collarbone (3). This is the most mobile joint in the human body, so the joint capsule (4) has folds (5) that provide a large range of movements. When there are problems with the shoulder joint, these folds often stick together, which limits the mobility of the shoulder. In the shoulder joint complex, one can also consider one independent, small, but very important joint between the clavicle and the scapula - the acromio - clavicular (6). The shoulder joint is equipped with muscles that provide not only flexion in different planes, but also rotation (the so-called rotator cuff).
The structure of the shoulder joint. (1) humerus, (2) scapula, (3) clavicle, (4) joint capsule, (5) folds, (6) acromio - clavicular joint.
The shoulder joint generally responds well to treatment, except in cases of significant destruction of the joint tissue. It is important not only to relieve inflammation and pain, but to pay attention to blood circulation in the joint, ensuring its nutrition, and proper muscle function. We often detect arthrosis or periarthritis of the shoulder joint due to infringement of the nerves in the cervical spine that control the shoulder muscles and the nutrition of the joint.
Typical shoulder problems
Humeral periarthritis (synonyms: bursitis, frozen shoulder syndrome, adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, glenohumeral periarthritis) is the most common problem of the shoulder joint. The essence of the problem is inflammation and loss of elasticity of the capsule and ligaments of the joint and surrounding muscles. Periarthritis usually begins with cervical osteochondrosis, a herniated cervical intervertebral disc or joint injury, with pinching or damage to the branches of the brachial nerve plexus. With periarthritis, it is important to relieve inflammation as soon as possible and begin to develop mobility of the shoulder joint. Read more…
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint usually develops after injury or inflammation. The volume of synovial fluid in the joint decreases, the cartilage becomes thinned and torn, hence pain and limited mobility in the shoulder joint. The diagnosis is easy to establish by examination and x-rays. Comprehensive treatment usually helps relieve pain and improve mobility. Read more…
Inflammation of the shoulder joint (arthritis) occurs with arthrosis and such serious rheumatic diseases as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, articular psoriasis, reactive arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus. For proper treatment, it is necessary to accurately find the cause of inflammation, and we do this with the help of modern laboratory tests. Read more...
The mobility of the glenohumeral joint can be restored using gentle and safe osteopathic methods.
Rules for preparing a patient for endoscopic examinations
Preparation for fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS)
FGDS is carried out on an empty stomach: in the morning on the day of the study, it is forbidden to have breakfast or eat any food, even if the study takes place in the afternoon.
In the morning on the day of the study before FGDS it is not recommended:
- smoke;
- take medications in tablets (capsules) orally;
- On the morning of the study, before the FGDS, the following is allowed:
- brush your teeth;
- do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and other organs;
- 2-4 hours before drinking water, weak tea with sugar (without bread, jam, sweets);
- take medications that can be dissolved in the mouth without swallowing or taken with you;
- give injections if food intake is not required after the injection and it is not possible to do it after FGDS;
The night before: easy-to-digest (no salads!) dinner until 18.00.
No special diet is required before FGDS, but:
- exclude chocolate (chocolate candies), seeds, nuts, spicy foods and alcohol for 2 days;
- when examining from 11 a.m. and later, preferably in the morning and 2–3 hours before the procedure, drink in small sips one glass of still water or weak tea (without jam, sweets, cookies, bread, etc.);
Before the examination, you need to remove removable dentures, glasses, and a tie.
X-ray of the hip joint
Posted at 14:51h in Services by doctor
If there is an injury or pain in the pelvis or upper third of the thigh, a person consults a traumatologist with complaints of pain, poor mobility, etc. The hip joint, or TJ for short, is a joint formed by the acetabulum of the pelvic bone and the articular surface of the head of the femur. There are several methods for examining the hip joint that a doctor can prescribe to make a diagnosis: ultrasound, x-ray of the hip joint, MRI, CT. Although they differ technically, they are equally effective in identifying the nature of pain.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
One day before the test, a light lunch is recommended. Recommended products: boiled white fish, chicken, eggs, cheese, white bread, butter, cookies, potatoes.
Not recommended foods: fruits and berries with seeds, red meat, vegetables, cereals, salad, mushrooms, nuts, grain bread, sweets.
- Dinner - tea.
- In the evening, do two cleansing enemas with an interval of 1 hour.
- On the morning of the test, again do two cleansing enemas with an interval of 1 hour.
- Don't have breakfast.
Taking laxatives is not required, because the center has modern equipment for bowel cleansing.
Elbow joint
The elbow joint is a movable connection of the humerus (1) with the radius (2) and ulna (3) bones. The articular ends of the bones that form the joint are covered with strong and elastic cartilage (4), and the cavity of the elbow joint is filled with slippery synovial fluid (5), which reduces friction, softens shock and transfers some nutrients. The joint is strengthened on all sides by strong ligaments. Three important nerves pass through the elbow joint: the radial, ulnar and median; Often these nerves are compressed due to swelling and deformation of the joint, which is manifested by pain and weakness of the hand muscles.
The structure of the elbow joint: (1) humerus, (2) radius, (3) ulna, (4) elastic cartilage, (5) synovial fluid.
The elbow joint usually responds well to treatment, except in cases of significant destruction of the joint tissue. It is important not only to relieve inflammation and pain, but to pay attention to blood circulation in the joint, ensuring its nutrition, and proper muscle function. We often find elbow joint suffering due to certain professional and sports activities (musicians, tennis players, athletes, drivers) and intra-articular fracture.
Common Elbow Problems
Epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is pain and inflammation of the ligaments and tendons at the points of attachment to the elbow joint, due to their constant overload (in musicians, athletes, massage therapists) and uncoordinated work of the arm muscles. The problem is often associated with the cervical spine. Read more…
Arthrosis of the elbow joint usually develops after injury or inflammation. The volume of synovial fluid in the joint decreases, the cartilage becomes thinned and torn, hence pain and limited mobility in the elbow joint. The diagnosis is easy to establish by examination and x-rays. Comprehensive treatment usually helps relieve pain and improve mobility. Read more…
Inflammation of the elbow joint (arthritis) occurs with arthrosis and such serious rheumatic diseases as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, articular psoriasis, reactive arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus. For proper treatment, it is necessary to accurately find the cause of inflammation, and we do this with the help of modern laboratory tests. Read more...
Immobility (contracture) of the elbow joint after injury or inflammation. Read more...
Infringement and damage (neuropathy) of the radial, ulnar or median nerves occurs after injuries, inflammation in the joint and arthrosis. In most cases, the nerve can be freed without surgery.
Preparation for radiography (irrigoscopy, intravenous urography)
1. One day before the test, you should not eat vegetables, fruits, mineral water, or dairy products.
2. On the eve of the study, the last meal is allowed no later than 18.00.
3. At 12:00 on the eve of the test, drink 50 ml of castor oil.
4. At 15.00 on the eve of the study, take 2 sachets of Fortrans.
5. On the day of the study in the morning:
- irrigoscopy is performed on an empty stomach,
- intravenous urography you need to have breakfast!
For irrigoscopy you must have a sheet and slippers with you.
Preparation for x-ray of the lumbosacral spine
- The day before the test, you should not eat vegetables, fruits, mineral water, or dairy products.
- On the eve of the study, the last meal should be no later than 19.00.
- At 15.00 on the eve of the study, you must take 1 sachet of Fortrans within 1 hour.
- On the day of the study, you need to have breakfast in the morning!
If it is impossible to take Fortrans, it is necessary to give one cleansing enema at 20.00 hours the day before and one cleansing enema in the morning at 06.00 hours on the day of the study.
Ankle joint
The ankle joint connects the talus bone of the foot (1) with the bones of the lower leg: tibia (2) and fibula (3). The articular ends of the bones that form the joint are covered with strong and elastic cartilage (4), and the joint cavity is filled with slippery synovial fluid (5), which reduces friction, softens shock and transfers some nutrients. The joint is strengthened on all sides by strong ligaments. The ankle joint provides mainly dorsal and plantar flexion of the foot, and is not intended for rotation and lateral bending (these movements are provided, for the most part, by other joints of the foot). This is why forced lateral movements in the ankle joint so often end in damage.
The structure of the ankle joint. (1) talus, (2) tibia, (3) fibula, (4) elastic cartilage, (5) synovial fluid.
The ankle joint usually responds well to treatment, except in cases of significant destruction of the joint tissue. It is important not only to relieve inflammation and pain, but to pay attention to blood circulation in the joint, ensuring its nutrition, and proper muscle function. We often find ankle injuries due to impingement in the lumbar spine of the nerves that control the muscles of the leg and foot.
Common ankle problems
Frequent twisting of the foot with sprained ligaments usually indicates weakness of the muscles that stabilize the joint when supporting the leg. These muscles are activated by nerve impulses passing through the sciatic nerve system. When the lumbar spinal roots or sciatic nerve are pinched, the lower leg muscles weaken due to insufficient supply of nerve impulses. The result is a ligament injury or even a broken ankle. This problem can usually be successfully treated. Read more…
Arthrosis of the ankle joint usually develops after an inflammatory disease, frequent minor injuries or fractures of the bones of the leg and foot. The volume of synovial fluid in the joint decreases, the cartilage becomes thinned and torn, hence pain and limited mobility in the joint. With arthrosis, we often find painful pinching of the nerves of the foot by thickened joint tissues. The diagnosis is easy to establish by examination and x-rays. Comprehensive treatment usually helps relieve pain and improve mobility. Read more…
Inflammation of the ankle joint (arthritis) occurs in osteoarthritis and in such serious rheumatic diseases as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, articular psoriasis, reactive arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus. For proper treatment, it is necessary to accurately find the cause of inflammation, and we do this with the help of modern laboratory tests. Read more...
Inflammation and damage to the Achilles tendon (Achilles, Achilles tendon) usually occurs with increased load on the Achilles tendon in athletes and with shortening of the calf muscle (wearing heels, injury, spinal kyphosis, etc.) or with inflammatory diseases of the joints. Read more…
Preparing for bicycle ergometry
No special preparation is required for bicycle ergometry. The day before, you can take fluids and food in the usual volumes, but on the day of the study, only a light breakfast is allowed no later than two to three hours before the procedure.
Two to three days before the study, in agreement with the attending physician, medications that affect myocardial blood supply and blood pressure are discontinued, unless otherwise leads to the development of life-threatening conditions. Such drugs include nitroglycerin and its derivatives, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and others.
The day before, you should avoid significant physical and psycho-emotional stress, and also avoid taking alcohol, nicotine and coffee, as all this can affect the functioning of the heart on the day of the test. It is better to come to the procedure in loose clothing that does not restrict movement and allows you to move freely on the bicycle ergometer.
You must have with you the results of previously conducted studies: ECG, EchoCG, Holter monitoring, bicycle ergometry (if performed).
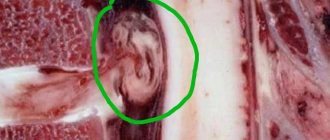
The picture visible on X-ray of the hip joint
Pictures are taken in two projections: anterior-posterior (direct) and lateral. First of all, on an x-ray, the radiologist sees the anatomical structure of the pelvic bones and hip joint
- pelvic bones (pelvic wings; ilium, ischium, pubic symphysis - they form the acetabulum, which is the attachment point of the femoral head to the pelvis)
- sacrum
- coccyx
- femoral head
- femoral neck
- femoral body
In the process of interpreting x-rays of the hip joints, the doctor assesses the condition of the pelvic bones; head, neck and body of the femur.
Joints of fingers and feet
The skeleton of the feet is formed by the tarsal bones (1), the five metatarsal bones (2), and the phalanges of the fingers (3). The articular surfaces of the bones, like all other joints, are covered with articular cartilage. The feet are provided with extremely strong ligamentous apparatus. Of particular importance is the plantar aponeurosis (4), a strong ligament that connects the forefoot and hindfoot, like a bowstring. When the plantar aponeurosis weakens, the foot becomes flat (flatfoot).
The structure of the joints of the fingers and feet. tarsal bones, (2) metatarsal bones, (3) phalanges, (4) ligament connecting the forefoot and hindfoot.
The feet contain a large number of sensitive nerve receptors that tell the brain about the movement of the body's center of gravity. Focusing on signals from the feet, the brain ensures proper control of the tone of the muscles that support the vertical position of the body. Impaired mobility of one small joint in the foot can cause “deception” of the central nervous system, and as a result, pain in the spine or large joint. Therefore, we pay great attention to the biomechanical well-being of the feet.
Osteopathic treatment of joints of the lower extremities, feet
Typical problems of the joints of the fingers and feet
Gout is a metabolic disorder in which excess uric acid accumulates in the body. Uric acid crystals tend to accumulate in joints and damage them. The most common type of gouty arthritis is inflammation of the big toe joint. Read more…
Gouty arthritis
Flat feet is a deformation of the foot with its spreading. Occurs with congenital weakness of the ligaments and with overload of the feet (stooping with a shift of the center of gravity anteriorly, excess weight, physical labor). In cases of flat feet, we restore the correct center of gravity and relieve the feet with the help of therapeutic insoles.
Inflammation of the finger joints (arthritis) occurs in serious rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, articular psoriasis, reactive arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus. For proper treatment, it is necessary to accurately find the cause of inflammation, and we do this with the help of modern laboratory tests. Read more...
Pinched nerves in the feet (meralgia) are a common cause of foot pain. The nerves in the feet pass through narrow canals formed by bones and tendons. Foot deformation (flat feet, gout, arthritis) leads to compression of the nerves and severe pain. We successfully treat such neuralgia.