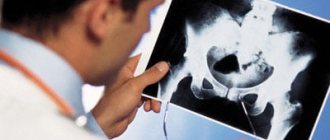
The hip joint is a complex multi-axial joint that performs flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, pronation and supination of the hips and takes on serious loads. Any disturbances in its functioning not only lead to serious discomfort for a person, but can also cause the development of serious disorders. X-ray of the hip joint (HJ) is a non-invasive diagnostic method, the value of which is difficult to overestimate.
It has found wide application in various fields of medicine, including traumatology, rheumatology, orthopedics, purulent surgery for diagnosing diseases and the consequences of injuries, to determine the extent of the upcoming operation or the effectiveness of the treatment. The procedure is quite safe, highly effective and simple, but at the same time it allows you to obtain valuable data on the condition of the patient’s hip joint.
X-ray of the hip joint - RUB 2,400.
15-20 minutes
(procedure duration)
If you don’t know where to get an x-ray of the hip joint, but want to be sure that the diagnosis will be carried out at a decent quality level, contact the diagnostic center of the CELT multidisciplinary clinic.
Advantages and disadvantages
X-ray of the hip joint, like other diagnostic methods, has its advantages. They include simplicity and accessibility, as well as low cost of the procedure. If the patient has an x-ray in hand, he can seek advice from different doctors, and the doctor will be able to monitor the dynamics of the disease during a re-examination.
Flaws:
- small doses of radiation exposure to the body;
- inability to fully assess joint function;
- there are other tissues near the area of study, so x-rays do not clearly visualize the structure of the joint;
- X-ray without contrast does not allow assessing the morphological structure of soft tissues;
- uninformative method.
Preparing for a hip x-ray
The study area is near the intestines, so preparation for the study is recommended to reduce gas formation in it. For this it is recommended:
- Adjust the diet - exclude from it foods that contribute to flatulence: legumes, cabbage, black bread, dairy products.
- Take activated carbon or other adsorbents the day before.
- Cleanse the intestines before the procedure (naturally, with an enema or laxative).
With X-rays with contrast, testing can be done in advance to rule out allergies. When prescribing the procedure, the doctor will tell you about the preparation rules in detail.
Indications and contraindications
If a patient has pain in the hip area, then he may be prescribed an X-ray of the hip joint in order to determine the cause of the pain. This diagnostic method is considered the first method for most diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
With the help of radiography, such pathologies of the hip joint are revealed as:
- traumatic injuries (dislocations, fractures);
- degenerative changes in the joint (cystic degeneration, arthrosis, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head);
- bone tumor, metastasis;
- inflammatory conditions (arthritis, osteomyelitis);
- congenital pathologies (dysplasia, hypoplasia);
- metabolic disorders (gout, osteoporosis).
An absolute contraindication to such examinations is pregnancy at any time, as well as diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys, and heart disease. Unless there is a compelling reason, it is best not to perform x-rays on children under 14 years of age. If such a procedure is carried out using a contrast agent, the list of contraindications will be much wider and includes the following body conditions:
- severe pathological changes in the liver and kidney;
- tuberculosis in the active phase;
- allergy to substances containing iodine;
- cardiovascular failure;
- serious condition of the patient.
Reviews
Svetlana
Pre-registration is a convenient thing. No need to spend the whole day waiting in line or waiting for a doctor. I made an appointment by phone, arrived at the appointed time, and within 15 minutes received the finished photographs. No inconvenience or queues
Fedor
Not all clinics in our city can boast of X-ray equipment of this level. The quality of the pictures is simply amazing. It is very convenient that they are provided in digital format. No need to carry bulky envelopes with film.
Anna
Thanks to the doctors for my healthy and strong child. If they had not promptly identified my gestational diabetes, it is unknown how this would have affected the baby. As far as I understand, this pathology can lead to serious consequences for the child. Thanks to the attention of the doctors, I was able to avoid trouble. However, everything was corrected with the help of a regular diet.
Olga
I had a severe form of gestational diabetes, and together with the doctor at your medical center, we worked almost throughout my pregnancy to prevent a significant increase in blood glucose levels. Nutritional correction was not effective enough. The doctor carefully selected medications for me so that I could carry and give birth to a healthy child, for which I am very grateful to him.
Preparation
- If you need to have an x-ray of your hip joint, no special preparation is usually required, but it is still worth paying attention to certain points.
- Since the area of interest is quite close to the intestine, its contents may affect image quality. In particular, this concerns the process of gas formation. To remove intestinal contents, it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the evening before the test and the next morning. The patient can also take any laxative before the procedure.
- If radiography is performed with a contrast agent, it is necessary to conduct a test in advance to determine an allergic reaction. The procedure is carried out if the result is negative.
08/14/2014 X-rays of the hip joint under scopic control.
They asked to clarify which screw the fragment was from and where it was displaced.
Series under copy, right. oblique
the screw fragment is displaced posteriorly and is located in the joint cavity.
Fragment from the top screw.
Fragment from the top screw. The last shot is strictly lateral through two joints? Volodya, have you tried to deduce it using Launshtein?
- Login to post comments
According to Launstein, this
According to Launstein, is this a type of axial? Then see the second and third images - also axial with a slight difference in angles. Well, yes, lateral, I can’t guarantee that it’s clearly lateral (through two joints), but close to it. I only regretted the exposure slightly; I should have given it 2 – 2.5 times more.
- Login to post comments
Thank you! Laying according to Launstein
Laying according to Lauenstein projection:
Another variation of this style is the frog pose:
- Login to post comments
And what new things could we do?
And what new could this styling add to us in this case? In general, I am fascinated by such placements on the hip joints, which can only be done on practically healthy people. With an operated joint, the frog pose is quite problematic to perform, I think.
- Login to post comments
such styling on
such placements on the hip joints that are only possible in practically healthy people.
This is true, the woman who was being twisted had great difficulty moving and turning, not because of her hip joint, but because of pain in her lower back. Similarly with triple-wrong functional tests, especially in the lumbosacral region
- Login to post comments
Features of the procedure
- Before the procedure, the patient removes tight clothing, all jewelry and metal objects, because they will cause artifacts to appear in the images. To examine the hip joint, x-rays are performed in several projections. Before the x-ray is performed, protective lead plates are placed on the patient.
- To image the pelvic area, an X-ray machine sends a beam of rays through the hip joint. At this time, the radiation begins to scatter and stops, and the extent of such scattering depends on the density of the tissue being tested. At the same time, images of organs and tissues through which radiation has already passed begin to appear on the film. The photo clearly shows the bone, which has maximum density. A radiologist can use an X-ray image placed on a lighted screen to assess the internal structure of the joint.
- If an X-ray of the hip joint is performed, then, as a rule, an X-ray is taken in two projections. The procedure lasts about 10 minutes and the patient receives a radiation dose of 1.5 millisieverts.
Interpretation of X-rays
X-rays may have certain inaccuracies. This is due to the fact that the X-rays that are sent by the cathode ray tube diverge in a stream. If the subject of study is not in the middle, but at the edge of the image field, the image may be slightly elongated. In this case, the dimensions of the compounds under study also change.
The accuracy of diagnosis largely depends on how qualified the radiologist is. Each disease has its own characteristics, which are revealed in the pictures:
- Fractures are visible bone fragments;
- dislocations - you can see displacement of the articular surfaces;
- osteoarthritis - narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes;
- aseptic necrosis - bone regeneration, areas of osteosclerosis;
- osteoporosis - thinned structures and decreased bone density are clearly visible;
- dysplasia - reveals incomplete or abnormal development of the femoral head along with the articular cavity;
- tumors - foci of darkening, space-occupying formations.
Femoral head: tangential view, Schneider positioning
Film dimensions: 24 x 30 cm (10 x 12″), the cassette is positioned longitudinally. Film sensitivity: 200. FR; 115 cm (40″). A screening grid is used. Big focus. Exposure at 77 kV is automatically set according to the central polarity of the exposure meter.
- Undress from the waist down, except for underwear.
1. The hip joint to be examined is flexed at an angle of 45° (30-60°), with the foot on the table.
2. The hip joint that will be examined is straightened, the foot is slightly rotated medially.
— The upper edge of the cassette is located at the level of the anterosuperior spine of the iliac wing,
— The genitals are shielded (with an apron, cap).
— The X-ray beam is directed vertically or offset at an angle of 30° craniocaudalally.
— The central beam is directed to the center of the femoral neck (center of the groin area) and then to the middle of the cassette.
— Centering, diaphragm, side marking.
— The patient stands with the joint being examined facing a vertical stand.
— The foot of the side being examined is located parallel to the vertical stand.
— The part of the pelvis with the thigh removed from the film is shifted posteriorly at an angle of 65° to the vertical post.
- Hands are placed above the head.
— The central beam is directed perpendicular to the femoral head of the hip joint being examined (2 RA medial to the middle of the groin area).
LOWER LIMBS
Shot 1: front outline
Shot 2: back outline
Criteria for a correctly performed radiograph
— The joint space is located in the center of the film.
— The contours of the articular surface of the femoral head are not bifurcated (1 - anterior, 2 - posterior contour).
Femoral head: tangential view, Schneider positioning
1. Tangential image of the femoral head (anterior contour)
2. Tangential image of the femoral head (posterior contour)
Lower limb belt
Criteria for a correctly performed radiograph
— The hip joint is completely visible.
— The neck of the femur is located in the center of the film, it is not shortened and is visible without overlays.
— The skewers are projected onto each other (1 and 2).
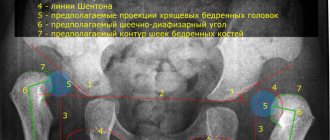
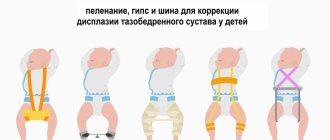
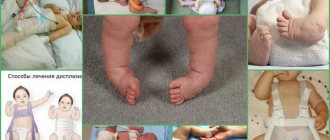
X-ray of the hip joint in children
X-rays of the hip joint are performed only according to strict indications, since X-rays can provoke hematological or oncological diseases in children. Therefore, research in children should be carried out by a high-level specialist who can conduct the examination with minimal harm to the child.
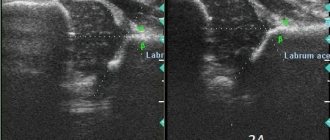
Children who are not yet a year old are usually prescribed an ultrasound scan, since in children under three months the muscles are still atrophied, and it is difficult to diagnose pathology such as hip dysplasia. In this case, x-rays cannot help. It is advisable to perform it when the cartilage is filled with calcium and turns into bone tissue.
Alternative Methods
- MRI is an effective diagnosis of pathology of non-bone structures (cartilage, ligaments and tendons), the presence of effusion/blood in the joint capsule;
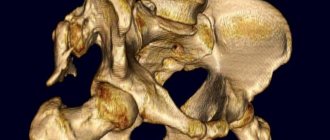
- — obtaining high-quality layer-by-layer images with the possibility of 3-dimensional modeling, the most accurate diagnosis of bone tissue diseases;
- Ultrasound - diagnosis of pathology of periarticular structures, inflammation of the hip joint, is indispensable when performing joint puncture, before and after surgery.