What it is
Physiological immaturity of the hip joints in newborns is observed much more often in premature babies, but even if the child was born on time, the joint is not yet fully formed. Final formation occurs by the 7th month of life. The term “physiological immaturity” refers to delayed formation of the hip joint.
If we are talking about dysplasia, then it means a violation of the formation of the anatomical structures that form the joint (cartilage, ligaments, bones). Previously, these 2 conditions were united under the term “dysplasia,” but now most experts distinguish between them. Thus, immaturity of the hip joint is a variant of dysplasia and, in the absence of the necessary correction, can lead to subluxation and dislocation of the hip joint.
Features of the hip joints in newborns
Even a baby born on time has an immature hip joint. In newborns it has the following anatomical features:
- The head of the femur is cartilage.
- Joint ligaments have increased elasticity, especially in girls.
- The acetabulum is flattened and more vertical than in adults.
All these features contribute to greater mobility of the femoral head, which can lead to its displacement (subluxation) or complete separation from the articular surface of the acetabulum (dislocation).
Causes of the disease
Joint dysplasia in infants develops due to the following factors that act negatively during intrauterine development:
- poor environment, poor quality food and drink;
- pregnancy in a woman over 35 years of age;
- overweight, acute and chronic diseases during pregnancy;
- toxicosis and medication use;
- hormonal disorders before and during pregnancy.
Infants at risk include:
- with a body weight in newborns of more than 4 kg - they have an increased load on the lower limbs;
- whose mothers adhere to old traditions and are supporters of tight swaddling - in this position the head of the femur is constantly in an inverted position;
- with a hereditary predisposition to joint diseases;
- with connective tissue dysplasia, in which the structure of connective tissue is disrupted throughout the body;
- girls - it's all about the relaxation hormone, which is produced in a woman's body to increase the elasticity of the pelvic ligaments before childbirth. The hormone also affects the fetus, but girls are more sensitive to it.
In some cases, dysplasia may be one of the consequences of injuries to the pelvic region, lower extremities, acquired deformities of the spine and spinal cord. This is a topic for a separate section and we will not consider it for now.
Causes of immaturity of the hip joint
The formation of the musculoskeletal system occurs in the prenatal period and actively continues in the first months after birth. Therefore, underdevelopment of the hip joints occurs much more often with the following risk factors:
- Large fruit.
- Breech presentation.
- Toxicosis in the mother.
- Taking medications during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Premature birth.
- Nutrient deficiency in the mother's diet while carrying a child (primarily a lack of calcium, iron, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium).
- Gender of the child. It has been noted that underdevelopment of the hip joint in newborn girls is 5 times more common.
Significant risk factors include hereditary predisposition, and in each subsequent generation the likelihood of developing pathology increases.
Characteristic features of the pathology
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists...” Read more...
Underdevelopment of the hip joint (HJ) is diagnosed in more than 20% of newborns, and four times more often in girls than in boys. Unlike dysplasia, with immaturity, the hip joints are able to form correctly, but this happens much more slowly than normal. Since children's joints and spine consist of a large amount of cartilaginous tissue, their temporary immaturity is quite physiological. The diagnosis is made on the basis of delayed development of ossification nuclei. Other signs of immaturity are considered normal:
- large size of the acetabulum;
- their flat shape;
- increased elasticity of the elements of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus.
But with the combination of such structural features and the immaturity of the hip joint, the development and progression of dysplasia is possible - a disease dangerous with its serious consequences. Therefore, pediatric orthopedists do not wait for the formation of foci of ossification, but take measures to ensure the full development of the hip joint.
Types of pathology
Depending on the anatomical features, joint underdevelopment is divided into several types.
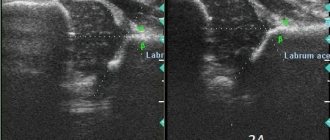
- Acetobular (pathology of the acetabulum). This is the most common pathology. It is also called “type 2a” according to Graf. In most cases, massage, therapeutic exercises and wide swaddling are sufficient for correction.
- Rotary. This is a type of anatomical disorder of bone structures in which there is a shift in the angle between the axis of the hip joint and the axis of the knee.
- Epiphyseal. In this type, the process of formation and ossification of the epiphyses of the bones that form the joint is disrupted.
Stages of pathology
The disease has several stages. The most recent is a dislocation, after which children clearly experience disturbances in movement and severe pain. There is also a distinction between subluxation and preluxation.
Pre-luxation
There is underdevelopment of the hip joint, but there is practically no displacement of the femoral head. This is the first stage of the disease and is the easiest to treat. However, difficulties may arise in detecting preluxation, since the symptoms are extremely vague.
This stage is well managed by massage and physical therapy. The main thing is to notice the violation in time.
Subluxation
With subluxation, the symptoms of the pathology are more pronounced; there is a slight displacement of the head from the acetabulum. Conservative methods of therapy are also effective.
Dislocation
Dislocation is the last stage, with which the child experiences difficulty in moving and lameness appears. The treatment is more thorough; the doctor can reduce the dislocation or prescribe surgical correction. After this, rehabilitation is required.
Symptoms
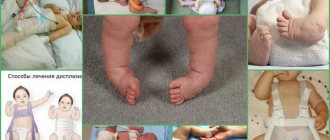
Immaturity of the hip joints in a baby may be suspected even in the maternity hospital. Early signs include asymmetry of the buttock, inguinal and femoral skin folds, different heights of the kneecaps. To determine this symptom in a baby lying on his back, you need to straighten his legs and then smoothly bend them at the knees. Normally, the kneecaps are located at the same level. Different range of motion in the hip joint.
Asymmetry of the gluteal folds
It should be remembered that in children in the first month of life such signs are not absolute. However, any suspicion of pathology requires a mandatory visit to a pediatric orthopedist and dynamic observation.
Signs of illness
To get rid of the disease, it is necessary to detect the disease and it is advisable to do this in 1 month of the child’s life. The difficulty is that the signs do not appear clearly at such an early age; they become more noticeable at 3-6 months.
Parents should know the main signs of the disease:
- Asymmetrically located folds of the thigh and buttocks.
- When the knees are bent, their different height positions are noticeable.
- Different limb lengths.
- A characteristic click when a child moves his leg.
- There is slight difficulty bending the leg. Babies have very good flexibility, so there should not be any difficulties. The best way is to compare how each limb bends.
- Small angle when spreading your legs to the sides. The norm is considered to be from 150°.
If you notice at least one or two similar signs in a newborn, you should immediately consult an orthopedic doctor.
You should undergo a preventive examination by a specialist at one month of age. There are signs that only an experienced doctor can notice. It is worth remembering that it is quite difficult to identify an immature hip joint by eye; the problem is in its complex structure. The best diagnosis is an echographic examination, but it is allowed only from 3 months of age.
Diagnostics
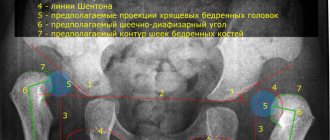
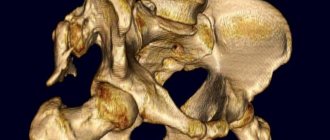
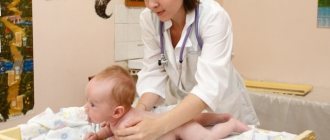
A preliminary diagnosis is made by an orthopedic surgeon during the initial examination. It is especially important to visit an orthopedist for premature babies, as they have a high risk of developing dysplasia. The doctor will conduct a series of clinical tests to detect mobility problems in the hip joint. In addition, he will find out how the pregnancy proceeded and whether there were cases of congenital joint pathology in the family. The final diagnosis is made after an ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound diagnostics in newborns
This method is absolutely safe and at the same time very informative. Until the baby is 3 months old, ultrasound is the only method to confirm the diagnosis. An important advantage is that ultrasound diagnostics can determine all types and stages of hip immaturity and dysplasia.
Reasons for delayed development of the hip joint ↑
The most common causes of hip dysplasia are:
- infectious pathologies of the mother during gestation;
- endocrine disorders during pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis, especially in the first trimester;
- late pregnancy;
- unbalanced nutrition of the expectant mother - deficiency of vitamins, minerals (especially calcium);
- hereditary predisposition.
Types of dysplasia ↑
Depending on the consequences of hip joint underdevelopment, the degrees of dysplasia are distinguished:
- Grade 1 – characterized by instability in the hip joint, which is called preluxation. There is no displacement of the femoral head relative to the acetabulum.
- 2nd degree – the femoral head is partially displaced from the acetabulum, this is a congenital subluxation of the hip joint.
- 3rd degree – accompanied by complete displacement of the femoral head from the glenoid cavity. This is a congenital dislocation of the hip.
The degree of pathology of the hip joint
The primary diagnosis is usually made by an orthopedic surgeon during a routine examination at the end of the neonatal period. The presence and degree of pathology are clarified using ultrasound of the joint and radiography.
Symptoms of delayed development of the hip joint ↑
In a baby under one year old, various degrees of dysplasia manifest themselves in the form of:
- Limitations of hip abduction - the severity of the symptom depends on the degree of impairment. Movement is limited as much as possible when the hip is dislocated. To identify the symptom, with the baby on his back, bend both of his legs at the knee and hip joints and gently move them apart. In this case, an obstruction to abduction is clearly visible on the affected side.
- The presence of asymmetry of skin folds - in the tummy position, the baby needs to straighten the legs and carefully examine the buttock and thigh folds. This sign is rather vague, but if it is present, hip dysplasia can be suspected.
- Clicking symptom - during abduction, you can hear or feel a clicking sound in the dysplastic joint. The sound effect is associated with the reduction of the femoral head into the glenoid cavity. The sign is also subtle and is usually observed in babies in the first days of life. But with hip dysplasia with muscle hypotonicity, the symptom persists for up to six months.
- Shortening of the leg is clearly visible in a baby lying on his back with his limbs bent at the knees.
- Pronounced outward rotation of the affected limb is observed when the baby is in a relaxed position, for example, during sleep.
Consultation in Kyiv
In the future, hip dysplasia manifests itself even more clearly, since the baby has a late onset of walking, lameness, the formation of increased lordosis in the lower back, and all the symptoms of the newborn period become pronounced.
Vertebrologists at the Ignatiev Clinic in Kyiv recommend examining the baby at the slightest suspicion of delayed development of the hip joint.
Treatment
The earlier the correction of dysplasia is started, the higher the likelihood of recovery. There are quite a few treatment methods, and which one is preferable in a particular case is determined by the attending physician.
Massage
For any type of hip immaturity, massage has a beneficial effect. The procedure is carried out by a specially trained specialist, since the baby’s joints are very fragile, and incorrect actions can cause harm instead of benefit.
Congenital clubfoot in children
Before performing a massage, you need to make sure that the room is warm and the baby is not hungry. It is better to conduct a session an hour before or an hour after feeding. During the procedure, the child should not experience discomfort, much less pain. If this happens, you should further consult your doctor.
The massage takes 20, maximum 30 minutes, and the first 5 minutes are spent on preparation: lightly stroking and kneading the chest, back, legs, buttocks. All this is aimed at creating positive emotions and relaxing the baby’s muscles. Finish the massage by kneading and stroking the feet.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics is recommended for all children not only as a treatment method, but also as a preventive measure. Physical education helps improve the child’s general condition, strengthens muscles and ligaments, and promotes the proper formation of the skeleton. After the specialist shows the necessary set of exercises, parents will be able to practice with the baby independently at home.
The main principle is regularity of classes and comfortable well-being of the child.
Before starting gymnastics, you need to do a light massage to prepare the muscles. Typically, the complex consists of the following exercises: bending the legs to the stomach at a right angle, circular movements of the hips, and the “bicycle” exercise. At the end, be sure to make stroking movements.
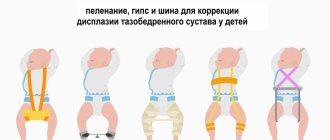
Wide swaddling
Wide swaddling is recommended for all newborns, regardless of whether there is dysplasia or not. The fact is that the natural position of the legs (half-bent and apart) during swaddling gently fixes the head of the femur in the acetabulum and contributes to the correct formation of the hip joint. There are special panties for wide swaddling, but with some skill you can use diapers folded in several layers.
Treatment methods for dysplasia
Typically, the tactics for managing hip dysplasia in infants are as follows. The diagnosis is made in newborns in a maternity hospital or in a clinic. Next, conservative treatment methods are prescribed and observed. Assessing the dynamics allows you to determine whether there is an improvement or not. If not, the orthopedist selects more radical methods.
Conservative treatment methods are used, which are based on the use of special devices or structures. They hold the limbs in a position of flexion and extension for a long time. Thanks to this, bone structures and cartilage develop proportionally.
All this time, the head of the femur is in a physiological position: subluxation or dislocation does not occur, and there is no load on the lower limb.
The following methods are used:
- Becker pants - in appearance the device resembles children's panties; between the legs there is a flexible hard pad that does not allow the legs to move together;
- wide swaddling - using ordinary diapers in the amount of 3 pieces, two of which are placed between the legs, the third fixes them;
- Pavlik stirrups are an orthopedic device made of soft tissue, which has a thoracic and abductor part. Consists of a chest bandage and an ankle bandage, reins and straps for fixation. The legs are fixed in a bent position, while the baby can move the legs;
- pillow (featherbed) Frayka - a cushion-shaped structure that is fixed between the legs with the help of belts.
The simplest devices also contribute to abduction of the hips in newborns and young infants: children's backpacks, baby carriers, kangaroo bags, slings. But the decision about which method is indicated in your case is up to the doctor alone.
Be sure to supplement your treatment with physical therapy and massage. They stimulate motor skills, prevent congestion, and promote the harmonious development of your baby.
Gymnastics at home
You can do gymnastics at home yourself. If in doubt, ask your doctor to show you the basic movements. This way you will be sure that you are doing everything correctly.
For good results, you need to do gymnastics regularly: 2 - 3 times a day, 10 - 15 repetitions. It is necessary that during the manipulations your baby is in a good mood and does not want to sleep. Make all movements carefully and gently so as not to frighten the child or hurt him. Watch his reaction. The exercises are:
- “Bicycle” is performed lying on your back. Bend your knees and hips and make movements that imitate riding a bicycle;
- Flexion and extension of the baby’s legs: first simultaneously, then alternately;
- “Ladushki” with the feet of the crumbs.
Prevention of hip dysplasia in newborns
In order for the hip joint to develop correctly, you need to keep your legs apart. Disposable diapers do this perfectly. Also do the exercises described earlier. Regularly visit doctors and undergo medical examinations - these measures will allow you to detect pathology in time and undergo treatment.
Complications
Treatment started in a timely manner (up to 3 months from the moment of birth), as a rule, does not lead to the development of complications. If joint immaturity is not detected in time and not corrected, quite serious undesirable consequences can develop:
- Lameness.
- Pain in the joint when walking.
- Atrophy of the muscles of the sore leg.
- Compensatory hypertrophy of the muscles of a healthy limb.
- Poor posture (lordosis, scoliosis).
- Vertebral displacement.
In children after 2 years of age, it is usually not possible to correct disorders using conservative methods. The issue of surgical treatment is being decided.
Prevention
Correcting underdeveloped hip joint requires a lot of patience and time. To minimize the risk of developing pathology, preventive measures must be taken at the stage of intrauterine development of the child. The development of the fetal skeletal system directly depends on the mother's diet. A woman should eat 5-6 times a day; her diet should contain foods containing large amounts of vitamins and minerals, as well as Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
As a rule, it is not possible to get everything you need from food, so the expectant mother, on the recommendation of a doctor, should additionally take special complexes. The future child and mother will benefit from frequent exposure to fresh air and special exercises performed by the pregnant woman. After the birth of the baby, the following preventive measures are necessary:
- Breast-feeding.
- Free swaddling technique.
- Massage and gymnastics.
- Routine examinations by an orthopedist.
Compliance with preventive measures, and, if necessary, timely treatment prescribed by a doctor, immaturity of the hip joint in newborns has a favorable prognosis and leads to the correct formation of the musculoskeletal system.
Clinical picture
Underdevelopment of the hip joints in newborns is sometimes discovered in the maternity hospital during the first examination by a pediatric orthopedist. But unlike dysplasia, hip joint immaturity does not manifest itself with severe symptoms, especially during the first days of a child’s life. Signs of delayed ossification and improper formation of joints usually appear after 3 months. What parents or a pediatrician may notice during the next examination:
- shortening of the thigh;
- decreased muscle tone;
- asymmetrical arrangement of skin folds;
- the occurrence of an obstacle when attempting to abduct the joint;
- a characteristic click when the hip joint is abducted.
The earlier the pathology is diagnosed, the faster and more successful the therapy. Underdevelopment can be detected by external examination, complaints from parents, and functional testing. The results of ultrasound and x-ray examinations help confirm the diagnosis. Although radiography is considered the most informative method, its use is contraindicated in children under 3 months. The degree of maturity of the hip joint is determined according to the parameters of Graf’s ultrasonic classification. For example, Graf type 2a is an immature dysplastic joint.