Have you been diagnosed with hip dysplasia (Hip Dysplasia)? Then it turned out that there was no dysplasia? Or, on the contrary, did they not determine and prescribe treatment in time?
DTBS
is a congenital pathology that develops as a result of internal and external factors during pregnancy, leading to improper development of the glenoid cavity and the thigh area adjacent to the pelvis.
There are 4 degrees of severity of pathology:
- Immaturity of the hip joint
is a borderline condition, more often observed in premature infants. Characterized by a lag in the development of articular structures: Slow formation of ossification nuclei - Border angle indicators
- the glenoid cavity is beveled, the angular values are significantly changed, but there is no displacement of the head of the femoral bone, provocative tests are negative.
- the cavity is more flattened and sloping, the head of the bone moves up and out, and with provocative tests it is able to come out of the glenoid cavity.
is the most severe form, in which the femoral head moves even higher, emerging from the socket.
Diagnostics
Clinically, hip dysplasia can be suspected based on:
- Asymmetrical arrangement of femoral and gluteal skin folds
- Limitations on abduction of legs bent at right angles at the hip joints and knee joints:
- For children in the first month of life, hip abduction is limited,
- from 2 months to a year, limited hip abduction or, conversely, excessive hypermobility is characteristic.
3. Shortening of the lower extremities. 4. Excessive hip rotation. 5. Symptoms of “slipping” or “clicking” in the hip joint. 6. External rotation of the feet. 7. Palpation of the femoral head behind the posterior edge of the socket. 8. Oblique location of the genital fissure in girls.
Heterotopic ossification
Heterotopic ossification is bone formations in the soft tissues of the body, where they should not appear. The disease appears most often as a result of spinal cord injuries or craniocerebral lesions. Occurs mainly in the joints, often in the femur. The pathology begins to develop 2-3 months after the injury.
Predisposing factors
BEFORE PREGNANCY:
Gynecological and other diseases of the expectant mother
(uterine anomaly, fibroids, anemia, rheumatic disease);
Poor nutrition and unhealthy lifestyle of the expectant mother
Unfavorable environment
Heredity for dysplasia.
DURING PREGNANCY:
Pathological course of pregnancy
(oligohydramnios, threat of miscarriage, toxicosis, taking medications)
Acute viral and other infections (
ARVI, influenza, syphilis, etc.), especially from 10 to 15 weeks of pregnancy.
DURING CHILDREN:
First or difficult birth
Features of the fetus
(large size, transverse position, breech presentation, multiple pregnancy)
AFTER CHILDBIRTH:
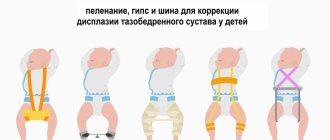
Tight swaddling
Komarovsky about ossification nuclei
Dr. Komarovsky talks about how ossification nuclei should form and develop. Most of all he talks about dysplasia, its occurrence and treatment.
First of all, the doctor says that doctors are afraid to miss dysplasia and other abnormalities in a child, so they pay excessive attention to the ossification nuclei. This is good, because it is better to find the disease in its infancy and cure it. But often, when such a diagnosis is made and doctors prescribe treatment, there is no need for this. Often the reason for the delay in ossification processes is individual characteristics, which disappear over time.
To prevent treatment, Komarovsky advises not to swaddle the baby tightly, as many do, but, on the contrary, to give more freedom to the legs and movements. In the first three months of life, swaddling should be loose, so that the legs are not pressed tightly. You can learn more about the technique using the video.
Delayed nuclear formation
Ossification nuclei should begin to appear by 3 months (0-5 mm) and by 10 months they are 9-11 mm.
If a child has only a violation of the rate of formation of ossification nuclei while maintaining angular parameters, then:
- up to 3-4 months dynamic observation;
- after 4 months - monitoring vitamin D, control ultrasound once a month, deciding on restorative treatment.
It is important to solve this problem by 6-7 months, when the baby begins to crawl. The nuclei should already be well formed by the beginning of walking (by 1 year), so that the part of the femur adjacent to the pelvis is able to withstand vertical load.
In cases of suspected THD, the child undergoes an ultrasound or x-ray. Currently, all children at the age of 1 month are recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the hip joint. The purpose of which is the early detection of improper formation of the hip joint.
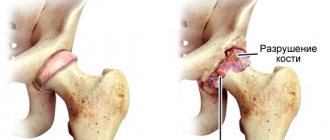
Congenital hip dislocation
is the most unfavorable variant of hip dysplasia. Its occurrence is 3-4 cases per 1000 normal births. Most often detected in the maternity hospital or in the first weeks of the baby’s life
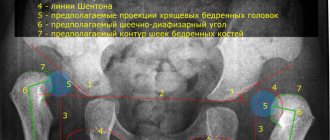
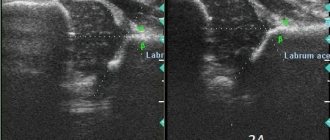
Ultrasound using the Graf method
1a and 1b. Normal hip joint. α >60, β < 55.
Type 2a and 2b (physiologically immature up to 4 months!) α=50-59, β>55. The bony protrusion is rounded, the head is centered, the cartilaginous part of the roof is wide, the bony part of the roof is sloping.
Type 2c Pre-dislocation α=43-49, β=70-77 The head of the femur is centered, but the cartilage does not cover it enough, the bony part of the roof is rounded. If the angles are outside the normal range, treatment is required.
Type 3. Subluxation. α <43, β >77. The head of the joint is located outside the glenoid cavity, the cartilaginous part of the roof is not defined. After 3 months of age, degenerative processes may begin, which will provoke coxarthrosis. Treatment is needed.
Type 4 Hip dislocation. α=43, β>77. The head is located outside the joint cavity, the symptom of “empty acetabular (articular) cavity” is noted. Treatment of such children must begin immediately.
In cases of abnormal angles according to ultrasound and/or suspicion during clinical examination, the child is sent for an X-ray examination. It is the most objective, and with a correctly performed image, it can confirm hip dysplasia, congenital dislocation and immaturity of the hip joint.
Why is the process of development of ossification nuclei disrupted?
Anomalies in the formation of nuclei in the femoral head and acetabulum appear under the following circumstances: - The mechanism is disrupted in the womb, when there are errors in the formation of bone tissue cells. The reasons are endocrine diseases of the expectant mother, infections or intoxication during pregnancy. “Most often, premature babies are susceptible to such diagnoses, since they are weaker, and not all important processes were completed in time before birth. — Underdevelopment of the nuclei can be caused by a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D, which also leads to skeletal disorders (including the hip joint).
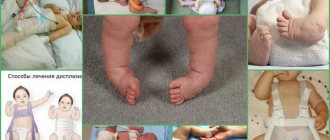
Therapy for dysplasia
Therapy should only be prescribed by a doctor, and parents must strictly follow his recommendations. Parents need to be patient and strong, because the treatment process will be long.
The process of establishing normal development of nuclei in the hip joint area includes:
- treatment and prevention of rickets using ultraviolet irradiation and vitamin D intake;
- using a splint to realign the joint;
- electrophoresis with phosphorus and calcium, aminophylline on the lower back, procedures with bischofite;
- paraffin applications;
- massage and therapeutic exercises.
After therapy, an ultrasound is repeated to assess the effectiveness of treatment. During treatment, the baby should not be sat down or placed on its feet. The earlier therapy is started, the better the result will be. Exercise therapy and massage are used to strengthen and develop muscles.
It makes sense to use exercise therapy even if the child does not have dysplasia as such, but does have a genetic predisposition. Then the exercises are performed lying down, without putting stress on the joints.
Carrying out a massage
It can be carried out even with tires, without removing them. For aplasia, stroking and rubbing are indicated.
Rules for performing massage:
- the child should lie on a changing table with a flat surface;
- cover the table with a diaper, because the child may wet himself;
- the baby’s mood should be cheerful and calm;
- the child should not be hungry;
- massage is performed once a day, a course of 10-15 procedures.
There should be only 3 courses, with breaks lasting 1.5 months.
The massage complex is selected individually by a specialist. After consultation with a doctor, the mother can massage the child independently and at home. Massage is not performed if the child has:
- heat;
- ARVI;
- hernias;
- congenital heart defects.
Preventative measures for the mother
Severe pregnancy - toxicosis, increased uterine tone, twin pregnancy - are risk factors for which the development of the hip joint slows down. To avoid consequences, the mother must eat rationally, consume vitamins and minerals. In the second half of pregnancy, control uterine tone and walk more in the fresh air.
At the beginning of pregnancy, a woman should tell her doctor if there is a history of hip disease in the family. After the birth of the child, the mother is obliged to bring the baby for regular examinations by specialists.
Statistics
Dysplasia is common in all countries (2-3%), but in different ways, depending on racial and ethnic characteristics. For example, in the United States, the likelihood of its occurrence is significantly reduced in African American children.
In the Russian Federation, in environmentally unfavorable regions, the probability of having a child with this diagnosis reaches 12%. A direct connection between the occurrence of dysplasia and tight swaddling of the baby's straightened legs has been noted.
The population of tropical countries does not swaddle newborns, they carry them on their backs, and the incidence rate here is noticeably lower.
Proof is that in Japan, for example, the tradition of tight swaddling was changed by a national project in 1975. As a result, the probability of congenital hip dislocation decreased from 3.5 to 0.2%.
The pathology most often occurs in girls (80%), a third of cases are familial diseases.
Congenital dislocation of the hip is detected many times more often with breech presentation of the fetus and toxicosis. More often the left hip joint is affected (60%), less often the right one (20%) or both (20%).
Carrying out gymnastics
You can learn to do gymnastics yourself. The conditions are the same as for massage. Exercises are done 3-4 times during the day. Children usually love this kind of gymnastics.
Any exercise should be done very carefully. Gymnastics in the absence of ossification of the hip joint includes the following actions:
- Forming the frog pose while lying on your back. Ideally, when spreading your legs, your knees should reach the surface.
- Imitate the crawling position by turning the baby onto his stomach.
- Turn the baby over onto his back again, bending his straight legs. You need to touch the baby's head with them.
- Straight, straightened legs spread to the sides.
- Pull the straight legs towards the head and spread them to the sides.
- Place the child's legs in the lotus position, placing the left leg on top.
- Alternately bend your legs at the knees and at the pelvis.
Decoding the results
An orthopedist, surgeon, or orthopedic surgeon can interpret the results. The research protocol usually contains the following information:
- the presence of pathological processes, a detailed description of the deviation.
- congenital or acquired changes inside the joint;
- condition of ligaments and nerve bundles;
- increase in the thickness of the joint capsule;
- functioning of adjacent muscles;
- features of cartilaginous structures;
- the amount of synovial fluid inside the joint.
- the presence of neoplasms, if any, their shape, structure, size and individual characteristics;
- information about the ilium, labrum and femoral head;
- metastasis of nearby tissues;
- presence of hematomas.
Please note that the result of an ultrasound examination is not a basis for making a diagnosis. If any inconsistencies or pronounced pathological processes are detected, it is additionally necessary to perform a computed tomography scan and pass various tests for laboratory research. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary (for example, if the doctor suspects a malignancy). The final diagnosis and necessary treatment are prescribed only after additional studies.
Treatment methods
Pavlik stirrups
At the age of up to 6 months, babies are recommended to wear stirrups without restricting joint mobility. After 6 months, if there is no progress in the formation of nucleoli, a fixation structure is needed - a crossbar between the separated legs. If the development of hip joints is delayed, calcium supplements, walks in the air, and sunbathing are additionally prescribed. If the child is breastfed, calcium supplements are prescribed to the mother.
Massage
Massage begins from the first days of life if examination reveals a delay in the development of the hip joint. With regular massage procedures, the pathology can disappear on its own by the age of three months.
Gymnastics
Physical therapy is also done early. This improves blood supply to the joints and helps strengthen muscles and ligaments. Exercises are done in two positions: lying on your back and on your stomach. During the treatment period, the child should not be seated or stood on his feet.
Paraffin applications
The temperature of the molten paraffin should be between 40 and 45 degrees for small children. The procedure is aimed at accelerating blood flow in the affected area. Muscle tissue develops better with thermal stimulation. Ozokerite is sometimes added to paraffin. To treat hip dysplasia, children are given a layer of paraffin from the buttocks to the foot in the shape of a boot. For newborns, the substance is kept on the body for 7 minutes. After 6 months – 10 minutes. After the procedure, a massage is performed. 20 paraffin wraps are recommended.