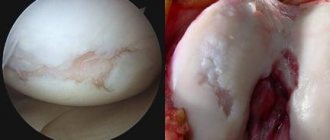
General description of the disease
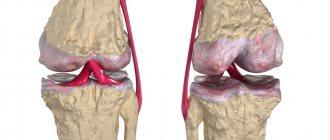
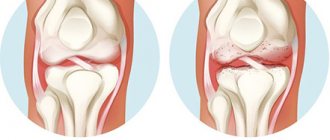
Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative joint disease in which the cartilage tissue of its surface is damaged.
This term combines a group of diseases in which the entire joint suffers (not only the articular cartilage, but also the ligaments, capsule, periarticular muscles, synovium and subchondral bone).
Forms of osteoarthritis:
- localized (one joint is damaged);
- generalized (polyostearthrosis) – several joints are affected.
Types of osteoarthritis:
- primary (idiopathic) – the cause of the disease cannot be determined;
- secondary – the cause of osteoarthritis is clearly visible and identified.
Causes of osteoarthritis:
The most common cause of this disease is considered to be various injuries. The second place in the frequency of cases is occupied by joint dysplasia (congenital changes in the joints). In sufficient quantities, osteoarthritis provokes an inflammatory process that can occur against the background of diseases of the autoimmune system (a striking example is rheumatoid arthritis), the disease can develop as a consequence of purulent inflammation of the joint (this process is mainly caused by gonorrhea, tick-borne encephalitis, syphilis and staphylococcal infection) .
Risk group:
- 1 genetic predisposition;
- 2 overweight people;
- 3 advanced age;
- 4 workers of a specific industry;
- 5 disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system;
- 6 lack of microelements in the body;
- 7 various diseases of bones and joints of an acquired nature;
- 8 frequent hypothermia;
- 9 poor environmental conditions;
- 10 previous joint surgeries;
- 11 increased physical activity.
Stages of osteoarthritis:
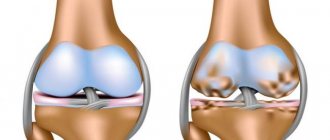
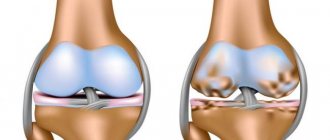
- first (initial) - an inflammatory process and pain occurs in the joint (changes in the synovial membrane begin due to which the joint cannot withstand the load and wear and tear occurs with friction);
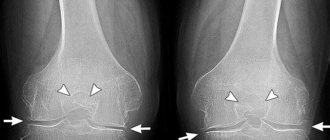
- second – destruction of the cartilage of the joint and meniscus begins, osteophytes (marginal growths of bone) appear;
- third (stage of severe arthrosis) – due to severe deformation of the bone, the axis of the joint changes (the person begins to have difficulty walking, natural movements become limited).
Symptoms of osteoarthritis:
- 1 crunch in the joints;
- 2 joint pains after physical activity (pain is especially felt in the evening or at night);
- 3 so-called “starting” pain (occurs during the start of movement);
- 4 periodic swelling in the area of the affected joint;
- 5 the appearance of growths and nodules on the joints;
- 6 disorders of musculoskeletal functions.
The purpose of the diet for arthrosis is to combat excess weight
The main enemy of joints is excess weight. Most patients suffering from arthrosis of the knee and hip joints are noticeably overweight. Reducing body weight leads to a noticeable improvement in the condition of the joints.
An effective diet for arthrosis should help reduce excess body weight, while fully providing the body with all the necessary substances.
When choosing a diet, doing cleanses or fasting, you need to be very careful not to harm yourself. Women over 50 should be especially careful about all kinds of diets. Calcium leaching can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, and potassium leaching provokes seizures and heart disease. Regarding your diet, be sure to consult with your doctor, especially if you have concomitant diseases.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis in many cases does not cause great difficulties. But there are exceptions, for example, patients with damage to the shoulder joint and symptoms of joint inflammation. Difficulties may also arise in diagnosing primary and secondary osteoarthritis, the occurrence of which is associated with metabolic or other diseases. During X-ray examination, signs of osteoarthritis are detected quickly (especially in older people) if clinical signs of osteoarthritis are present. In order to make a final diagnosis, X-ray and laboratory data are not enough. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a number of additional studies to identify the exact cause of joint pain.
Diet for arthrosis - what doctors recommend
It is believed that jellied meat or jelly prepared on the basis of bone broth is useful arthrosis This broth contains a large amount of collagen, which is necessary for the construction of cartilage and bone tissue, muscles and ligaments. Edible gelatin is also useful. The substances it contains - chondroprotectors - help restore cartilage tissue. Proteins are used to build new tissues, including the restoration of cartilage tissue covering the articular surfaces of bones. Dairy products are especially useful for restoring joints. Milk protein is easily absorbed by the body; in addition, dairy products (especially cottage cheese and cheeses) contain a lot of calcium, which is necessary to strengthen bone tissue. Animal protein is found in lean meat and fish, vegetable protein is found in buckwheat porridge, beans and lentils. To ensure that proteins are better absorbed, it is preferable to include boiled, stewed or steamed dishes in your diet.
Carbohydrates provide the body with the energy necessary for the smooth functioning of metabolic processes. But carbohydrates are different. Simple sugars (sweet and rich foods) are easily absorbed by the body and provide a quick burst of energy, some of which is stored as fat reserves. Complex carbohydrates (found in vegetables and fruits) are absorbed slowly, so they do not turn into fat. This is very important from the point of view of preventing excess weight.
Fats are also necessary; without them, metabolic processes slow down sharply. But the diet of patients with arthrosis should consist mainly of vegetable fats and butter.
Vitamins and minerals are of great importance for proper metabolism. Vitamins of group B are especially useful. Thus, vitamin B1 is found in peas, baked potatoes, whole grain bread, and beans. Vitamin B2 - in dairy products, bananas, eggs, B6 - in bananas, potatoes, chicken meat, nuts. Folic acid (vitamin B12) - in bananas, lentils, cabbage.
The best way to maintain healthy joints is to eat a diet that is low in carbohydrates, limited in protein and calcium, and rich in fruits and vegetables.
Authorized Products
The diet for osteoarthritis of the knee includes:
- Soups prepared with vegetable broths and well-cooked cereals.
- Lean meat/poultry of low-fat varieties. When processing meat, trim fat/remove skin.
- Sea/river fish (cod, flounder, tuna, hake, pollock, mackerel, blue whiting), seafood (shrimp, crabs, mussels), seaweed.
- Dishes based on natural chondroprotectors - gelatin (fruit jellies/jelly), jellied fish, various jellies, baked pig ears.
- Fresh and processed vegetables (all types of cabbage, pumpkin, eggplant, beets, green peas, zucchini, potatoes, carrots) both alone and as side dishes.
- Whole grain cereals.
- Fruits/berries, raw or in the form of decoctions/compotes, sesame and flax, bran.
- Rye/grain bread (with bran), products made from whole grain flour with the addition of bran, sesame.
- Cheeses 20-30% fat, low-fat milk/fermented milk products (yogurt without additives, acidophilus, biokefir), nuts/seeds.
- Unrefined, first-pressed vegetable oils.
- Freshly squeezed fruit/vegetable juices, rosehip infusion, green tea with lemon, still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| pumpkin seeds | 24,5 | 45,8 | 4,7 | 556 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir 2.5% | 2,8 | 2,5 | 3,9 | 50 |
| Ryazhenka 2.5% | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,2 | 54 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| sardine in oil | 24,1 | 13,9 | — | 221 |
| herring | 16,3 | 10,7 | — | 161 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
| tuna | 23,0 | 1,0 | — | 101 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| cucumber juice | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 14 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How to eat with arthrosis
- Remember that any alcoholic beverage increases your appetite.
- Serve food in small portions.
- Serve food in small plates - portions will appear larger.
- Eat slowly, chewing each bite as thoroughly as possible.
- Take short breaks while eating.
- Never eat if you don't want to, and don't force others to.
- When you feel full, stop eating immediately. Don't overeat!
- After each meal, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- After every meal, take 100 steps.
- If possible, do not eat after 7 pm.
- Watch your weight!
- Watch the chair. There should be a bowel movement every day.
arthrosis with diet alone , however, following basic nutritional recommendations and losing excess weight in combination with other therapeutic measures contributes to the overall health of the body and the improvement of the condition of the joints.
Read more about NANOPLAST forte
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for osteoarthritis of the knee excludes:
- Products with food additives (flavor enhancers, dyes, preservatives).
- Fatty meat/fish, sausages, solid animal fats, semi-finished meat/fish products, smoked meats, offal, canned fish/meat, fast food products, hydrogenated fats (mayonnaise/margarine).
- Fried foods, meat and fish broths, fatty dairy/fermented milk products.
- Puff pastry products, cakes, pastries, cream pies, semolina, chocolate, ice cream.
- Snacks, salted/pickled vegetables, salt.
- Sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol, strong tea/coffee.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
Fruits | ||||
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| baked milk | 3,0 | 6,0 | 4,7 | 84 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| Ryazhenka 6% | 5,0 | 6,0 | 4,1 | 84 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| mutton | 15,6 | 16,3 | 0,0 | 209 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fried fish | 19,5 | 11,7 | 6,2 | 206 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| white dessert wine 16% | 0,5 | 0,0 | 16,0 | 153 |
| red dessert wine | 0,5 | 0,0 | 20,0 | 172 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Exercises for osteoarthritis of the hands
Therapeutic gymnastics is an indispensable element of treatment. It allows you to reduce the symptoms of the disease and the number of medications taken.
Correctly selected exercises increase the range of motion in the joint and strengthen the surrounding muscles. The exercise program should be supervised by a physical therapist and continued at home. It has been noted that people who exercise regularly experience less pain, unlike patients who ignore physical activity.
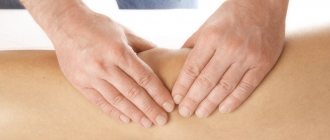
Separately, it is worth noting the use of manual therapy for arthrosis. Manual treatment is a method of physical influence on the affected areas. Special massage techniques are used to enhance the effect of the main treatment. Chiropractic care is often recommended as an addition to medication to quickly relieve pain and restore normal joint mobility.
Degrees
Orthopedists distinguish 4 degrees of the disease:
- Grade 1: there are no symptoms, but with exertion a person may notice slight pain or discomfort; all cartilage damage occurs at the microscopic level;
- 2nd degree: pain occurs not only during exercise, but also at rest; x-rays reveal a narrowing of the joint space and isolated bone growths;
- 3rd degree: destruction reaches its peak, surrounding tissues are involved in the pathological process; the pain becomes constant, and the pictures clearly show deformation, narrowing of the joint space and numerous osteophytes; Often at this stage, dislocations and subluxations of the joint occur due to weakening of the ligaments;
- 4th degree: bone growths completely block the joint, movement is impossible.
Treatment methods
Treatment of coxarthrosis is aimed at reducing pain, restoring joint fluid and cartilage, improving limb mobility and overall quality of life. Coxarthrosis is treated with a conservative or radical (surgical) method. At stages 1 and 2, conservative treatment is sufficient. Treatment of stage 3 coxarthrosis of the hip joint is possible only surgically.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of coxarthrosis inhibits the development of the disease, relieves pain, and improves mobility of the hip joint. To relieve an abscess in the joint and reduce pain, chondroprotectors, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
The doctor prescribes general painkillers (tablets, injections and intra-articular injections) or local ones (ointments, gels, rubs, patches). In the initial stages of coxarthrosis, patients are prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. At later stages, hormonal drugs are prescribed. The medicine is administered intramuscularly or directly into the joint. The last option is more effective.
In case of inflammation accompanied by muscle spasm, it is necessary to take muscle relaxants - drugs that reduce the tone of skeletal muscles. They are used in conjunction with painkillers.
Chondroprotectors contain substances that restore cartilage tissue. Getting into the synovial fluid, they stabilize its consistency and the production of cartilage cells. Drugs such as Artradol improve joint mobility, reduce pain and swelling, and stop the progression of the disease. The course is designed for 25-35 intramuscular injections administered every other day. It is combined with other treatment methods, diet and healthy lifestyle. The therapeutic effect of chondoprotectors is enhanced by drugs that improve blood microcirculation. To increase the efficiency of blood supply to articular and periarticular tissues, warming ointments are also prescribed. The dosage, quantity and method of administration are determined only by the attending physician.
Surgical intervention
For grade 3 coxarthrosis, drug treatment does not give the desired effect - the pain syndrome cannot be completely relieved with the strongest painkillers. Patients are recommended to undergo surgery. In most cases, hip replacement is performed. This term refers to the replacement of a worn-out joint with an artificial implant. The prosthesis completely replicates the shape and structure of the original joint and is capable of providing all motor functions. An artificial joint is selected individually for each patient. In severe cases of coxarthrosis, endoprosthetics is the only method of relieving excruciating pain.
Physiotherapy for osteoarthritis of the hands
For joint pathologies, several methods of physiotherapy are popular, which include:
- Cryotherapy. The procedure involves applying an ice pack to the sore joint for 10-15 minutes. After which you need to massage the hand. Cryotherapy applied to the affected joint effectively reduces pain and symptoms of inflammation.
- Thermotherapy. Therapy is carried out using heated components such as paraffin or bischofite. Also, thermal effects can be carried out due to current of different frequencies. The procedure improves metabolism, accelerates tissue regeneration, and increases local immunity.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hands
Treatment of the disease begins after it is confirmed. The diagnosis of “osteoarthrosis of the hands” is made on the basis of characteristic clinical manifestations. In case of diagnostic doubts or an atypical course of the disease, an X-ray examination of the patient can be performed. During the diagnosis, it is possible to identify certain changes in the joint - osteophytes and narrowing of the joint space.
Treatment of arthrosis is multifaceted and depends largely on the severity of the disease. As a rule, therapy is aimed at maintaining physical fitness for as long as possible and combating the pain that accompanies the disease. Today, there are three therapeutic tactics: therapeutic exercises (exercises), physiotherapy and prescription of medications.
Do you have arthrosis?
Have you tried all the remedies and nothing has helped? Are you in constant pain? And now you are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that will give you the long-awaited feeling of well-being!
An effective remedy exists. Doctors recommend Read more>>
!
Our readers recommend
For the prevention and treatment of ARTHROSIS, our regular reader uses the increasingly popular method of NON-SURGERY treatment, recommended by leading German and Israeli orthopedists. After carefully reviewing it, we decided to offer it to your attention.
reduce the severity of the inflammatory process by cleansing the body of saturated fats; prevent complications of the disease (osteoporosis) by obtaining an optimal combination of nutrients (vitamins plus minerals) from food.
It may seem that eating right and at the same time treating osteoarthritis is quite easy, but the diet for diseases of the joints (knee, hip, shoulder or various parts of the spine) should be prescribed and monitored by the attending physician.
Causes of coxarthrosis
The main reasons for the development of coxarthrosis of the hip joint primarily include hereditary predisposition, trauma, and inflammation of the musculoskeletal system. All this provokes the onset of degenerative-dystrophic pathology. In most cases, the destruction of healine cartilage is the result of the coincidence of several unfavorable factors:
- injuries, dislocations, bruises, fractures, unsuccessful joint operations;
- high physical activity (professional sports and dancing, standing work);
- congenital malformations (dislocation, joint underdevelopment);
- inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis);
- obesity, which creates increased axial load on the joint;
- metabolic, endocrine and hormonal imbalance (diabetes, menopause);
- insufficient blood flow in the lower extremities;
- unfavorable hereditary factor
With age, the likelihood of the occurrence and progression of coxarthrosis increases many times.
Dietary principles for RA
The goal of choosing food for rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce inflammation, strengthen the connective tissue of the joints, and speed up metabolism. It is important to take into account three important indicators:
- In what phase does the disease occur: active or inactive.
- What is the degree of damage to the bone and cartilage structures of the joints.
- Are there any complications? For example, deterioration of blood circulation, disturbance of protein metabolism (amyloidosis).
The general principles of developing a nutritional protocol for rheumatoid arthritis are to create a balance between the physiological needs of the body and the diet. At the same time, the consumption of certain fats and easily digestible carbohydrates is limited, food allergens are excluded, and salt intake is sharply reduced.
Many prescribed medications worsen the condition of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Small meals are required, at least five, preferably six times a day. Heat treatment comes down to baking, steaming and boiling.
When it comes to what you shouldn’t eat and drink if you have rheumatoid arthritis, doctors recommend using table No. 10 according to Pevzner. The Mediterranean and gluten-free diets follow the same principles. Types of products that contain preservatives, flavoring additives, improvers, and dyes are limited or completely prohibited. Restrictions apply to red meat, dairy products and citrus fruits.
An important aspect is caloric content. With normal weight, it should not be below 2400 kcal. If you are overweight, caloric intake is reduced by 20–25%, depending on your body mass index. Liquid intake - from 800 to 1000 ml, salt - less than 5 g. Complete refusal of salt is not recommended, as this can disrupt nerve conduction.
For clarity, let’s consider how much you need to consume the main ingredients, salt and water in the acute phase, when there is swelling, severe pain, signs of water-salt imbalance, shown:
- 1700–1800 kcal;
- fats 70–75 g, primarily vegetable;
- protein 70 g (animal - at least 60%);
- water up to one liter;
- salt 3 g.
A decrease in energy indicator is achieved by reducing the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, cereals) in favor of slow ones (fruits, vegetables, certain types of cereals). Pure sugar - no more than four teaspoons per day.
Any canned food, pickles, or pickled foods are prohibited. When the acute stage passes, the amount of protein returns to 90–100 g. It is necessary to remember: in 100 g of meat (beef) there is only 29 g of protein, and in 100 g of cow's milk there is only 3.3 g of protein. Based on these indicators, it is necessary to draw up prescriptions for rheumatoid arthritis.