Medical editor: Zemereva N.Yu., physiotherapist November, 2020
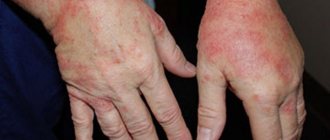
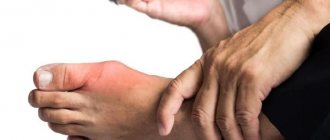
When one or more joints become inflamed and swollen, and movement in them becomes painful or impossible, we speak of a disease such as arthritis.
The causes of arthritis are varied; depending on the etiological factor, various forms of arthritis are distinguished:
- rheumatoid;
- gouty;
- reactive or inflammatory;
- psoriatic.
Proper nutrition plays a major role in the treatment of joint inflammation and helps alleviate the course of the disease.
Basic rules of diet for arthritis
The goal of therapeutic nutrition for arthritis is to normalize the immune response, reduce inflammatory reactions and restore full range of motion of the affected joint.
Nutrition for arthritis is selected by your doctor and depends on:
- forms of the disease;
- degree of joint damage;
- concomitant diseases;
- severity of clinical manifestations.
Therefore, there is no single diet for arthritis, but it is possible to determine the general principles of diet, as well as recommended and prohibited foods.
In general, nutrition for arthritis corresponds to the standard diet (general version) or treatment tables according to Pevzner No. 15, 10, 6, which are prescribed for different types of arthritis. The energy value of the diet is 2170-2400 kilocalories per day, and the nutrient content corresponds to the following scheme:
- proteins - 85-90g, of which 45-50g are animal proteins;
- fats – 70-80g, of which 25-30g are vegetable fats;
- carbohydrates - 300-330g, of which no more than 30-40g complex sugars.
If you are overweight, a hypocaloric diet is indicated, the energy value of which is 1340-1550 kilocalories per day.
Nutrition principles:
- diet; Meals should be frequent and small, up to 4-6 times a day, the last meal no later than 2 hours before bedtime. Fractional nutrition consists of meals in small quantities and saturation in small volumes, which does not overload the gastrointestinal tract and prevents overeating and excessive weight gain.
- culinary processing; Food should be boiled, baked, steamed or stewed. Dishes prepared using these methods retain their nutritional value and vitamins in larger quantities, while during the frying process carcinogens and other toxins are formed, which increase inflammation processes, and therefore pain, and also impede the functioning of the liver, whose function is to inactivate harmful substances, formed during inflammation of the joints.
- food temperature; The optimal temperature of prepared food should be between 15-60 degrees Celsius. Warm food is better digested, does not irritate the stomach lining and does not burden the liver.
- salt and liquid; Table salt is limited to 6-10g, especially for gouty arthritis. This is due to the fact that, firstly, excess salt causes blood thickening, impairs microcirculation in the joints and provokes the deposition of salt deposits on the articular surfaces. And, secondly, when you are addicted to salt, the functioning of the urinary system deteriorates, which makes it difficult to remove inflammatory mediators, toxins and other harmful substances from the body. It is necessary to consume 2-2.5 liters of free fluid per day, it increases the volume of circulating blood, reduces the concentration of inflammatory and harmful substances, prevents the deposition of salts on the articular surfaces and improves the composition of the intra-articular fluid.
- weight; The diet for arthritis is also aimed at combating excess weight, so the content of complex sugars and easily digestible carbohydrates in food is significantly reduced. The consumption of animal protein is also limited due to its high content of purines (especially with gouty arthritis) and fats. The diet should include foods containing substances that dissolve lipids. Excess weight increases the load on the musculoskeletal system, in particular on sore joints, which aggravates the course of arthritis.
- alcohol; Alcohol slows down the regeneration processes in the affected joint and increases inflammation, and also destroys vitamins and minerals, impairs microcirculation in tissues.
- vitamins; The food of patients with arthritis should be rich in vitamins, especially A, E, C, D and group B, which have a beneficial effect on the condition of the joints and normalize metabolism.
- caution in choosing products. In the mechanism of joint inflammation, the allergic component is of no small importance, so you should be careful when taking foods with high allergenic activity.
The effect of drug therapy for RA on the body
Traditional treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of both types (seropositive and seronegative), in addition to basic drugs that have a delayed effect (at the choice of a rheumatologist, gold drugs, cytostatics, antimalarials, sulfonamides, D-penicillamine), includes painkillers and hormonal drugs, which have many side effects. Proper nutrition is aimed at minimizing the harm caused by medications. On the other hand, the task of a nutritionist when selecting a menu is to ensure that the patient receives the maximum of nutrients and to exclude foods that cause an exacerbation of the pathology (more on this below).
Groups of auxiliary drugs and their effect on the body of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- corticosteroids.
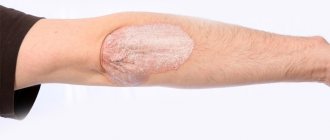
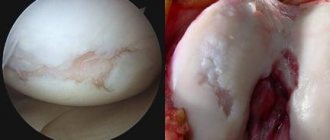
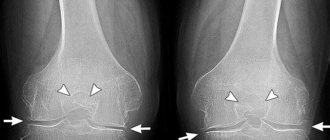
On the left is a stomach ulcer due to long-term use of NSAIDs, on the right is bone loss (osteoporosis) due to long-term hormonal therapy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Medicines in this group have a negative effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, provoking an exacerbation of the patient’s existing gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, or causing their appearance with long-term use. The diet of a patient with RA should include foods (meals) that would protect the gastrointestinal tract from such aggressive effects.
Corticosteroids
Hormonal drugs have a destructive effect on most organs and systems of the human body, especially with long-term use. However, if the patient’s arthritis activity is off the charts, such remedies cannot be avoided. In such a situation, proper and balanced nutrition comes first, helping in a number of cases (increased blood sugar levels, increased blood pressure, irritation of the gastric mucosa up to the appearance of ulcers, increased blood viscosity and increased risk of blood clots, decreased bone density) to minimize the negative impact of treatment.
On a note. Banana is a fruit that can replace most antacids (neutralize the effect of gastric juice). In addition, it contains a lot of potassium and carotene, which is good for the heart, which often suffers from rheumatoid arthritis, as well as other vitamins, macro- and microelements. A couple of bananas a day can, in a fairly short time, regulate blood pressure and sugar levels, improve mood and have a beneficial effect on the stomach. However, if the prothrombin index is high, eating them is not recommended.
Prohibited Products
The list of prohibited foods includes foods rich in purines and nitrogenous substances, which contribute to the deposition of salts on the surface of the joint. Basically, it is protein of animal origin.
Spicy and hot dishes are also excluded, since such food increases the permeability of the vascular wall, which leads to increased absorption of harmful substances. In addition, spicy, salty foods and essential oils irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and disrupt the absorption of nutrients and microelements.
You should avoid or limit your consumption of highly allergenic foods, as they activate inflammatory mediators and aggravate the course of arthritis. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fat in the diet, especially of animal origin (refractory): they contribute to weight gain, disrupt the processes of digestion and the removal of uric acid salts from the body.
In order to reduce body weight, easily digestible carbohydrates and foods containing yeast are excluded or limited.
The list of prohibited products includes:
- fresh wheat bread, rich pastries, cakes and pastries, pancakes, pancakes, pies;
- meat and poultry, especially fatty varieties;
- canned meat and fish (preservatives, flavor enhancers and other harmful and allergenic substances);
- pickles, smoked meats, marinades;
- seasonings (hot and allspice, horseradish, coriander);
- sauces based on meat and fish broth, mayonnaise, broths made from meat, fish, poultry and mushrooms (due to the high content of extractives and purines);
- black coffee, tea (due to the stimulating effect, vasospasm, deterioration of microcirculation);
- sausages, fast food;
- offal (source of hidden fats, purines);
- sour vegetables and some fruits and plants (spinach, sorrel, celery), which increase the acidity of urine, contribute to an increase in the level of uric acid in the body;
- vegetables of the nightshade family (tomatoes, eggplants, bell peppers, potatoes);
- chocolate, jam, honey, butter creams, ice cream (easily digestible carbohydrates);
- lard, margarine, beef and lamb fats;
- high-fat milk and fatty fermented milk products;
- eggs (source of cholesterol, allergen, animal fats).
What does the body of a RA patient require?
As a rule, basic therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is aimed at suppressing the patient’s overly strong immune system. Most often, the drug of choice for rheumatologists is Metatrexate. Despite good tolerance by patients and smoothed side effects against the background of a pronounced positive effect, damage is still caused to the body. In such a situation, it must be supported with nutrition - introduced into the diet:
- Diet for rheumatoid arthritis - allowed and prohibited foods, recipes with photos
- ascorbic acid (acts as a hormonal stabilizer, a strong antioxidant);
- bioflavonoids (reduce the permeability of the vascular wall, bind free radicals);
- Niacin (helps the stomach and strengthens blood vessels).
Ascorbic acid or vitamin C is found in Brussels sprouts, broccoli, bell peppers, rose hips, persimmons, sea buckthorn, jacket potatoes, peaches, apricots, fresh green peas, and sauerkraut.
Bioflavonoids of various types are found in the following products: bee propolis, medicinal herbs - tansy, cornflower, knotweed, St. John's wort, immortelle (maximum concentration in juice), berries - blueberries, red grapes (especially the skin), lingonberries, strawberries, blackberries. Green tea is also rich in them.
Niacin (niacin or vitamin B3) can be obtained from tuna, turkey and chicken meat, liver, sunflower seeds, legumes, mushrooms, wheat and buckwheat sprouts, and yeast.
On a note. Even knowing where what nutrients are found, it is difficult to create the right menu on your own. You should not experiment on yourself - seek help from a rheumatologist and nutritionist.
Authorized Products
First of all, the diet for arthritis should be rich in fresh vegetables and fruits. They alkalize urine, contain large quantities of vitamins, improve the excretion of feces and, along with them, toxins, prevent constipation and normalize weight.
It is also necessary to consume foods that are rich in polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil). They reduce the content of prostaglandins, which are produced during inflammation, reduce platelet aggregation, as a result of which blood microcirculation improves and cholesterol levels normalize.
Vitamin D prevents degenerative changes in joints, takes part in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, prevents the development of osteoporosis, and suppresses inflammation.
Calcium stimulates the growth of cartilage tissue.
Vitamin A has antioxidant properties, increasing the effectiveness of resisting prostaglandins, stimulating the growth of cartilage, and increasing the body's defenses.
Ascorbic acid is necessary for the production of collagen - a protein of connective tissue (cartilage), in addition, it has an anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effect.
Vitamins B1, B5, B6 enhance the regeneration of damaged articular surfaces.
Vitamin E is an antioxidant; it inactivates lipid peroxidation products and reduces inflammation.
The list of permitted products includes:
- bran bread, rye or dried, crackers, biscuits;
- vegetarian soups or soups with cereals and pasta;
- buckwheat, oats, rice, lentils, beans, millet, corn and pearl barley - fiber, vegetable protein, B vitamins;
- greens (parsley, lettuce, dill) – sources of vitamin C, folic acid, iron, calcium;
- carrots and beets (with caution), pumpkin, zucchini, white cabbage, cucumbers;
- lean meats and poultry without skin (1-3 times a week);
- sea fish (tuna, trout, cod, mackerel) – polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids, phosphorus, vitamin D;
- fermented milk products with reduced fat content and live biocultures - vitamin D, protein;
- bananas, peaches, kiwi, apricots, citrus fruits (with caution), apples, preferably red ones;
- raspberries, lingonberries, cranberries, strawberries (with caution), black currants, sea buckthorn - vitamins E and C;
- sunflower and pumpkin seeds, nuts (with caution);
- vegetable oil, preferably flaxseed (it is better absorbed and contains omega-3 fatty acids);
- green tea, freshly squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits;
- jelly, jelly, aspic, jellied meat from bones and joints - chondroitin, necessary for cartilage tissue.
General recommendations
The combination of exercises (physical therapy or aerobic training) with the right food and medications has the greatest effect. To improve your general condition it is recommended:
- eat regularly (5-6 times a day);
- strengthen the muscles of the limbs;
- eat plant foods;
- give up junk food.
It is recommended to add more fish products to the menu and choose fresh products. There is no fundamental difference between the diet of an adult woman and a man. A nutritionist will make an exact weekly grocery list for a child and an adult. You should not try to recover from serious illnesses on your own, since poor nutrition will cause more harm than good and lead to dangerous consequences.
If you have osteoarthritis, you need to eat a balanced diet. A large amount of calcium and phosphates in the diet helps strengthen cartilage tissue, ligaments (tendons), spine and blood vessels. In case of severe inflammatory diseases of the knee (knee), ankle, shoulder (shoulder), hip joints, as well as disorders of the lumbar or other parts of the spinal column, you should consult a doctor. Improper treatment or its absence can have a detrimental effect on certain disorders: osteochondrosis, vertebral fracture, protrusion or herniation of the intervertebral disc, gout, menopause, coxarthrosis, muscle pathologies and other bone and joint diseases.
Coxarthrosis
It is necessary to treat joints (bone joints), blood vessels, sports injuries and other pathologies after consultation with a doctor. Chondroprotectors (Chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine, Collagen and other drugs) help improve the elasticity and flexibility of joints (fingers, hands, feet, jaws), but they can be taken for various syndromes only according to a doctor’s indications.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/RU_NL5ctVs8
Proper nutrition for healthy cartilage and joints
Naturopaths and alternative medicine advocates believe that changes in diet can help relieve chronic inflammation without medication. Rheumatologists defend drug therapy and believe that diet does not have a statistically significant effect on patients. Some warn that nutritional deficiencies are a risk of developing rheumatism. The incidence of rheumatism is growing every year.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/qbs—u5gjrc
When it comes to their own health, most take the pragmatic route: try everything. They use:
- emergency medicine;
- modern surgery;
- powerful products of the pharmaceutical industry.
Many use “energy” medicine (kinesiology, homeopathy), spiritual medicine, or traditional healing systems.
Homeopathy
Rheumatology, based on scientific concepts and arguments, denies the possibility of diet influencing inflammatory rheumatism or arthrosis. A balanced and healthy diet can improve the condition of patients suffering from these ailments, however, there is no convincing evidence of the clinical effectiveness of this treatment method.
Research shows that certain foods influence inflammatory activity. For decades, research has confirmed that short periods of fasting (up to 9 days) lead to dramatic, but only temporary, relief from RA symptoms.
Most studies on nutrition and rheumatism refer to patients with RA. But the results may be transferable from rheumatoid arthritis to other forms of inflammatory rheumatism, such as psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Cooking recipes
Avocado, tomato and cheese salad Ingredients:
- avocado fruits - 1-2 pcs.;
- fresh tomatoes - 2-4 pcs.;
- garlic - 1-2 cloves;
- feta cheese or feta cheese - 100-200 g;
- lemon juice - 1 teaspoon;
- herbs, flaxseed or olive oil, salt - to taste.
Method of preparation: Carefully cut the avocado in half, remove the pit, and peel the peel. Grind the vegetable components of the dish and cheese indicated in the recipe into cubes. Add salt, chopped herbs, thoroughly washed under water, and lemon juice. Season with a small amount of vegetable oil. Mix carefully.
Brussels sprouts puree soup Ingredients:
- Heads of Brussels sprouts - 300 g;
- Potatoes - 200 g;
- Onion - 1 pc.;
- Cheese (feta or other varieties based on goat or sheep milk) - 50 g;
- Salt, ground pepper, herbs - to taste.
Method of preparation: Rinse the Brussels sprouts thoroughly under water, cut each fruit into two parts. Peel the onion and potatoes, cut into cubes. Place all vegetables in boiling water, add salt and cook for about 20 minutes. Bring the prepared soup to a puree consistency using a blender. Garnish the dish with chopped herbs and finely chopped pieces of cheese.
Oatmeal with fruits and berries Ingredients:
- Oatmeal – 150 g;
- Water or milk – 300 g;
- Fruits - banana, apple, mango, kiwi, raisins;
- Honey – 1 teaspoon;
- Berries – strawberries, raspberries.
Method of preparation: Pour Hercules flakes into boiling water or milk. Cook over low heat until done. Place chopped fresh ripe fruits, pre-washed, into the resulting porridge-like mass. Add natural honey to the dish laid out on a plate. If desired, you can use fresh strawberries or raspberries and almonds as flavoring additives.
The quantity and variety of fruits indicated in the recipe are selected according to personal preferences and availability of purchase.