Symptoms of foot arthrosis
Arthrosis of the foot is accompanied by many characteristic symptoms, but their intensity depends on the degree of arthrosis and the severity of the pathology. This disease usually develops over a long period of time and in its early stages can go undetected for a long time. The first signs of the disease - rapid fatigue when walking, a feeling of fatigue and heaviness in the legs after physical activity, crunching in the joints - are usually not perceived as something serious and remain unattended.
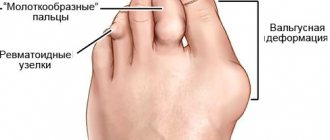
If treatment is not started on time, the condition gradually worsens. More pronounced symptoms appear that cannot be ignored: severe and prolonged pain in the legs after exercise, and sometimes at rest, “overgrowth of the bone” of the big toe, swelling and redness of the legs, calluses on the feet, gait disturbance, lameness. Aching pain can also occur as a reaction to cold water or changes in weather. All this significantly reduces comfort and quality of life, makes it impossible to fully engage in household and work activities, and limits the patient’s mobility.
Thus, the main symptoms of arthrosis:
- Morning stiffness and immobility in the joints, which goes away after a little warm-up and physical activity;
- In the later stages of the pathology, the range of movements sharply decreases, the person involuntarily tries to unload the sore foot, due to which the gait changes, the person begins to limp. This occurs due to a pronounced change in the range of motion in the affected joint and the appearance of pain when walking;
- Swelling and redness of the skin over the affected area, local increase in temperature;
- The appearance of a feeling of fatigue in the legs during exercise;
- Crunching in the foot when walking;
- Pain in the joints: at first they arise due to stress and go away after rest, but as the damage intensifies they become constant and appear even at rest;
- Aching pain in the legs as a reaction to cold or weather change;
- The appearance of corns, calluses on the feet, bone deformation and changes in the shape of the foot;
Surgery
Approaches to surgical treatment of DOAP are based on expert opinion and the results of small retrospective studies, in which the majority of reconstructive operations for DOAP were performed by creating arthrodesis according to standard approaches to internal fixation. And to date, there is no convincing data indicating the benefits of one or another form of bone fixation (internal, external or combined) in patients with DOAP of the foot or ankle. An undoubted condition for the use of these methods is the complete subsidence of the inflammatory process and osteolysis, since otherwise surgical intervention may contribute to the emergence of new foci of destruction.
Generally accepted recommendations for surgical treatment of DOAP are:
- surgical intervention is necessary in case of violation of the supporting function of the foot, which cannot be corrected with the help of orthopedic devices and shoes (exostoses, deformities);
- the primary treatment strategy for a fracture with DOAP should not differ from approaches to fractures of other etiologies;
- lengthening the Achilles tendon or gastrocnemius tendon reduces excess plantar pressure on the foot, aligns the ankles and foot in the anterior and middle sections;
- arthrodesis may be useful, despite incomplete consolidation of bone fragments, in patients with instability in the foot, pain and recurrent ulcers during conservative treatment;
- For severe forms of DOAP involving the ankle joint, surgery may be considered as the primary treatment [32].
After surgery, the patient is recommended to be immobilized for up to 7-8 months with dynamic x-ray control and resolve the issue of loading the foot without immobilization. Subsequently, patients often require the manufacture of individual orthopedic shoes.
Causes of foot arthrosis
Arthrosis of the foot often develops in adulthood, after 45-50 years. The cause of this pathology may be structural defects - for example, flat feet, due to which the load on the tissue is constantly distributed unevenly. This contributes to excessive wear and damage to cartilage surfaces, ligaments and bone structures. People with excess body weight are especially susceptible to this risk, as it leads to increased pressure on the foot.
Wearing inappropriate and uncomfortable shoes, too tight or loose, can play a big role in the development of the disease. Women often fall victim to the harmful effects of high-heeled shoes on their foot health. In such shoes, the foot does not perform a shock-absorbing function; the main support falls on the toes and metatarsophalangeal joints, which leads to arthrosis of the big toe.
Often arthrosis occurs secondary, as a result of some other disease:
- Injuries: fractures, dislocations, sprains and torn ligaments. Post-traumatic arthrosis is especially common among athletes;
- Congenital dysplasia, that is, tissue development abnormalities;
- Autoimmune connective tissue disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Untreated arthritis or other acute inflammatory diseases;
All these reasons lead to spasms of small and large muscles, deterioration of blood circulation in the legs. The cartilage does not receive sufficient nutrition, loses moisture, collapses, the joint space narrows, and typical symptoms of arthrosis occur.
Uncontrolled inflammation
Bone fracture is known to release proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α and intelekin-1β, which increase the expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) polypeptide from local cells. RANKL activates the transcription of nuclear factor-κβ (NF-κβ), which in turn stimulates the maturation of osteoclasts from progenitor cells, thereby increasing bone resorption and loss.
At the same time, NF-κβ stimulates the production of the glycopeptide osteoprotegerin (OPG) from osteoblasts, an effective antagonist of RANKL [12,27]. However, recent genetic studies in patients with DOAP have identified single polymorphisms in the OPG gene, contributing to changes in the OPG/RANKL ratio and, as a consequence, an imbalance in bone remodeling towards increased resorption [25,31].
Due to the fact that, against the background of diabetic neuropathy, a fracture of the foot bones occurs without serious pain and the patient continues to walk, repeated injuries to the affected limb occur. This leads to the constant production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn support osteolysis, completing a vicious circle [21].
In addition, peptides released from nerve endings, in particular those associated with the calcitonin gene (cocalcigenin, calcitonin gene-related peptid - CGRP), play an important role in the pathogenesis of DOAP, since it is known as a RANKL antagonist. Thus, the decrease in CGRP due to nerve damage also leads to strong expression of RANKL [22 ].
A number of researchers talk about the role of osteopenia in the development of DOAP and a higher incidence of osteopenia in patients with type 1 diabetes, although the incidence of DOAP is the same in type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Some studies have shown a higher incidence of systemic manifestations of osteopenia, in particular in the femoral neck in patients with type 1 diabetes, than locally in the feet [18,30].
Factors in the development of DOAP also include osteopenia due to insulin deficiency, conditions associated with vitamin D deficiency with or without renal failure and secondary hyperparathyroidism, when taking thiazolidinediones for type 2 diabetes and glucocorticoids as immunosuppressants in people who have had a kidney transplant and/or pancreas [26]. It is known that increased formation of advanced glycation end products, reactive oxygen species, and lipid oxidation during chronic hyperglycemia can also increase RANKL expression [22].
Degrees of foot arthrosis
There are 3 degrees of arthrosis, varying in depth of pathology and intensity of symptoms of the disease.
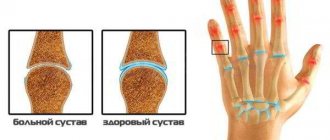
Arthrosis of the foot of the 1st degree is characterized by the absence of pronounced morphological changes in the form of destruction of articular tissues. There are no external signs of deformation. However, already at this stage the nutrition of the articular cartilage with synovial fluid is disrupted, and inflammation appears. Subjective symptoms at this stage are mild. The patient may notice fatigue when walking, aching pain with prolonged exercise.
Arthrosis of the foot of the 2nd degree is characterized by the appearance of morphological signs: the structure of the cartilage is disrupted, the synovial surfaces begin to collapse, and the joint space narrows. Joint function suffers. Pain in the legs becomes constant, more intense, and does not go away with rest or after rest.
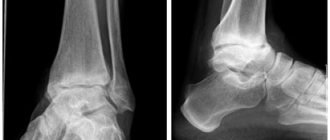
Arthrosis of the foot of the 3rd degree is an advanced pathological process; this stage of the disease is characterized by extensive destruction of structures, the appearance of bone growths, and noticeable deformation of the foot. The range of motion in the joint is lost until complete immobility. Pain in the legs becomes so pronounced that a person strives to free the leg as much as possible from the load and transfer the weight to the healthy side, which leads to lameness.
What to do with arthrosis of the feet
The danger of this disease is that in the early stages it often goes unnoticed, and in the later stages the fight against it becomes difficult. That is why it is so important to notice the first signs of arthrosis in time and prevent the development of severe irreversible changes characteristic of arthrosis of the second and especially third degree.
Remember: arthrosis does not go away on its own, and without treatment it steadily progresses. The appearance of pain and discomfort requires immediate consultation with a doctor to clarify the diagnosis and timely treatment.
The specialists of the Dr. Bubnovsky Center have accumulated enormous experience in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
The treatment of arthrosis here is approached in a comprehensive manner: Dr. Bubnovsky’s method provides not only symptomatic treatment that relieves acute pain, but also pathogenetic treatment, that is, influencing the mechanism of development of the disease and stopping its progression.
Review of ointments
- Anti-inflammatory – relieve inflammation:
- Diclofenac – emulgel, voltaren, dicloberl.
- Indomethacin.
- Ketoprofen - fastum, ketonal, bystrum.
- Dimethyl sulfoxide - dolobene.
- Nimesulide – nimulide, niz.
- Ibuprofen – relief, long lasting.
- Warming - based on irritating substances, they increase the permeability of the capillary system.
On poisons - apisatron, apiriven, virapin, voltaren, viprobel.
On the pepper there is espol.
Other warming ointments are menovazin, gevkamen, nicoflex.
- Ointments from folk herbal recipes:
Ural ointment, ointment with hops, sweet clover and St. John's wort, honey pastes
How to treat arthrosis of the foot joints
The original method of kinesitherapy used at the Center is aimed at restoring the physiological functions of the joints and activating the body’s own resources.
This happens due to a number of factors:
- Activation of muscle function;
- Relieving spasm and, as a result, restoring blood flow;
- Improved nutrition of cartilage tissue as a result of regular, proper exercise;
- Elimination of tissue dystrophy;
- Preventing or stopping the destruction of cartilage;
- Preventing the progression of arthrosis.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor conducts a complete diagnostic examination of the patient. A manual examination and myofascial testing are required to determine the degree of joint mobility impairment and characteristic pain sensations. As additional methods, the doctor may prescribe an X-ray, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the joint. These studies reveal morphological changes characteristic of stages 2 and 3 of the disease: narrowing of the joint space, deformation and destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, and the appearance of bone growths.
Having studied the results obtained, the doctor determines the degree of arthrosis, because the proposed treatment plan depends on it.
Despite the fact that the general principles of therapy are the same for all stages of the disease, the intensity of the therapeutic effect and its effectiveness largely depend on how advanced the pathological process is.
How to treat arthrosis of the 1st degree?
At this stage of the disease there are no noticeable morphological changes, but there are only prerequisites for their possible appearance in the future, which can be easily corrected.
To treat the first manifestations of the disease and prevent severe complications, an individual kinesitherapy program is drawn up, taking into account the characteristics and needs of the patient. The absence of severe pain and noticeable limitation of mobility at this stage allows you to choose active tactics and create an intensive program of exercises performed both on a gymnastic mat without additional equipment, and on special simulators.
How to treat arthrosis of the 2nd degree?
Treatment of arthrosis at stage 2 requires greater care and caution on the part of the attending physician in order to prevent the appearance of pain during the process of kinesitherapy.
The exercises are performed on the Bubnovsky multifunctional block simulator, which allows you to specifically engage the desired muscle group without provoking pain. Each lesson is supervised by a kinesiotherapist, and the technique of performing the exercises is supervised by experienced instructors.
Treatment started at the second stage helps improve impaired joint movement, relieve pain, as well as stop the progression of arthrosis and prevent a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life.
How to treat grade 3 arthrosis?
Unfortunately, at this stage of the disease, morphological changes reach significant severity and become irreversible, so a complete recovery of the patient is impossible.
Often patients suffering from grade 3 arthrosis come to the Center after surgery. However, surgery itself does not restore joint function. Proper and complete rehabilitation is necessary, including individually selected physical activity and additional procedures: massage, physiotherapy, thermal effects.
The prescribed program includes exercises and procedures that are most effective and safe at this stage. Thanks to a competent combination of these drugs with physical activity, the maximum therapeutic effect and prevention of the progression and complications of arthrosis are achieved.
ethnoscience
When carrying out complex therapy, one should not forget about traditional treatment at home. A home first aid kit includes ointments, compresses, infusions, and decoctions made from natural plant and animal ingredients.
There are folk recipes that have a therapeutic effect, restore metabolic processes in the musculoskeletal and joint structure of the musculoskeletal system, ensure normalization of blood flow in the system, and regenerate damaged tissue structures.
The following folk recipes, which will be effective together with the officially prescribed treatment, will help alleviate suffering and ensure the functioning of joints.
Therapeutic compresses:
- Grind 200 g of chalk into powder and add low-fat kefir to obtain a curd consistency. This healing mixture is applied to the affected area, covered with cling film and wrapped in an elastic bandage. The compress procedure is performed once a day before bedtime;
- Thickly cooked oatmeal helps a lot with arthrosis. After cooling to a comfortable temperature, the medicine is applied to the foot and secured in the same way as the previous one;
- to reduce swelling and eliminate heat in the joints, it is recommended to apply a leaf of white cabbage, holding it lightly in a water bath;
- a similar procedure can be performed using a fresh fern leaf;
- A compress made from dead bees is very effective for rheumatic and arthrological diseases. A tablespoon of beekeeping product waste is mixed with vegetable oil (100 ml) and sent for 2-3 weeks to a cold place with a temperature of no more than +5ºС. The medicine is applied to the affected joint 2 times a day, morning and evening. The therapeutic effect of the compress occurs after 5-6 sessions of home therapy.
Home rub:
- relieves joint pain with a mixture of propolis and olive oil, in a proportional ratio of 2:1;
- Having prepared the following recipe, it must be kept for 1.5-2 hours. Ingredients: 100 ml of 96% alcohol, 100 ml of glycerin, a tablespoon of honey and iodine. The healing mixture is rubbed in successive circular movements for at least 5-7 minutes. This traditional medicine recipe is not suitable for people with problematic skin conditions, microcracks or skin ulcers;
- two tablespoons of ammonia, two chicken yolks, a spoonful of turpentine - this is another means of treating arthrosis of the foot;
- an equally effective analgesic and decongestant treatment would be crushed horseradish root mixed with glycerin in a 1:1 ratio;
- Dandelion flowers collected in spring (200 g) are poured with a liter of alcohol-containing liquid. Leave for 3-4 weeks in a dry, dark place. You can rub your feet 3-4 times a day.
“Medicines” for internal use:
- roots and stems (100 g) of cinquefoil pour 500 ml of vodka or diluted alcohol. The medicine is infused for 3-4 weeks. It is recommended for internal use no more than 2-3 times a day, one tablespoon. The same remedy can be rubbed on sore feet;
- You can calm the nervous system and relieve painful swelling of the joints using a decoction of bay leaves. For 30 g of dry product, take 500 ml of boiled water. The medicine is infused for 2-3 hours. Take a tablespoon no more than 3 times a day. The recipe is undesirable for people with problems of the genitourinary system;
- to prepare the following recipe you will need: 10 lemons, 200 ml of cognac, 5 homemade eggs (yolks), 250 g of honey. Lemon juice is squeezed out and mixed with egg yolks. Honey and cognac are added to the prepared semi-finished product. This composition is taken for one week in equal proportions 3 times a day.
Other treatments:
- healing bath with hay dust. A liter jar of hay dust is filled with 3 liters of boiled water. After cooling to a comfortable temperature, you can take water treatments;
- A warm bath with sea salt or coniferous plants is no less effective;
- Pork lard helps well with arthrosis.
Alcohol-containing folk recipes are not recommended for people with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidney or liver failure.
When treating at home, you should not forget about joint mobility. To maintain muscle activity and healthy blood flow, it is necessary to carry out a complex of therapeutic massage and physical exercises daily.
Light circular stroking along and across the foot, shaking the foot, pulling movements of the foot up/down, left/right - all this enhances the mobility of the joint.