Gelatin - what is it?
We all come across gelatin in one way or another, even if we don’t know it. It is used to make marmalade, jelly and aspic and at the same time has many nutrients.
Gelatin is a type of protein obtained from the partial hydrolysis of collagen. Gelatin is of animal origin, as a result of which it contains important amino acids, the “building blocks” of protein.
In fact, the unique composition of gelatin is the source of all its beneficial properties, which we will discuss below.
What is gelatin?
What is gelatin made from? Do animals suffer in the production of gelatin?
Gelatin is a type of protein produced in the form of a dry powder. It is obtained from isolated and dehydrated animal parts, including skin, bones and tissue.
It doesn't sound very appetizing, but it has no taste or smell.
In cooking, gelatin is used to make jellies, desserts and candies. It acts as an adhesive. The gelling properties of gelatin actually make it very useful, as it helps form strong cartilage and connective tissue, which gives the body elasticity.
Fortunately, gelatin is present not only in desserts with a high sugar content, but also in aspic, jellied meat, jelly, bone broth, canned fish and meat.
Did you know that bone broth is a rich source of gelatin? Beef bone broth, for example, is used to make beef gelatin. For this reason, broth is also often used to combat food allergies and intolerances, digestive problems, leaky gut syndrome, autoimmune disorders and more.
Gelatin contains amino acids, including glycine, which strengthen the intestinal lining and therefore reduce inflammation. Doctors use glycine to improve digestion and skin condition, strengthen joints, cardiovascular system and cognitive health.
Where does it come from?
Gelatin can be used for weight loss, health improvement, and simply in everyday cooking for preparing low-calorie and beautiful dishes. This cheap product contains a huge amount of nutrients, a minimum of calories and has the ability to create a jelly-like consistency, which is very much appreciated by housewives.
This combination of qualities is invaluable if you watch your figure and love to eat with taste. But there is one caveat that should be warned, especially if you follow a vegetarian diet or fast. Gelatin granules are of animal origin - they are made from the bones, tendons and skins of cows and pigs. But this circumstance does not detract from the enormous benefits of edible gelatin, and there is no harm.
The fact is that it contains a lot of protein (collagen and several amino acids), which is responsible for the condition of our bones and joints, as well as skin, hair and nails.
Benefit for health
Do we need additional gelatin intake?
For most people it is truly necessary. Our ancestors' diets typically included large amounts of gelatin due to their habit of eating whole prey.
Today, the average person consumes relatively small amounts of this substance (along with other animal-derived compounds such as collagen) as we eliminate many edible animal parts. There is no gelatin in chicken breast or filet mignon, and we simply throw out the “gelling” components, for example, skin, bone marrow and tendons.
Of course, our body is able to produce many amino acids on its own, but as we age, in case of severe inflammation, intestinal disorders or weakened joints, we need an increased amount of amino acids.
As for vegetarians, they do not use gelatin at all. Vegans and vegetarians avoid consuming animal products and use agar-agar as an alternative to gelatin.
A properly formulated vegetarian diet is very healthy, but it increases the risk of a lack of essential amino acids in the body, which is associated with the refusal of sources of “complete proteins”: meat, fish, eggs and dairy products.
But gelatin has many beneficial properties:
Improves intestinal health and digestion
Like collagen, gelatin can prevent intestinal disorders and strengthen the gastrointestinal mucosa, preventing the occurrence of permeability and leaky gut syndrome.
A healthy gut lining is one of the body's most robust defense mechanisms, as it keeps food particles, bacteria and yeast within the digestive system, preventing them from entering the bloodstream and causing inflammation.
Gelatin is able to normalize the production of a sufficient amount of gastric juice, which is necessary for proper digestion of food and absorption of nutrients. Glycine in gelatin helps restore the gastric mucosa and maintain the balance of digestive enzymes and gastric juice.
Without getting enough enzymes/stomach juice10, you may experience digestive problems including nutritional deficiencies, acid reflux, bloating, intestinal upset and anemia. Older people tend to be more prone to digestive disorders because the aging process reduces the production of digestive juices.
Finally, gelatin has the ability to absorb water and other fluids, helping prevent fluid retention, bloating, and constipation.
Protects joints and relieves joint pain
Gelatin and collagen are known to help relieve symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is especially common in older people and is one of the most common causes of joint pain. With age, joints become less elastic and mobile, this is due to the destruction of collagen in them.
Gelatin and collagen help slow down chronic inflammatory responses, reducing pain and slowing the progression of diseases that can cause joint problems, such as degenerative joint disease.
Research suggests that people with osteoarthritis, joint pain, osteoporosis, and exercise-related injuries and pain may benefit from gelatin supplementation. In clinical trials, volunteers who consumed about 2 grams of gelatin per day reported decreased inflammation, joint or muscle pain, faster recovery, and even improved physical performance compared to the placebo group.
Helps improve sleep quality
Some studies have found that taking three grams of gelatin before bed helps people suffering from insomnia or poor sleep quality.
Scientists have studied the effect of gelatin on subjective sleep quality and found that it helps relieve daytime sleepiness, improve cognitive function during the day, improve sleep quality and efficiency (sleep time/time in bed), and reduce the time to fall asleep and improve the slow sleep phase. sleep without changing normal/healthy sleep architecture.
Glycine may be no less effective than traditional sleeping pills, which have side effects.
Lifts your mood and improves cognitive abilities of the brain
The amino acid glycine is considered an “inhibitory neurotransmitter.” This means that it acts as an antidepressant and sedative, but without complications or adverse effects.
Treatments using glycine and other forms of amino acids naturally increase mental clarity and reduce anxiety, as amino acids help reduce the production of “stress hormones” (such as norepinephrine) and increase the production of “happy hormones” (such as GABA).
About half of the inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord use glycine. Research shows that if this substance is not properly metabolized, the risk of developmental disorders, such as lethargy, seizures, and mental retardation, increases.
Improves skin quality
Worried about wrinkles, sun damage, age spots and other signs of aging? We have good news for you: taking gelatin (and directly applying collagen) helps improve your appearance through its positive effects on skin health and cellular repair.
Collagen is called the main building block of the skin, on which youth and a healthy appearance largely depend.
Gelatin is involved in the skin cell turnover process and also helps protect against UV and free radical damage, wrinkles, and possibly even the development of some forms of cancer.
One of the reasons why signs of aging appear is a decrease in the amount of collagen in the skin. This process begins by the age of 30 and then only gains momentum. With the loss of collagen, cellulite begins to appear and the skin becomes less elastic.
The older we get, the more necessary additional sources of collagen become to help us mask the effects of stress and poor ecology on our skin. Increasing your gelatin intake will help you naturally improve skin quality, stimulate the production of unfragmented collagen, restore skin strength, and improve the condition and appearance of hair, nails and teeth.
Helps support heart health
One of the main beneficial properties of gelatin is its ability to neutralize the effects of chemical compounds that we get from meat. Animal products - meat (chicken, turkey, beef, etc.), eggs - are rich sources of the amino acid methionine.
Despite the undoubted benefits of methionine in excess, this essential amino acid increases the risk of developing heart problems and other ailments, as it increases the amount of homocysteine in the blood. The more methionine we consume, the more other nutrients we need to combat the negative effects of homocysteine.
High concentrations of homocysteine in the blood are associated with increased levels of inflammation and the risk of developing diseases such as atherosclerosis and other forms of cardiovascular disease, stroke, cognitive impairment and bone loss.
But this does not mean that you need to give up animal products. Simply balance your diet and make sure you are getting all the nutrients you need.
Supports bone strength
The skeletal system requires a constant supply of nutrients to maintain its density and strength. Gelatin contains large amounts of substances such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, silicon and sulfur, which help protect bones from cracks, fractures and loss of density. Also, these substances are actively involved in bone restoration.
Research to date suggests that gelatin (collagen hydrolysate) may act as a safe therapeutic agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, even when used long-term in cases of chronic disorders.
Promotes satiety
A number of studies have shown that, like any source of protein, a dietary supplement with gelatin (up to 20 grams) promotes a faster feeling of fullness and helps control the production of hunger hormones.
At the moment, there is no information proving that gelatin can be used as a means to combat fat mass. However, this substance can increase the production of satiety hormones, such as leptin, and reduce the production of appetite hormones, such as ghrelin, in people who are overweight.
Kinds
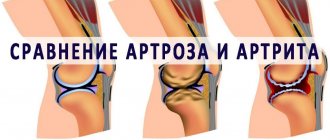
Depending on the location, arthrosis is of two types:
- joints of the hands and fingers.
- small joints of the foot, big toe.
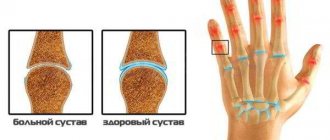
Arthrosis of the joints of the hands and fingers
Arthrosis of the hands is often found among typists, pianists, programmers, and secretaries. The disease affects the interphalangeal joints. With arthrosis of the fingers, the joint tissues dry out and crack. Subcutaneous small nodules often appear in the joints of the hands. Usually they don't disappear anymore.
As the disease progresses, the bone tissue becomes denser and growths appear on it. They cause severe pain when moving your fingers. In advanced cases, a person loses the ability to move the hand and fingers.
Symptoms of the disease: crunching in the joints when moving the fingers, pain in the fingers after exercise, seals on the joints of the fingers, swelling of the periarticular tissues.
Doctors at the Health Workshop treat arthrosis of the hand using non-surgical methods.
Arthrosis of the foot joints
Ballerinas, dancers, gymnasts, wrestlers, and jumpers are susceptible to arthrosis of the feet. The disease affects the joints of the toes. Bone growths appear on the small joints of the foot. Because of them, it is painful for a person to move his foot. As the disease progresses, the deformation of the joints is very noticeable, the person practically cannot move the foot.
Arthrosis of the big toe is the most common type of arthrosis of the feet. When the disease occurs, a “bone” forms in the area of the thumb joint. Osteoarthritis of the big toe occurs due to wearing tight shoes.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the foot: pain in the foot after physical activity, crunching in the joints when moving, an increase in the size of the joints. When walking, a person limps and rests on the outer edge of the foot.
When treating arthrosis of the foot, doctors at the Health Workshop use laser therapy, magnetic therapy and other methods.
Nutritional properties
After isolation from collagen, gelatin in dry weight consists of 98-99% protein. It contains “an unusually high amount of the amino acids glycine and proline,” which are conditionally essential and are synthesized in our bodies only in small quantities.
Gelatin contains the following amino acids:
- 21% glycine
- 12% proline
- 12% hydroxyproline
- 10% glutamic acid
- 9% alanine
- 8% arginine
- 6% aspartic acid
- 4% lysine
The most valuable amino acid we get from gelatin is glycine. Glycine, along with other amino acids, such as proline, contains collagen, which is necessary to give connective tissue strength and durability.
Fruits and vegetables: what's the difference?
Glycine is also important for removing heavy metals and toxins from the body that we get from food and the environment.
By consuming large amounts of glycine, we increase the production of glutathione, which helps cleanse the liver and blood of harmful substances.
Gelatin also contains a lot of proline, which has the following beneficial properties:
- Together with glycine, it participates in the formation of collagen and connective tissue.
- Participates in the breakdown of other proteins in the body.
- Helps form new cells.
- Supports healthy muscle tissue.
- Protects the digestive system from permeability.
- Prevents muscle loss in long-distance runners and athletes.
Composition, calorie content, balance of BJU
This product contains almost 90% protein, 0.7 grams of carbohydrates, and only 0.4 g of fat, the rest being water. Let's take a closer look at what protein components are present and how they affect the body:
- glycine - maintains normal brain function, helps maintain psychological stability;
- proline and lysine are amino acids that are involved in the process of cartilage restoration; it is thanks to these components that they have a very beneficial effect on cartilage tissue;
- Alanine - regulates energy metabolism, sugar levels, the functioning of the immune system, largely because of this substance they take gelatin and notice weight loss.
It should also be said about the rather rich content of minerals - calcium, copper, iron, phosphorus, magnesium are present here. Of the vitamins, there is only nicotinic acid.
The calorie content of the dry product is high - more than 350 kcal, but it is almost never consumed in this form. There are only 58 calories in 100 g of jelly.
How to get
The best way to obtain gelatin is to eat all parts of the animal, from nose to tail, while using bones and connective tissue to make broths and soups.
To make gelatin from bone broth at home, you need to:
- Prepare about 1.5 kg of grassland meat, 3-4 liters of filtered water and 1 tablespoon of sea salt. You can also add herbs, vegetables or vinegar to taste.
- Place all ingredients in a slow cooker and cook for at least overnight, but no more than two days.
- Using a slotted spoon, skim the gelatin from the surface.
- Leave in the refrigerator until the fat hardens completely.
- Skim off the fat and reserve it for cooking. Gelatin can be stored in the refrigerator for a week or up to a year in the freezer.
Possible harm
The only known side effects from gelatin are burping, bloating, and indigestion. But even these reactions occur quite rarely. There was a period when gelatin was considered a potentially harmful substance. It was believed that humans could become infected with animal diseases, such as mad cow disease. But these assumptions have never been confirmed by science.
Another danger is taking gelatin as a dietary supplement for too long. It can cause excessive blood viscosity and high blood pressure.
How to use (Recipes)
If incorporating animal parts containing collagen and gelatin or bone broth into your diet is not possible, powdered gelatin may be an alternative.
Using gelatin in cooking will add volume and smooth texture to dishes for a small amount of calories. It also increases the amount of protein in the dish, making it more nutritious.
Gelatin is a natural thickener, stabilizer and texturizer.
- If you do not plan to make gelatin at home, then you can purchase gelatin powder from your local supermarket or online.
- Hydrolyzed gelatin powder is added to a liquid, such as broth, juice or smoothie.
- When choosing gelatin, you can find plates, granules and powder on the shelves. It is usually soaked in water, which it absorbs and turns into a gel.
- Most versions of powdered gelatin must be kept in cold water before use and then dissolved in warm or hot water. Swollen gelatin can be easily mixed into liquid without forming lumps. Once it has dissolved in the hot liquid, you can cool the mixture so it will have a jelly-like texture.
Interesting information
Many housewives wonder how to melt gelatin in the microwave; is this possible? The process of melting gelatin is quite possible with the help of modern technologies. If you don’t have time to prepare a water bath, a microwave oven will come to the rescue. To do this, food gelatin should be placed in a special container suitable for microwaves, then pour in a little water and set the oven to minimum power for 2-3 minutes. At the same time, the answer to the question: is it possible to boil food gelatin will be negative, since, despite the variety of brands and appearance of the product, during heating it turns into a sticky, viscous mass that cannot be used in the future.
Any recipe for dishes with jelly as a base requires attention from the hostess. It is necessary to study the composition, for example, food gelatin is used, instructions for use for jellied meat or jellied meat, this means that the resulting jelly will be quite hard. In the same case, if you use sheet gelatin, the instructions for use of which allow for the preparation of desserts, then the mass will be more mobile and transparent.
Thus, whether gelatin is used in food leaves, the instructions for use of which are very simple, or in granules, the preparation process is associated with the solidification of the protein base, which allows you to enjoy dishes that are incredible in taste and appearance. Regular gelatin n 11 will help any housewife transform the menu; the instructions will allow you not to make mistakes in the proportions, so it should always be in the house.
What does gelatin taste like?
Gelatin has neither taste nor smell. Its aroma is imparted by dishes to which it is added, for example, ingredients in desserts or smoothies.
How much gelatin is recommended to consume every day?
The recommended intake of gelatin for an adult is 1-2 servings of the dietary supplement per day. A serving is typically one scoop of powder, which contains approximately 19 grams of protein. The serving is designed for 0.5 liters of liquid (to completely dissolve the gelatin, the temperature of the liquid must be at least 80°C).
Gelatin is used to prepare the following recipes:
- Healthy homemade jelly (you can use stevia or monk fruit instead of regular sugar)
- Homemade gummies (choose 100% natural juice with no added sugar)
- Quick Bone Broth with Gelatin
- Strawberry mousse
You can also add some gelatin to soups, stews, baked goods and desserts such as puddings, mousses, custards and even pie dough.
Contraindications
Despite the wide range of beneficial properties, gelatin also has a number of contraindications. You should refrain from using it if you have the following pathologies:
- cholelithiasis and urolithiasis;
- kidney diseases;
- gout;
- problems with constipation, hemorrhoids;
- increased blood clotting;
- thrombophlebitis;
- thrombosis;
- phlebeurysm;
- heart or vascular diseases.
In some cases, individual intolerance to the substance may occur.
Risks and side effects
Gelatin is well tolerated even by those who suffer from digestive disorders. However, it is best to “start getting acquainted” with this substance by using a small amount, for example, half a serving, and gradually, in the absence of an adverse reaction, increase to the recommended amount.
It is worth remembering that the highest quality gelatin and collagen are found in the bodies of animals that have been raised properly. For this reason, try to choose sustainable and organic meat products, which also contain more beneficial minerals, fatty acids (more omega-3 and less omega-6) and less harmful elements.
We recommend purchasing gelatin and collagen that comes from free-range animals that have not consumed feed containing GMOs or chemicals. It is important not only what, but also where you buy gelatin. Be especially careful when choosing beef gelatin, as low-quality product can cause you to become infected with spongiform encephalopathy, also known as mad cow disease.
- Gelatin is a type of protein made from collagen. It is present in some parts of animals and contains large amounts of amino acids, the “building blocks” of proteins.
- By dry weight, gelatin is 98-99% protein. It is believed to be unusually high in amino acids such as glycine and proline.
- Most people don't consume enough gelatin because we don't eat animal parts like skin, bone marrow, and tendons (like our ancestors did).
- Often used to relieve symptoms of food allergies and intolerances, digestive disorders, leaky gut syndrome, and autoimmune disorders, bone broth is a rich source of gelatin.
- Gelatin helps to cope with the causes of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as intestinal inflammation. It also protects joints and relieves joint pain, maintains skin elasticity, strengthens the heart and skeleton, and promotes satiety.
You can leave a request for planned hospitalization on our website and we will contact you.
Why is it useful?
The high nutritional value of the product explains the fact that gelatin is beneficial to the human body and practically does not cause harm, read more about how to take it and how it affects the body:
- Improves digestion - this is due to the fact that a dish based on gelatin granules can enhance the secretion of gastric juice, and there are no contraindications for those with high acidity. It also restores the integrity of the mucous membrane. Another favorable factor is the ability to retain water in the digestive tract, which generally has a beneficial effect on its functioning.
- Optimizes liver function - amino acids promote more efficient removal of toxins.
- Increases skin elasticity - collagen is responsible for this characteristic, the production of which in the body decreases with age.
- Improves the condition of teeth, hair and nails - this is due to the presence of keratin in the composition.
- Helps accelerate regeneration and reduce inflammation.
- Normalizes sleep and the activity of the nervous system - glycine is to thank for this.
- Accelerating metabolism and gaining muscle mass - it is for this property that gelatin granules are loved in the sports community; in combination with honey, they are used as an alternative to expensive supplements.
Nutritionist's comment:
This inexpensive protein product has justifiably earned a reputation as a good assistant in losing weight and improving health. It is advisable to introduce it into your diet if you want to enrich your menu with low-calorie ingredients with high biological value.
Reviews:
Margarita
I got into the habit of eating a portion of jelly every day. I cook it myself using food grade gelatin. From time to time I make compresses from it. I can boast that my knees have stopped hurting and the crunching has disappeared.
Valeria
I didn’t believe that gelatin could help; the treatment turned out to be very cheap. But I tried it anyway. I drank for 3 months with short breaks. I work tirelessly (they were sick), I even became visually younger. I only regret one thing: why I didn’t start earlier.
You may be interested in: Wormwood: uses and contraindications.
Read about: calcium for children.
Features of use
In any case, the main thing is not to overdo it. Before starting gelatin therapy, you need to figure out how to drink and how long to continue the course. Otherwise, side effects are possible in the form of: difficulties with bowel movements, bloating, weight gain.
Recommended admission rules:
- treatment courses are carried out over 10 days at similar intervals;
- to avoid constipation, the diet is enriched with foods high in fiber and stimulating stool loosening: dried apricots, carrots, kefir, cabbage, apples, prunes, seaweed;
- the daily dose should not exceed 10 grams;
- For better absorption of collagen protein, the jelly-like substance is not chewed, but dissolves.
Treatment with gelatin at home begins when:
A frank interview with a German rheumatologist after working in Russia for Russia Today
Dr. Klaus Maier
Head of the Department of Joint Surgery at the Clinic for Traumatology, Orthopedics and Sports Medicine Bonn
Read the interview
“Russian medicine is a mystery to me. They treat joints for years instead of 3 weeks and reject new effective remedies!” Click the “Read interview” button
- painful syndrome and aches in the joints;
- a kind of crunching sound during physical activity;
- joint stiffness and decreased range of motion.
The product is indicated for use in cases of fractures, cracks, and dislocations of bones that result in injury to cartilage tissue. As a preventive measure, it reduces the risk of developing pathologies associated with degenerative changes in cartilage.
Attention! When using gelatin, it should be taken into account that low stomach acidity is not the best environment for absorption. Experts recommend parallel use of ascorbic acid preparations.
Contraindications for use of the product:
- formation of stones in the kidneys, ureter, gall and bladder, bile ducts;
- diseases of the stomach and esophagus;
- tendency to form blood clots;
- increase in circulating blood volume;
- inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- heart failure;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- individual intolerance to the component.
The use of gelatin should be perceived as an additional method in the complex treatment of joint diseases.