A lot of complaints are received from patients about different types and localizations of pain. Many people say that the lower back hurts when you sit, but when you get up on your feet or are in a lying position, it all goes away without the use of medications. This is a very peculiar clinical symptom. It may indicate the development of numerous pathological processes. We will talk about most of them in today's article.
Let's start with the fact that lower back pain in a sitting position can occur with osteochondrosis. This is a degenerative dystrophic process that affects the cartilage tissue of the spinal column. To understand the mechanism of development of pain syndrome, we suggest finding out how everything is arranged and works. The same knowledge will help to understand why similar unpleasant sensations arise in other pathologies.
So, the human spinal column is conventionally divided into 5 sections. The first is the cervical one, it consists of 7 vertebrae. The second is the thoracic one, there are as many as 12 vertebrae and the costal arches are attached to them (using joints). The third is lumbar. It is the most loaded, therefore it consists of the five most massive vertebral bodies. Next come the sacrum and coccyx. Both of these sections in an adult are single bones. Each of which consists of five separate vertebrae.
Between the coccyx and the sacrum there is a joint that provides minimal mobility of the terminal part of the spinal column. Due to this, the tailbone may deviate slightly back and forth. The pelvic bones are attached to the sides of the sacrum using the iliosacral joints. Thus, the maximum shock-absorbing load from the lower extremities falls here.
Between the sacrum and the lumbar region there is the conditional center of gravity of the human body. This is the L5-S1 intervertebral disc. It is quite massive, but quickly undergoes degenerative dystrophic changes. This is due to the physiological characteristics inherent in all intervertebral discs. The fact is that they do not have their own blood vessels.
Their nutrition and supply of fluids is possible only through diffuse exchange with surrounding tissues. Most of the nutrition is carried out by the paravertebral muscles. They support the spinal column in an upright position and allow for many movements. When they contract, they release fluid enriched with oxygen and nutrients. And when relaxing, they learn what the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs releases when compressed.
Osteochondrosis, which in most cases is the direct cause of the development of pain, is a consequence of a violation of the process of diffuse nutrition.
Also, the stability of the spinal column is ensured by the ligamentous apparatus. It includes the short transverse and yellow ligaments. They are located between adjacent vertebral bodies. Long longitudinal ligaments (anterior and posterior) run from the coccyx to the occipital bone. They provide overall stability to the position of all vertebral bodies.
Between the individual vertebral bodies there are intervertebral joints (facet, uncovertebral, facet, etc.). Inside the spinal canal, formed by the vertebral bodies together with the arcuate processes, there are segments of the spinal cord. They are clothed in hard shells. Paired radicular nerves depart from them. These structures branch and form nerve plexuses, large nerves responsible for the innervation of certain areas of the body.
For example, in the lumbar region there is the lumbosacral nerve plexus. A number of large nerves depart from it: inguinal, iliac, sciatic, femoral, subcutaneous lateral, etc. Below, in the area of the coccyx, where the terminal filaments of the spinal cord exit, is the cauda equina nerve plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of the pelvic organs, ensures the functionality of the lower extremities, etc.
Damage to any of these structures of the lumbar, sacral or coccygeal parts of the spinal column entails the development of serious pain syndrome. The intensity of its manifestation when in different body positions indicates a particular disease. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to make a diagnosis without medical help. In most cases, serious differential diagnosis is required. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you visit a doctor as soon as possible. For these purposes, it is better to make an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist.
In Moscow, experienced doctors provide free consultations to patients in our manual therapy clinic. A vertebrologist, orthopedist, neurologist, and chiropractor are at your service. A full inspection will be carried out. The doctor will give you a preliminary diagnosis and tell you what additional examinations may be required. Then he will give individual recommendations for complete treatment.
Consequences of sedentary work
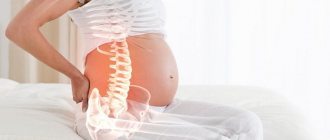
From all sides we are bombarded with information about how harmful physical inactivity is. And the body itself signals us about this: the back and neck hurt from sedentary work, the legs swell, and chronic fatigue syndrome develops. Scoliosis, osteochondrosis, protrusion and hernia of the spine - all these are faithful companions of a sedentary lifestyle. Stagnation in the pelvis from prolonged sitting leads to varicose veins; coxarthrosis of the hip joints often develops with age. During pregnancy, sitting on a chair causes especially many troubles - the lower back and tailbone ache.
How is the treatment carried out?
Before carrying out treatment, it is necessary to establish why there is pain in the lower back and it hurts to sit, what disease causes the appearance of such a symptom. If your lower back hurts while standing and sitting, then most likely this is a manifestation of osteochondrosis, complicated by protrusion of the intervertebral discs. The root nerves and their branches are pinched. The muscle fibers are also overstrained compensatory. Microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid is blocked. Ischemia begins to occur.
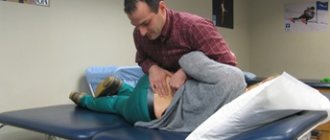
In such a situation, it is correct to begin treatment with several sessions of manual traction of the spinal column. This procedure allows you to restore the normal height of the intervertebral spaces. Blood supply to all tissues improves, lymph circulation increases, and regeneration processes begin.
But this is not enough to completely restore the health of the spinal column. As the acute pain syndrome is eliminated, the doctor will develop an individual set of treatment procedures for the patient. It may include the following types of impact:
- osteopathy is necessary for the complete restoration of microcirculation processes of blood and lymphatic fluid in the lesions;
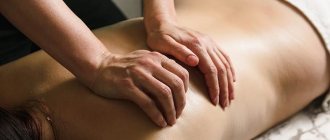
- massage normalizes muscle tone in the lumbar region, improves their functioning, helps accelerate the processes of diffuse nutrition of the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral discs;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy improve the condition of the muscle frame, increase blood flow, increase adaptive resistance to physical and shock-absorbing loads;
- physiotherapy and laser treatment accelerate the recovery process and trigger metabolism at the cellular level;
- Reflexology allows you to use the hidden reserves of the human body and start the process of natural regeneration of damaged tissues.
If you are bothered by pain in the sacrum while sitting, then you do not need to endure it. Contact our manual therapy clinic for a free initial appointment with a vertebrologist. The doctor will develop an individual treatment plan for you.
Why is this happening?
A mandatory attribute of sedentary work is a chair or office chair. 99% of them have a horizontal seat , which prevents the pelvis and spine from taking their natural position and independently maintaining a straight back position. According to the biomechanics of our body, when sitting on a chair with a horizontal seat, a rotation moment arises in the pelvis, which tends to tip our pelvis back. As a result, the lower back, and behind it the entire spine, curls up and the back takes on the shape of a “banana”. This is the root of all the problems listed above that arise from sedentary work. It manifests itself simply: first, after sitting for a long time, when getting up from a chair, local pain is felt in the knee or back. But these are just flowers. Over time, it becomes impossible to sit in a chair - the lower back or even the back in general hurts.
Note that buying a “sophisticated”, supposedly anatomical, office chair does not help to minimize the harm from sedentary work.
Even if the back is kept straight thanks to the bolsters under the lower back and neck, but the seat of the chair remains horizontal (parallel to the floor), then the moment of rotation in the pelvis does not disappear and tension in the pelvic-lumbar region remains.
Maximum back support is a disservice. Yes, while you are sitting on such a chair, you may be comfortable and sedentary work will become a little more comfortable for a while. However, if you remain in such a relaxed, unnatural position for a long time, the deep back muscles lose the habit of maintaining balance. After sitting on such a “throne,” the muscles do not stabilize the spine well for the rest of the day. In such a “loose” state, any simple movements, be it walking, jogging, walking back from the store with bags in hand, washing floors, or even working out in the gym, gradually lead to protrusions and hernias. Therefore, even using such chairs, it’s only a matter of time before you get back pain (for example, in the lumbar region) both while sitting and after.
What to do if you have lower back pain when sitting
The first thing to do if it hurts to sit and your lower back hurts is to take a horizontal position. Lie down on a hard, flat surface and try to relax the overly tense muscles in your lower back. They can block blood supply, drainage of lymphatic fluid, etc. All of this causes quite a lot of pain.
If you have constant pain in the lower back when you sit, then you need to see a doctor (for example, an orthopedist or vertebrologist). He will conduct an examination and, based on the results of functional diagnostic tests, will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis. Depending on this, he will prescribe a number of additional examinations:
- X-ray image of the lumbosacral spine (on it you can see both signs of damage to the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies and their processes, as well as a decrease in the intervertebral spaces, which indirectly indicates the development of osteochondrosis and protrusion);
- X-ray of the iliosacral joints and hip joints (to exclude deforming osteoarthritis);
- diagnostic blockade of the iliosacral joint;
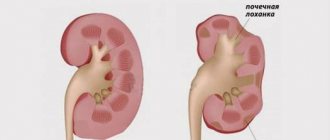
- Ultrasound of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and kidneys;
- MRI of the lumbosacral spine (shows the real current condition of all soft tissues, such as cartilaginous intervertebral discs, ligaments, muscles, tendons).
After all of the above examinations, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an individual treatment plan.
What to do with sedentary work?
The only option that comes to mind is to find another, more flexible job. Or try to compensate as much as possible for the harm from sitting with physical activity outside of the working day. We try to sit less, walk more, and sign up for fitness classes. Some even take radical measures - they go to the countryside and engage in subsistence farming.
Until the consequences of sedentary work have reached a critical scale, a person is temporarily helped by prevention in the form of exercises in the morning or simple gymnastics in the office right at the workplace. When a person, as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, encounters serious back pain, then, at best, he follows the advice of trainers and doctors, and pumps up his back by performing special exercises. But, alas, these measures do not eliminate the harm from sitting on a chair, but only partially compensate for it.
When it comes to improving nutrition, it is obvious to us that in addition to adding healthy natural products, it is important to first eliminate the most harmful ones - fast food, fried foods, sugar. The same applies to the musculoskeletal system: in addition to playing sports, it is important, first of all, to exclude from your daily life sitting in a crooked, non-physiological position.
Yogis know that sitting on a chair is unnatural and ideally prefer to do important things in the lotus position. But does this mean that we should all immediately sit on the floor and cross our legs?
Diagnostic and treatment methods
If your tailbone hurts when you sit and stand up, a comprehensive examination is necessary. The following are used today as effective diagnostic methods:
- X-ray
: allows you to identify pathologies and injuries of the coccygeal bone; - ultrasound examination: necessary to identify pathologies of organs and soft tissues of the pelvis;
- examination of the intestines using endoscopic and non-endoscopic techniques: this is an effective way to confirm the diagnosis with a proctologist;
- tomography: necessary for a detailed examination of already identified pathologies.
A patient with this symptom requires consultation with a number of specialists: proctologist, surgeon, neurologist, gynecologist
or
urologist
. How to treat the tailbone, which hurts when you stand up and sit, the doctor decides based on the diagnosis. The patient may be prescribed the following treatment methods:
- Medication: in this case, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling and spasms.
- Physiotherapy: gentle pressure on the muscles improves blood supply to the coccygeal area and speeds up recovery.
- Massage: aimed at improving blood circulation, suitable for chronic pain.
- Exercise therapy: helps not only to improve the patient’s condition, but also to prevent relapse of the disease.
- Surgery: performed only in extreme cases, when other treatment methods have not brought the expected result over a long period of time.
It is worth knowing that if the tailbone hurts when you sit and stand up, especially severely, and the disease is in the acute phase, some treatment methods are contraindicated. Therefore, using them without the knowledge and consent of a doctor is strictly not recommended.
Sedentary work in a natural position
As we have already said, problems from sedentary work arise due to the fact that sitting on a regular chair with a horizontal seat does not allow the body to assume its natural position. For more information about the biomechanics of the sitting process, watch our video.
The Smartchair company studies the geometry of natural human postures to create the right chairs. The full range of Smartchairs is here. Thanks to the inclined seat, the right chair does not prevent the spine from taking its natural position and the muscles easily keep the back straight during sedentary work.
There are only two categories of proper chairs - saddle chairs (simulating sitting on a horse) and knee chairs (an inclined seat with emphasis on the knees).
Both types of chairs provide an obtuse angle between the body and the hips, allowing the body to assume its natural position during sedentary work. Read detailed instructions on how to choose the right Smartchair here. Elimination of the key negative factor of sedentary work - a horizontal chair - leads to the disappearance of back pain, legs stop swelling, and beautiful posture is quietly formed. Due to the fact that the chest expands on such a chair, excess pressure in the abdominal cavity disappears, digestion improves and excess weight disappears. Thus, the harm from sedentary work is reduced by 80-90%! (4-5 times).
To personally feel the convenience and joy of sitting on a Smart Chair, come to our brand stores in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Do exercises
Here are three simple exercises:
- Bird. Stand straight, bring your legs together, leave your arms free along your body. Rise on tiptoes, move your arms back and bend your back forward. Spread your wings - turn your hands with your palms facing out. Smoothly return to the starting position.
- Pendulum. Stand up straight, clasp your fingers in front of you - let your palms face outward. Raise your arms up and stretch. Make several tilts alternately left and right - swing the pendulum. Move only in the thoracic region - the pelvis should be motionless. This exercise can also be done while sitting.
- No problem. Clasp your hands and place them on the back of your head. Press your hands on your head and allow your neck to fall smoothly. Stay in this position for 10 seconds. Gently try to push your arms out while smoothly lifting your head. You can do this exercise with your eyes closed.
If gymnastics does not help and the pain does not subside, consult a doctor: a therapist or an orthopedist. Get examined - sedentary work provokes the development of scoliosis and osteochondrosis, leads to the development of “tunnel syndrome” and other health problems. Keep your body in good shape so you can continue to lead your usual lifestyle and work at the computer.