Approximately 70% of people over 45 years of age complain of back pain. Discomfort in the spine is considered the second reason after respiratory diseases, forcing Russians to see a doctor to restore their ability to work.
Therefore, the question remains: why does pain appear, what can it be like, and what can be done to prevent the development of spinal diseases?
Why does pain occur?
The most common reason for back pain and difficulty walking, sitting or lying down is considered to be dystrophic and degenerative changes occurring in the spine. The pathological process may affect the intervertebral discs or ligaments, which causes pinching or irritation of the nerves, resulting in back discomfort.
Another reason is spinal deformity. This often occurs due to a disorder in the biomechanics of the step, which is caused by impaired shock absorption of the foot and different lengths of the limbs.
Dorsopathy often appears due to poor posture caused by a disorder in the stabilization of muscle function. Any pain negatively affects muscle function, which leads to local weakness or hypertonicity. This upsets the stabilization of the spine and contributes to the development of various pathologies.
Another factor in the development of back pain is blocking of the intervertebral joints, which impairs motor function. Dorsopathy also appears when intervertebral hernias appear, which compresses nerve fibers and leads to paralysis.
Discomfort in the back can be caused by a wide variety of diseases that indirectly affect the spine, starting with lung cancer and ending with infectious lesions of the vertebrae. Often, the occurrence of back pain is caused by pregnancy, psychological disorders, and obesity. Other factors are nervous strain, stress and poor nutrition, which leads to the leaching of calcium from the body.
External causes and risk factors
External causes of acute back pain include spinal injuries, which often occur in accidents or falls. But most often, acute or chronic back discomfort appears due to professional sports activities. According to statistics, 10% of all injuries in athletes are associated with the spine.
Weightlifters, football players, wrestlers, skiers, gymnasts and others are at risk. The cause of damage is overloading the spine, ignoring pain, and improper lifting of weights.
Other external reasons include sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow or mattress, muscle fatigue. Back pain also develops with a lack of physical activity and prolonged work in a monotonous position.
The main risk factors causing back pain are:
- Sedentary lifestyle or improper muscle load;
- Wearing shoes that do not support the foot;
- Driving for a long time, sitting or standing;
- Age over 35 years;
- Poor stretching or no stretching at all.
- Bad habits.
- Insufficient rest.
- Improperly carrying a bag or briefcase.
- Genetic predisposition.
Possible causes of lower back pain when bending over
There are many reasons for worsening pain in the lumbar region when bending the body. First of all, pain in this area differs into primary and secondary.
Directly primary lower back pain occurs due to soft tissue diseases or problems with the spinal column in this area. It can be:
- lower back injuries (blows, falls, bad turns, sprains);
- intervertebral hernia;
- displacement of the vertebrae or intervertebral disc;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region, radiculopathy;
- myositis, tuberculosis, lumbar polio.
Secondary pain is reflected from other organs, which are thus transmitted to the lower back. In this case, we may be talking about diseases of the genitourinary system and intestinal tract.
Pain in the lower back when bending over can also be a warning about an unhealthy lifestyle or inadequate physical activity in this area. It may be associated with prolonged stay of the body in one position (sedentary work, long periods of driving), lack of sports activity, or, conversely, overwork in the gym.
How does back pain manifest?
Spinal diseases often appear at a young age. Therefore, several years may pass from the onset of the disease to the appearance of the first signs.
The most common symptoms of dorsopathy are numbness of the arms or legs, nagging discomfort in the lower back, dull or sharp pain.
If the cause of back pain lies in changes in the spine or pinched nerves, then this will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Discomfort in the lower back, neck, shoulder blades;
- The pain often radiates to the sternum;
- Headache;
- Pain worsens with movement, lying or sitting;
- When the nerve roots are compressed in the damaged area, numbness and muscle weakness occur.
If acute back pain develops when bending and turning along with lifting weights, is accompanied by weakness in the leg, and intensifies with tension, coughing and sneezing, this indicates the presence of an intervertebral hernia. And sudden acute discomfort in the lower back that appears after bending forward and turning indicates radiculitis.
Pain in the shoulders, back of the head, or when turning the head indicates cervical spondylosis. Poor chest mobility and discomfort during deep inspiration indicate ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Indirect signs accompanying back pain:
- Leg cramps;
- Discomfort in the back when standing for long periods of time;
- Tension in the lower back;
- Increased pain when sitting;
- Feeling of numbness in the legs;
- Gastrointestinal diseases that cannot be treated;
- Pain in the hip joints and knees;
- Discomfort in the pelvis and coccyx, aggravated by sitting or being in a sauna;
- Impotence in men;
- Problems with conception and menstrual cycle in women.
Non-mechanical spinal injuries
However, in some cases, joint displacement can occur without mechanical damage. For example, in some cases, pain in the middle of the spine is an indication that the cause is somewhere in front of the spine. In such cases, diagnosis is not an easy task, since the cause of pain can be an illness in any of the organs located under the ribs.
In addition, one of the causes of back pain can be strong worries and experiences, which cause involuntary muscle contractions. The muscles are compressed into a “lump”, as a result of which a spasm occurs, and the muscle tightens part of the back. With such spasms, a person unconsciously begins to slouch, causing the back to bend, forming an angle with the apex in the middle section of the spine. It is at this point that the greatest static and muscle pressure falls. The pressure causes the joints to shift, which in turn causes an effect that doctors call a “spinal block.” It is this effect that causes pain, which can be different in nature:
- sharp, sharp, almost unbearable pain between the shoulder blades;
- aching pain that affects not only the middle spine, but also spreads higher and lower in the back;
Diseases accompanied by back pain
There are a lot of diseases that contribute to the development of dorsopathy, starting with damage to muscles and bones, and ending with pathologies of internal organs. Most often, an unpleasant symptom is provoked by osteochondrosis. The disease is characterized by changes in the intervertebral disc, joints, body, ligaments or muscles of the spine, which leads to the occurrence of radicular syndrome.
If your back hurts and it’s hard to stand for a long time, then the reason may lie in changes in the vertebral joints (spondylosis), problems with posture (stooping, scoliosis), displacement of the vertebrae (listhesis), or inflammation of the vertebrae.
Other diseases that cause back discomfort:
- Radiculitis is a spasm of the spinal muscles.
- Bechterov's disease is a systemic disease of the joints, leading to immobility due to ankylosis.
- Spondyloarthrosis is the destruction of the cartilage of the intervertebral disc.
- Protrusion is excessive mobility leading to wear and tear of the vertebrae.
- Arthritis is a malnutrition of the intervertebral discs.
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic process in the bone marrow or bone.
- Pancreatitis is damage to the pancreas.
- Spinal stenosis is compression of the lower spinal nerves that innervate the legs.
- Facet syndrome is a lesion of the intervertebral joints.
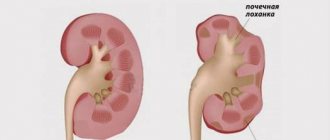
Pain above the lower back can cause cardiovascular diseases, disruption of the digestive system, tumors, including malignant processes. Discomfort below the lower back is often provoked by diseases of the genitourinary organs, such as pyelonephritis, cystitis and others.
Back pain is caused by diseases of the lungs (pleurisy), liver (cholecystitis), and diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis, cancer). Unpleasant sensations in the spine can provoke metabolic disorders, in which Paget's disease, hyperparathyroidism, and osteoporosis develop. Back pain is also present with tuberculosis, depression, and myofascial syndrome.
The whole truth about pain in the spinal column
Any pain is a signal of some pathological condition that has arisen in the body. But, as you know, in order to begin to treat something, you must first find out the underlying cause of the clinical symptoms. That is why, when the first symptoms appear in the form of pain in the spinal column, you need to seek qualified medical help.
Why does the spinal column still hurt?
All problems with the spine will make themselves felt by pain. Pain is considered a specific clinical syndrome that can occur for various reasons. These include the following pathological conditions:
- osteochondrosis of various parts of the spinal column, in which intervertebral discs, as well as the adjacent upper and lower surfaces of the vertebral bodies, are involved in the pathological process;
- spondylosis, which in other words can be called arthrosis of the facet and other joints connecting the elements of the vertebrae into a single whole;
- inflammatory diseases of the vertebrae (spondylitis);
- ruptures of fibrous rings;
- pain in deep muscles;
- narrowing of the lumen of the spinal canal.
Also, similar pain of varying degrees of intensity and severity can occur with ankylosing spondylitis, osteoporosis, malignant neoplasms, infectious diseases of the spine, various mental and somatic diseases.
What symptoms can characterize a pathological process that has arisen in the spine?
With the above diseases of the spine, the patient may be disturbed by various subjective sensations. Typically these symptoms include:
- nagging pain when bending or squatting, a feeling of stiffness in the spine;
- non-acute pain that occurs in certain areas of the spine, especially during palpation. Most often in such cases, discomfort sensations are localized along the spinal column, without going beyond its limits;
- severe, shooting pain in the back;
- pain in the lower back during an artificial increase in the severity of lumbar lordosis;
- pain in the body or spinous process of one or more vertebrae, which appear only after pressing on them;
- dull pain localized in the lumbosacral spine.
For each case described above, therapeutic measures are selected individually.
How can pathological conditions arising in the spinal column be correctly diagnosed and treated?
To understand the causes of pain in this area of the human body, you need to thoroughly know the anatomical, physiological and other features of the spinal column and the soft tissues surrounding it. Only qualified doctors can handle this task efficiently, and you should contact them if any of the presented types of pain in the spine occur.
The doctor will carefully question you, perform an examination, conduct a palpation examination of the affected bone and cartilaginous structures or soft tissues, and also prescribe additional laboratory and instrumental research methods. Usually, in addition to clinical research methods, radiography of the spinal column and chest organs is carried out, which in special cases can be supplemented with more modern studies in the form of computer or magnetic resonance imaging. They also take blood and urine tests to determine acute phase indicators (markers of inflammation), and perform an ultrasound examination of the internal organs of the human body.
As for treatment, it can be conservative, performed with the help of medications (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs), as well as surgical (more radical).
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Stitching pain in the back
Most often, stabbing pain in the back develops due to damage to the nerve roots. This occurs in the presence of compression radiculopathy, provoked by stenosis of the spinal canal or intervertebral hernia.
Also, stabbing pain in the back can appear due to indirect diseases that cause discomfort in the spine. For example, for gastrointestinal disorders, kidney or gallbladder diseases.
The stabbing pain often intensifies during rest and may subside during exercise, and vice versa. Sometimes the discomfort becomes more pronounced at night, which makes sleep incomplete.
Dull pain
This type of pain is often chronic. Discomfort can appear in almost any part of the back and radiate to the lower limbs.
Dull back pain is very debilitating, making it difficult to carry out everyday activities. Mild discomfort in the spine can bother you for a long time and be difficult to treat.
The causes of dull pain may lie in trauma, spinal stenosis, rheumatism, damage to the intervertebral disc, curvature of the spine. This type of pain is also characteristic of glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. These diseases of the genitourinary organs are often accompanied by discomfort in the spine.
Acute back pain
Lower back pain is not the body's only reaction to pathology. Other symptoms depend on the underlying disease. They can be classified as follows:
- In diseases of the spine (curvatures, injuries, osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis), crunching, clicking, limited mobility, numbness of the limbs and tingling are observed.
- Spinal infections - pain on palpation, swelling and symptoms of general intoxication of the body in acute cases (temperature, chills, fever).
Acute back discomfort develops due to a new injury or reappearing pathology. Often its appearance is promoted by problems with ligaments or muscles, lifting heavy objects, staying in one position for a long time, or an unsuccessful turn.
Typically, acute back pain is sharp and very severe. But most often it appears due to injuries or fractures.
Also, acute discomfort is caused by diseases of the spine or a violation of its natural “geometry”. This can cause pinching of the roots, which contributes to the appearance of acute discomfort. Acute pain usually lasts up to 6 weeks.
Prevention of back pain
To prevent the development of dull, sharp, stabbing or sharp pain in the back, you should adhere to a number of preventive measures. So, doctors recommend doing exercises every morning, which will help maintain the muscle corset.
Those who lead a sedentary lifestyle, work in an office, sit a lot or drive, need to take short and frequent breaks once every 1 hour. You can stretch and walk for 5 minutes.
It is equally important to sleep on a properly selected orthopedic mattress and pillow. After all, every person spends a third of their life sleeping, and an orthopedic set helps maintain the vertebral curve in the correct position.
Doctors also recommend controlling weight, because obesity is always accompanied by back pain. To maintain beautiful posture and strengthen the muscle corset, it is recommended to play sports, dance or visit the pool a couple of times a week.
You also need to watch your diet. The diet should be balanced, healthy, rich in vitamins, microelements and calcium. Also, to prevent back diseases, you need to take professional massage courses 1-2 times a year.
The cause of all diseases lies in the spine, Hippocrates believed. What can we say, if in 70% of cases pain in the heart (the main “engine” of the body) is an echo of diseases of the skeletal system.
How to understand that your back is “asking” for help, what leads to deformation of the intervertebral discs, what rules should become a habit? Chiropractor Oleg Mikhailov tells.
— To determine whether you are at risk for spinal diseases, I suggest taking a short test.
- Try to answer the following questions honestly:
1.
Do you periodically experience a feeling of heaviness in your neck or lower back?
2.
Do you spend at least two hours driving a car every day?
3.
Do you have a sedentary, sedentary job?
4.
Do you often slouch?
5.
Do you lift weights often?
6.
Do you always wear high heels?
7.
Are you overweight?
8.
Do you rarely exercise?
9.
Is it difficult to call your diet rational and balanced?
10.
Do you have bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol)?
If you answered “yes” to at least two questions, you should think about preventing spinal diseases.
If there are three or more affirmative answers, you need to start improving your back health without delay! There are many reasons for the disorders that you are very likely to have soon or have already appeared. Let's look at the main ones.
Reflex pain of the spine
— Pain occurs when various anatomical structures of the spine are irritated. For example, if you turn poorly or hypothermia occurs, your muscles are overextended when lifting weights and cannot relax. Yes, such problems can cause serious discomfort, but, as a rule, they are harmless.
A good chiropractor can solve this problem quite quickly using massage and gentle manual therapy techniques. But the pain itself goes away, as a rule, within 5-7 days.
Scoliosis
— It is important to monitor posture in childhood, when the skeletal system is being formed. Otherwise, a lateral curvature of the spine with mandatory rotation of the vertebral bodies is possible, that is, scoliosis.
In children, too much stress is placed on the spine due to the fact that during the formation of the skeleton, muscles and ligaments do not always have time to quickly strengthen. The treatment complex includes physical therapy, various massages, swimming helps very well, as well as the correct daily routine (alternating educational activity with physical activity), if necessary, use of special corsets.
It is important to do all this before the age of 18-25; a young body has a high chance of self-recovery. In the future, it is impossible to get rid of scoliosis. It’s only realistic to prevent the problem from getting worse and support the body with exercises and special procedures to improve the quality of life.
Osteocondritis of the spine
- This is one of the most common causes of back pain. Almost every second person aged 25 to 55 years suffers from neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis.
- Osteochondrosis
is a degenerative lesion of the intervertebral disc cartilage associated with changes in the nucleus pulposus and reactive changes in the adjacent vertebral bodies.
Let's take a closer look. An anatomical complex consisting of two adjacent vertebrae with corresponding joints and musculo-ligamentous apparatus and one intervertebral disc is called the spinal motion segment. For various reasons (heavy lifting, uncomfortable posture at the desk, improperly organized physical activity, injuries, etc.) degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc can occur. Inside the disc is the nucleus pulposus, which is actually a shock absorber. It all starts with problems in this very place, when the disk core is displaced. Pain syndrome occurs as a result of neurological complications of this process.
Recently, the disease has become much younger. Young people aged 20-25 come to us and, upon examination, are diagnosed with herniated protrusions of intervertebral discs. Unfortunately, despite all conservative measures, osteochondrosis remains with a person for the rest of his life. Moreover, every year the patient’s condition worsens, the pain intensifies, and more and more pathological changes are visible on radiographs.
Hernia
— Intervertebral disc herniation
- This is a protrusion of the nucleus of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. This process is considered the last or almost the last stage of osteochondrosis. And it cannot be ignored.
A herniated disc can compress the spinal nerve and radicular artery, causing muscle paresis or paralysis and sensory disturbances. In extreme cases, this requires surgery.
One of the most modern methods of surgical treatment of disc herniation is radiofrequency nucleoannuloplasty.
. This is a minimally invasive (by puncturing the skin) surgical procedure. The standard time of stay in the clinic's day hospital from the moment of admission to discharge is 3-4 hours.
Uncomplicated disc herniations can be treated without surgery. This usually requires an integrated approach. Along with drug treatment, the complex should include physiotherapy, physical therapy, gentle manual therapy techniques, etc. This treatment is carried out in courses; sometimes it takes up to six months or more to obtain a stable result.
Remember, having operated on a hernia or undergoing a course of conservative treatment, you automatically fall into the risk group of people who may experience a recurrence of the disease. I recommend that you do not wait for an exacerbation, but undergo preventive treatment outside of the exacerbation. This could be a spa treatment, a preventive course with a chiropractor or a regular massage. The main thing is that you are the master of the situation, not your illness.
Rules for the prevention of spinal diseases
- Keep your posture. Yes, we often forget about it. But try to form a dominant in your head: when you sit or stand, your back should always be straight. It is important that this becomes a habit, then the muscles will automatically maintain posture.
- If you have to sit for a long time, organize your workplace correctly. It is desirable that the office chair follows the physiological curves of the spine, allowing the back to be as straight as possible and have full support on the back. The body should not “hang” over the table.
- Make it a rule to get up every 45 minutes and do light exercises. Stretch slightly, do a couple of bends forward, backward and to the sides, and walk around the office. The critical mark for staying in one position is 2 hours. Try not to wait too long to take a break. By the way, one little trick helps: get up every time you get a phone call.
- When sitting behind the wheel, it is not recommended to recline the seat too much. Otherwise, the pelvis moves forward and the physiological curves of the spine are disrupted. When reversing a car, the driver should turn not only his head, but his entire body.
- Lift and carry weights correctly. Keep in mind that if this rule is neglected, the load on the intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine increases several times. That is, if you lift a weight of 10 kg while bending forward, the intervertebral discs in the lumbar region can receive a load of 20 or more kilograms, but if you lift the load with a straight back, bending your legs, the load will be evenly distributed throughout the entire spine.
- Don't skimp on a good orthopedic mattress and pillow. The spine should be even when a person is sleeping.
- Visit the pool. In water, the gravitational load on the body is minimized, and the spine and paravertebral muscles are completely relaxed. The only rule: if you have problems with the cervical spine, you cannot constantly swim with your head raised, straining your neck muscles. Use swimming techniques that involve inhaling above the water and exhaling into the water, or float on your back.
- Eat a balanced diet. Firstly, this will help to avoid excess weight, and therefore excessive load on the spine; in addition, the musculoskeletal system will receive all the necessary elements to function safely. By the way, in order for all the nutrients and vitamins to reach each vertebra and intervertebral disc, movement is necessary. It’s not enough to eat rationally; it would be nice to take a walk after that.
- If you smoke, quit. Here's a compelling argument: smoking causes vasoconstriction. Metabolism is disrupted. The skeletal system does not receive enough nutrition. All this leads to degenerative-dystrophic processes.
- If you are at risk or have any spinal diseases, be sure to consult with specialists and undergo a course of restorative procedures. A properly selected rehabilitation program will help: eliminate functional blocks, improve blood supply to the brain, restore mobility to the spine, increase muscle elasticity, improve the functioning of internal organs, strengthen the immune system and more.
Source:
103.by
Author:
Prol Ekaterina
Photo:
Dmitry Ryshchuk