Common causes of pain
With a long-term cough, muscle tears occur and back pain occurs. If when coughing it radiates to the left or right shoulder blade, this may indicate natural factors and pathologies:
- a cold that is prolonged or not treated in a timely manner can develop bronchitis and pneumonia, in which pain from coughing is a natural symptom;
- overexertion - excessive physical activity can lead to muscle tissue tearing, which causes severe pain in the back and chest;
- osteochondrosis – pathology is accompanied by severe muscle tension, which can cause back pain;
- Smoking - nicotine negatively affects the lungs and the body as a whole, which leads to pain in different localizations.
Some heart and respiratory diseases also cause coughing and discomfort.
Causes of back discomfort in various pathologies
If coughing attacks are accompanied by pain that radiates to the back in the area of the shoulder blades, you should not take this as an accident. Often this is a signal of serious disturbances in the functioning of the body. It is worth noting that pain in many cases appears only after the desire to cough arises. At the same time, the muscles of the bronchi contract, causing a change in the intensity of pressure in the chest. Thus, discomfort under the shoulder blades or in this area begins after a person begins to try to cough.
During the coughing process, there is a direct effect on some structures, skeletal muscles are compressed, and nerve endings may be stretched. Because of this, attempts to cough lead to back pain.
Pain of varying intensity when coughing can cause considerable discomfort. These symptoms most often provoke pathological conditions that ultimately turn into serious complications. It is worth getting treatment as quickly as possible, while there are no problems with the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, or with other organs.
When the cough is heard in one of the areas of the back, this may indicate problems with the functioning of the following parts of the body:
- Bronchi, lungs;
- Heart;
- Muscles;
- Intercostal nerves and so on.
Spinal pain can provoke a dry cough of great intensity.
When trying to cough up mucus accumulated in the lower bronchi, significant tension is applied to the intercostal muscles. This can lead to pain, the same with thoracic radiculitis and neuralgia. Discomfort increases when coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
No specific effective line of action on the body to get rid of the disease has been developed. To select treatment, the doctor will determine the cause of coughing and evaluate the signs accompanying pain under the shoulder blades and in the lower back. Pain in this area may indicate not only how affected the respiratory organs are, but also problems with the blood flow systems. Therefore, it is worth describing in more detail to the doctor during the visit all the symptoms present.
Diagnostic measures
When diagnosing patients, doctors conduct a detailed survey to determine the characteristics of the symptoms in the back, between the shoulder blades. Doctors will find out:
- Place of pain.
- Character and strength.
- Duration, frequency of occurrence.
- In what cases do they become stronger or weaker?
The characteristics of cough are detailed:
- Time of appearance.
- Connection with unpleasant sensations.
- Is there phlegm?
After collecting information, the doctor establishes probable causes and diagnosis. After this, a physical examination is done, which includes:
- Visual inspection. Allows you to identify bruises on the body, in the area of the ribs, if there are injuries.
- Palpation. Allows you to identify the location of discomfort.
- Percussion. The sound determines lung damage, especially if the patient has pneumonia.
- Auscultation. Allows you to detect arrhythmia, which is characteristic of a heart attack or pleural noise.
To establish a more accurate diagnosis, doctors take additional measures. To do this:
- Blood analysis.
- ECG.
- X-ray.
- Ultrasound.
- CT and MRI.
- Sputum analysis.
After determining the exact diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for the underlying cause, which will help cope with the pain. Therapy differs and depends on the severity of the disease and additional symptoms. Recovery is carried out at home or in the hospital.
What diseases can cause cough and back pain?
The appearance of pain when coughing can depend on various reasons. Often these symptoms are not the only ones - they are accompanied by fever, nausea and vomiting, and a rise in temperature. Most often, the organ that causes the disease is located away from the shoulder blades. Symptoms may initially be dull, but gradually become aggravated. In this case, pain can spread to other parts of the body. The root causes can be a variety of body conditions.
Complex therapy
The treatment method is characterized by an established diagnosis. Pain under the shoulder blade in the back and its therapy are aimed at removing the root causes:
- If there is pain between the shoulder blades when coughing due to inflammation in the lungs, then antibiotics, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Doctors prescribe bronchodilators and mucolytics as auxiliary agents.
- If the shoulder blades hurt when coughing due to diseases of the spine, then painkillers are used for therapy, as well as medications that relieve inflammation.
- If there are symptoms of an acute infarction, the patient is urgently hospitalized for complex therapy in an intensive care unit.
- For tumors of various kinds, doctors relieve pain, diagnose the tumor, and then select treatment tactics.
- If a vertebra or thoracic area is injured, urgent surgery is possible.
- To treat heart disease, painkillers, drugs to protect the heart muscles, and bed rest are prescribed. Therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the guidance of a doctor.
Pain between the shoulder blades and in the back can lead to serious consequences and death. Symptoms cannot be underestimated; self-relief of discomfort is also prohibited. As soon as coughing and discomfort in the back begin, you should immediately seek medical help. The sooner the causes are identified and treated, the better the prognosis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis back symptoms treatment
Therapy
The therapeutic course is based on data obtained during examination, as a result of laboratory and instrumental studies.
An increase in temperature parallel to back pain is a symptom of dysfunction of the respiratory organs. The course of treatment consists of:
- taking or administering in the form of injections antibacterial medications;
- antitussive and expectorant medications;
- inhalation.
Lung cancer and other diseases bordering oncology may require surgery followed by chemotherapy.
If your back hurts when you cough, and the decisive factor for provoking the disease is myositis (inflammation of the muscles), the doctor will prescribe ointments and physiotherapy.
For spinal disc deformation, the following are recommended:
- medications to relieve inflammation;
- drugs for relaxing muscle tissue;
- massages;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture.
Severe spinal injuries, ring ruptures, hernias can only be eliminated surgically. However, doctors recommend surgery if your back hurts when you cough and the symptom cannot be eliminated with medication. Medicine offers patients minimally invasive therapy methods that do not require incisions of the skin or internal organs. The hernia is removed using the radio wave method through punctures.
For pericarditis, the course of therapy is selected depending on the cause. Infectious pericarditis is treated with antibiotics, antiviral and anti-inflammatory medications. For cancerous tumors and traumatic injuries, surgery will be required.
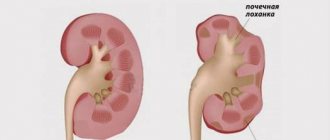
Kidney diseases require a comprehensive course of therapy for the urinary organs. The cause is most often an infection that can be treated with antibacterial agents.
Intercostal neuralgia is a consequence of vertebral disorders. After eliminating the hernia, displacement or proliferation of discs, pain and cough go away.
The treatment program may be based on:
- laser therapy;
- point exposure with magnets or pharmacological agents;
- vacuum treatment;
- electrical stimulation;
- manual influence.
What to do when your back hurts from coughing?
If a person feels discomfort in the back, in a specific area on the back, then he should analyze the nature of the pain with a doctor. The doctor will be able to fully assess the danger of the symptom. Self-medication is fraught with blurring the clinical picture, which leads to loss of time and delay in providing the person with the necessary help.
Who should you contact when your back hurts in the area of your shoulder blades when you cough?
There are several options:
- therapist;
- neurologist;
- surgeon;
- vertebrologist;
- pulmonologist
Traditionally, patients first turn to their primary care physician due to the occurrence of a corresponding symptom, which progresses during treatment of respiratory disorders.
To determine the cause of the problem, the doctor analyzes the person’s complaints, assesses the nature, type and time of occurrence of the symptom. The maximum discomfort for the patient is caused by a dry, unproductive, hacking cough.
Clarifying the diagnosis requires the following procedures:
- ECG is a method for assessing heart function;
- X-ray of the chest organs. The procedure is necessary for pathologies of the lungs and pleura;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys. An examination should be done if calculous cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, acute pancreatitis is suspected;
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
In difficult diagnostic cases, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed - expensive methods of visualizing the internal structures of the body. With the help of these measures, it is possible to accurately determine the localization of the pathological area.
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the spine
The nature of pain in an adult patient and a child may differ. For differential diagnosis of relevant pathologies in children, consultation with a pediatrician is required.
Important! You should not treat back pain on your own. To effectively eliminate a symptom, it is necessary to accurately determine the root cause of the problem. Therapy uses drugs aimed at eliminating specific pathological conditions. In this situation, you cannot do without consulting a doctor.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a condition, interviewing the patient is of considerable importance. This helps clarify the specifics of back discomfort. When diagnosing, the localization of pain, its duration, frequency, intensity, and nature of occurrence are taken into account.
Information about such characteristics of cough as the time of onset, the presence of sputum, and the connection with discomfort in the back area is of considerable importance. Additional symptoms are no less important in order to more accurately determine the diagnosis.
Physical examinations, which are performed using different methods, provide the doctor with some information based on which he can suggest the cause of spinal pain. This could be the following information:
- During palpation, the doctor can determine the most painful area.
- During a visual examination, sometimes bruises are found on the skin, suggesting a contusion of the chest.
- Percussion allows you to determine the dullness of sound over the affected area of the lung, inflamed as a result of pneumonia.
- During auscultation, cardiac arrhythmia is sometimes detected, which indicates myocardial infarction. You may also hear a noise indicating problems with the pleura.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional research options are certainly prescribed. Their type and volume depend on the disease that the doctor suspects. The results of such studies may be enough to understand why coughing causes such unpleasant sensations. Once the diagnosis is established, the doctor prescribes treatment. Depending on how severe the patient’s condition is, as well as on the prognosis, it will be decided where it is more appropriate to carry out treatment - at home or in a hospital setting. Some types of treatment can be carried out at home, without constant medical supervision.
Detailed descriptions of common diseases that cause pain
Shortness of breath and a dry cough with pain radiating to the shoulder blades can be a symptom of pneumonia.
There are many diseases that cause back pain below the shoulder blades and cough. However, they are often accompanied by additional sensations. Often diseases develop slowly, causing a gradual increase in unpleasant symptoms.
Lung diseases
When inflammation begins in the lungs, discomfort forms in the back area. Gradually, as pleuropneumonia or other disorders develop, the lower, middle or upper lobe of the lungs is affected. Then the processes move to the pleura, which no longer leads to dull pain, but to severe discomfort in the area of the shoulder blades.
Spinal pain indicates dry pleurisy, which develops against the background of other diseases of the pulmonary tract:
- peripheral cancer;
- gangrene or abscess;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- bronchiectasis;
- pleuropneumonia.
If the upper lobe of the lung becomes inflamed, pain occurs above the shoulder blades. With pathologies of the lower lobes, the pain is localized under the shoulder blades on one or both sides, and can radiate to the lower back. Very often, the same symptoms occur with oncological pathologies of neighboring organs, from where metastases occur in the lungs. Symptoms often radiate to the lower back, neck and arms.
Spinal diseases
Hypothermia can cause inflammation and muscle pain.
In addition to such a common pathology as osteochondrosis, there are other diseases of the spine and muscles that cause pain between the shoulder blades:
- radicular syndrome due to compression of nerve endings;
- hernias and protrusions;
- spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis, spondyloarthritis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- myositis.
With all these pathologies, there are no symptoms if the person is in a calm position.
Chest injuries
Acute pain under the left or right shoulder blade when coughing can occur after a fracture or crack of the ribs, fusion of bones, with the appearance of calluses and false joints. Fractures are especially dangerous, in which fragments are formed that can penetrate soft tissue.
- Lower back pain radiating to the leg - complete analysis, causes, treatment and prevention
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
In case of heart pathologies, a cough often indicates the onset of pulmonary edema, provoked by various acute conditions. Pericarditis, angina pectoris, arrhythmia - all these disorders in acute manifestations can cause adverse symptoms.
Other causes of pain when coughing
When the esophagus is compressed, the pain can radiate to the back; coughing only intensifies it.
Discomfort in the area of the shoulder blades can also occur against the background of other diseases:
- kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, as well as pathologies associated with inflammation of the urinary ducts and cystitis;
- diseases of the esophagus - GERD, as well as hiatal hernia, in which the esophagus can be compressed by part of the stomach;
- neoplasms in the spine, bone marrow - compress the nerve endings, causing very severe pain.
Symptoms for all these conditions may be similar, but it is impossible to independently determine the cause of pain without the use of diagnostic procedures.
Causes
The physiological reason why the back hurts a lot when coughing is spasmodic processes in the back muscles. Regular coughing leads to pain in the muscle tissue: when it weakens, it goes away. The pain is called myogenic. It is provoked by overstrain of the muscular frame of the lower back. Research results do not show pathogenic changes.
Pathologies are generated by pathogenic deformations. The main ones relate to the vertebral area:
- Hernia. When coughing, the back hurts, the patient ceases to feel the limbs. On X-rays and MRIs, the doctor sees deformations of the spinal column and accompanying degeneration of the joint tissue. Bend forward causes severe pain. The range of muscle action is narrowed.
- Stenosis. Disease of the lumbar region associated with the client’s advanced age. The patient has difficulty walking and feels weak in the legs. Medical studies show a decrease in the thickness of the vertebral discs.
- Facet arthropathy. The patient is injured. When coughing, the back hurts greatly, but the discomfort goes away if the client bends in the direction of the injury. The muscles come into tension on the affected side.
- Injuries to the fibrous ring. The cause is injury. The patient does not feel the limbs. Movement, sitting, bending provoke pain. To overcome discomfort, analgesics are administered.
- Tuberculosis. The disease affects the lungs and bone tissue. Passes with a debilitating cough.
- Osteochondrosis. A common cause of back pain after coughing. The patient notes limitations in the functioning of the spinal column.
A sore spine is not the only reason why your back hurts after a strong cough. Pathologies of other organs become a concomitant or decisive factor:
- Pleurisy, pneumonia. When coughing, the back hurts, the patient has a fever and chills. Other respiratory organs may also be affected: bronchi, trachea. In severe cases, oncology is diagnosed.
- Pericarditis is a heart pathology in which the heart sac is affected. To reduce discomfort, if the back hurts after a strong cough, the patient tries to lie on the affected side of the body.
- Kidney diseases. Associated with disorders of the immune system. Traditionally, pathologies of other organs are added.
- Intercostal neuralgia. The back hurts severely when coughing if the nerve roots are pinched by deformed vertebral discs. The pain has a girdling character.
The course of therapy depends on the diagnosis identified by the doctor. The patient needs to be attentive to himself and seek medical help for any discomfort in the back.
Localization of pain
When coughing, the back often hurts in the area of the shoulder blades. Discomfort may occur due to hypothermia or excessive physical exertion. In the latter case, muscle overstrain occurs. Advanced inflammatory pathologies can also cause discomfort. More often this happens when the clinical manifestations of a cold are ignored. Refusal to visit a doctor can lead to pneumonia or chronic bronchitis. Lung function is impaired by smoking. Addictions are a factor that disrupts the functioning of all vital organs. If the pain is localized in the upper back, the patient may be diagnosed with intercostal neuralgia. This disease affects the nerve fibers located near the ribs. With urolithiasis and other ailments of the excretory system, pain radiates to the lower back and chest. It is necessary to note the increased body temperature. If such signs are present, acute renal failure is suspected. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient suffering from pain and cough is urgently hospitalized.
Pain in the back muscles (lumbar region) and cough indicate polymyositis. The patient is not recommended to:
- sitting - blood circulation is impaired;
- eat food containing large amounts of protein and salt;
- take medications of synthetic origin;
- exercise.
Osteochondrosis is a disease whose negative impact extends to the cartilage and discs that form the spine. Due to dystrophic changes, both elasticity and strength decrease. The pain in this case spreads to the chest, upper and lower back.
How to treat a cough that causes back pain under the shoulder blades
The tactics that will be determined for treatment will depend on the diagnostic results. When treating cough and back pain, all efforts are aimed at eliminating the causes of their formation.
- If discomfort develops due to the inflammatory process occurring in the lungs, antibacterial, antiviral, non-steroidal or hormonal drugs that help fight inflammation are prescribed for treatment.
- If it is determined that the patient’s poor health is due to a spinal disease, drugs for pain relief and inflammation, and blockade of nerve roots are added to the list of medications.
- If pain occurs due to myocardial infarction, the patient should be admitted to the hospital as soon as possible. A set of therapeutic measures will be carried out for him.
- When the cause of pain is the growth of a tumor in the spinal column or lung area, pain relief is performed first, then diagnostics is carried out. This is necessary to determine the tactics for managing the disease.
- If it is determined that the pain began as a result of an injury to the chest or spine, the question of surgery will be raised.
You should not be inattentive to conditions in which the cough radiates to the lower back. With self-medication, the severity of symptoms can significantly decrease, which seriously complicates the diagnosis.
Causes and types of pain under the left shoulder blade from behind from the back
The reasons for the development of this pathology are different, they have their own symptoms. Pain on the left side under the shoulder blade from the back is characterized by the following sensations:
- acute;
- dull;
- pulling;
- piercing;
- shooting.
Pain under the left shoulder blade from the back can be of the same type or alternating. There are times when one type of discomfort gives way to another, for example, stabbing turns into shooting. The pathology is caused by various injuries and their consequences, disorders of the musculoskeletal system:
- rib damage – discomfort is felt throughout the shoulder;
- osteoporosis, arthritis – affects the neck and shoulders in addition to the shoulder blade;
- Disc displacement – pain causes spinal canal stenosis;
- wear (aging) of the skeletal system - unpleasant sensations in the scapula area can occur when the bone structure changes in old age;
- bursitis - the formation of exudate due to inflammation of the periarticular bursa also causes pain;
- tear of the rotator cuff - sharp, acute pain in the area of the left shoulder blade from the back with the inability to rotate the arm indicates a violation of the shoulder muscles or tendons responsible for coordinating the shoulder joint;
- dislocation - discomfort in the left side of the back may be a consequence of dislocation of the collarbone or shoulder joint;
- nerve damage - pinching of the dorsal scapular nerve is also characterized by painful sensations in the back (under the left shoulder blade).
Referring back pain in the area of the shoulder blades on the left is considered a signal indicating the following pathologies:
- abscess pneumonia;
- acute inflammation of the bronchial mucosa;
- focal pneumonia;
- pulmonary pleurisy;
- stomach ulcer;
- esophageal spasm;
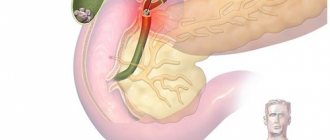
- pancreatitis;
- gastroreflux.
Heart disease may be another reason why a patient has back pain on the left side under the shoulder blade:
- heart attack;
- pericarditis;
- angina pectoris;
- mitral valve prolapse.
In addition, it causes discomfort and pain under the left shoulder blade from the back - increased muscle tone:
- poor posture;
- uncomfortable position while sleeping;
- neck muscle strain.
Only a visit to a specialist will help to correctly determine the causes of a burning sensation under the left shoulder blade from the back.
Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system
Pain above the left shoulder blade from the back can occur with problems with the lower respiratory tract (bronchi, lungs, pleura). The main cause of respiratory pathologies are considered to be diseases provoked by pathogenic viruses and bacteria:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy.
New growths in the lungs or bronchi can also cause a burning sensation under the left shoulder blade from the back.
Pleurisy of the lungs
Increased pain under the left shoulder blade at the back when coughing, breathing or sneezing is characteristic of dry pleurisy. The process occurs with an increase in temperature (up to 38°C), a feeling of general weakness, sweating, headaches, as well as aching pain in the muscles and joints.
Pneumonia
If the left back hurts under the shoulder blade for a long time, this may be a sign of pneumonia. Its symptoms are similar to pleurisy and are often accompanied by the following signs:
- bloody clots in saliva;
- wet cough (less often dry);
- lack of oxygen;
- elevated body temperature (37.5°C – 37.9°C).
Gastrointestinal tract
One of the most common causes of scapular back pain is diseases of the digestive system, especially peptic ulcers and pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis
Back pain under the left shoulder blade, which is based on pancreatitis, is not observed so often. They usually occur in parallel with lower back pain and convulsive contractions. They appear unexpectedly in the area of the heart, chest, or back.
Peptic ulcer
When a peptic ulcer develops, a person experiences belching or heartburn. A significant proportion of patients (about 75%) feel relief after vomiting, which is caused by significant pain with preliminary nausea. Initially, discomfort is observed in the epistragal region, and then the pain can spread to the left side (nipple, sternum, back). Often, increased pain occurs after eating.
The cardiovascular system
Pain under the left shoulder blade from the back is not considered a sign characterizing a specific disease, but malfunctions in the cardiovascular system are considered one of the important factors. The main diseases characterized by these symptoms include: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, hypertensive crisis and pericarditis.
Angina pectoris
With angina pectoris, a person experiences acute left-sided subscapular pain from the back, to relieve which nitroglycerin is used. An attack of angina pectoris can be caused by physical exertion, psychophysical factors, hypothermia, overeating and drinking a significant amount of alcohol.
Myocardial infarction
The characteristic pain under the shoulder blade on the left back from the back can be caused by a complete lack of coronary blood supply to one of the areas of the myocardium due to blockage of the vessel. The causes of a heart attack are:
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis.
When a blood clot (plaque) breaks off, it enters the heart with the blood flow and, once in the small-diameter coronary arteries, they block the vessel and interrupt the delivery of blood to the tissues. With a lack of oxygen, the process of death of myocardial cells begins.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction include sharp and throbbing pain concentrated in the left side of the sternum. Distributed in the area:
- left hand;
- shoulder blades;
- lower jaw.
It is impossible to relieve pain during a heart attack with analgesics, and nitroglycerin can only slightly reduce pain.
Aortic aneurysm
In half of cases of thoracic aortic aneurysm, there are no signs of disease in the early stages. Symptoms depend on the location of the aneurysm, its size and the presence (absence) of dissection. In addition to pain in the scapula area from the back, the following complaints are possible:
- discomfort in the left side of the back, neck, lower jaw;
- chest pain;
- cough, hoarseness, difficulty breathing.
May be accompanied by signs of heart failure due to heart failure. Symptoms may occur unexpectedly and include sharp pain in the chest and left side of the back.
Hypertensive crisis
Contrary to popular belief, a hypertensive crisis is not characterized by any standard blood pressure numbers; they are purely individual. In addition to the sign that the patient has colitis under the left shoulder blade from the back, the symptoms of a hypertensive crisis include:
- headache in the back of the head;
- pulsation in temples;
- shortness of breath;
- nausea and vomiting;
- vision problems;
- skin redness;
- increase in diastolic blood pressure values above 110-120 mm Hg. Art.
When a hypertensive crisis occurs, the risk of complications from a number of systems and organs, the central nervous system, etc. increases.
Pericarditis
Patients may present with symptoms of inflammation (acute pericarditis) or signs of fluid collection (pleural effusion). They vary depending on the degree of inflammation and the volume of pericardial fluid. In acute pericarditis, pain occurs on the left side under the scapula from the back, in the chest, and sometimes shortness of breath is noted. The first manifestation may also be tamponade with the development of hypotension, shock or pulmonary edema.
Musculoskeletal system
Various destructive pathologies in the spine and bones can cause back pain under the left shoulder blade. In addition, these include: intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia.
Intercostal neuralgia
Pain in the back in the area of the shoulder blades on the left with neuralgia has its own characteristics, for example, it intensifies during physical activity, and the pain point can be determined by palpation. Neuralgia pain is long-lasting and cannot be minimized with nitroglycerin.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is often a common cause of pain under the shoulder blade on the left side of the back and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- muscle spasms, numbness;
- development of dizziness;
- the appearance of “goosebumps” (paresthesia);
- frequent headaches.
Intervertebral hernia
A herniation occurs when the annulus fibrosus surrounding the intervertebral disc ruptures, resulting in displacement of the disc core. Symptoms of a herniated disc depend on its location. The most important symptom of a herniated disc is pain in the left side of the back, which increases exponentially when moving or lifting heavy objects.
Psychosomatic diseases
One of the causes of pain under the left shoulder blade from the back can be considered psychosomatic diseases. Not every specialist will be able to recognize this disease and its true causes, since they often do not have special features. Different organ systems can have a direct relationship with the dynamics of the patient’s mental state:
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- vascular-cardiac system;
- nervous system;
- immunity.
Treatment of pain under the left shoulder blade from behind from the back in psychosomatic diseases occurs without the use of traditional therapy. In such cases, it is important to establish psychological motives and carry out treatment with a psychotherapeutic focus.