Back pain is one of the most common reasons for visiting doctors. It often becomes the cause of disability around the world. According to statistics, more than 70% of the world's population have experienced back and lumbar pain at least once. Fortunately, in most cases there are ways to prevent or treat back pain. Quite often, the pain goes away on its own within a few days due to the activation of the body’s own protective mechanisms. It can have a different character:
- muscle pain;
- shooting or stabbing pain;
- pain radiating to the leg;
- limiting back mobility
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Why does my back hurt?
Pain in the spine can occur directly after injuries, pathologies of the vertebrae, ligaments and discs, or damage to soft tissues. It depends on the position of the body, the level of physical activity, but can also be reflected, for example, in diseases of the internal organs. To some extent, the back itself is vulnerable due to its structure.
Its basis is the spine, which provides supporting, protective, motor and shock-absorbing functions. This is due to the cartilage of the intervertebral discs, muscles and ligaments, which tend to wear out over time with the wrong lifestyle and cause degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Inside the spinal column is the spinal cord, its paired roots innervate almost all organs and tissues. Any disturbance in this complex system can cause pain. The cervical and lumbar regions suffer most often due to their greatest loads and mobility.
What to do if you have back pain?
A doctor's examination is required to determine the cause, especially if the pain has become frequent. Only a specialist can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. You can't do self-diagnosis.
First, you can contact a therapist, who will identify a set of symptoms and refer you to the right specialist. If the cause is known and obvious, you can continue the prescribed therapy. Neurologists, orthopedists, and vertebrologists treat back problems.
Localization of lumbar pain
- Pain in the lumbar region and above the sacrum
can occur due to injury, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system, as well as injuries, oncology or simple overexertion. Often this zone manifests itself after unsuccessful sports activities, especially with poorly placed blows, an untrained fall, or failure to comply with the technique of performing exercises. - below the lower back (above the tailbone)
due to overexertion when lifting loads, standing or walking for long periods of time, or when bruised on ice or other hard surfaces. Sometimes the cause of aching pain in the lumbar region can be an infection or hypothermia. The most common pain is due to working or resting in an uncomfortable, non-physiological position - for example, due to spending time at the computer or driving in a half-bent banana position. Pain due to disorders of the intestines and genitourinary system (constipation, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, dysmenorrhea) is less common. “Low” pain localization may also indicate problems with the hip joint, especially in older people or athletes. - If it hurts to the left of the spine
, this does not exclude a problem with it - for example, scoliosis and/or osteochondrosis, impaired blood circulation, and even an infection of the spinal canal. - Particularly characteristic of infections and osteochondrosis is persistent aching pain
, which intensifies with the slightest physical exertion. - If the pain periodically subsides
and still gives the patient a break, the issue may be a displaced intervertebral disc, a pinched nerve root, or radiculitis. Also, pain in the lumbar region can be caused by diabetes mellitus or hypothermia. - If the patient often feels that he has been “overstaying too long” and feels pain after several hours of sedentary activities
, the pain may indicate an incorrect lifestyle, which has not yet developed into pathology, but requires urgent changes - not just pain relief for lumbar osteochondrosis, but complex therapy.
Please note that pain may radiate to the lower back in case of serious pathologies of the heart and digestive organs. If there is pain under the left shoulder blade and in the side at the same time, it is important to urgently rule out a heart attack. If you suffer from attacks of sharp pain - “as if you are cutting to the living” - a stomach or intestinal ulcer.
Causes of back pain
Back pain is a nonspecific symptom that can be caused by a variety of reasons.
Physiological (common) causes:
- increased weight;
- recent childbirth or pregnancy;
- hypodynamic work - in the office, at the computer, driving a car;
- standing work - hairdressers, waiters and salespeople, street advertisers, surgeons, teachers;
- heavy physical activity combined with sudden turns of the body;
- overload during training;
- postmenopausal with a tendency to osteoporosis.
Pathological reasons:
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, tumors, arthritis, osteomyelitis, Reiter's syndrome) and spinal cord;
- growth diseases - scoliosis and kyphosis;
- infectious lesions of the spine;
- osteoporosis, osteomalacia;
- diseases of internal organs - kidneys, pancreas, stomach, spleen, liver;
- atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta.
Acute pain can occur with disc protrusion, spondyloarthritis, spinal cord epiduritis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, atypical appendicitis and intestinal obstruction, kidney stones, fractures and sprains, spinal cord strokes, inflammation of the appendages in women and prostate cancer in men.
Types of diseases based on the nature of back pain
Causes of aching pain:
- hypothermia;
- Crick;
- myositis;
- prolonged uncomfortable posture during sleep or work;
- lumbago (caused by labor);
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia or displacement of intervertebral discs due to sudden lifting of weights or sudden turning of the body;
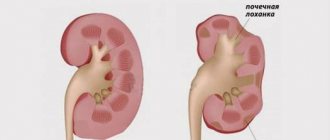
- kidney diseases - cause back pain due to the close location of the kidneys to the lower back;
- stomach diseases.
Causes of shooting pains:
- intervertebral hernia - with them the condition worsens with any physical stress;
- radiculitis - this type of back pain often occurs on one side, radiates to the thigh or buttock, causes numbness in the legs and also depends on physical effort;
- osteochondrosis - the patient may experience nagging pain that radiates to the leg and intensifies when coughing, sneezing, straining, walking, bending.
Etiology of throbbing pain:
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- lumbago;
- spondylosis - are acute and cannot be relieved with analgesics.
Bursting back pain:
- ischemia;
- heart attack;
- TELA;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- a sharp increase in pressure;
- atherosclerosis.
Why does my back hurt after sleep?
Most people often feel back pain in the morning after sleep, the reasons may be:
- overload the day before, if you lifted weights and moved sharply;
- weak back muscles;
- hypothermia;
- vertebral hernia or osteochondrosis;
- scoliosis - curvature of the spine leads to uneven muscle contraction;
- pregnancy - when the center of the body shifts;
- obesity - the load on the spine is also uneven.
Sleeping conditions are also important. The bed should not be too hard or soft - in any case, a person is forced to take an uncomfortable, unphysiological position in sleep, which causes the muscles to overstrain and not rest at night. Posture is so important that even an orthopedic mattress cannot help. It is recommended to sleep on your back with your legs elevated.
Also, the causes of pain after sleep can be diseases of the spine and internal organs (urological, gastrointestinal tract, including oncological).
Diseases associated with joints and the spinal column
All pathologies that cause back pain have a common basis - uneven load on the spinal column. These include:
- Ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammation of the ligaments and joints that causes chronic spasm of the surrounding muscles. The process is autoimmune; over time, the vertebrae begin to fuse together, which dramatically disrupts the functioning of the spine.
- Spondylolisthesis - the vertebrae are in an abnormal position. They are displaced and affect the brain or roots.
- Osteochondrosis - intervertebral discs become thinner, crack, and are replaced by bone tissue. Depreciation becomes impossible.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune inflammation of the joints. Most often affects the cervical spine.
- Osteomyelitis is inflammation of the bone marrow and surrounding soft tissue. Causes severe pain.
- Reiter's disease is a rheumatic simultaneous lesion of the urogenital tract, joints and conjunctiva of the eyes. The small muscles of the back are affected. More often typical for young people, it develops gradually. The pain is severe in the morning and decreases in the evening.
- Spinal canal stenosis - the cause may be a herniated disc or protrusion (protrusion into the spinal canal). More often, the process involves the lowest roots of the spinal cord, which innervate the legs. The pain is felt from the lower back to the foot, intensifying both at rest and when walking.
- Facet syndrome is a lesion of the intervertebral (facet) joints. The pain can be local or radiate to the groin, tailbone, or thigh. Physically dependent. In the evening the condition worsens, after rest it improves. Occurs more often in the elderly.
Muscle-related diseases
Muscle tissue is affected secondarily, against the background of pathology of bone tissue or joints. Painful spasms and tightness appear in the muscles, mobility is impaired:
- Fibromyalgia is a pain syndrome from the neck to the lower back. Neurological symptoms may occur: increased sensitivity when pressing certain points on the back, stiffness and stiffness.
- Polymyositis - occurs due to hypothermia, injury, sprains or severe physical exertion. Muscle weakness appears, in which even turning to the side is painful and problematic.
- Dermatomyositis is a chronic disease of the muscles, organs, and skin, often of an autoimmune nature.
- Charcot's disease is an inflammation of the peripheral nerves that run along the spine. This leads to changes in gait, muscle weakness and increased sensitivity of the nerve roots.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica is the negativity of the environment in the form of hypothermia, overload, uncomfortable posture, etc. Leads to spasms in individual muscles and the appearance of pain. So-called trigger points appear, when pressed the muscle reacts with acute pain. Neurologists know about this. Pain of this kind is eliminated with warming ointments and the Kuznetsov applicator.
Spinal cord pathologies
These include infringement of the spinal cord, which has 31 paired branches, where each nerve is responsible for the innervation of its area. This condition occurs when:
- injuries (spinal fracture);
- tumors;
- osteochondrosis or disc herniation;
- inflammation as a result of an abscess, hematoma;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- myositis;
- deficiency of minerals and vitamins;
- complications of HIV or neurosyphilis;
- sclerosis.
Back pain due to psychosomatics
In recent years, back pain has begun to appear due to psychosomatics. In this case, if there are complaints of back pain, the examination does not reveal pathology. This condition occurs with chronic stress, depression, and lack of libido. The result can be not only pain, but also a change in gait, exacerbation of lumbago and sensory disturbances.
Invasive methods
Therapeutic and diagnostic blockade
The blockade is performed under ultrasound or x-ray control, with a mixture of drugs injected directly to the nerves involved in transmitting pain impulses or into the thickness of the spasmodic muscle. The blockade not only relieves pain, but also helps to relax muscles, normalize blood flow and improve tissue trophism.
Radiofrequency denervation (RFD)
Radiofrequency effects on nerve structures are performed, as a rule, in cases where the therapeutic and diagnostic blockade has demonstrated sufficient effectiveness. In terms of execution technique, the manipulation differs little from a blockade, at least from the patient’s point of view, but it takes slightly longer (less than an hour in typical cases). For successful implementation of the blockade, communication between the doctor and the patient is important. During the procedure, the doctor will ask you to report any characteristic sensations during test stimulation. This allows you to increase the accuracy of RFD and improve the result.
When is this technique used?
- If drug therapy is insufficiently effective - when drugs taken orally do not sufficiently relieve pain or cause unwanted side effects;
- With a long wait for surgery, the patient often finds himself in a situation where he has to wait more than several months for surgery. In this case, RFD can reduce the intensity of pain and make the wait for the operation more comfortable;
- In cases where neurosurgical treatment did not bring relief or the pain returned after a previous operation. The decision to perform blockades and RFD is made jointly with neurosurgeons;
How is radiofrequency denervation performed?
After a standard examination by an algologist, additional examination and diagnostics if necessary, a decision is made to perform radiofrequency denervation.
- The procedure does not require hospitalization. Under sterile conditions, the doctor, under X-ray control, inserts special needles into the area of the posterior (sensitive) branch of the spinal root. After the doctor is sure that the tip of the needle is exactly in the right place, a local anesthetic is injected so that the denervation is painless. After this, a thin electrode is inserted through the needle channel, which is connected to a radio frequency generator and the tip of the needle is heated to a predetermined temperature. The patient, as a rule, does not experience discomfort; the most painful moment of the procedure is the moment of skin puncture, which feels indistinguishable from a regular intramuscular or intravenous injection.
- To clarify the position of the needle, in most cases, an iodine-containing contrast agent is used. If you have previously had an allergy to iodine, tell your doctor. We will definitely ask you the appropriate question.
- In some cases, a therapeutic and diagnostic blockade is first performed in order to determine the potential effectiveness of RFD in a particular case. Unlike RFD, the block uses conventional needles through which a small amount of anesthetic and anti-inflammatory drug is injected into a clearly defined area. The technique differs little from that when performing RFD.
Causes of back pain by location
Pain can occur in a variety of places in the back. Then they talk about its localization.
Pain on the right side
The right side of the back may hurt due to spinal curvature, kyphosis, lordosis, myositis, intervertebral disc displacement, and obesity.
Somatic pathologies can also cause pain in this area:
- formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system;
- inflammation of the vermiform appendix of the cecum (appendix);
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- nephritis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- salpingitis.
Pain on the left side
This area of the back may hurt in the following cases:
- splenitis;
- ICD;
- root pinching;
- duodenitis;
- oophoritis.
Pain localized above the lower back may be associated with inflammation of the serous membranes covering the lungs, damage to the bronchi, intercostal neuralgia, and ischemia.
Pain in the lumbar region
The lower back suffers very often, as it bears a colossal load. This section becomes inflamed when the nerve roots are damaged, osteochondrosis or hernial protrusion. Less commonly, the cause may be spinal tuberculosis, arthritis, lumboischialgia, decreased density and disruption of the structure of bone tissue, Reiter's syndrome - a combination of urethritis and prostatitis.
Pain in the lumbar region is usually chronic.
In the lumbar area on the right
Pain in the lumbar region occurs with scoliosis, tuberculosis, myositis, neuralgia, tumor, osteomyelitis, spondylitis. An acute attack can be caused by urolithiasis or pyelonephritis.
Shooting is typical for diseases of the lower back with frequent involvement of the spinal roots (radiculitis). Constant dull and monotonous pain is more typical for an organ such as the liver.
Left lumbar region
Most often, the left side begins to hurt after physical activity. The condition improves after rest. Pain can also occur with diabetes or root pinching. If it does not go away at rest, the reasons may be:
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis (with a sedentary lifestyle or poor posture);
- vertebral infections;
- circulatory disorders.
Pinched nerve
Most often, the sciatic nerve is pinched - sciatica. Its myelin sheath is not damaged. This is usually a consequence of osteochondrosis. When pinched, a sharp and acute pain occurs, radiating to the leg, sacrum, and lower back.
With compression radiculopathy, the roots of the spinal nerves are also compressed due to a herniated disc or a decrease in its height and, as a result, the distance between the vertebral bodies. Such pain is felt as “superficial”, it sharply intensifies when coughing, exertion or sneezing.
Intervertebral hernia
A herniation is an extrusion of the core of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. More often it becomes a consequence of untreated osteochondrosis. The central part protrudes towards the spinal cord, compressing it. Even a small load in such cases leads to a decrease in the height of the cartilage and an even greater protrusion of the hernia. The pain is sharp and sharp, radiating to the arm or leg.
In the area of the shoulder blades
Pain characteristics may indicate a diagnosis:
- A stomach ulcer is a growing dull pain. Eliminated with medications.
- Intercostal neuralgia is a disease characterized by acute pain with any physical effort.
- Osteochondrosis - dizziness, changes in pressure, numbness of the hands.
- Exacerbation of angina - pain is localized in the area of the left shoulder blade, radiating to the chest and under the collarbone.
Pain along the spine and in the back
More often they occur when nerve endings are pinched. Exacerbations are associated with spinal curvature. If the pain is not pronounced, we can talk about protrusion. With increasing pain, you can think about osteochondrosis. Pain along the spine is characteristic of myositis, fractures, thinning and wear of intervertebral discs, and spondyloarthritis. They are always sharp and constant.
Causes of pain below the lower back
Such pain is often associated with osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis. Less commonly, such sensations may appear when:
- diseases of the genital area in women (endometritis, adnexitis, vulvitis, cervicitis, oophoritis);
- pregnancy;
- menses;
- ulcerative colitis;
- appendicitis;
- diseases of the prostate or bladder - in men.
Reason 2. Degenerative-dystrophic diseases
Caused by wear and tear of the intervertebral discs, brittle bones, and loss of elasticity of spinal tissue. Moreover, such changes are not necessarily age-related. Today, young people also suffer from arthritis, spondylosis, and osteochondrosis.
Over time, pathological processes in the spine become degenerative, i.e. irreversible. In this case, it is necessary to use surgical treatment methods - joint replacement, surgical restoration of vertebrae and other structures. Arthrosis, osteoporosis, and radiculitis often develop into a degenerative form.
Of course, such changes do not occur without symptoms. Often patients note lumbago, acute pain in the affected area, limited mobility, stabbing pain, crunching, pain with certain movements (for example, in the lower back when bending forward). As a rule, a person can clearly determine exactly where it hurts.
Treatment of degenerative-dystrophic diseases is carried out by a rheumatologist, osteopath, chiropractor, traumatologist, neurologist and a number of other specialists. Don't know who to contact? Make an appointment with a general practitioner first.
Situations requiring urgent medical attention
Urgent consultation with a doctor requires back pain that occurs in the following cases:
- injury;
- neurological symptoms in the form of tingling and numbness in the limbs;
- temperature is combined with back pain;
- numbness in the arms and legs, weakness and tingling sensation;
- gait has changed or legs are lost;
- there is a history of cancer;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- urination and defecation are impaired - a person cannot control these processes;
- back pain radiates to the chest, jaw and neck;
- consciousness is confused and dizzy;
- numbness in the genitals and weakness, “wooliness” in the legs;
- leg cramps;
- problems with conception or erection;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, for which treatment by a gastroenterologist does not help;
- pain in the coccyx and pelvis area, intensifying with changes in body position;
- increased pain when sitting or standing for a long time.
Specialists at the AXIS center in Zelenograd will help you find out the cause of the pain. It contains a diagnostic database of the latest generation equipment. All doctors are highly qualified and have extensive work experience.
The nature of pain in lumbar osteochondrosis
It is necessary to distinguish between primary pain in the lumbar vertebra (associated with degenerative-dystrophic, inflammatory processes and spinal injuries) and secondary, “referred” pain that arises due to functional disorders in the muscles and internal organs. Primary aching pain in the lumbar region occurs as if by itself and is rarely accompanied by additional symptoms (usually in the later stages, for example, with advanced protrusions of the intervertebral discs). Secondary pain is almost always accompanied by bloating, changes in urination and bowel movements (they are rare, frequent, painful, or have other uncharacteristic features), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. The type of pain in the lumbar region can also tell a lot about the problem:
- paroxysmal (“grabs you by the gut”) - diseases of the kidneys and pelvic organs;
- increasing every day - inflammatory process (for example, in the epithelial coccygeal passage), abscess, cyst;
- sharp stabbing (especially after injury) - rupture of an internal organ (liver, spleen, kidney, bladder, etc.) or vessel, internal bleeding, stomach or intestinal ulcer, blockage of a vessel by a detached blood clot (consult a doctor immediately if such pain occurs!) ;
- periodic shooting - characteristic of compression of the spinal roots (radicular syndrome), may be accompanied by spasms;
- dull continuous - indicates a disease of the liver, kidneys, spleen, and some endocrine glands;
- pulling, intensifies with movement - injuries to the spine and adjacent tissues.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of back pain, the neurologist prescribes a comprehensive examination:
- Blood tests. They help identify the presence of infection and inflammation in the form of leukocytosis and increased ESR. A decrease in hemoglobin will indicate anemia, which can have many causes, and one of the possible reasons is oncology.
- MRI (hospital does not provide MRI services).
Visualizes the condition of all components of the spine. Helps differentiate the type and nature of the tumor, determines the distance between the vertebrae and the degree of compression of the roots. - CT. Detects fractures and allows you to find the smallest fragments after injuries. All this in three dimensions.
- Radiography. The most inexpensive way to diagnose back pain and identify the condition of bone tissue. Prescribed for suspected fractures, arthritis, scoliosis, osteoporosis, spondyloarthrosis.
- Electromyography (EMG). Determines indicators of bioelectrical activity of muscles and peripheral nerve endings.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain. In triplex or duplex mode, it is used to assess the patency of blood flow through arteries and vessels. Their condition is checked - wall thickness, permeability, etc.
Spondylolisthesis
This condition occurs in 5-7% of the population, although it is diagnosed much less frequently (most often people simply do not pay attention to chronic lumbar pain). With spondylolisthesis, the leg of one of the vertebrae (usually the 5th lumbar) is deformed, which is why the vertebra “crawls” onto the lower one, protruding forward or backward. The corresponding part of the spine becomes like a ladder, not a pillar.
The symptoms are still the same - pain in the lower back, sometimes in the buttocks, rarely radiating to the lower extremities. A displaced vertebra can compress the roots of the nerves extending from the spinal cord, which leads to pain.
Treatment for back pain
There are several methods for treating back pain. A neurologist will select the optimal treatment for you, taking into account the patient’s age, lifestyle, level of physical mobility and clinical manifestations.
In the drug treatment of back pain, NSAIDs, analgesics, muscle relaxants, and B vitamins are usually used. Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, IRT, massage, spinal traction, and muscle relaxation are also prescribed.
For back pain, to ensure quality treatment, it is advisable to see one doctor. This is not difficult to do with qualified specialists from the AXIS center.
Who is a neurologist and what does he treat?
The specialist treats diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. Back pain is a symptom of PNS pathologies, so to find the cause and establish a diagnosis, turn to a neurologist.
The doctor’s competence includes checking:
- coordination of movements;
- muscle strength;
- sensitivity;
- index samples;
- skin and tendon reflexes;
- pressure on the body from objects of different weights;
- balance with closed legs, outstretched arms and closed eyes.
The doctor studies the connections between neurons, the functions of the brain and spinal cord.
People turn to a neurologist not only for back pain. Indications for a visit to a specialist:
- frequent headaches and dizziness;
- loss of consciousness and fainting;
- ringing in the ears, spots before the eyes;
- poor coordination of movements and unsteadiness of gait;
- cramps, tingling of hands and feet;
- goosebumps;
- muscle weakness;
- sleep disorders;
- poor memory, decreased visual acuity and hearing.
Prevention
Prevention measures:
- learn to maintain posture and stand correctly;
- don't slouch;
- keep your back straight when sitting, place a stand under your feet;
- organize your sleeping area correctly;
- do not jump up suddenly after waking up - stretch slowly, do simple exercises with your arms and legs;
- distribute weights on both hands - do not carry everything in one hand, refuse a bag over your shoulder - a backpack is better;
- do not carry the child in your arms bending backwards;
- lift weights by squatting;
- do not wash floors without a mop, leaning forward or kneeling;
- balance your diet with a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins;
- give up smoking and alcohol;
- do not forget about physical exercise - swimming, Nordic walking, yoga;
- take a contrast shower in the morning;
- take care of the liver, it produces collagen for the spinal ligaments and vertebral bodies;
- strengthen immunity;
- control weight;
- It is advisable to undergo a course of manual therapy every 6 months for 5-10 sessions (on the recommendation of a specialist);
- avoid stress;
- Don’t forget about medical examinations with a doctor.
If you experience back pain, contact your doctor. Here you will always receive proper assistance. Remember, any disease is easier to treat in the initial stages.