Reactive arthritis in children
Your child complains about joints, what to do?
Read the recommendations of our pediatrician and rheumatologist
Nadezhda Ivanovna Manaeva...
We are already accustomed to the diagnosis of ARVI, as well as to the fact that the symptoms go away on their own within a week. But are these simple, at first glance, runny nose and sore throat so harmless?
After the symptoms disappear, 10-14 days later in the morning, a seemingly healthy child cannot get out of bed, cries, and complains of pain in his leg.
When trying to get out of bed, he limps or loses his leg. These symptoms force parents to immediately consult a doctor. When interviewed, it turns out that the child was, in fact, not healthy. After the disappearance of acute manifestations of nasopharyngeal infection, the child maintained a slight increase in body temperature to 37.3 * C, the child quickly got tired, was capricious, and lethargic. Parents usually attribute this to the rehabilitation period after a cold. And one “beautiful” morning the child wakes up with pain in his leg. The child has developed “reactive arthritis,” a condition that requires immediate medical attention and treatment. What is reactive arthritis and why does it develop?
Reactive arthritis is an inflammation of the joint(s) that occurs in response to an infection, in particular a nasopharyngeal infection. Most often, large joints (hip, knee, ankle) are affected in the form of monoarthritis (damage to one joint), rarely – polyarthritis (affecting several joints). Symptoms, in addition to joint damage, may include increased body temperature, weakness, fatigue, and decreased appetite.What should parents do?
If “articular syndrome” appears, low-grade fever persists (body temperature 37.3-37.5* C) after curing ARVI, or the child gets tired quickly, consult a doctor.
First of all, the child should be examined by a pediatrician. Of the studies, first of all, OAC, CRP, FPP, RF, ASLO, OAM, ultrasound of the affected joints are needed. Reactive arthritis is a condition treated by a rheumatologist.
He will prescribe the necessary additional examination, appropriate medications and determine further tactics for monitoring the child. Articular syndrome is a difficult syndrome to diagnose and treat and requires referral to a professional. Other, more serious diseases can occur under the guise of reactive arthritis. If any of the above symptoms occur, consult a doctor promptly.If your child is often sick or complains about joints, do not self-medicate, go to the doctor, start with a pediatrician and rheumatologist.
Remember
that with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the risk of subsequent diseases, exacerbations and complications is reduced!
Make an appointment with our doctors,
and we will definitely help your baby, whether small or big, but still a child!
Sign up for tests, ultrasound of joints, see a pediatrician and rheumatologist!
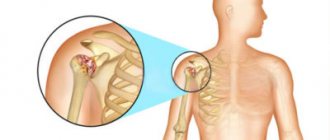
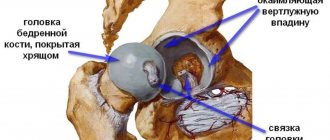
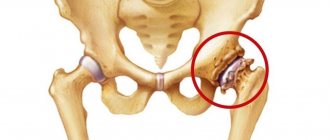
Symptoms of hip arthritis
The most common forms of arthritis of the hip joint encountered in clinical practice are tuberculous and acute purulent coxitis. Other forms are observed much less frequently.
With purulent coxitis, there is a rapid onset of the disease with a predominance of symptoms of general intoxication: fever, weakness, sweating, loss of appetite, headache. Local changes are significantly pronounced: the skin over the joint area becomes tense, hyperemic and hot to the touch. There is a sharp pain (shooting, pulsating), which intensifies even more with movement. Due to inflammatory infiltration and the formation of purulent effusion in the joint cavity, the shape of the latter changes significantly.
Other forms of hip arthritis are characterized by gradual development. In the initial stages, dull, aching pain predominates in the groin area, on the outer side of the thigh, and buttocks, which limit the range of movements or make walking difficult. Due to the stiffness of the hip joints, movements become constrained, uncertain, and the gait becomes limping (Trendelenburg gait). Most often, pain and stiffness in the hip joint occurs after prolonged fixation in one position in an uncomfortable position, for example, when sitting or standing for a long time. Over time, patients may develop atrophy of the femoral and inguinal muscles, fibrous or bony ankylosis.
Psoriatic coxitis is accompanied by the appearance of a characteristic bluish-purple coloration of the skin over the inflamed joint, pain in the lower parts of the spine. In rheumatoid arthritis, the hip joints are affected symmetrically. Progressive dystrophic changes in the joint over time lead to the development of secondary coxarthrosis.
General information
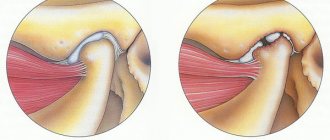
Arthropathy is a secondary lesion that occurs against the background of concomitant non-rheumatic diseases. Activation of pathological processes can occur in diseases of various etiologies.
The key manifestation of arthropathy is painful conditions without affecting the shape and functionality of the joint. In some cases, reactive arthritis occurs.
Localization is in the joints mainly of the lower extremities, therefore in medical practice arthropathy of the knee joint is most often diagnosed. The manifestation is inflammation, swelling, as well as rapid fatigue and difficulty in making movements.
It is important to note that the key difference between the condition under consideration is the dependence of the existing syndrome on the course of the “main” pathological process.
Severe pathologies develop extremely rarely. With a competent approach to eliminating the underlying disease, arthropathic symptoms are significantly reduced or completely disappear.
Etiology and list of the most likely causes of joint arthropathy
Arthropathy of the knee joint or other joints of the musculoskeletal system (MSA) of the human body can be diagnosed in people of different ages, in particular in children.
Considering the stages of the course of secondary pathology, we can distinguish:
- acute period, the duration of which can reach two months;
- a protracted form is observed throughout the year;
- The chronic form involves a long course with remission and the occurrence of periodic relapses.
It is important to note that regardless of the type or form of the disease being considered, there is a list of the most likely causes of its development. Each cause has certain consequences, which largely determine the form of the disease being diagnosed.
Among the most common causes of secondary pathology of this type are:
- allergic reactions;
- associated painful conditions;
- infectious and parasitic lesions;
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- overweight;
- disruption of internal organs.
Features of arthropathy treatment
Treatment of arthropathy is determined individually based on the characteristics of the existing disease and the results of the diagnosis.
In order to achieve the most effective result, a complex of physiotherapeutic and medicinal methods is used. At the rehabilitation stage, therapeutic physical education (PT) is used.
In case of severe inflammation, as well as a recurrent course of the pathology, transfer of the patient to inpatient treatment is allowed.
Strategy
The entire treatment strategy consists of following the simplest rules:
- Rejection of bad habits
- Eating balanced food.
- Maintaining optimal body weight.
- Following the instructions of the attending physician (compliance with the intended plan and features of drug therapy).
The effectiveness of a particular treatment regimen for arthropathy is determined by the onset of recovery or positive dynamics of the clinical picture of a particular case. The use of therapeutic methods should help reduce pain and restore functionality.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a special branch of medicine that involves the use of a methodological complex that can have a beneficial effect on human health. The methods used differ in the influence of natural or artificial factors (light, water, etc.) on the body.
In the treatment of arthropathy, radon baths, climatotherapy, exposure to electric current, etc. are actively practiced.
The intensity and duration of therapy is determined solely by the attending physician and depends on a large number of factors (features of drug therapy, general health, age and much more).
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of arthropathy involves taking such pharmacological groups of drugs as:
- antibiotics - used to eliminate agents that provoke the progression of the disease;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – relieve inflammation, eliminating visual manifestations;
- chondroprotectors – activate tissue regeneration, thanks to the enrichment of articular tissues with building material.
The most important role is played by chondroprotectors, which largely help the body overcome diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Artracam is considered to be one of the best drugs of this pharmacological group.
In order to improve the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy, a combination of medication and physiotherapeutic treatment is used, which makes it possible to significantly speed up recovery and achieve such positive results as:
- relieving inflammation;
- reduction in intensity or complete relief of pain;
- improving blood circulation in the affected joint.
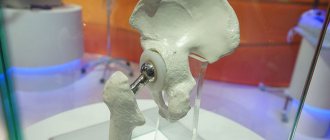
Surgical intervention
Like any other pathology of the musculoskeletal system, arthropathy can lead to the need for complex surgical intervention.
The main goal of the radical method is to eliminate the consequences of the progression of pathologies and restore the functionality of the site of its localization.
Exercise therapy as a method of rehabilitation
Exercise therapy is an excellent way to speed up the restoration of the previous level of health and consolidate the results of treatment of pathological conditions of the musculoskeletal system.
A set of exercises is selected individually for each patient, which allows for targeted action and activation of the full functioning of the muscle frame, which in turn has a positive effect on the stability and functionality of the bone joint.
Complications and prognosis
Delayed consultation with a doctor, self-medication, as well as violation of the established regimen for taking medications or visiting physical therapy can lead to a number of complications, for example:
- limitation or complete loss of joint mobility;
- infection;
- the need for surgical intervention;
- disability.
With a timely, high-quality approach, we can talk about positive forecasts. Despite the impossibility of completely getting rid of the disease, there is an elimination of unpleasant sensations and the ability to control the existing disease.
Varieties
Today, it is customary to distinguish several types of secondary diseases. Arthropathy of the knee, hip, elbow, etc. can be:
- reactive - occurs against the background of a specific tissue reaction to the development of systemic pathologies of the body. Occurs in leukemia and endocrine system disorders;
- dystrophic - progression is due to insufficient nutrition of cartilage tissue. Occurs in people over 55 years of age when natural disorders affecting the functioning of the entire body are detected;
- pyrophosphoric (chodrocalcinosis) - has a connection with metabolic disorders, namely, the exchange of salts and calcium in the tissues of the human body. Often, the provocateurs of this type of illness are injuries to large joints;
- allergic – provoked by allergic reactions;
- psoriatic – occurs with psoriasis;
- idiopathic - defined in a situation where it is impossible to establish reliable causes for the development of a pathological condition of a secondary type;
- hereditary form - transmitted at the genetic level, established on the basis of the collected anamnesis.
Main events
In order to make a correct diagnosis, everyone who seeks medical help must be prepared for such manipulations as:
Additionally, if signs of inflammation in the joints are detected, the patient is referred for examination to an ophthalmologist.
As a result of passing all diagnostic measures, the attending physician determines further treatment, taking into account the degree of damage, the presence of concomitant diseases, age and other characteristics.
Risk factors for joint arthropathy
There are certain factors that indicate an increased risk of secondary pathological disease. These include:
- autoimmune diseases;
- hemophilia;
- excessive stress on the joints;
- genetic predisposition;
- alcohol abuse;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- chlamydia infection;
- impaired metabolism;
- accumulation of uric acid in joint tissues.
Prevention of joint arthropathy
According to available data, arthropathy is a secondary pathology and develops against the background of other diseases. The main goal of prevention is to prevent the development of any pathological processes or at least their timely elimination.
To significantly reduce the risk of developing joint arthropathy, it is recommended:
- systematically monitor your general health;
- maintain at least a minimal level of physical activity;
- adhere to the basics of proper, nutritious nutrition;
- monitor body weight and prevent obesity;
- give up bad habits;
- reduce the likelihood of infection;
- attend preventive examinations with your doctor;
- promptly seek medical help and treat pathologies, infections and other diseases in accordance with the scheme approved by the doctor;
- carry out prophylactic administration of drugs from the pharmacological group of chondroprotectors (Artracam, etc.) in order to maintain the quality of joint tissues.
Health is something that cannot be bought, but can be maintained. Maintain an optimal level of quality of life by following simple recommendations for the prevention of various diseases.
Description of the disease
Arthritis is accompanied by pain in the affected parts of the body and is dangerous due to its complications.
In some cases, the disease leads to the development of joint deformities or the formation of contractures. In the future, this may reduce the patient’s ability to work and cause disability. According to statistics, 1 child in 1000 suffers from arthritis. Boys experience joint damage 2-3 times less often than girls. Pathology can occur in children from 0 to 18 years of age. However, patients under the age of 5-6 years are most often affected.
Regardless of their origin, arthritis is capable of triggering autoimmune processes in the body, which are characterized by a systemic nature. The pathogenetic links of the disease, in addition to the joints, begin to affect the skin, muscles and internal organs.
Types of arthritis in children:
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA). An autoimmune disease that often causes joint deformation and subsequent disability in adulthood.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. The disease is a consequence of the negative effects of streptococci. In addition to the joints, the cardiovascular system is often involved in the pathological process.
- Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis. A rarer form of arthritis, accompanied by damage to the spine with the gradual development of its deformation.
- Reactive arthritis. A group of pathologies that are characterized by damage to the joints against the background of the activity of bacteria and viruses that multiply primarily in the gastrointestinal tract or urinary system of the patient.
The disease can be acute or chronic. The task of parents and doctors is to timely identify pathology and prevent its transition to a latent state. this approach reduces the risk of complications.