Make an appointment Ask a question
Page navigation:
- Symptoms of trochanteritis
- Manifestation of trochanteritis
- Types of trochanteritis
- Who is at risk?
- Causes of trochanteritis
- Diagnosis of trochanteritis
- Treatment of trochanteritis
- Prognosis for the treatment of trochanteritis
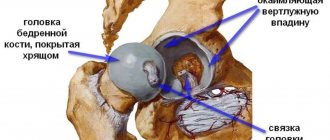
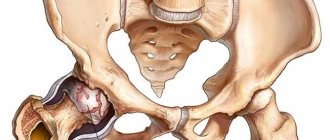
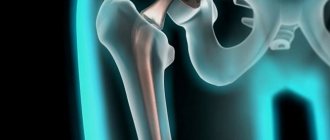
Trochanteritis of the hip joint is a degenerative-inflammatory disease of the femoral tendons, in which they are affected at the junction of them with the femur. This place is called the greater trochanter, or trochanter (from the Latin trochanter), hence the name of the pathology.
The trochanter is a protrusion on the femur to which the tendons of the pelvic, gluteal and thigh muscles are attached. The anatomical complex of the listed muscles is responsible for the movements of the hip joint, and when the tendons of the complex are damaged, attacks of pain are observed, localized along the outer surface of the thigh.
Symptoms of trochanteritis
Most often, pain makes itself felt when moving; it can be quite pronounced, but usually subsides at rest. The pain also bothers you at night, especially when lying on the affected side. In most cases, the disease is unilateral; cases of bilateral inflammation are rare. The disease does not affect other joints except the hip.
In the initial stages of the disease, pain is periodic, occurs during exercise and quickly passes at rest. They are sharp and pulsating, but disappear when physical activity ceases, so few people pay attention to them. Over time, the situation worsens, the pain intensifies and no longer depends on physical activity. The pain syndrome intensifies when palpating the femur at the site of the trochanter.
In an advanced state, the patient may experience intense night pain, aggravated by lying on his side, when the body weight presses on the affected joint. In the later stages of the disease, pain can also be observed in the groin and gluteal regions, and in the lower back.
Manifestation of trochanteritis:
- Pain in the area of the greater trochanter, which can be easily felt under the skin;
- Also, the pain intensifies when pressing on the greater trochanter area, and radiates along the outer side of the thigh;
- The pain intensifies with active movements;
- Hip pain occurs when lying on your side;
- With rest, the pain goes away;
- The range of motion in the joint is preserved;
Which doctor is treating you?
Inflammation of the tendons of the hip joint will manifest itself as arthralgia, which is constant or periodic, aching or pulling. Soreness manifests itself accordingly on the affected side. The symptom complex is very similar to the usual coxarthrosis of the 1st degree. In order to determine the diagnosis, the following signs are distinguished:
- painful sensations on the surface of one of the involved joints;
- discomfort at night or during activation;
- local temperature increase and systemic temperature reaction, which sometimes reaches high numbers;
- swelling due to edema and increased production of intra-articular fluid.
The disease differs from similar conditions in the complete preservation of motor activity without morning or evening stiffness. The criterion must be assessed, since this will regulate the future examination plan. A doctor should be consulted in the initial stages. His specialization will depend on the symptoms and the data obtained.
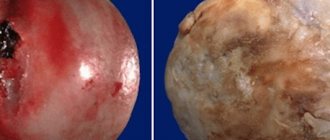
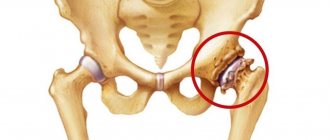
| Trochanteritis of the greater trochanter of the hip joint, the site of inflammation is shown in red |
Types of trochanteritis
The described disease can be of several types:
- Infectious (septic). When there is a permanent source of infection in the body (chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, cholecystitis), pathogenic microorganisms enter the tissues surrounding the trochanter through the blood and lymph. Another possible reason is that the infection enters the tissue by contact from an open wound of the thigh or from an area of inflammation located next to the trochanter. Symptoms are pronounced signs of intoxication of the body, poor general health, increased body temperature, loss of appetite.
- Tuberculosis. A tuberculosis focus is localized in the area of the hip bone in question. Symptoms in this case are moderate and appear gradually. Children get sick more often; the prognosis for this type of disease is unfavorable; the solution is competent treatment of the underlying disease.
- Non-infectious (aseptic). The most common type of illness occurs for reasons not related to infection - injuries, weight gain, hypothermia, high stress. There are no symptoms of intoxication, general health does not suffer. This variety responds best to treatment.
Who is at risk?
Women are more susceptible to inflammation of the tendons in this area; in men, all tendons are stronger by nature. In people leading a sports lifestyle, the disease is extremely rare. The main risk group is women of menopausal age who are experiencing hormonal changes in the body, accompanied by weakening of muscle and tendon tissue. There are exceptions when trochanteritis of the hip joint affects very young people, but in this case, as a rule, several unfavorable factors occur.
The main causes of pain in the groin area
Pain in the groin after endoprosthetics most often has a positional or adaptive nature. This means that they are caused by lengthening of the leg after surgery or changes in anatomical parameters in the hip joint area.
However, other reasons cannot be ruled out:
- stenosis (pathological narrowing) of the superior and inferior gluteal arteries;
- excessive tension and injury to the psoas major muscle (m.iliopsoas);
- inguinal and femoral hernias, abdominal aortic aneurysm, damage to the spinal roots at the L2-L5 level (in the case of persistent pain).
Let's take a closer look at the main causes of postoperative groin pain.
Excessive lengthening of the lower limb
Pain in the groin area occurs in almost half of patients with lower limb lengthening. Moreover, the longer the leg after surgery, the more intense the pain. The problem is faced by those people whose lower limb after surgery has lengthened by 1-4 or more centimeters.
An example of significant lengthening of the operated limb.
It is curious that such pain is often combined with pain in the anterior thigh and lumbosacral spine. Those, in turn, are caused by a secondary distortion of the pelvis against the background of tension in the muscles and fascia of the thigh, as well as the psoas major muscle.
Pain due to unequal limb lengths can significantly worsen a person’s quality of life after endoprosthetics. And the stronger they are, the more limited the patient’s activity is. Patients with intense pain may find it difficult to move around and do normal daily activities.
Impingement of m.iliopsoas
Impingement is characterized by damage to the muscle fibers of the psoas major muscle. The pathology is manifested by pain in the groin area, which occurs when the leg is extended at the hip joint. This can cause a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Layout of m.iliopsoas.
Impingement can develop for two reasons:
- due to damage to the psoas major muscle with unequal length of the lower limbs;
- due to injury to the m.iliopsoas by the cup of the installed endoprosthesis (usually with cement installation).
For impingement syndrome, a person requires treatment, including pain medications and physical therapy.
Vertically installed acetabular component
In this case, the head of the endoprosthesis tends upward and outward during walking, injuring the periarticular tissues. This is what leads to the appearance of pain. Note that pain during vertical installation of the acetabular component appears soon after walking, as well as with active flexion and strong adduction of the hip. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture, radiographic data and, if necessary, MRI.
Excessive anteversion of the acetabular component
Pain often occurs when the acetabular component is tilted too far forward. In this case, the person experiences pain when rotating the hip outward, both active and passive. To make a diagnosis in this case, X-ray examination and MRI are also required.
Definition of anteversion.
Causes of trochanteritis
The main cause of the pathology is considered to be a decrease in the elasticity of the ligaments. It is inevitable in women during this period of life. An inactive lifestyle and sedentary work can aggravate the situation. Against this background, the starting point for the development of the disease can be banal hypothermia, carrying heavy objects, or unusually long walking. The following factors can provoke the development of the disease:
- Overload of the hip joint;
- As a consequence of infectious and colds;
- Hip injury;
- Overweight;
- Metabolic and endocrine diseases;
- Systemic osteoporosis;
- Too active or, conversely, passive lifestyle;
Diagnosis of trochanteritis
Very often, damage to the femoral tendons is confused with arthrosis of the hip joint. Indeed, the symptoms of these two diseases are very similar. In addition, standard age-related changes are often mistaken for coxarthrosis on X-ray films.
When the trochanter is inflamed, it is important to have a clear history - the presence of chronic foci of infection, tuberculosis, injuries of the hip joint. The nature of the pain is assessed, the presence of pain when pressure is applied to the affected joint when the patient lies on his side. Motor tests are carried out to assess the range of motion of the joint - whether its activity is preserved or limited.
To exclude pathologies with similar signs, instrumental studies are performed: X-rays, ultrasound, MRI or CT. Tomographic examination methods are not always used, only in complex, doubtful cases; often the picture of the disease is clear even without them. The general picture of the disease is supplemented by laboratory diagnostic methods: urine and blood tests, specific tests for BK, rheumatic tests.
The main differences between trochanteritis, allowing a correct diagnosis to be made:
- the presence of characteristic painful points on the outer side of the thigh, in the so-called “breeches zone”, easily identified by palpation;
- preservation of the motor abilities of the affected joint - when the patient relaxes the leg, it rotates in all directions without problems (coxarthrosis makes such movements impossible due to pain in the joint).
Trochanteritis of the thigh.
In other scientific literature, the disease can be found under the name bursitis of the greater trochanter of the femur. It has several forms, which are divided according to the time frame of manifestation. Characteristic signs begin to worry when there is a quantitative and qualitative change in the lubricating substance. This increases friction and reduces the elasticity of the cartilage surface. As a result, 48-72 hours after the damaging effect, a symptom complex appears. Sometimes this occurs after 10-15 years. The following forms are distinguished:
- subacute;
- spicy;
- chronic.
The fundamental problem of the subacute course is the combination of infection and hypothermia. Unilateral or bilateral trochanteritis can appear after influenza. Symptoms come on gradually and the first signs may appear after 7 days or more. Increased sensitivity increases when pressure is applied or palpation is performed. Patients also suffer from discomfort at night, severe fever and clammy sweat. At the same time, mobility is almost completely preserved with minor limitation during prolonged walking or climbing stairs.
The acute stage is characterized by the appearance of a traumatic component, performing heavy physical activity or engaging in strength sports. Sometimes the signs coincide with long walks, hiking trips with ascents and descents. Unilateral or bilateral damage has differences in more rapid development and severe symptoms after the first 24 hours. The person will experience persistent arthralgia with fever and visible swelling. The entire length of the thigh can be involved. The state of health deteriorates significantly throughout the day.
Orthopedic doctor Andrey Sergeevich Litvinenko comments:
Separately, there is a chronic form, which may not cause concern and may remain latent for a long time. As a result, this requires replacement of the ligamentous apparatus with expensive implants and special structures. Peritrochanteritis is often considered a rapidly progressive disabling factor.
Treatment of trochanteritis of the hip joint
Trochanteritis of the hip joint is much easier and faster to treat than arthrosis of the hip joints. The method of treating the pathology depends on the nature of the inflammation. Any type of illness requires an integrated approach aimed at eliminating inflammation, eliminating pain and preventing possible complications.
Infectious inflammation requires an antibacterial course of treatment, tuberculous trochanteritis requires specific anti-tuberculosis treatment. In most cases, the disease is helped to overcome conservative methods, which include:
- Drug therapy. To eliminate inflammation, anti-inflammatory nonsteroids are prescribed, and analgesics are prescribed to relieve pain. For severe pain, glucocorticoid drugs are administered directly into the affected periarticular tissues.
- Physiotherapy. The most effective physical procedures include shock wave therapy, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, PRP therapy, and electrophoresis. These sessions help improve nutrition of the affected area and significantly reduce the inflammatory process.
- Massage and exercise therapy. Regular massage courses help alleviate the condition and avoid relapses of the disease. After eliminating acute symptoms of trochanteritis, physical therapy is indicated. Special exercises activate blood flow in the affected area, help strengthen muscles and stretch ligaments. Good results are achieved by post-isometric relaxation - special exercises aimed at stretching the tendons.
- Conservation therapy. A prerequisite for achieving good treatment results is limited mobility and gentle treatment of the affected joint for the entire duration of therapy. Exertion can reduce the effect of treatment to zero.
Surgical interventions for this disease are rarely resorted to - only in the presence of a purulent inflammatory process. In this case, the tendon bursa containing purulent exudate is opened, it is cleaned and thoroughly washed with an antiseptic. A drainage tube is inserted into a wound that is not completely sutured for several days so that the accumulated fluid can drain out and the wound can be washed and cleaned several more times.
We use the following methods to treat trochanteritis:
- Shock wave therapy
- Physiotherapy
- PRP therapy
- Manual therapy
- Neurac therapy
- Decompression kinesiotherapy
- Surgical
Prognosis for the treatment of trochanteritis
The latent course of the disease often becomes the reason for the patient’s untimely access to doctors. There are also medical errors in diagnosing the disease.
And yet, with timely access to really good specialists, the prognosis is very, very favorable - trochanteritis of the hip joint responds well to complex therapy, and in a short time. Expected effects of treatment for trochanteritis:
- Elimination of pain;
- Restoring movement without pain;
- Restoring and improving the quality of joint tissue;
Trochanteritis of the hip joint: symptoms
Trochanteritis can occur as unilateral or bilateral. The first symptom is the appearance of pain. The pain increases during sports, when lifting and carrying heavy objects, and walking. The pain may go away during rest, but often occurs when the body is positioned on its side during sleep or rest. It is difficult to diagnose trochanteritis; in most cases, apart from pain, there are no other manifestations of the disease. The hip joint moves well, there are no restrictions of movement.
During trochanteritis, pathological changes occur in the trochanter of the thigh, the uppermost point of the thigh, and tendons. When the disease becomes chronic, the pain becomes constant, disturbs during rest, sleep, and intensifies when the body is positioned on the side of the affected trochanter. Trochanteritis is easier to treat at an early stage of development. If pain in the hip joint is accompanied by swelling, redness of the skin, and a rise in temperature, this may indicate the development of septic trochanteritis or tuberculous trochanteritis.
At the Yusupov Hospital, a patient can undergo diagnosis and treatment of trochanteritis using physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and other procedures. In the hospital, the patient will be able to engage in physical therapy with an instructor; exercise therapy exercises are developed individually for each patient. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Treatment of trochanteritis in Kyiv
Kiev Center for Orthopedics and Rehabilitation “ZARTA” invites everyone who needs to undergo treatment for trochanteritis in one of the best clinics in the capital. Our clinic specializes in injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Modern equipment, responsible specialists and our own rehabilitation department are the key to fast and successful treatment!
We are located at Lobanovsky Avenue 4B.
Trust your health to the best!
Center for Orthopedics and Rehabilitation "ZARTA". +38 +38