Hello, site visitors! We invite you to find out why fluid in the hip joint is dangerous in a child. Fluid accumulation may be associated with bursitis, which involves inflammation in the joint capsule.
The primary diseases of disorders in the synovial membrane include synovitis. The inflammatory process is often associated with metabolic problems.
Synovitis does not rarely occur in children aged 1.5 to 16 years. It can occur in a painful and acute form. The disease affects the left and right side of the thigh with equal frequency.
There is a risk that the inflamed synovium in the lower region may result in lameness.
Causes of the disease
Let's consider the causes of the disease. Synovitis can be infectious or aseptic in nature. Aseptic disease develops when exposed to the following factors:
- Allergic reactions.
- Injury to joints.
- For problems with the nervous system.
- Endocrine system disorder.
- Autoimmune diseases.
An infectious disease occurs when pathogenic microorganisms enter the joint cavity.
Main symptoms
Diagnosis of fluid accumulation in the pelvic bones is most often carried out in the later stages. It is important to know the symptoms of the disease in order to recognize it in time.
At the very beginning of violations, they cannot be identified. The disease can occur without pain. One of the first signs is swelling on one side and pain in the leg. During an acute inflammatory process, severe pain occurs, which can only be treated with painkillers. It is also worth noting the signs by which fluid accumulation in an adult can be determined:
- Soreness and enlargement of the thigh.
- Redness of the skin in the affected area and a swollen appearance.
- The temperature may rise.
- Pulsating sensations at rest.
- Sharp pain when moving.
As the process progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced. Joints become less mobile. Convulsive muscle contractions occur near the affected area. In the chronic form of the disease, bursitis is added to synovitis in adjacent tissues. In this case, inflammation appears in the joint capsule. Synovitis can cause cartilage atrophy and bone destruction.
Diseases and their causes
The accumulation of fluid in the joints and the primary causes of the anomaly lead to the development of various diseases:
- Hemoarthrosis. Occurs after receiving mechanical damage. After this, blood enters the joint, accumulating in this area.
- Synovitis. The disease is inflammatory in nature. During its development, the synovial membrane of the joint is affected, which ultimately leads to the patient experiencing a pronounced pain syndrome. There are several types of disease, differing in the initial cause of occurrence. Immune type, characterized by abundant secretion of interarticular fluid. Most often, it is a consequence of a strong reaction of the body to an allergen or a serious illness. Purulent inflammation can occur due to the entry of harmful microorganisms into the synovial bursa, causing chlamydia, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, dysentery and more. The aseptic type develops after injury, an infectious infection, or as a consequence of severe hypothermia. The liquid does not contain viruses or purulent microorganisms.
- Arthrosis. One of the most common pathologies that occurs after severe mechanical injuries or natural age-related wear and tear of the joints. There are two stages of the disease. In the first, the amount of fluid near the joint decreases sharply and pain occurs, in the second, the fluid, on the contrary, accumulates in the affected area, due to which a tumor forms there.
- Arthritis. This is a whole group of joint diseases that occur in an inflammatory form. The causes may be disorders of the immune system, regular stress on the same muscle group, mechanical damage, mental trauma, infectious diseases and allergic reactions. Most often it occurs in people who are overweight, exercise little, eat poorly, and live in regions with poor environmental conditions.
- Bursitis. Occurs after infectious diseases or injury. Inflammatory processes develop in the synovial bursa, as a result of which fluid begins to flow into it. This disease can be considered an occupational one, since most often it develops in people who constantly experience stress on certain joints or muscle groups at work.
Also, the causes of the development of pathology in the joints and the occurrence of edema are often fractures of the articular bones.
Diagnostic measures
Synovitis in childhood is not at all a rare occurrence. The disease begins abruptly and develops quickly. Particular pain is felt in the morning.
The child may have difficulty moving the joint. Doctors say that synovitis in a child often occurs due to colds, for example, due to the flu. It is necessary to begin timely treatment, as the disease can have unpleasant consequences in the form of lameness.
In some cases, an analysis of the fluid that is taken from the bone cavity using a puncture is required.
When analyzed, no microorganisms should be detected in the liquid. A biochemical examination is also carried out, which allows us to obtain data on the condition of the joint lining and vascular system. The protein content indicates the degree of membrane permeability. Comprehensive diagnosis includes a routine examination, cytological examination, biopsy and arthroscopy .
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of the disease is carried out in several directions: destruction of pathogens, symptomatic treatment and bacterial therapy.
First of all, you need to remove the causes that caused the disease. Infectious diseases, colds and other pathologies should be cured.
For children under 4-5 years of age, gentle treatment methods are used, which should be prescribed by a specialist.
The joint must be kept immobile, and this can be achieved by using a cast or a pressure bandage.
The doctor prescribes medication to prevent the development of a purulent infection. The following drugs are used in the treatment of synovitis:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain and symptoms of inflammation. They can be taken orally, as well as in the form of ointments and injections. Non-steroidal drugs include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac and Nimesulide.
- Corticosteroids are effective in inflammatory processes. The most commonly prescribed drug is Dexamethasone.
- Drugs that stimulate proteolytic enzymes are administered simultaneously with the puncture.
- Medicines that regulate circulation help repair damaged tissue. Of these drugs, it is worth noting Thiatriazolin and Nicotinic acid.
- Antibacterial agents are also injected into the joint cavity.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system.
If synovitis is complex, surgical intervention – synovectomy – may be required. In this case, the joint capsule is opened and suppuration and necrotic tissue are removed. The cavity is then treated with antibiotics. After surgery, if there is no more fluid, treatment with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and hemostatic agents is also carried out. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also carried out - exercise therapy, UHF and electrophoresis .
Causes of synovitis of the hip joint and its treatment
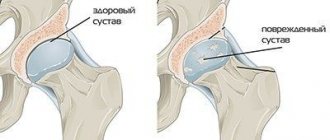
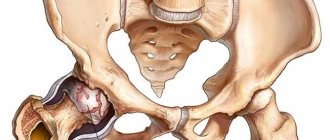
Synovitis of the hip joint is an inflammatory disease that affects the synovium and is accompanied by the accumulation of effusion in the joint capsule. This disease is especially common in boys under 10 years of age. In terms of prevalence, it ranks second, the first being synovitis of the knee joint.
Classification of synovitis
According to the method of origin it can be:
- Causes of synovitis of the hip joint and its treatment: traumatic (most common) - develops with mechanical damage to the joint (fractures, dislocations, punctures, bruises);
- Causes of synovitis of the hip joint and its treatment: infectious - detected when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the joint cavity;
- Causes of synovitis of the hip joint and its treatmentreactive (a type of allergy) - occurs in response to the development of various diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis) or the accumulation of toxic substances in the body;
- Causes of synovitis of the hip joint and its treatmenttransient (mainly diagnosed in children) - manifests itself as a result of increased loads on the hip joint or after viral diseases (influenza), manifests itself suddenly and develops rapidly.
Depending on the type of effusion, synovitis is divided into:
- serous;
- serous-purulent;
- purulent.
The latter type is characterized by the accumulation of pus in the joint capsule and the appearance of weakness and fever. The cause of the disease can be a postpartum infection, bruise or injury, leading to the development of sepsis. Synovitis can occur in acute or chronic form, the latter develops with improper treatment or its absence.
Causes of the disease
Inflammatory processes can be provoked by:
- injuries that violate the integrity of the synovial membrane;
- allergic manifestations due to intoxication of the body;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems;
- infections;
- degenerative processes in joints;
- ligament weakness;
- hemophilia;
- severe stress.
Symptoms of inflammation
Synovitis of the hip joint is usually accompanied by:
- pain;
- limitation or complete loss of mobility;
- the appearance of effusion (fluid accumulation);
- muscle spasms;
- swelling and edema;
- joint deformation;
- redness of the skin;
- local temperature rise.
Treatment of synovitis
For treatment to be successful, it must be comprehensive and focus on:
- elimination of the causes of inflammation;
- relief from symptoms of the disease;
- restoring the functionality of the joint;
- general strengthening of the body.
Therapy of inflammatory processes is carried out in several stages:
- puncture - a needle is used to pierce the joint and remove synovial fluid;
- immobilization - joint mobility is limited for 5-7 days using a special patella or pressure bandage, in some cases plaster splints or splints are installed;
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
Several groups of drugs are used in the fight against synovitis:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, voltaren, indomethacin, diclofenac, movalis) – suppress the inflammatory process and relieve pain;
- glucocorticosteroids (dexamethasone, Kenalog-40) – necessary for severe disease;
- inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes (Gordox, Trasylol) – stop degenerative and necrotic processes;
- antibiotics – prevent the development of secondary infection after puncture;
- drugs that stimulate blood microcirculation (troxevasin, trental, nicotinic acid, ATP);
- Dietary supplements (Collagen Ultra) – prevent the transformation of the disease into a chronic form;
- vitamins – strengthen the immune system.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used both internally and topically in the form of creams and ointments. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises. If conservative therapy is unsuccessful, they resort to surgery, during which partial or complete removal of the synovial membrane is performed.
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of synovitis of the hip joint, you must:
- Do regular moderate exercise;
- avoid injuries and stress;
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- maintain the normal functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of synovitis, recipes from traditional medicine can also be used as an auxiliary therapy. They are used to speed up recovery processes, but are not effective as the main treatment. The following recipes will work:
- Bay leaves are crushed and filled with unrefined oil. Then the mixture is infused for half a month in a dark place. Rub this mixture over the affected areas.
- A compress can be made from propolis tincture with vodka.
- A special decoction is made from birch leaves, willow bark and elderberry flowers.
Before using alternative treatment methods, you should consult your doctor.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures involve timely consultation with a doctor in case of injuries, the occurrence of inflammatory processes and metabolic disorders. When playing sports, it is important to follow safety precautions and also be careful not to cause harm to the muscular-articular system. Nutrition should be rational and balanced.
A sufficient amount of protein must enter the body. If injuries occur, you should immediately seek help from a traumatologist.
This will avoid complications. Among the negative consequences, it is worth highlighting chronic arthritis, inflammation of muscle tissue and decreased physical activity. The prognosis of the disease depends entirely on correct diagnosis and quality therapy. If you follow all medical instructions, then in most cases you can expect a complete recovery, as well as restoration of motor function.
Particular attention should be paid when unpleasant symptoms appear in children. In any case, you should not despair, but you need to immediately take certain measures.
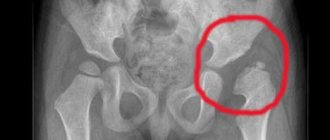
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
Symptoms increase gradually. The higher the degree, the more new signs there are.
Limited movement
With an active inflammatory process and rubbing of bones, bone tissue grows compensatory. The range of movements decreases. In the later stages, the symptom provokes deviations:
- transition of inflammation to the synovium;
- growth of fibrous tissue into the joint.
Stiffness of movement appears at each stage. With stage 1 disease, rotational movements are limited. At 4 – a person cannot walk, squat, stand up, or turn his leg to the side.
Pain syndrome
At stage 1, there is practically no pain, the person may feel discomfort. Arthralgia occurs in grade 2. If a person rests for a long time, it decreases. Acute pain is provoked by the following factors:
- active mobility;
- lifting heavy objects;
- hypothermia;
- viral, bacterial infections of systemic type;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (synovitis).
Periodically, a stage of remission occurs. The person stops feeling pain. But exacerbation occurs immediately after the influence of negative factors.
Crunch
Joints crunch when moving:
- flexion, extension;
- walking;
- rotation of the hip joint.
When moving, crunching, clicking, and crackling sounds appear. The sign occurs when bone processes and osteophytes interact. The more they rub, the greater the inflammation and damage. Usually the crunch is accompanied by pain.
Lameness
Develops at stages 3-4. The man has a strong limp and requires a cane to walk steadily. Cause of condition:
- flexion contractures;
- extensive damage to the bone surfaces inside the joints;
- deformation of the articular cavity.
The patient's leg does not straighten completely; each step causes lameness combined with pain. When walking, he tries to lean on his healthy leg, this changes the center of gravity.
Shortening of the lower limb
The symptom develops no earlier than stage 3. The leg is shortened by 1 cm. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the reduction of the lower limb will be stronger. Reasons for shortening:
- atrophic processes in muscles;
- abrasion of cartilage;
- reduction in the volume of the articular cavity;
- damage, deformation of the femoral head.
The greater the shortening, the more severe the lameness.
Muscle spasms
With coxarthrosis, the patient periodically experiences muscle spasms. Causes:
- weakness of the ligamentous apparatus - the muscles go into a state of spasm to maintain the integrity of the hip joint;
- inflammation of the synovial membrane;
- damage to nerve endings by osteophytes for compensatory pain suppression.
The symptom does not persist throughout the course of the disease. He appears periodically.