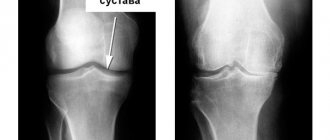
The ankle joint, or, as it is popularly called, the ankle, is a joint that is an important element of the musculoskeletal system. Largely thanks to this joint, people can walk fully and straight and perform various maneuvers that the situation requires. The ankle joint ensures correct and rational distribution of the load on the foot area. Thanks to this, it can support the weight of the entire human body.
However, despite the high endurance of the joint, it is not always able to cope with loads. In this case, synovitis of the ankle joint develops.
What is synovitis of the ankle joint?
Several anatomical structures are involved in the formation of the ankle joint. Because of this, the articulation is usually classified as complex. Participating in the formation:
- three bones - little (lateral malleolus) - and tibia (medial malleolus), talus;
- articular ligaments that provide stability, capsule, synovium.
Naturally, only the harmonious work of all the constituent parts of the anatomical formation ensures the correct performance of its functions. However, in some cases the functionality is severely impaired. This happens, for example, with the development of synovitis of the ankle joint.
Synovitis of the ankle joint is an inflammatory process in the joint, which primarily affects the synovium.
Not all patients understand what inflammation of the synovial membrane is.
It's actually quite simple! The synovial membrane normally covers the joint on the inside. Thanks to it, normal metabolism is ensured in cartilage, which is deprived of its own vessels. The synovial membrane also secretes a special fluid, which is known as synovial fluid. The liquid acts as a shock absorber, reducing damage to anatomical structures due to friction. As soon as the synovial membrane becomes inflamed, fluid begins to be produced in larger volumes than necessary. As a result, the joint increases in size due to swelling, begins to hurt, and the patient experiences a pronounced limitation in the mobility of the joint.
Causes of synovitis of the knee joint
So, in most cases the cause of inflammation is:
- fur damage character that emerged as a result of traumatic experience. Pathologies cause destruction of the connective tissue of the joints;
- changes inside the joint cavity caused by loss of mobility and elasticity of tissues. In such situations, a slow infection develops and pus appears.
The traumatic type of synovitis is considered the most common. It has been studied almost completely and has a wide range of treatment variations.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of synovitis are important for an accurate diagnosis. Among the signs of synovitis that indicate inflammation, there are several dominant ones that are inherent in all varieties of this disease:
- dull pain;
- the formation of exudate in a huge amount, which leads to an increase in the size of the joint;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the joint.
Knowing the symptoms will help you determine the nature of the injury in a short time. If the above signs of inflammation are detected, you should seek help from a specialist as soon as possible.
Causes
Damage to the synovial membrane by the inflammatory process is a problem that not all people face during their lives. Doctors identify a number of factors that contribute to the development of the disease.
Injuries
Among the main reasons for the development of the disease are traumatization. Most often, synovitis is caused by sprains and ruptures of ligaments, and fractures in the ankle joint.
Birth defects
Often in the practice of an orthopedic traumatologist there are congenital defects that contribute to the development of the disease. This could be, for example, hallux valgus or flat feet. In this case, the load is distributed incorrectly, which leads to inflammation.
Diseases
Osteochondropathy of the talus. As a result, the articular surfaces are deformed, and a free osteochondral articular fragment may form. The above factors cause synovitis.
Shoes
Incorrectly chosen shoes can contribute to the development of symptoms of synovitis. For this reason, the disease affects women who are forced to wear high-heeled shoes, due to which the load on the ankle joint is very high.
High physical activity
Another important factor is intense physical activity. The joint does not have an infinite reserve of strength, and sooner or later its functionality begins to decline, which leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Surgery
Pathogenetic therapy of traumatic synovitis involves restoration of anatomical features in the joint. The treatment regimen in each individual case is determined individually, taking into account the scale of changes, the severity of general disorders, the prospects and risks of the need for surgery and other points. In the postoperative period, drug correction of local metabolic disorders is prescribed and rehabilitation is carried out.
If irreversible changes in the synovial membrane develop during the chronic course of the disease, surgery is performed - partial, subtotal or total synovectomy. In the postoperative period, immobilization is performed, antibiotics, painkillers, exercise therapy and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Types of synovitis of the ankle joint
Like any other ailment, the inflammatory process in the ankle joint is divided into several types.
The first classification is based on the severity of symptoms and the rate of fluid accumulation. There are acute and chronic pathologies. In the first case, liquid accumulates due to some negative impact in a short period of time. The symptoms in this case are pronounced and difficult to ignore.
In the second case, fluid accumulates slowly in the joint cavity. As a result, symptoms can either be mild or develop progressively. The chronic disease occurs in waves: periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations with quite pronounced symptoms.
The second classification is based on the reason that served as the impetus for the development of the inflammatory process. Highlight:
- an infectious form that develops due to the entry of pathological microorganisms into the joint cavity and is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication, malaise, and weakness;
- the trophic form, which is mainly found in patients who suffer from decompensated diabetes mellitus for a long time without taking the disease under control, is characterized primarily by impaired blood supply with the subsequent development of inflammation;
- traumatic (post-traumatic) form, which develops due to improper treatment of joint injury (the duration of injury for the development of synovitis is not decisive; the joint suffers, even if the injury occurred years ago);
- autoimmune form, which is a consequence of aggression of a person’s own immunity on joint tissues (in the ankle area it is rare, but it cannot be excluded), etc.
Additionally, to classify the disease, an assessment of the composition of the joint fluid is used. The disease can be fibrinous, serous, purulent or hemorrhagic.
Signs
The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. In the acute form, pain, swelling, and redness of the skin occur in the joint area. Movements are limited due to pain. In the chronic form, the same symptoms are present, but they are less pronounced. They then subside, then a new exacerbation develops. Inflammation of the articular membrane when an infection is attached can turn into a purulent form. The joint swells even more, severe pain occurs, and pus accumulates under the skin. The general condition of the patient is disturbed, body temperature rises.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Symptoms
The signs of the disease, regardless of its origin, are the same. True, they can appear at different time intervals. Symptoms characteristic of synovitis are:
- increased fatigue under loads that a person could previously easily cope with;
- feeling of discomfort in the problem area;
- pain localized in the ankle area, which can affect surrounding tissues with severe swelling;
- redness and swelling of the area involved in the pathological process;
- an increase in temperature and the appearance of symptoms of general intoxication (with an infectious form) are possible.
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease. The first alarm bell is always pain, which initially appears only when performing rotational movements. Gradually, the pain increases so much that it accompanies the patient even at rest, disrupting sleep and normal functioning in general.
How to diagnose the disease?
The diagnosis of ankle synovitis is made on the basis of a patient interview (clarification of the circumstances of the occurrence of the disease and predisposing factors), as well as an examination. The latter involves palpating the affected area and identifying the characteristic symptom of fluctuation: the doctor places one hand on the ankle and taps the joint area with the other. If a specialist feels characteristic “shocks” with a motionless hand, this indicates an accumulation of fluid in the synovium - i.e. about synovitis.
Among additional research methods, the “gold standard” is puncture - a puncture of the articular membrane with sampling of the contents of the joint. The resulting liquid is examined for the presence of characteristic microflora, protein and enzymes. And when infectious agents are detected, their sensitivity to antibiotics is determined.
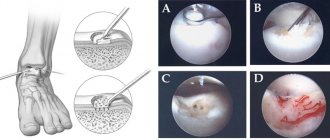
In some cases, arthroscopy may be necessary, a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting video equipment into the joint cavity for diagnostic or treatment purposes. Often the manipulation is accompanied by the removal of tissue from the articular membrane for further research - biopsy.
To exclude concomitant pathologies (trauma, arthrosis, etc.), ultrasound and X-ray examinations are prescribed. Sometimes computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may be needed to study synovitis. Also, as a general rule, a clinical blood test and determination of acute-phase indicators are carried out (indicating the activity of the inflammatory process). It is possible to prescribe allergy tests if immune mechanisms for the development of the disease are suspected.
Diagnostics
Synovitis of the ankle joint does not begin to be treated until the diagnosis is confirmed. The following diagnostic methods are used in combination, which allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and eliminate errors:
Visual assessment
Inspection of the joint is a mandatory stage of the diagnostic search. Moreover, it is assessed not only at rest, but also in motion. For example, when walking or performing any simple actions.
Instrumental techniques
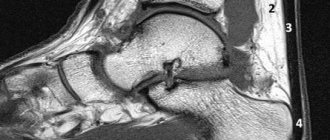
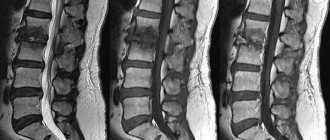
Sometimes the swelling of the surrounding tissues is so severe that it becomes difficult to evaluate the joint. In this case, ultrasound, MRI, and radiography are used as auxiliary measures.
MRI of the ankle
Performing a puncture
The method of obtaining intra-articular fluid is not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic. On the one hand, the doctor can evaluate the bacterial composition of the synovial fluid and identify the infectious agent, if any. On the other hand, excess fluid that interferes with normal functioning is removed from the joint cavity, which alleviates the symptoms of the disease.
Only after the doctor is confident in the diagnosis will he begin to choose the optimal treatment.
Conservative therapy
In the treatment of synovitis of the ankle joint, it is first necessary to try to stop the pathological condition using conservative techniques. For this:
- the patient is taught to properly fix the affected joint to reduce the load;
- carry out physiotherapeutic measures that will help relieve inflammation and improve regeneration processes;
- select medications that can relieve pain and eliminate swelling of the affected area;
- after the onset of stable remission, courses of physical therapy are recommended to improve joint mobility and prevent relapses of the disease.
Puncture of joint fluid can also be part of conservative therapy. By removing excess fluid, the functionality of the joint can be improved. However, puncture is a measure that gives only temporary results. Treatment in any case should be aimed at eliminating the causes of the pathology. For example, it may be necessary to clear up an infection with antibiotics or fight an autoimmune process.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the cause of the pathology and make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. After collecting anamnesis and systematizing the data obtained about the patient’s complaints and previous diseases, a visual examination is carried out. In this case, the injured knee is palpated, the gait and the patient’s ability to straighten the joint are analyzed. The patient is asked to do:
- Puncture.
In this case, the surgeon numbs the pain, and then pierces the joint cavity with a thin needle, collecting the synovium. In laboratory analysis, attention is paid to the color, transparency and viscosity of the liquid. Next, it is subjected to microscopic and cytological examination to determine the cause of inflammation. The results obtained make it possible to choose the right treatment tactics. - MRI.
Using this method, you can see the structure of the synovial membrane. If there is liquid, the device allows you to estimate its quantity. Thanks to MRI, the specialist will receive a detailed description of the functionality of the joint, as well as information about the condition of the surrounding tissues, blood vessels, and nerve fibers. - Ultrasound.
Used to visualize changes in the thickness of the inflamed synovium. This is one of the signs of synovitis activity. At the same time, it is possible to examine in detail the structure of soft tissues and detect the pathological process at an early stage. - Arthroscopy.
This therapeutic and diagnostic procedure makes it possible to examine the affected joint, differentiate the nature of the lesion, and also study the relief of the synovial membrane along its entire length.
Based on these data, the specialist determines the diagnosis, clarifies the form and degree of development of the disease, and prescribes treatment.
Complications
In the absence of proper treatment for purulent synovitis of the ankle joint, infectious agents may spread throughout the surrounding tissues (purulent arthritis, cellulitis) or throughout the body with the development of sepsis, a serious condition requiring intensive care in intensive care conditions.
With prolonged synovitis, dropsy of the ankle joint may develop. In this case, “looseness” of the ankle occurs, stretching of the ligamentous apparatus and subsequent destabilization of the articular surfaces.
Treatment of ankle synovitis
Therapy for ankle synovitis begins with resting the affected limb. The ankle is tightly bandaged (with periodic loosening every 3-4 hours), the leg is given an elevated position. In case of severe pain in the first two days, you can apply a cold compress for 20 minutes every 5 hours.
Conservative therapy
Further assistance depends on the nature of the synovitis:
- For a non-infectious process, the main treatment is physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation, as well as UHF with anesthetics (Lidocaine) for pain relief. If the amount of effusion in the joint capsule is sharply increased, it is possible to perform a therapeutic puncture to remove the fluid. Only a doctor can prescribe medications. In case of prolonged course, phonophoresis with hydrocorticosteroids (Cortisol) is indicated.
- For purulent inflammation, a course of antibiotic therapy (Amoxicillin, Cefotaxime), as well as a therapeutic puncture, is required. The latter involves removing the pus, but in some cases it may be necessary to rinse the joint cavity with antiseptics or antibiotics. If the infectious process is specific (tuberculosis or syphilitic), the use of etiotropic drugs (Rifampicin or Benzylpenicillin, respectively) is indicated. In case of severe purulent inflammation, the articular sac is opened and drained.
- Treatment of chronic synovitis of the ankle consists of stabilizing the primary disease (arthrosis, hemophilia, etc.). Patients are usually prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesil, Voltaren) in tablet or gel forms. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also effective: electrophoresis, UHF, paraffin baths. With frequent exacerbations, it is possible to introduce the antienzyme drug Aprotinin into the joint sac.
Surgical treatment
In case of prolonged synovitis with persistent relapses or irreversible changes in the articular membrane, surgical treatment is performed. The latter consists of complete or partial excision of the synovial bursa - synovectomy. At the rehabilitation stage, patients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics (Cefuroxime, Cefotaxime), as well as anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesil) and physiotherapy (ozokerite, electrophoresis, etc.).