The structure of the formations, their size and type of contents vary, depending on the location and duration of the onset of the pathological process. They are true (inside lined with epithelial cells) and false (without lining). Based on the type of appearance, neoplasms are divided into:
- retention (usually formed due to a disruption in the process of outflow of secretions in tissues and organs, occurring in the mammary glands, uterus, cervix, ovary, etc.);
- ramolitic (usually found in the ovaries, brain and spinal cord, can form in areas of tissue necrosis, for example after a stroke);
- parasitic (appears in different organs, is the shell of the parasite);
- traumatic (due to bruises);
- dysontogenetic (usually congenital, include different tissues of the embryo);
- tumor (formed due to metabolic disorders, have cavities filled with physiological fluids).
Nature of education
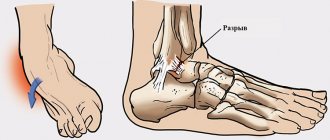
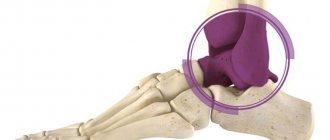
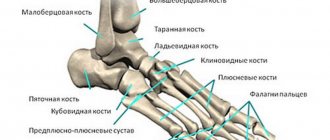
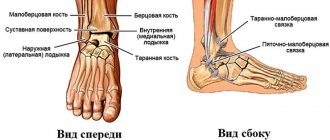
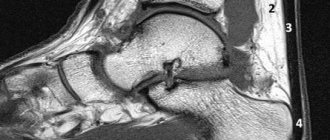
The cyst itself is a pathological cavity containing fluid inside. It is connected to the articular tissue and appears due to mechanical injuries, various degenerative diseases, as well as inflammatory processes. This pathology most often affects the most mobile joints of the human body, which includes the ankle. It has clear boundaries and at the same time a solid and very elastic shape, due to which it can be easily detected during palpation.
The pathology is often localized in the tendon of the joint or, in some cases, in the projection of the synovial bursa. It usually develops on the back side, but does not connect to the skin or the underlying fatty tissue. From the outside, such an anomaly has no obvious signs of its existence; even the surface of the skin that is located above it does not change.
It should be emphasized that cystic formations in the ankle joint do not have a tendency to degenerate into malignant ones. Most often, they exist in an asymptomatic form, due to which there are no painful expressions, which also do not appear during palpation of the formation. However, feelings of pain may appear during the operation of the joint itself. In addition, such joint anomalies are quite labile, due to which they can change their size, and in some cases even disappear on their own after a certain time.
Complications
May occur:
- capsule rupture;
- inflammation of the cyst and surrounding tissues.
Capsular rupture occurs when the capsule is large in size, has high physical activity, or is injured in the area of formation. When the capsule ruptures, its contents leak into the joint and can cause inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
With hypothermia and inflammatory diseases of the ankle joint, inflammation of a cystic formation may develop. Its contents fester, which can also lead to rupture. Timely surgical treatment is an effective prevention of these complications.
Symptoms and manifestations
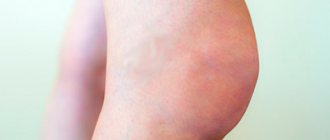
An ankle cyst is an abnormal formation with clear boundaries.
At the same time, it is well palpable on the back of the joint. If the neoplasm is of significant size, then visually it can be identified as a small swelling. Moreover, the larger the size of the pathology, the stronger the pain that occurs in the ankle while walking. Due to the appearance and development of such an anomaly, the possibility of joint movement is limited. And when compression of the nerve endings occurs, sensitivity will be significantly reduced, and in extreme cases the area may even become numb. This pathology, under certain circumstances, causes thrombophlebitis, as well as varicose veins. Similar processes will take place if a cystic formation develops against the background of inflammatory and degenerative processes. If the anomaly is large, it can also be injured by shoes. In addition, many women with this disease are worried not only about the present cosmetic defect, but also about the inability to wear certain shoes.
Diagnostics
Includes:
- inspection (a rounded formation is visually determined);
- palpation (feeling), while determining the consistency, adhesion to surrounding tissues, mobility, size of the formation;
- Ultrasound (allows you to more accurately determine the size);
- MRI (the most reliable diagnostic method with high resolution);
- fluoroscopy;
- puncture (determine the nature of the contents, the presence or absence of inflammation).
Treatment methods
Treatment of the ankle joint can be carried out not only by surgical methods, but also using conservative therapy. The latter includes the following types of influence:
- Crushing. In this case, the contents of the cystic formation are mechanically squeezed out directly into the joint cavity. But this method has only a temporary effect. The fact is that the capsule of the anomaly remains in place and over time, new synovial fluid is produced, due to which the pathology regains its previous size. The use of this treatment was common in the 80s, but today it has lost its relevance;
- Puncture. During this procedure, the contents are removed from the anomaly cavity using a thin needle. After this, special anti-inflammatory and sclerosing agents are introduced into the place of the extracted fluid, which lead to gluing of the walls of the pathology. In this case, the joint should be immobilized through the use of a pressure bandage. This is necessary to reduce the amount of synovial fluid produced by the cyst in the future.
This method is used today in cases where radical treatment is not possible. However, here, just like with crushing, there is a high chance of the cyst reappearing;
Drug treatment
Drug treatment. Various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as analgin, ibuprofen, and others are used as the main active element. However, this treatment is symptomatic and only temporarily relieves pain and inflammation, but does not treat the cause of the disease.
Surgical treatment
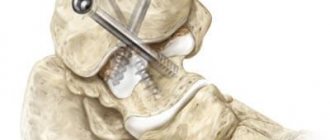
The most radical method is surgical treatment. In this case, the abnormal formation is completely removed along with the capsule. After this, suturing is carried out, as well as strengthening of the ankle joint. When the operation was performed successfully, the pathology does not reappear. In general, surgical treatment is prescribed in cases where there is:
- Rapid growth or presence of already large anomalies;
- Inflammation with the formation of pus;
- An obvious cosmetic defect that interferes with life;
- Serious problems in the ankle joint caused by a cyst.
This surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia, and to avoid postoperative scars, only a small incision is made. The best method for this is the endoscopic method, which is the most gentle. In addition, after such an operation there is a very short rehabilitation period, after which the joint’s functionality is restored quite quickly. Read more about the types of treatment for joint cysts in this article.
The main types of cystic formations
Ovarian
This is a fluid-filled bladder that causes the ovary to enlarge, leading to pain and sometimes infertility. The main reason for its appearance is hormonal imbalance. The disease often occurs without symptoms; when the formation is large, the cycle is disrupted, pain is felt in the lower abdomen, a false urge to urinate occurs, and bleeding occurs outside of menstruation. Methods of surgical treatment: oophorectomy (complete removal of the ovary), laparoscopic cystectomy (excision of the cyst), adenxectomy (surgery to remove the uterine appendages). In most cases, the choice is not classical surgery, but gentle endoscopic removal of the cyst while preserving the patient’s reproductive function.
Read more about ovarian cyst removal
Coccygeal
Most often occurs in men aged 15-30 years. It is an opening in the area of the gluteal fold, approximately 10 cm from the anus. Externally it looks like a fistula. It can be congenital or acquired - due to too much hair in this area. It manifests itself as pain when walking, sitting, redness of the tailbone, a feeling of discomfort and the presence of a foreign body in the area where it is located. At a later stage, pus is released from the hole.
Read more about the treatment of coccygeal cyst
Bartholin gland
Appears due to blockage of the gland duct due to infection or chronic inflammation. The formation has a capsule and is filled with secretion, which gradually gels. If it is large, it interferes with walking and sitting, makes intimate intimacy inaccessible, and can become infected and lead to an abscess. Usually reaches 2 cm, but there are formations up to 9 cm. The main causes are chronic bartholinitis, candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, decreased local immunity.
Where and how to remove a Bartholin gland cyst
Eye
A hollow formation filled with non-inflammatory fluid - products of the activity of the cornea or conjunctiva. May originate from the cornea, iris, conjunctiva and other eye membranes. Causes: inflammation and trauma, congenital anomalies. The disease is manifested by pain, a feeling of fullness, blurred vision, and the presence of translucent dots in the field of vision.
Read more about surgical treatment of cysts in ophthalmology
Maxillary sinus
A cavity containing fluid and having a membrane attached to the wall (usually the lower) of the maxillary sinus. A cystic formation can be true (its walls consist of mucous membrane) or pseudocyst (the mucous membrane is split and fluid accumulates in it). It manifests itself as headache, difficulty breathing through the nose, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the eye and cheek area, mucus discharge from the nose and its flow down the wall of the pharynx, discharge of yellow transparent fluid from the nose, frequent sinusitis with suppuration. It is formed due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the nose, blockage of the excretory duct of the glands of the maxillary sinus, inflammation of the teeth, spreading to the roots.
Read more about the treatment of abscesses and cysts of the ENT organs
Mammary gland
A cavity bounded by a capsule of connective tissue and filled with fluid is formed in the ducts and can be single or multiple. It is formed due to an increase in the duct of the mammary gland, the accumulation of secretions in it. The lesion may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The disease is asymptomatic for a long time; over time, pain and burning appear in the mammary gland, and may be accompanied by suppuration and inflammation. One of the varieties is a fatty cystic formation that occurs when the sebaceous gland of the skin is blocked and filled with secretions. The main provoking factors are mastitis, thyroid disease, inflammation of the genital organs, and ovarian dysfunction.
Learn more about symptoms and treatments
Uterus and cervix
These are dilated and clogged glands, inside of which secretions (mucus) accumulate. The disease occurs against the background of endocervitis, cervitis. Provoking factors: abortion, childbirth, infections, menopause, hormonal imbalance, use of an intrauterine device, infections. Nabothian cystic formations are localized in the vaginal area of the uterus and are not removed until they reach a certain size. Retention occurs due to an excessive amount of secretion in the gland duct. The disease is often asymptomatic; its indirect signs are frequent inflammation.
Read more about surgical treatment of uterine and cervical cysts
Brain
A cystic formation is an accumulation of fluid in the substance or membranes of the brain. When large in size, it entails intracranial hypertension and puts pressure on the surrounding brain structures. Can form at any age. Depending on the location, cerebral (intracerebral) and arachnoid formations are distinguished. The first are found in the internal structures of the brain, in areas of necrosis. The second ones are in the meninges. Provoking factors: inflammatory diseases, trauma, including birth, cerebrovascular accident, parasites, complications after surgery. They manifest themselves as nausea, a feeling of pressure on the eyes, decreased performance, sleep disturbances, pulsation or noise in the head, and visual impairment.
Thyroid gland
Small formations (up to 5 mm) may not have pronounced symptoms. If the thyroid cyst has dense inclusions and a complicated structure, then special studies (for example, ultrasound), tests and biopsy are needed, because such a condition may be a sign of malignant degeneration.
Read more about surgical treatment of thyroid cysts
Larynx
Cysts of the larynx can be located in any part of the larynx. They do not grow into the mucous membrane, but grow towards the lumen of the larynx and thereby narrow it. The cause of retention cysts is blockage of the excretory ducts of the laryngeal glands. There are cysts of the vocal cords that arise due to constant irritation.
More information about surgical treatment of laryngeal cyst (laryngocele)
You can find out the prices for cyst removal endoscopically or by another method, as well as the cost of preoperative diagnostics on our website or by calling honey. +7 (812) 435 55 55.