There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Features of the use of pins Operations using a plate External fixation devices Indications for osteosynthesis Rehabilitation and prognosis
Osteosynthesis (from the English osteosynthesis) of the shoulder is a traumatological treatment method based on the use of metal structures (plates, pins, external devices) to restore the integrity of bones during fractures. Such operations are carried out when, due to injury, fragments have formed and displacement has occurred. The main task of the surgeon is to compare the fragments and firmly fix them until complete fusion.
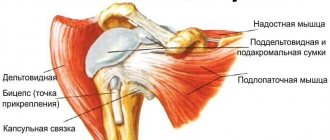
In case of damage to the humeral head (intra-articular fractures of the head and neck of the humerus with complete displacement and separation of the proximal part), osteosynthesis is performed using the open fixation method. The operation is indicated when the fragments are adequately supplied with blood and the integrity of the cartilaginous segment is not compromised. If the head is crushed and its nutrition is disrupted, there is a risk of necrosis. Therefore, in this case, it is better to undergo joint replacement.
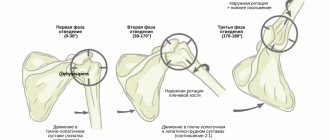
Depending on the clinical picture, osteosynthesis of the shoulder joint can be extramedullary (using plates) or intramedullary (using wires). These two types of operations belong to the group of internal, that is, submersible. In this case, screws, knitting needles, pins, plates, and wire can be used to fix fragments. The external (percutaneous) option is the installation of external fixation devices, the most famous is the Ilizarov apparatus.
Features of using pins
During intraosseous surgical treatment, pins are inserted into the medullary cavity of the long parts of the tubular bones. The advantages of the technique are low trauma, the ability to put a load on the injured limb after just a few days. The operation is performed for transverse bone fractures with sufficient volume of the bone marrow cavity. For more durable fixation, pins with holes for screws are used, which are passed through the bone. This is BIOS, that is, blocked intramedullary osteosynthesis. Self-locking Fixion pins are also used. They allow you to perform the operation as quickly as possible and are used even for comminuted fractures.
Features of the procedure
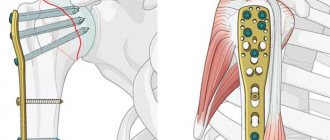
In case of a complex fracture with displacement of bone fragments, simply setting the bones and applying a plaster will not work. A structure is required that will fix the fragments in the desired position. Otherwise, the fragments may grow together incorrectly. It is in such situations that you cannot do without pins, plates and screws. The plate reliably fixes all parts of the bone and even allows the patient to perform simple operations with his hand. If you put a cast on, your hand needs rest. However, if a plate is available, the arm must be developed the very next day after surgery.
Plate is a conventional name for the structure. It can take different forms depending on the characteristics of the fracture. Often three-dimensional elements that have curved parts are created for the patient. For fractures in the body of the bone, the plate will be straight.
In addition to plates, pins are used to fix bone fragments. Plates and pins are not just different types of bone fixation structures. When installing the plate, a longitudinal incision is made, leaving a long scar at the installation site. The pin is installed through a small incision, the scar is almost invisible.
However, pinning is not always appropriate - a pin can be installed only if the fracture:
- closed;
- simple.
In this case, the bone fragments should be located at a relatively close distance. The introduction of a pin is called intraosseous osteosynthesis. The pin has the shape of a rod; it may have holes or hooks necessary for fixing the fragments. To insert a pin, a small hole is first made, then a channel is drilled into the bone. The prepared pin is inserted into the canal. The product is made from biocompatible materials.
For simple and fresh fractures, the operation is performed under local anesthesia; in all other cases, doctors use general anesthesia. The pin installation operation takes no more than 2 hours.
External fixation devices (percutaneous technique)
The technique allows you to reposition and carefully fix the fragments without exposing the fracture area. Its essence is to pass rods or knitting needles through the bone tissue, which are fixed externally in a special apparatus. Now there are monolateral, circular, sector, semicircular, bilateral and combined devices. Preference is often given to rod models. The use of external fixators is an indispensable method of treating highly sensitive injuries, such as mine explosions and gunshots, which are accompanied by significant damage to both bones and soft tissues. The peripheral blood supply to the limb must be preserved.
Relative readings:
- Psychological discomfort associated with the presence of metal structures.
- Women who are planning childbirth (the effect of alloys on fetal tissue has not been studied).
- Persons for whom the presence of metal structures causes discomfort in everyday life (wearing shoes, when playing sports, etc.).
Many traumatologists are inclined to believe that the supporting limbs (lower limbs) need to be removed, since there is a high risk of re-fracture in the area of the metal structures, and the possibility of prosthetics in the future. An exception can be considered elderly patients operated on at the level of the proximal femur with the presence of asymptomatic metal structures, when the risk of recurrent fractures and the appearance of new complaints after removal is very high.
Implants from the upper extremities are removed if indicated. For example, impingement between the plate in the proximal humerus and the acromion of the scapula, limiting movement in the shoulder joint; screws that create a risk of damaging the tendon, etc.
If removal of an asymptomatic implant is very traumatic or there is a high risk of complications, then removal is not recommended. For example,
- removal of the plate from the shoulder during placement, which exposed the radial nerve during the operation,
- removal of asymptomatic plates from the diaphysis of the forearm bones, which is subsequently accompanied by a significant risk of recurrent fractures and is not recommended by many traumatologists,
- metal structures in the proximal femur, etc.
In each specific case, only after examination, a comprehensive examination of the patient, and the patient’s lifestyle requirements, the “risk-benefit” of surgical intervention is assessed and a decision is made to remove the metal structures.
If you have any questions, come for a consultation with an orthopedist-traumatologist at ACMD-MEDOX. Always happy to help! Be healthy!!
In what cases are such operations carried out?
Main indications for osteosynthesis:
- fractures that cannot heal without mechanical fixation of the fragments;
- divergence of fragments;
- intra-articular fractures;
- fractures in which there is a high probability that fragments will damage the skin, that is, the injury will change from closed to open;
- the presence of soft tissue between bone fragments;
- fractures complicated by damage to a nerve or great vessel;
- secondary displacement of fragments during conservative treatment;
- inability to perform closed reduction of fragments;
- non-united or slowly healing fractures;
- false joints.
Removing pins
Pins made from conventional materials are removed after approximately 8-10 months. The exact period is determined by the doctor. If you skip this period, the structure may become overgrown with bone tissue. You cannot leave the pin inside - this can lead to complications. If you arrive on time, the pin can be removed without unnecessary injury. The hole left by the structure will fill up fairly quickly. There will be no scars left after removal - the structure will be removed by making an incision where it was last time.
Today, special biodegradable materials are also used for osteosynthesis. There is no need to remove such pins - they dissolve in the bone cavity. No additional intervention is required when performing the procedure with modern materials.
Prognosis and rehabilitation after surgical treatment
To monitor healing, patients undergo radiography, CT, etc. Typically, the healing time is 4-6 months, regardless of the area of the fracture and the type of fixation. After 1-1.5 years, patients return to the doctor to remove the metal structure. However, this is not necessary, you can live with it - titanium does not enter into any reactions with tissues and does not oxidize. The plate may cause subtle discomfort, which people gradually get used to if they do not want to have to have their shoulder re-operated.
In the first week after surgery, there is pain, which can be relieved with painkillers, swelling of the arm, and body temperature may rise. After about 12-14 days, the stitches are removed. In the postoperative period, it is recommended to develop the shoulder, even through pain.
Patients are prescribed physical therapy aimed at accelerating regeneration, resolving compactions, and preventing the formation of keloid scars. For this purpose, laser physiotherapy is performed.
Another recovery technique is exercise therapy. Exercises are prescribed individually to restore mobility to the elbow joint. This is necessary because the joint loses flexibility very quickly when immobilized for a long time. And after surgery, sometimes the limb is immobilized for 2 months. It is not necessary to visit the exercise therapy room all the time. After 2-3 lessons with a trainer, you can master the technique of doing the exercises and do them at home.
The discomfort will persist for about six months. The joint will not fully extend, the scar will be compacted and red. Patients also note morning stiffness in the joint, pain when leaning on the elbow, and arm weakness. Gradually all this will pass, and the scar will turn white and become soft.
How is osteosynthesis performed?
The surgeon controls all manipulations using optical surgical equipment, which transmits a full-color image in high resolution under high magnification to the monitor screen. Through a skin incision of 2-3 cm, structures made of titanium or other metals that are safe for health are introduced into the fracture zone. They can be rods, screws, screws, plates, etc. During the operation, the fragments are securely fixed with these structures. After installing the fixators, the soft tissues are sutured in layers, and an aseptic dressing is applied.
Osteosynthesis can be performed on the day you visit the clinic or 1-2 days later. The period of hospitalization after surgery is usually 1-3 days.
Types and localization of mandibular fractures
Non-gunshot, most often linear fractures of the mandible occur in the area of the condylar process, the angle of the mandible, the central incisors, the canine and the mental foramen. These places are usually called “places of weakness.”
Direct fractures of the mandible occur at the site of application of force.
Reflected fractures are localized due to the direction of impact and the area of damage. For example, as a result of a lateral impact, a reflected unilateral fracture of the neck of the lower jaw often occurs. The maximum tension in the bone tissue in the midline area is created due to bilateral compression of the mandibular bone in the region of the molars (sixth, seventh and eighth teeth).
How the fragments will be located during a fracture of the lower jaw depends on several factors. These include: the strength of the damaging factor, the volume of the injured area, as well as muscle groups attached to the surface of the injured area.
Types of jaw osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis with a metal plate for a jaw fracture is carried out in different ways. It is divided into types according to 2 characteristics - the method of fixing the plates and the technology of the operation itself.
- According to the method of fixing the plate for a jaw fracture, osteosynthesis can be: focal, when the elements of the plate are installed so as to cross the fracture gap and adjoin it;
- extrafocal, in which the plate is fixed outside the jaw fracture gap or passes through it above the mucous membrane and skin (without touching damaged tissues).
- open is carried out with dissection of soft tissues and “opening” of the ends of bone fragments (separation of the periosteum);
The closed method provides accelerated healing, since it does not involve complications that are possible due to impaired microcirculation in soft tissues. But the lack of visual control during closed osteosynthesis of the jaw makes it difficult to properly connect the bone elements and carry out the manipulation in general. This requires a very highly qualified specialist.
The open method of installing plates for jaw fractures (with visualization of the bone) makes it possible to most accurately compare the fragments, as well as remove damaged (interposed) soft tissues or small fragments of hard tissue. The main difficulty of the operation is the risk of tissue hypoxia, which is a common cause of enchondral osteogenesis.
The latter involves the transition of callus to the stage of cartilage, which is not typical for the lower jaw. With enchondral osteogenesis, the formation of a typical (ossified) callus of the lower jaw slows down.
Modern methods also include ultrasonic osteosynthesis with plates . It is carried out using special modern technology and is less traumatic. Installing plates for fractures using ultrasound equipment reduces the likelihood of complications.
Installation
Installation of plates for a jaw fracture using the open method is carried out in 4 stages:
- a soft tissue incision is made to visualize and connect the fragments;
- connecting bone fragments using a plate;
- fixation of bone elements with glue, staples, quick-hardening plastics used in modern surgery;
- suturing.
The main difficulty of open surgery is trauma. The doctor works with the area in which the nerve endings and salivary glands are located, which creates the risk of damage to them, and therefore determines high requirements for the qualifications of the specialist.
A safer and less traumatic method is ultrasonic osteosynthesis of the jaw. It not only reduces the risk of complications during fixation, but also reduces the time for fracture healing.
Indications for osteosynthesis of the jaw with plates
The main indication for installing metal plates for osteosynthesis is the prevention of complications that cannot be effectively prevented by applying a traditional splint. In the case of osteosynthesis, an important task for the surgeon is to compare the fragments and fix them in the correct position. If successful, fusion will take up to 3–4 weeks.
Indications:
- fracture behind a row of teeth;
- inflammation that provoked injury;
- significant displacement of bone elements;
- high mobility of teeth at the fracture site;
- incorrect position of the jaws relative to each other.
Recovery after surgery
Rehabilitation after installation of a titanium plate for a jaw fracture takes 6 months. The specific recovery time depends on how much time has passed from the moment of injury to treatment, as well as on the patient’s age, his condition, the severity of the injury, and the method of osteosynthesis.
Rules during rehabilitation:
- immediately after the manipulation, a bandage is applied for fixation; it must be worn constantly;
- it is important to exclude any movements (talking, chewing, opening and closing the mouth);
- drug rehabilitation involves taking a course of antibiotics and restoratives, the drugs are selected individually and prescribed by a doctor;
- for recovery, the patient is prescribed decongestant and anti-inflammatory physiotherapy (from day 2 - UHF, from day 4 - magnetic therapy, after 2 weeks you can start a course of electrophoresis);
- classes in LVF (therapeutic and restorative physical education) begin 3–5 weeks after removing the fixing bandage, their goal is to restore normal speech function, normalize chewing, and facial expressions.
For the entire recovery period after installation of a plate for a fracture, the patient is prescribed a diet (liquid meals, purees, strictly at room temperature, taken through a straw). Solid food is introduced into the diet gradually after the bandage is removed and chewing functions are restored.
To avoid complications, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene. You can brush your teeth only after removing the bandage and restoring mobility, so in the first weeks hygiene comes down to rinsing your mouth, which should be done up to 10 times a day (including after each meal).
Osteosynthesis for forearm fracture
Most often, forearm fractures occur as a result of direct mechanical impact on the limb.
This may be a consequence of impacts at a high speed of falling: from a height, as a result of an accident, or a strong blow. The osteosynthesis method used in traumatology involves the surgical installation of metal fasteners on the bone. It is used to fix collected fragments in the treatment of a fracture. Used in cases of complex fractures and bone displacements.