General symptoms
Signs of pathology differ depending on the type of dislocation. Experts have identified a list of common signs characteristic of dislocations of any location:
- Redness of the skin over the injured joint.
- Severe pain that intensifies with the slightest movement.
- Upon examination, the altered shape and size of the damaged joint is determined.
- Severe tissue swelling in the area of injury.
- Loss of sensitivity due to impaired innervation of the limb.
- Limitation of movements.
- Heat.
A common specific symptom of dislocations is the appearance of springy resistance when attempting to carry out passive movement.
Types of joint dislocations
In traumatology, several types of classification of joint dislocations are used:
- By localization - dislocation is characterized by the underlying part of the limb or by the overlying vertebra.
- By origin - acute (up to 3 times in one joint, recorded by x-ray), habitual (after 3 acute injuries in one joint), pathological (formed during diseases, oncological lesions of the joints), congenital (the result of birth injuries) dislocations.
- According to the volume of damage - complete and incomplete dislocations. With complete dislocations, total divergence of the articular components is observed. In case of incomplete joints, the articular surfaces partially touch.
- Depending on the integrity of the skin in the area of injury - open or closed.
- According to the period from the moment of injury - fresh (up to 3 days), stale (up to 4 weeks), old (more than 4 weeks).
The method of treatment and rehabilitation depends on the location of the injury.
Treatment
The essence of any method of treating a dislocation is to straighten the articular limbs and return them to their usual physiological position. All therapeutic measures for this category of patients must be carried out under local or general anesthesia. The choice of type of anesthesia directly depends on the location of the dislocation and its complexity.
The specialist begins to reduce the joint only after complete immobilization of the damaged limb. The reduction process must be done very carefully. The doctor should not make any sudden movements that could aggravate the situation. The joint will fall into place along with a characteristic sound – a click.
Treatment of traumatic dislocation after reduction of the joint consists of physiotherapeutic manipulations (massage, therapeutic exercises, acupuncture). Pathological dislocations sometimes require surgery to restore joint function. It is also necessary to treat the underlying disease if joint dislocation is its consequence.
Typically, it takes one month for a person to fully restore the functions of an injured limb. During this period, it is recommended to reduce the load on the joint as much as possible. In the second month, you can begin physical activity, gradually increasing it.
Congenital dislocations are treated differently. Therapy should be started as early as possible, the optimal age is up to two years. Otherwise, you will need to apply special splints, wear orthopedic shoes, or even undergo surgery.
Rehabilitation
After removing the plaster cast, patients must undergo rehabilitation, due to which the motor function of the joints will be fully restored.
Everyone, without exception, is recommended to:
- undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- engage in physical therapy;
- visit the pool;
- take walks in the fresh air, etc.
Prevention
In order to prevent dislocations, you must first of all take care of your health. Every person should avoid falls and other types of injuries that can cause sprains. Regular exercise will strengthen your joints and make your ligaments more elastic. Don’t forget about proper nutrition and the use of vitamin and mineral complexes, which contain components necessary for the proper functioning of joints.
Author of the article:
Kaplan Alexander Sergeevich |
Orthopedist Education: diploma in General Medicine received in 2009 at the Medical Academy named after. I. M. Sechenov. In 2012, she completed postgraduate studies in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the City Clinical Hospital named after. Botkin at the Department of Traumatology, Orthopedics and Disaster Surgery. Our authors
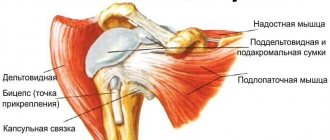
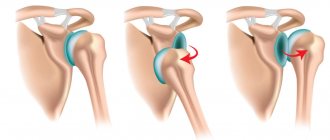
Shoulder dislocation
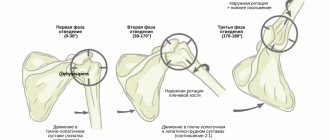
The injury occurs as a result of falling forward, to the side, on outstretched arms. In this case, the joint capsule ruptures, the head of the humerus falls out of the glenoid cavity. The damaged articular joint is deformed, asymmetry of the shoulders is determined, and the inability to perform movements is determined. A weak pulsation is detected on the radial artery.
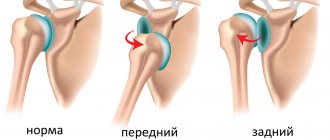
The diagnosis is made based on examination. X-ray images show the location of the articular head, the integrity of the ligaments and bones. The doctor determines the type of dislocation - anterior or posterior, and eliminates the possibility of a fracture.
3. Clinical picture of habitual dislocation
The first dislocations are usually associated with some extreme stress on the shoulder. In this case, the person experiences pain, weakness in the arm, and takes a forced, gentle position. The injury may also be accompanied by numbness of the limb, bruising, and loss of sensation in the shoulder. The patient is able to definitely say what was the factor that caused the disturbance in the shoulder.
After treatment - reduction and further rehabilitation - repeated dislocation within six months is highly likely to indicate developed instability of the shoulder joint. The injury begins to recur more and more often. In this case, performing ordinary actions becomes a risk factor.
Simply placing your hand behind your head or combing your hair can lead to another traumatic episode. The patient already has difficulty determining which movements caused the dislocation.
The symptoms smooth out over time, the dislocation does not cause acute pain or swelling. At the same time, it becomes visually more and more clearly visible that the shape of the shoulder has changed. It becomes angular, with depressions and protruding bumps.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Knee dislocation
Damage to the knee joints often occurs due to sports injuries, intense physical activity, as a result of car accidents, and falls from a height. As a result of the injury, a sprain or rupture of the ligaments occurs, the structure of the joint capsule is disrupted, and the patella is displaced.
To clarify the nature of the damage, an x-ray of the joint is performed. You should ensure that there is no fracture, as this will determine the type of treatment required. It is advisable to perform an ultrasound of the knee joint. In controversial diagnostic situations, MRI and arthroscopic examination are prescribed.
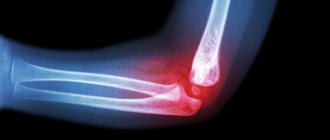
Elbow dislocation
The elbow joint loses stability due to falls on outstretched arms and blows. Most often this occurs as a result of car accidents, during sports activities, which are accompanied by jerking and excessive movements in the joint. Dislocation of the elbow joint may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the joint capsule and rupture of the brachial artery. Characteristic symptoms are loss of sensitivity, weakening or absence of pulsation in the wrist vessels.
Elbow dislocations require detailed diagnosis in order to exclude serious injuries. The patient is prescribed radiography, ultrasound, arteriography. In some cases, consultation with a neurologist is required.
Hip dislocation
Severe damage to the hip joint, in which the head of the joint falls out of the acetabulum. The main causes of hip dislocations are serious car accidents, industrial emergencies, and natural disasters. Due to mechanical action, a sharp flexion or rotation of the joint occurs inward (med.) or outward. The process is accompanied by rupture of the capsule, ligaments and the exit of the femoral head from the articular cavity.
The traumatologist makes a diagnosis immediately; to do this, it is enough to examine the victim.
Dislocation of the wrist joint
The wrist joint is a complex structure consisting of several bones. Dislocations of various types occur as a result of falls, strong blows, or lifting heavy weights. Quite often, injury occurs during a massage performed by an untrained massage therapist.
Making a diagnosis is not difficult. The patient experiences severe pain. The joint area suddenly swells, turns red, and becomes hot. Quite often, bruises and hemorrhages appear due to rupture of blood vessels. Movement in the joint is limited or completely absent. For diagnostic purposes, an x-ray of both hands is performed.
1. Why “habitual” and what is the difference from a normal shoulder dislocation
p>Dislocation of any joint is a geometric displacement of its elements relative to the normal position.
An ordinary traumatic dislocation is always the result of some kind of overload, force or spatial, when there is too sudden a movement, too heavy an effort, too much or sudden compression. In most cases, this is the result of an accident, a rapidly developing dangerous situation, or extreme circumstances. Any controlled and conscious actions normally do not lead to injury to any body structures.
The concept of “habitual shoulder dislocation” has entered medical terminology to denote an injury that occurs in the absence of excessive loads or external influence on the joint, that is, in a familiar environment. Chronic joint dislocation is a phenomenon that brings constant discomfort into a person’s life due to the expectation of another injury that cannot be predicted or prevented. Normal activities and daily activities for such patients serve as a never-ending risk factor. The situation is aggravated by the fact that over time the frequency of episodes of such trauma increases and the frequency of exacerbations can reach ten times a year.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Ankle dislocation
There is a huge load on the ankle joint. During physical work, walking, and sports training, the ankle holds the human body. Joint dislocation occurs due to several reasons:
- heavy physical activity;
- driving on uneven surfaces;
- unfavorable weather conditions – ice, puddles;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes, high-heeled shoes;
- joint diseases.
After an injury, swelling and hyperemia of the skin in the area of dislocation develops. The patient cannot stand on his leg, movements in the joint are severely limited or impossible. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, X-rays and MRIs of the damaged joint are performed.
First aid for sprains
Correctly provided first aid for a dislocated joint, regardless of location, helps to more quickly restore motor functions, reduce the rehabilitation period, and also prevents the development of post-traumatic complications. If you suspect a dislocation, it is important to follow a number of rules:
- Under no circumstances should you adjust a dislocation yourself!
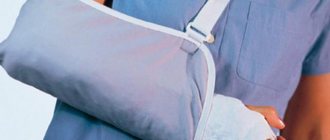
- Ensure immobility of the injured joint. To do this, the joint is left in the position in which it is located, fixed with the help of improvised means, a scarf, scarf or splint.
- Open skin lesions are treated with antiseptics - hydrogen peroxide, alcohol.
- An ice pack and a piece of frozen meat wrapped in a kitchen towel are applied to the sprained area. Cold prevents the development of soft tissue swelling.
- The victim is given painkillers.
- If you lose consciousness, give a cotton ball soaked in ammonia to sniff.
- The injured limb is placed on a bolster and placed in an elevated position.
The main task is to transport the injured patient to the hospital as quickly as possible.
Main features
Pathological displacement can be one- or two-sided, this affects the clinical picture. Bilateral posterior dislocation is characterized by the following symptoms:
- normal mouth closure is difficult;
- the lower teeth are behind, their position is unnatural;
- severe pain is observed below the ears, after some time reporting develops in this area;
- there is copious secretion of saliva, speech becomes slurred;
- in a horizontal position, suffocation is experienced; the patient can only stand or sit.
Unilateral posterior pathology manifests itself in the same way, but there is pain and swelling only on the affected side, asymmetry of the jaw, and curvature of the mouth are observed.
With lateral bilateral pathology, the following signs are observed:
- swelling, severe pain in the area below the ears;
- slurred, impaired speech;
- the presence of increased salivation;
- the lower jaw is strongly displaced, this is not only visible from the outside, but is also strongly felt by the patient himself.
For bilateral, the following clinical symptoms are observed:
- the jaws do not close, the mouth is constantly open;
- slurred speech;
- Below the ear area there is severe swelling and pain;
- hypersalivation (saliva secretion) appears.
A unilateral anterior dislocation has the same symptoms, but the mouth is skewed to only one side. A person cannot swallow saliva; jaw movements are possible, but they are limited and accompanied by pain.
Features of treatment
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
Treatment of TMJ must begin with reduction, for which the doctor sits the patient down and stands directly in front of him. Next, he takes hold of the lower jaw on both sides, his thumbs should rest against the teeth, and the rest completely cover the jaw. Then with your thumbs you should press on the jaw, lowering it, and at the same time lifting its front part up. The fact that the joint is in place is indicated by a click and a feeling of sinking of the lower jaw. Then a sling-shaped bandage is applied to the joint area, the duration of its wearing is up to 5-7 days. At this time, the patient will be able to take only pureed and liquid food to consolidate the result. The same diet is followed after the treatment of the dislocation is completed.
Before realigning the jaw, the doctor must make sure that there is no jaw fracture, otherwise serious harm may occur. In addition, the reduction itself must be performed strictly according to established rules; a mandatory examination is required before starting treatment. In some cases, surgery will be required.
Which doctor should I contact?
To treat dislocations, you should contact a traumatologist or orthopedist. Only these specialists will conduct a competent examination, make a diagnosis and be able to help the patient. Treatment of dislocations requires certain skills, without which it is impossible to perform a reduction, prescribe adequate drug therapy and draw up a rehabilitation program.
During the examination, the doctor clarifies the circumstances under which the injury occurred:
- the nature of the actions performed;
- appearance of the first symptoms;
- intensity of painful sensations.
The specialist must be informed of the presence of elevated body temperature and what actions were performed after the injury. It is important for the patient to remember whether similar injuries have occurred before.
4. Treatment of habitual shoulder dislocation
First aid for a habitual dislocation is the same as for a normal one. It is necessary to immobilize the arm in a suspended position using a bandage or scarf secured around the neck. If there are signs of internal bleeding, ice is applied. Pain syndrome is relieved with analgesics. The patient must be taken to a traumatologist to exclude a possible fracture.
If, based on the results of an examination and collection of anamnestic information, a doctor diagnoses “habitual dislocation,” treatment tactics are developed individually and may include not only physical procedures aimed at restoring and strengthening the periarticular apparatus. Often, a chronic dislocation requires surgical treatment, and patients agree to surgical treatment because they live in constant anticipation of a new injury, their quality of life is reduced, and they are limited in many activities and hobbies.
Modern surgery offers effective, gentle methods of restoring the functionality of the shoulder in case of habitual dislocation. The most commonly performed procedure is the Bankart operation, which is aimed at creating a connective tissue cushion around the shoulder capsule and fixing the cartilaginous labrum. After surgery, the mobility of the humeral head is significantly reduced, and the joint becomes stable.
The type of disorders in the shoulder joint with a diagnosis of “habitual shoulder dislocation” requires careful study and an individual approach in each individual case. In total, there are more than 200 types of surgical care for this disease. Conventionally, they can be divided into 4 groups:
- Strengthening the joint capsule;
- Plastic surgery of muscles and tendons;
- operations using transplants;
- Combined surgical care.
In all cases, after surgery, the hand is immobilized for a month, and only after complete healing and fusion of tissues, massage, therapeutic passive and active gymnastics, exercises to develop and strengthen the joint are prescribed.