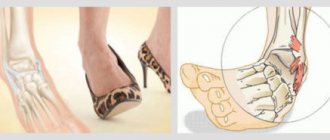
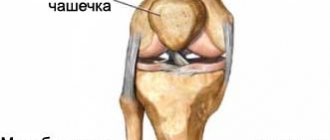
The ankle (ankle, ankle) is one of the most vulnerable areas of the body. Daily stress, active sports, all kinds of injuries - all this creates more than “favorable” soil for the emergence of such a problem as a dislocation in the ankle.
In this case, a problem can arise even in the absence of visible provoking factors: sometimes it is enough just to unsuccessfully lean on your leg or slip to cause a dislocation.
You are invited to learn more about the possible causes of its appearance, characteristic symptoms and treatment methods below.
Causes of dislocations
Most often, sprains in the ankle area occur due to sports injuries.
In accordance with their characteristic features, they can be classified into several categories, namely:
- excessive bending of the leg at the ankle;
- pathologically abnormal movements of the leg in conditions of a fixed knee joint;
- a sharp twisting of the foot against its natural axis.
In accordance with the nature of the injuries, they are classified into combined and isolated. The former are characterized by a secondary occurrence against the background of loss of fixing articular supports. Isolated dislocations appear as a result of severe trauma, for example, a car accident or a fall from a great height.
Injury such as fracture-dislocation should be included in a separate category. In accordance with average statistical data, it is diagnosed more often than other types of injuries in the category being studied. Accompanied by displacement of the foot in relation to the fixing fork and inevitable stretching/rupture of the articular tendons.
Signs and symptoms of a dislocation
The main symptoms of a sprained foot are:
- Pain that occurs suddenly, immediately after exposure to a traumatic factor on the foot. However, after the cessation of exposure, the pain remains. It gets worse when you try to lean on the injured limb.
- Edema . The area of the damaged joint increases in volume, the skin becomes stretched. There is a feeling of the joint bursting from the inside. This circumstance is associated with concomitant injury to soft tissue formations, in particular blood vessels.
- Loss of function . It is impossible to make any voluntary movement in the damaged joint; attempting to do so brings significant pain.
- Forced position of the foot - part of the foot or the entire foot is in an unnatural position.
Be careful and attentive! It is impossible to distinguish a dislocated foot from a sprain or fracture of the foot visually without an X-ray machine.
© irinashamanaeva — stock.adobe.com
Characteristic manifestations
The problem under consideration is characterized by all the manifestations noted with any kind of dislocation: deformation, painful effects, swelling, limited mobility. More detailed information on this matter is covered in the table.
Table. Symptoms of a sprained ankle
| Symptoms | Description |
| Pain | Occurs immediately at the moment of injury. Accompanied by sounds similar to crunching. Then the pain subsides against the background of a decrease in the sensitivity of the corresponding receptors due to their overexcitation, after which it arises with renewed vigor and causes suffering to the patient when making the slightest movements of the damaged part of the body. |
| Edema | They intensify over time, spreading around the circumference. May differ in immediate appearance. In such situations, they manifest themselves as bluish skin, as well as hematomas. |
| Deformations | The nature of their severity is determined by the type of dislocation obtained and the intensity of displacement of the injured foot. For example, in the case of subluxations, there are no visually noticeable deformities. With a complete dislocation, the damaged foot may remain in a bent state. |
| Mobility restrictions | The patient cannot walk or put weight on the affected leg. Complete dislocation makes even the slightest passive movements impossible. |
Foot structure
The foot is a complex anatomical formation. It is based on a bone frame represented by the talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid and sphenoid bones (tarsal complex), metatarsal bones and fingers.
Bone base
- The talus serves as a kind of “adapter” between the foot and the lower leg, due to its shape providing mobility to the ankle joint. It lies directly on the heel bone.
- The calcaneus is the largest bone that forms the foot. It is also an important bony landmark and attachment point for the muscle tendons and aponeurosis of the foot. Functionally, it performs a supporting function when walking. In front it comes into contact with the cuboid bone.
- The cuboid bone forms the lateral edge of the tarsal part of the foot; the 3rd and 4th metatarsals are directly adjacent to it. With its medial edge, the described bone is in contact with the scaphoid bone.
- The navicular bone forms the medial part of the tarsal region of the foot. Lies anterior and medial to the calcaneus. In front, the scaphoid bone is in contact with the sphenoid bones - lateral, medial and medial. Together they form a bony base for attaching the metatarsal bones.
- Metatarsal bones are related in shape to the so-called tubular bones. On the one hand, they are motionlessly connected to the bones of the tarsus, on the other, they form movable joints with the toes.
© rob3000 — stock.adobe.com
There are five toes, four of them (from the second to the fifth) have three short phalanges, the first - only two. Looking ahead, the toes perform an important function in the walking pattern: the final stage of pushing the foot off the ground is possible only thanks to the first and second toes.
© 7activestudio — stock.adobe.com
Ligamentous apparatus
The listed bones are strengthened by the ligamentous apparatus; they form the following joints among themselves:
- Subtalar – between the talus and calcaneus bones. It is easily injured when the ankle ligaments are sprained, with the formation of a subluxation.
- Talon-calcaneonavicular - around the axis of this joint it is possible to perform pronation and supination of the foot.
- In addition, it is important to note the tarsometatarsal, intermetatarsal and interphalangeal joints of the foot.
© p6m5 — stock.adobe.com
The most significant for the formation of the correct arch of the leg are the muscles located on the plantar side of the leg. They are divided into three groups:
- external;
- internal;
- average.
The first group serves the little finger, the second group – the thumb (responsible for flexion and adduction). The middle muscle group is responsible for flexing the second, third and fourth toes.
Biomechanically, the foot is designed in such a way that, with proper muscle tone, its plantar surface forms several arches:
- external longitudinal arch - passes through a mentally drawn line between the calcaneal tubercle and the distal head of the fifth phalangeal bone;
- internal longitudinal arch - passes through a mentally drawn line between the calcaneal tubercle and the distal head of the first metatarsal bone;
- transverse longitudinal arch - passes through a mentally drawn line between the distal heads of the first and fifth metatarsal bones.
In addition to the muscles, the powerful plantar aponeurosis, mentioned above, takes part in the formation of such a structure.
© AlienCat — stock.adobe.com
Classification of dislocations by degree of damage
There are mild, moderate, and severe degrees of dislocation. About them in the table.
Table. Degrees of dislocations
| Possible degrees | Description |
| Lightweight | Accompanied by sprained ligaments. Moderate swelling and tolerable pain appear. |
| Average | An incomplete ligament rupture is noted. The swelling is more severe. The temperature rises. Painful sensations are more pronounced. |
| Heavy | A complete rupture of the damaged ligaments occurs. At the moment of dislocation, a click is heard, indicating that the bone is being pushed out of its natural location. |
The main difference between a dislocation and a fracture directly in terms of sensations is the fact that in the case of the second injury, the pain is of an increasing nature. With a dislocation, as noted, it occurs at the moment of injury, after which it subsides for a while, and then intensifies again. To minimize discomfort, the injured limb should be left alone.
Dislocations are also classified into internal and external, in addition to this - incomplete and complete forms. The external form is characterized by the emergence of the distal part of the fibula from the so-called. joint capsules, for the internal one – displacement of the tibia. In the case of a complete form of dislocation, the surfaces of the joint completely diverge, in the case of an incomplete form - partially.
Sprained leg: severity
In medicine, there are three degrees of severity of dislocation of the joints of the lower limb, depending on the degree of damage to the ligamentous apparatus and displacement of the ends of the bones. These include:
Mild foot sprain
- Minor. There is a violation of the integrity of the ligaments and their stretching. There are no tears. Associated symptoms are mild swelling and moderate pain.
- Moderate. The x-ray shows a partial rupture of the ligamentous apparatus. The pain is so severe that it can be treated with painkillers. There is also an increase in body temperature and swelling.
- Seriously. At the moment of injury, a click is heard, which indicates that the bone has left its normal place. The pain is strong and sharp. Ligament rupture is observed.
Treatment depends on the size of the dislocation, which is determined by x-ray examination.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis, a specialist listens to the patient’s complaints and examines the damaged part of the body. An x-ray is prescribed. As a rule, it is performed in 2 projections with an increase in the number if necessary. Based on the results of radiography, the type of dislocation obtained is determined and the accompanying damage is determined.
Information regarding existing types of damage is given in the table.
Table. Types of Ankle Sprains
| Nature of the dislocation | Peculiarities |
| Side | Can't be isolated. Diagnosed in combination with a fracture. |
| Subluxation | There is a partial discrepancy between the surfaces of the joint. Accompanied by a rupture of the connection in the area of the tibia. |
| Front | Diagnosed extremely rarely. |
| Rear | Formed in case of a fracture of the posterior ankle. |
| Habitual | Appears due to improper treatment of dislocation. It can also develop against the background of an initially complex injury, accompanied by tendon ruptures. Characterized by complete instability of the joints. Has a tendency to relapse even with minor loads. |
Treatment of dislocation
Treatment for a dislocation involves straightening the leg and returning it to its natural position. Reduction can be closed, without surgical intervention, or open, that is, through a surgical incision.
It is impossible to give any specific advice on what and how to treat a dislocated foot at home, since this cannot be done without the help of an experienced traumatologist. After adjusting the sprain, he can give you some recommendations on what to do if you have a sprained foot to quickly restore motor function.
After the reduction procedures, a fixing bandage is applied for a period of four weeks to two months. It should not be surprising that when fixing the lower leg, the splint will be applied to the lower third of the thigh - with fixation of the knee joint. This is a necessary condition, since the process of walking with a stationary ankle is very dangerous for the knee joint.
© Monet — stock.adobe.com
First aid to the victim
It is impossible to leave a dislocation unattended and try to cure it on your own - this will only worsen the situation. The maximum permissible amateur activity is first aid to an injured person.
Important! The names of all medications are provided for informational purposes only. Specific drugs and the order of their use are determined by the doctor.
First, the leg must be left alone and secured in an elevated position, for example, by placing a rolled-up blanket under it. This will help reduce swelling.
Secondly, cold must be applied to the damaged area. Better - an ice pack. Otherwise, even frozen meat or a cold can of drink will do. Cold is applied for no more than 15 minutes at a time.
Thirdly, it is necessary to ensure correct fixation of the joint.
Attention: it is prohibited to set it in the absence of appropriate medical skills. For fixation, the joint is wrapped with an elastic bandage. Don't wrap it too tightly - you risk cutting off blood circulation. To avoid this, control your skin color.
Providing first aid for a sprained ankle
Timely first aid in case of injury guarantees minimization of consequences and reduction of rehabilitation time. Precautions to take immediately after a sprain include:
- Normalization of blood circulation. To do this, it is necessary to get rid of all factors that can negatively affect blood circulation. These include tight shoes, tight socks or tights. Please note that if the victim is wearing high shoes, such as boots, during a dislocation, it is not recommended to take them off. Since if a fracture was sustained, this can only lead to a worsening of the situation.
- Ensuring immobility. First, place a pillow or bolster under the injured foot. Secondly, the ankle joint must be secured with a bandage or elastic bandage.
- Relieving symptoms. In order to reduce the likelihood of extensive swelling, you should apply ice to the damaged area. If acute pain occurs, painkillers may be taken.
Despite the fact that first aid can temporarily improve the condition of the victim, only a specialist can completely cure the injured limb. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after first aid.
Treatment methods
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor will realign the affected joint. Before going to the doctor, it is better not to eat or drink - it is possible that you will have to be given an anesthetic. It is better for the dislocation to be reduced within the first few hours after the injury.
The damaged area is fixed. Traditionally, plaster is used for this (applied for an average of 2-3 weeks), but other options are possible at the discretion of the doctor. To prevent re-injury, the patient is prohibited from leaning on the injured leg - movements are minimized and carried out only on crutches.
For severe pain, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, for example, Ibuprofen or Analgin.
Important! Before prescribing drug treatment, notify your doctor about the presence of existing ailments and the medications you are taking, if any are present and used. So, for example, some medications used in the treatment of dislocations may be contraindicated in the presence of a number of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
In the fight against painful sensations, special ointments demonstrate high effectiveness. At the same time, they help reduce swelling. Most often, ointments of anti-inflammatory and anesthetic groups are prescribed, for example, Fastum-gel, Indovazin, etc.
Special physiotherapeutic procedures play an important role in therapy. The start time of classes is set exclusively by the attending physician. Regular gymnastics allows you to quickly restore ligaments and tendons, restore your muscles to their former tone and forget about the existing problem.
Massage helps a lot. In addition to pleasant sensations, proper exposure improves blood circulation and helps the damaged area recover faster.
Physiotherapy procedures such as warming up, paraffin therapy, etc. will not be superfluous.
If the dislocation involved ligaments, the doctor will prescribe additional exercises to restore balance.
Among folk remedies, it is worth noting compresses made with green tea, tansy and various medicinal herbs. Compresses can be used only with the approval of a doctor and no earlier than 3 days after the reduction of the damaged joint.
Types of foot dislocations
Foot sprains can be divided into three types:
Subtalar foot dislocations
With this type of foot injury, the talus remains in place, and the adjacent calcaneus, navicular and cuboid bones seem to diverge. In this case, significant trauma to the soft tissues of the joint occurs, with damage to the blood vessels. The joint cavity and periarticular tissues are filled with an extensive hematoma. This leads to significant swelling, pain and, which is the most dangerous factor, to disruption of blood delivery to the limb. The latter circumstance can serve as a trigger for the development of gangrene of the foot.
Dislocation of the transverse tarsal joint
This type of foot injury occurs due to direct traumatic impact. The foot has a characteristic appearance - it is turned inwards, the skin on the back of the foot is stretched. When palpating the joint, the scaphoid bone, displaced inwards, can be clearly felt. The swelling is as pronounced as in the previous case.
Dislocation of the metatarsal joint
A fairly rare foot injury. Most often occurs with direct trauma to the front edge of the foot. The most likely mechanism of injury is landing from an elevated position on the balls of your feet. In this case, the first or fifth phalangeal bones can move in isolation, or all five at once. Clinically, there is a step-like deformation of the foot, swelling, and the inability to step on the foot. Voluntary movements of the toes are significantly difficult.
Sprained toes
The most common dislocation occurs in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe. In this case, the finger moves inward or outward, with simultaneous flexion. The injury is accompanied by pain, significant pain when trying to push off the ground with the injured leg. Wearing shoes is difficult, often impossible.
© caluian — stock.adobe.com
Preventive recommendations
Prevention of this kind of damage is extremely simple: you need to take care of your feet. People involved in active sports should be especially careful - during training, the risk of dislocations becomes very high. Before each workout, you should definitely warm up. Additionally, you need to work on increasing strength, elasticity and muscle tone. Stretching exercises help a lot.
Girls are strongly advised to give up uncomfortable shoes and too high heels - all this puts a lot of strain on their feet. And it’s extremely easy to trip on huge stiletto heels. Control your gait and periodically give your legs a rest.
You need to carefully choose shoes for children. It should have a high back and ensure that the foot is fixed in the correct position.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!