Constant pain in the joint makes habitual activities unbearable. Many people are looking for a way to alleviate their condition every day. Ointments, creams, physiotherapy give temporary peace of mind. Orthopedists and rheumatologists often recommend targeted action - injecting drugs directly into the joint. For this purpose, various medications are used today. If you are offered intra-articular injections, first figure out what exactly you will be injected with and how this drug works.
In case of arthrosis, you need to act deliberately
Knee pain - causes
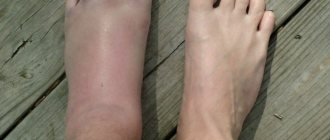
With age, the vast majority of people face the acute question of how to treat arthrosis of the knee joint, with the typical symptoms inherent in this disease at its different stages. This includes the appearance of swelling in the knee area, redness around these swellings, creaking and rustling, clearly audible in silence when the knee moves, especially during squats, and a distinct pain syndrome of varying degrees of intensity. Pain can appear immediately after normal, everyday physical activity or after physical exercise that is inappropriate for age in duration and intensity. When touching on the underlying causes of this pain, we must keep in mind that its appearance can also be the result of:
- Inflammatory process in the knee joint. That is, be a consequence of arthritis. It occurs as an independent pathology or as a complication from other diseases.
- Arthrosis is a degenerative process during which the tissues of the joint are destroyed, it loses mobility, and if the course of arthrosis has been prolonged, it also causes deformation of the joint.
- Injuries. Most often it occurs from a fall, a blow to the knee, or a blow to the knee on a hard surface. The joint may become deformed.
- Ligament damage. Ligaments hold the joint in the correct position, preventing it from moving. But when they are damaged (stretched, displaced, ruptured), the joint also suffers - with severe pain and the appearance of a tumor. In order not to aggravate the injury, in such cases, urgent medical attention and rest for the injured leg are needed.
- Damage to the meniscus of the kneecap. This protruding, round, movable cartilage in the knee can be injured even when squatting or turning sharply. It is not always detected visually due to swelling of the knee joint that often occurs in such cases. Accurate diagnosis is made using ultrasound, x-rays, and palpation by an experienced specialist.
- Popliteal cyst (Becker's cyst). As a result of inflammation, fluid is formed in the joint, which accumulates in the inner side of the popliteal fossa, in the area of the tendons.
- Inflammation of ligaments and tendons (tendinitis). They cause unpleasant, painful sensations localized along the ligaments and are accompanied by swelling. The pain intensifies when the knee is used (flexion and extension), radiates to the area along the muscles along the ligaments and nerves, above the knee, into the femoral ligaments and muscles, and below - into the lower leg.
- Ischemic pain, from impaired blood circulation in the knee joints. They can appear from a sudden change in weather, severe hypothermia for a long time. Examples are sailors who work for a long time in high (arctic) latitudes. In most cases, the localization of pain is symmetrical, equally intense, and at the first stage does not affect joint mobility.
The most serious mistake in such cases would be to ignore the pain and hope that if you just rest, “everything will go away on its own.” Only a specialist can give recommendations for treatment and make a correct diagnosis, therefore treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is unacceptable at home only on the basis of advice from “knowledgeable people”, and even purely using traditional medicine. Effective treatment is possible only with a combination of medications in the form of tablets, rubbing, ointments, and the use of physiotherapy. Sometimes, in severe or advanced cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
Establishing diagnosis
An orthopedic surgeon can make a diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joint after movement tests and medical history. The following procedures are usually prescribed as additions to diagnostics:
- Relating to laboratory tests, such as a biochemical blood test and bacterial microflora, smear, puncture of joint fluid and/or bone marrow, serological analysis, that is, a study for the presence of antibodies and antigens contained in the blood serum.
- Instrumental studies, which may include ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, densitometry and others.
- Examination of the internal joint capsule using an arthroscope - a device for a minimally invasive procedure for penetrating the cavity through an incision. Most often, this method is used after damage to the meniscus or with cracks and severe wear of the cartilage tissue, as well as to restore the anterior cruciate ligaments. Although recently the anthroscope has rarely been used as a diagnostic tool, it has been successfully replaced by a completely non-invasive diagnostic method using MRI.
- Just “by ear” - with a 3rd degree articular lesion, extraneous sounds in the form of creaks, rustles, and clicks are clearly audible in the joint.
The information obtained is brought together into a general history, and only on the basis of it can full and effective treatment begin.
Intramuscular and intravenous injections
Intramuscular and intravenous injections
- the medicine enters the blood instantly, and not after several hours, which is important when the patient’s condition is rapidly deteriorating;
- those drugs that are not able to be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract can be absorbed (this occurs both due to the characteristics of the drugs themselves and in certain conditions of the patient).
Neither the first nor the second advantage for arthrosis matters. This is a chronic disease that lasts for years. Although both chondroprotectors and NSAIDs are available in the form of injection solutions, their use in this form is extremely rare. Because these same drugs exist in tablets, and they are cheaper and easier to use.
How to treat gonarthrosis?
Restoring joint mobility is not a matter of one month. The treatment is complex, it is expensive due to the high cost of drugs, and the result depends only on the patient’s desire to cooperate with the doctor and strict adherence to all medical recommendations and prescriptions.
But first. What needs to be done is to immediately reduce the load on the affected joint(s). If the work involves such stress, negotiate with management (if necessary, with doctor’s notes in hand) about changing your type of activity. For a while or forever - life will tell. Although often at first, bed rest may be required for the initial restoration of joint function. Remember: a joint is not a muscle, you cannot “work it out” with intense exercise, it will only make it worse. Activation of life with intense movements may be required later, after the most acute inflammation has subsided. But even when increasing the load, you need to use means of support in the form of elastic elastic bandages, a cane, a crutch, etc. Sometimes you cannot do without special orthopedic insoles or even custom-made orthopedic shoes.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is also possible at home, using outpatient medications prescribed by a doctor - chodroprotectors, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Depending on the degree of damage to the joint and the type of inflammation, the doctor may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But for all their effectiveness in relieving symptoms, they do not eliminate the causes of the disease.
Do not heat sore joints with arthrosis! On the contrary, apply an ice pack to the inflamed area - it will help relieve swelling, redness and inflammation.
The use of chondroprotectors, on the contrary, does not relieve pain. But the restoration of cartilage tissue will proceed slowly but surely. The only question is the effectiveness of the drug, but you should try to use proven and certified medications for treatment. Preferably internationally recognized.
For some types and degrees of joint damage, applying and permanently (or temporarily) wearing a tightening bandage that fixes the joint can help. But this measure should be used only if the method is approved by the attending physician, since in some types of arthrosis, wearing such a bandage can aggravate the course of the disease.
You cannot completely immobilize yourself if you have knee pain. Moreover, with some types of inflammation, moderate physical activity only benefits the joint. An orthopedic doctor will tell you when and how much to exercise. Moreover, complete passivity in terms of physical activity will cause weight gain, and this will further aggravate the situation, loading the joint.
Drug treatment is usually combined with courses of physiotherapy, the most favorable for the treatment of arthrosis: magnetic and laser therapy (coherent laser radiation is used at safe frequencies), mechanical vibration and ultraphonotherapy, microwave installations with deep effects on tissue - when this is therapeutically justified.
In diagnosis, three degrees of arthrosis of the knee joint are distinguished.
Arthrosis I degree
The mildest degree of the disease. It is characterized by the fact that treatment does not require a large degree of medicinal influence, the list of medications is small, and measures involving physiotherapy, massage, and exercise therapy help well. One of the most effective methods is considered to be laser therapy, which significantly reduces pain, stimulates the regeneration of irradiated areas, and reduces inflammation. In addition, the use of coherent radiation with a strictly defined wavelength eliminates the need to use glucocorticosteroids in treatment, which cause a lot of side effects.
Arthrosis II degree
It is characterized by more intense and acute processes of inflammation and degeneration of cartilage tissue. In the acute period, special medications are prescribed, a special diet is recommended, and physical therapy designed for such cases is recommended. Physiotherapy and massage are excluded during these periods.
Recommendations: reducing the load on the affected joint, limiting walking, avoiding any movements associated with squatting. Special orthoses may be prescribed for the knee joint - devices that fix the joint and severely limit its mobility.
In the medical arsenal for the treatment of arthrosis of the second degree, along with chondroprotectors with glucosamine and chondroitin, steroid drugs, as well as anti-inflammatory non-steroids, may be present. It is possible to inject hyaluronic acid and other drugs into the joint capsule to facilitate the sliding of cartilage surfaces relative to each other.
A special diet with excess collagen is prescribed: jellied meat, jelly, aspic, and from confectionery products - gelatin soufflé. Including fish oil in your diet is beneficial.
Arthrosis III degree
When the knee joint is affected by arthrosis of the third degree, the treatment is not much different from the previous condition - except that the frequency of use of medications increases with a slight shift towards glucocorticosteroid hormones. If there are no results, there is a need for surgery followed by joint replacement.
Injections for joints: what to expect from the procedure and how much will the treatment cost?
Interview with an orthopedic doctor, Ph.D. Litvinenko Andrey Sergeevich
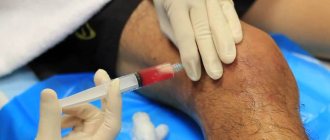
With chronic joint pain, morning stiffness and limited movement, a person is ready to use any means to quickly restore his well-being. If the pills do not help, it makes sense to pay attention to intra-articular injections. Using this method, you can achieve fairly rapid improvement and at the same time maintain a positive result for a long time after the procedure.
We asked Andrey Sergeevich Litvinenko, Candidate of Medical Sciences, an orthopedic doctor with 15 years of experience, to tell us what joint injections are and how effective they are.
Andrey Sergeevich, recently, more and more often, orthopedists are prescribing intra-articular injections to patients. What is this procedure and what are its advantages over, for example, intravenous or intramuscular injections?
A.S. Litvinenko (hereinafter - A.S.):
The essence of the method is already reflected in its name - it is an injection of drugs into the cavity of the affected joint.
With the help of injections, substances can be delivered into the joint cavity that will relieve inflammation, relieve pain, restore cartilage tissue, or even become substitutes, synovial fluid prostheses. The main advantages of this method are speed and targeted impact.
After intravenous or intramuscular injections, the active substance is distributed throughout the body through the bloodstream and only then, in a small concentration, enters a specific organ. But it is not always necessary, for example, to suppress inflammation throughout the body. When an anti-inflammatory drug is injected into a joint, we act directly on the “sore” area, and all other organs work as usual.
Are there any studies confirming the effectiveness of the approach?
A.S.:
Yes, sure. Research on the effectiveness of drugs for intra-articular injections for various diseases is carried out every year.
For example, interesting studies have been conducted on the use of hyaluronic acid preparations (editor’s note - Olyunin Yu.A. The use of hyaluronic acid preparations in the complex therapy of osteoarthritis // Yu.A. Olyunin Modern Rheumatology. 2021. No. 2. pp. 64–69)
, platelet-rich plasma
(editor's note - G.D. Lazishvili. The use of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of osteoarthritis // G.D. Lazishvili, K.A. Egiazaryan, A.P. Ratiev, M.A. Danilov / Moscow Surgical Journal . 2015. No. 5 (45). pp. 14–21)
and even ozone therapy
(editor’s note - Zakhvatov A.N. The effectiveness of intra-articular ozone therapy for traumatic injury to the knee joint in an experiment // A.N. Zakhvatov, A.N. Belyaev, S.A. Kozlov, M.I. Piyanzina, S.I. Kuznetsov, A.M. Leshchanov / Bulletin of RUDN, series Medicine. 2009. No. 4. pp. 301–303)
for the treatment of osteoarthritis and traumatic joint injuries . Such methods can relieve inflammation, improve cartilage regeneration and synovial fluid production. This is an excellent alternative to traditional anti-inflammatory drugs.
I think in the coming years there will be new research, new drugs and treatments that will help more effectively manage pain and improve joint mobility.
Most people associate the procedure with intra-articular injections in the knee. Is the scope of application of the approach limited to this?
A.S.:
The knee is a complex joint that is very easy to injure.
That’s why we hear most often about treating the knee joint with injections. But intra-articular injections are also used for damage to the shoulder, elbow, hip joints and even the wrist and hand. From the Editors Around the world, every fifth person consults a doctor with complaints of limited mobility or pain in the joints.
In Russia this is about 25 million people [1]. For injections into small joints, thin and short needles are used, like an insulin syringe. For the shoulder or knee joint, the needles must be longer in order to reach the joint cavity itself. And if an injection into the hip joint needs to be given to an overweight patient, sometimes you have to select a special needle.
Intra-articular injections are used in the treatment of arthrosis, injuries, tunnel neuropathy, bursitis, rheumatoid joint damage, tendinitis, tenosynovitis. That is, in cases where it is necessary to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, stimulate cartilage restoration, and increase the volume of synovial fluid.
Are there any contraindications?
A.S.:
Do not use drugs to which the patient is allergic or intolerant. If there are lesions or rashes on the skin at the injection site, it is also better to postpone the injection. The same applies to infectious diseases - there is no point in going to an orthopedic doctor when you have the flu or a cold.
How much pain does the patient experience when the drug is injected directly into the joint?
A.S.:
The sensations from an injection into a joint and from the injection of medicine into a muscle are almost the same. Before the procedure, the patient must undergo a consultation with an orthopedist, and in some cases, additional examination. You need to make sure that the injections will be effective and will not cause harm. The doctor selects the drug and sets the time for the procedure. Drugs for intra-articular administration can be quite expensive, so they are sometimes delivered to order.
During the procedure, the doctor treats the injection site and inserts the syringe needle so that it enters the joint cavity. If the technique is followed, the needle passes through soft tissue without touching either nerves or bone. Of course, there is discomfort, but no more than with a regular injection. The drug is administered slowly, especially if it has sufficient viscosity.
From the editors An injection into the same joint can be done in several ways. For the shoulder joint, there are two access points that the doctor can use. An injection into the knee joint is usually done in one way, but in order to pump out excess fluid from the joint, the doctor can use as many as three points.
In difficult cases, the medicine is administered under ultrasound guidance. This allows the doctor to accurately enter the joint cavity. This additional control is more often used for injections into the hip joint. The joint itself has a complex configuration and difficult access. And if the patient is overweight, then successfully performing a “blind” injection becomes a non-trivial task.
After the injection, you will need to make several movements in the joint. This way the drug will be more evenly distributed in it. After this, they can apply a tight bandage or simply cover the injection site with a sterile napkin and adhesive tape. Actually, this is where the procedure ends. No rehabilitation or recovery period is required.
Are there possible complications after the procedure?
A.S.:
If you strictly follow the rules for intra-articular injections, there are no complications. Carefully ensure that the doctor cleans his hands before the procedure, puts on gloves, and be sure to treat the future injection site. He must remove the syringe from the sterile package and open the ampoule with the medicine. After the procedure, the injection site should be covered with a sterile napkin. Not the one that was used to wipe the skin, but a new one. If all these rules are followed, then the patient will not face any infectious complications.
Another option is errors when performing the injection. For example, a needle can scratch the periosteum or enter a nerve or vessel. But even here, if the doctor knows the anatomy and follows the technique of the procedure, this will not happen.
What requirements does the technique impose on the qualifications of a specialist giving injections into the joint?
A.S.:
Intra-articular injections can be given not only by orthopedists, but also by surgeons, rheumatologists and even sports doctors. Indeed, in sports, joints are subjected to particularly intense stress, and emergency assistance is often required.
The main requirements are higher medical education, practical training and excellent knowledge of anatomy.
The therapeutic effect is determined not only by the nature of administration, but also by the drug. Tell us, are there any specific drugs for injection specifically into the joints or are we talking about the same drugs for injection as usual?
A.S.:
Preparations for joints can be divided into several groups: local anesthetics, glucocorticoids, chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid preparations, specific drugs such as platelet-rich plasma and ozonated solutions.
Injections of anesthetics to restore joints will not help, but they will quickly relieve pain for a while. They are often used not separately, but together with other drugs.
Glucocorticoids are anti-inflammatory drugs. The effect of their use lasts on average from 1 week to 1 month. But it is not recommended to do them more than 3–5 times a year on the same joint.
To restore cartilage tissue, intra-articular injections of chondroprotectors, blood plasma, and hyaluronic acid are given. Hyaluronic acid compounds are also called synovial prostheses. In terms of their viscosity and elasticity, they approximately correspond to the synovial fluid, which is normally found in the joint cavity and prevents its surfaces from abrasion.
I would especially like to note the treatment of joints using plasma therapy. In this case, the patient's plasma, enriched with platelets and devoid of other blood cells, is used for injections. It is injected into the joint itself and into the tissues surrounding it. Plasma contains a large amount of nutrients and biologically active substances. And platelets are concentrates of growth factors.
After such injections, symptoms do not just go away temporarily. Cartilage tissue begins to recover, inflammation decreases, and nutrition of the joint improves. The possibilities of plasma therapy are now being actively studied, but its effectiveness has already been proven in research and in real clinical practice.
The specific drug for intra-articular injections, of course, must be selected by the doctor, taking into account all the clinical data and the capabilities of the medical organization where the patient went.
Is this method available in public clinics?
A.S.:
Of course have. This is a standard treatment method in orthopedics. It is included in clinical guidelines for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints and is described in the national orthopedic guidelines.
But you will need to ask in advance what kind of drugs are used in the medical institution. If you are interested in a specific medicine, you may have to order it or buy it elsewhere. And the injection can be done in the clinic.
At the first appointment with a doctor at a state clinic, I also advise you to clarify whether such treatment is included in the compulsory medical insurance system or is provided for a fee, what tests, referrals and other papers will be needed. This will avoid surprises.
How much will the service cost in a private clinic in Moscow?
A.S.:
This depends on the clinic’s pricing policy and on the affected joint. But to a greater extent - from the drug that will be administered. Glucocorticoids for intra-articular injections are inexpensive, about 300–700 rubles per ampoule. Plasma therapy for joints will cost an average of 7,000–8,000 rubles per procedure. But the cost of hyaluronic acid preparations can reach 13,000–14,000 rubles and more.
The cost of an intra-articular injection excluding the drug can vary from 1000 to 2500 rubles and more, depending on the pricing policy of the clinic and the type of joint. If the procedure is carried out under ultrasound or fluoroscopy control, then the cost of one injection of new generation chondroprotectors can be 2000–4000 rubles.
Andrey Sergeevich, thank you for such informative answers. I would like to wish you successful work and your patients a speedy recovery.
A.S.:
Thank you, good health to you!
Intra-articular injections are one of the methods for treating arthrosis and arthritis. Using injections, substances are delivered directly into the joint cavity that relieve inflammation and pain, stimulate the restoration of cartilage tissue, or serve as a replacement for synovial fluid. But only a doctor can select a specific drug, taking into account the results of the examination.
License No. LO-77-01-008730 dated August 6, 2014, issued by the Moscow Department of Health.
Sources:
1 Bodoev A.V. Experience in the treatment of gonarthrosis with injections of drugs through intra-articular puncture//A.V. Bodoev, B.B. Tushinov/Bulletin of the Buryat State University. 2015. No. 12. P.148-150
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint
All of the above applies mainly to people of working age, when organic damage to the knee joint is caused by extreme circumstances and is in no way related to the aging of the body.
A completely different picture emerges when a person passes the age of 50 - when the flexibility of ligaments is lost, processes of tissue dehydration begin, and metabolism slows down.
Under these conditions, the development of gonarthrosis begins - deforming arthrosis of varying severity. In the classification accepted in medicine, gonarthrosis of the knee joint is divided into degrees I, II and III.
This disease, once it begins, progresses very quickly. Refers to acquired age-related pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. To one degree or another, it is inherent in all patients after 50 - another thing is that by leading a healthy lifestyle and avoiding extreme physical activity, the integrity of the cartilage layer in the joints can be preserved both after 70 and after 80 years.
Possible onset of the disease
Located between the tibia and femur bones, the knee joint in the human body bears perhaps one of the heaviest loads. An example would be regular running on a hard (most often asphalt) surface: each step in such running causes a shock load on the knee joint.
This joint also includes the largest sesamoid movable bone - the patella, located at the crown of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris muscle. The articular surfaces are covered with a thick, up to 2.5 mm, cartilaginous membrane consisting of chondrocytes. Medicines under the general name chondroprotectors help restore these cartilage tissue cells, which are primarily affected by gonarthrosis.
There are primary and secondary arthrosis of the knee joints. The etymology of the first is not fully understood and may have different reasons. When - from a sedentary lifestyle, and when, vice versa, from too much physical activity. Poor ecology, excess weight, and addiction to smoking or alcohol can also have an impact. Doctors consider identifying the first stage of arthrosis a great success, since the cause of the pathology is difficult to analyze.
Regular hypothermia of the feet can also provoke the onset of the disease. Therefore, it is better for people with a tendency to such diseases not to choose professions related to the cold (refrigerators, navy working in northern latitudes), etc.
In women over 45 years of age, the frequent development of gonarthrosis is associated with long-term use of contraceptives due to a decrease in the natural synthesis of estrogen. It also often occurs during menopause or under the influence of gynecological diseases such as fibroids, fibroadenomas, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia. Often in women, gonarthrosis is also provoked by strict diets for weight loss, during which many useful minerals and vitamins are removed from the diet.
It is much easier to decide on ways to influence secondary arthrosis, which can be a consequence of:
- Defects in the development and formation of tissues;
- The influence of neurodystrophic processes in the cervical and lumbar spine;
- Arthritis of the knee joint;
- His injuries and microtraumas;
- Meniscectomy, that is, surgical removal of the meniscus;
- Hormonal imbalances and endocrine chronic diseases;
- Heavy and constant physical activity, including sports. To prevent joint injuries after 40 years, it is better to significantly limit and later abandon all exercises associated with extreme loads on the knee joint (in the form of running on hard surfaces or squats with a load);
- Abnormal joint mobility. This condition occurs when the ligaments that hold the joint in the correct position are underdeveloped or naturally weak;
- Stress and constant nervous tension.
Signs and symptoms of the onset of the disease (stage 1, or degree)
- Stiffness of the knee joint in the morning;
- The appearance of pain in the knee if you walk a distance of a kilometer and a half;
- Pain in the joint after prolonged standing (even if without movement);
- Pain in the knee even after complete rest, up to 2 hours, in a sitting position;
- Pain before going to bed or in the first half of the night while sleeping.
These signs need to be paid the most serious attention, because if you do not consult a doctor during this period, the disease begins to progress rapidly, which leads to the second stage of the disease.
Gonarthrosis II degree
Which is typical:
- Night pain, as well as pain in the first minutes of the morning when getting out of bed.
- Pain when moving up flights of stairs.
- Possibility to use public transport with restrictions.
- Slightly pronounced lameness.
- The occurrence of pain when moving at a distance of up to 800-1000 meters.
- Limited ability for self-care.
Often, measures to simply increase the production of synovial fluid by the joint become an effective way to cure even the second degree of gonarthrosis.
Gonarthrosis degree III
Characterized by:
- pain that begins immediately after rest or occurs after 500 meters of quiet movement;
- severe lameness, when the help of improvised means (canes, crutches) is required;
- stiffness after waking up for up to half an hour or even more;
- the inability to climb stairs or enter high-level vehicles independently or without assistance;
- night pain even without moving the joint.
The affected joint develops ankylosis, a condition in which the articular ends of adjacent opposing bones fuse. The leg completely loses its mobility, and the only way to return it is to replace the joint with an artificial one.
The choice of drugs and treatment methods depends not only on the degree of damage to the cartilage tissue, but also on the age of the patient, his ability to tolerate certain drugs and physiotherapeutic methods of influence.
When diagnosing, a distinction is often made between unilateral and bilateral arthrosis, and among unilateral arthrosis, right- and left-sided. The latter is often diagnosed in left-handed people.
Nutrition for gonarthrosis
First of all, doctors advise excluding red meats and offal such as liver from the diet. Priority should be given to fruits and vegetables, cereals with a high content of gluten and fiber, without salt and sugar. As well as fermented milk products, fish and nuts.
The last time you eat food should be no later than 19:00. The frequency of food intake can remain familiar, as it has developed over many years. But it’s better to eat in fractions – in small portions 5-6 times a day in the morning.
Breakfast should be the most plentiful - it sets the body in the mood for work and maintains strength until lunch.
If, especially at first, the feeling of hunger becomes unbearable, trick your stomach - eat an apple or chew a carrot. Just don't eat high-calorie bananas and grapes!
Don't give up jellied meats. Carrying collagen to the body and joints - the raw material for the construction of cartilage tissue.
Drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day: water and/or natural juices.
Eliminate from your diet:
- Red meat;
- Lard, smoked meats of any kind;
- Everything is spicy;
- Semi-finished products of unknown origin;
- Carbonated drinks with sugar;
- Vegetables: white cabbage, tomatoes, red bell peppers.
Potatoes because they are high in calories (carbohydrates!) and help you gain excess weight. Therefore, the Dukan diet will be relevant.
Treatment of gonarthrosis in the Solnechny sanatorium
In our institution, a wide range of physiotherapy, mud therapy, acupuncture, and various massages are used as methods of treating arthrosis of the knee joint.
One of the advanced treatment methods is intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid. They compensate for the lack of production of their own hyaluronic acid, which serves as a lubricating element for the surface of the joint and protects it from abrasion. The effect of this procedure is felt on the first day. The effect of one injection lasts on average for a month. Patients in advanced stages of arthrosis feel a significant reduction in the pain that has tormented them for many years in the very first days, and people with a moderate course of the disease, grade 1-2, after a course of 5 injections in most cases forget about the pain completely for about six months. A rehabilitation treatment program for knee arthrosis has been successfully applied . See here .
Intra-articular injection into the ankle joint
An ankle block, as with injections inside other joints, allows the medicine to be delivered specifically to the lesion. Thanks to some medications, pain is eliminated and the inflammatory process is relieved, while with the help of others, cartilage is built up. But the effect of treatment in this case is achieved faster; the course therapy in this case is shorter.
An injection inside the ankle joint is performed by an experienced doctor after the disease has been accurately diagnosed. What medicine will be used to set the blockade is also determined by the attending physician.
The accuracy of the procedure determines how effective the therapy will be, as well as the development of possible consequences. Therefore, intra-articular injections must be performed by a highly qualified specialist in a hospital setting. In addition, it should be taken into account that such treatment of joint tissue has some limitations. So, before proceeding with the blockade, the patient must be comprehensively examined in order to exclude all possible contraindications.