Clinical picture
Bone fracture in the ankle area
The main cause of ankle injuries is high stress on the lower extremities. Typical for people involved in sports, ballet and circus acrobatics. However, overload often accompanies gardeners who strive to obtain the highest possible yield.
At the same time, a crack in the ankle can form due to simple carelessness. It is enough to stumble on a step or on an uneven sidewalk, especially when a woman is walking in high heels.
Cracks also occur due to external mechanical influence - blows, bruises, after which a person cannot stand on his leg.
Ankle band ruptures are classified as fractures of the extremities, and are usually combined with:
- fractures with shifts;
- self-sprained ligaments;
- tearing off a bone fragment;
- tear of ligaments;
- formation of an interarticular gap.
Ankle injuries occur when the leg is unexpectedly twisted at high speed, while running, when, along with the formation of a crack, the articular joint may become displaced. A careless fall causes a rupture of the syndesmosis, severe pain, and the inability to stand on the leg.
Types of cracks
Depending on the location of the bone relative to the axial line, the following injuries are distinguished: spiral, oblique and linear. Also, based on the number of cracks formed, they are divided into single and multiple.
It should be taken into account that often cracks and even minor microcracks in the ankle go shoulder to shoulder with such diverse injuries as stretch marks, fractures, ruptures, as well as damage to ligaments and muscles. Moreover, all these injuries have very similar symptoms, so without a special examination it will be very difficult to distinguish them from each other.
Symptoms of a cracked ankle
Ankle injury manifests itself:
- intense pain;
- changes in the physiological position of the joint;
- severe swelling;
- unnatural position of the lower leg when the articular joint is displaced;
- redness of the injured area.
These symptoms of a cracked ankle allow the doctor to correctly recognize the injury. He prescribes x-rays for the patient in several projections so that the images show the degree of ankle deformity. At the same time, x-rays make it possible to exclude fractures and damage to the membrane and evaluate the shape of the crack. Descriptions of the images are made by experienced radiologists, and surgeons complement what they see with their experience.
Trauma in children
Particular attention should be paid to ankle injuries in children. Quite often they occur in children who are not even 1 year old yet. The complexity of the situation is that in such a return any damage to bone tissue can be accompanied by injury to blood vessels and the appearance of a hematoma. In addition, in children the bone is often damaged, but the periosteum remains intact.
However, the advantage of children is that such injuries heal much faster and better in them than in adults.
Treatment for cracked ankles
Fissures not complicated by fractures are treated with classical therapy. Swelling and pain are relieved by injection of Novocaine. Healing will take a long time, and a lot of patience will be required for all stages of rehabilitation. You need to be careful not to step on your injured leg.
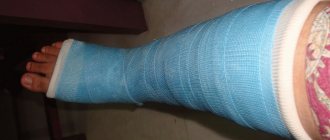
To heal the crack, the ankle is covered with a “boot”-shaped plaster cast. It involves the area above the injury to fix the displaced articulation.
The duration of wearing “branded” shoes is at least two months. You can get up with crutches almost immediately after applying a plaster cast.
After the doctor allows you to walk without a “boot,” it is simply replaced with a removable splint, open in front, with which you have to walk for another 2 weeks.
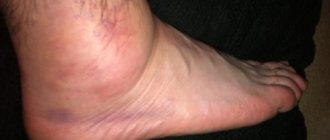
Swelling of the ankle and foot due to injury
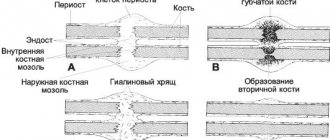
The doctor decides how long to walk in a cast for a non-displaced fractured ankle, based on the readings of control X-rays and the general condition of the patient. It takes a lot of time for complete healing, but the effort is worth it - the crack heals, the range of movements is usually completely restored.
At the same time, patients begin massage, gymnastics and physiotherapeutic procedures. The physiotherapist will tell you how many procedures to undergo and what movements to choose.
This stage is required so that the blood in the lower leg does not stagnate and the usual range of movements gradually returns. But first the crack must heal completely.
A crack in the ankle takes 1.5-2 months to heal. In some cases, more time is needed, this is due to weak immunity and an age-related decrease in regeneration processes.
If the injury occurs in a child, healing of the cracks occurs much faster than in adult patients. The doctor recommends when you can step on your foot after a fractured ankle without displacement, but often patients themselves determine this period based on their well-being.
In some cases, conservative treatment does not give a positive result, then doctors prescribe surgery.
Surgical treatment involves:
- the use of tie bolts, compression screws, making the ankle fork stronger, tightening the crack on the affected joint;
- tendonoplasty, in which femoral tendons are transplanted to the site of an ankle injury. The newly formed ligament is inserted into recesses specially drilled into the shin bone. Practice has shown that the implanted tissues grow well and the person recovers completely.
Conservative treatment includes pain relief, taking medications aimed at reducing swelling, relieving hematoma, and severe symptoms. At the same time, conditions are created for effective healing of the crack and restoration of range of motion.
It is important to perform a puncture of the joint capsule fluid; if there are signs of blood, be sure to carry out sanitation. In order to relieve pain and reduce swelling, the doctor injects Novocaine directly into the joint. If the temperature manages to rise, the doctor assumes intra-articular contamination and rinses the synovial space with Novocaine and Saline.
Cleansing the joint prevents the accumulation of exudate, which can lead to tissue inflammation and the formation of chronic post-traumatic arthritis.
Drug therapy combines taking pills, injections and external pain-relieving ointments. Chondroprotectors are used to activate the growth and regeneration of damaged tissues. This treatment is also used for injuries to the lateral and medial joints.
Painkillers of the modern generation also have a parallel anti-inflammatory effect. Non-steroidal drugs also have a dual effect - they relieve inflammation and effectively relieve pain. To stimulate the regeneration of damaged tissues and strengthen blood vessels, calcium supplements are prescribed.
Local application of ointments is recommended in the absence of a skin reaction. It happens that the same drug works effectively in injections but is completely unsuitable in ointments.
Intra-articular fracture - symptoms and treatment
Complications of intra-articular fractures are divided into local (only in the fracture zone) and general (located in any part of the body).
Local complications include bleeding into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis). The accumulation of blood in the joint requires additional therapeutic manipulations - removing it from the joint. Lack of treatment for hemarthrosis leads to impaired movement in the joint in the long term [8].
A common local complication is injury to blood vessels or nerves , the result of the mechanical impact of fragments and tension of soft tissues at the time of fracture. A vessel or nerve passing near a fracture may be crossed or compressed by the sharp edges of the fragments. Sometimes unnatural stretching of muscles after a fracture leads to tearing of blood vessels and nerves, which significantly affects the healing process [1].
Case syndrome is another local complication. Its name is associated with an anatomical feature: all the muscles of the limb are located in dense, inextensible sheaths (fascia). When a fracture occurs, the muscles may swell and become enlarged, causing them to become compressed in the stubborn fascia. This leads to cessation of blood circulation and gradual death of muscles.
A complication such as fat embolism can not only aggravate the patient’s condition, but also lead to death. The complication is associated with droplets of fat: normally they are located inside the bone, but are released during a fracture. Drops of fat enter the lumen of small vessels injured by a fracture. The flow of blood carries fatty inclusions to distant parts of the body (for example, the brain or lungs) and disrupts their blood circulation, clogging the capillaries [2][9].
Thrombotic embolism is a common complication with a similar mechanism. Only in this case, it is not a drop of fat that migrates and blocks blood circulation, but a blood clot. A thrombus initially forms in the injured limb due to damage to surrounding vessels and concomitant blood stagnation [6].
Traumatic shock is another common complication associated with blood loss and intense pain from a fracture. The occurrence of traumatic shock with several fractures is especially natural [7]. Shock develops as a result of stimulation of a huge number of receptors. Their massive response leads to an extreme load on the nervous system - the flow of pain and other sensitive impulses from the fracture zone causes excitement of the entire body, including hormonal systems.
During traumatic shock, the blood vessels of the extremities spasm: this allows peripheral blood to be collected and brought to vital organs - the brain, heart and lungs. This stress response allows you to save life in conditions of significant blood loss and pain. At the same time, the patient appears active and underestimates the severity of his injuries, which can be falsely perceived as a satisfactory state after injury. The duration of this condition is up to several days.
Traumatic shock without treatment goes into a phase of oppression, when the body’s strength is depleted, until the onset of a terminal state (death). In this phase, the patients' behavior changes sharply towards inhibition and indifference to the environment.
General complications of an infectious nature occur only with an intra-articular fracture with damage to the skin by fragments, that is, with an open fracture. In this case, a septic condition cannot be ruled out when infecting bacteria enter the blood from the wound. This condition is due to the fact that the infection is spread by contaminated blood throughout the body.
There is a separate group of complications of intra-articular fractures - “late” complications [6]. They develop weeks and months after injury:
- displacement of fragments occurs (with an initial fracture without displacement);
- the fracture does not heal properly;
- the fracture heals too slowly;
- lack of healing of the fracture;
- joint stiffness;
- the muscles of the limb atrophy;
- deforming arthrosis of the joint is formed.
Complications after injury
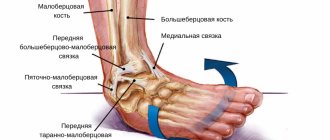
Syndesmosis at the site of fixation
Connecting low-moving membranes fix and provide sufficient movement of the two tibia bones - small and large. The syndesmosis at the site of fixation is an interosseous membrane with a lower tibiofibular membrane.
The fibrous tissue of the membrane has a complex structure, consisting of several layers. Inside, the fibers tightly intersect. The outer fibers are more susceptible to injury; they tend to stretch and tear, causing instability of the joints.
Cracks in the ankle joint can be treated both surgically and non-surgically. Both types of treatment can cause complications:
- tissue infection after surgery. In this case, osteomyelitis, gangrene, and purulent arthritis develop;
- formation of a false joint;
- development of habitual dislocation;
- a crack in the synovial membrane leads to the development of secondary deforming arthrosis;
- chronic neuropathy develops, tissue sensitivity is lost, the muscle strength of the leg weakens, and as a result, lameness appears.
These are the most common complications, therefore, with any ankle injury, it is important that a full examination is carried out and the most correct treatment is prescribed, reducing the risk of developing unpleasant complications to zero.
Common Causes
So, some of the most likely factors that can lead to the occurrence of a crack include:
- Incorrectly planned training sessions. You take great risks when you suddenly increase the intensity of your sports activities, or perform a new exercise that is completely unfamiliar to you.
- Inconvenient shoes that do not secure the foot well and cause terrible discomfort when walking or running.
- Severely low bone density.
- An incorrectly selected diet, which leads to a lack of calcium and other beneficial microelements in the body.
- Various diseases of the thyroid gland.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs and anabolic steroids.
- Disrupted menopausal cycle in a woman.
- The movement is too sudden.
- Insufficient amount of fat, or vice versa, its excess.
In this case, a crack occurs when the strength of the fabric is significantly less than the load force.
Rehabilitation period
After a set of urgent therapeutic measures, rehabilitation is prescribed aimed at restoring the motor function of the ankle. At the first stage, nutrition is adjusted towards foods high in vitamins D, C and calcium. Next, a set of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed, which pursue several goals:
- Remove swelling.
- Reduce pain.
- Maintain muscle tone.
- Accelerate regeneration.
At a certain point, exercise therapy (therapeutic physical education) is prescribed. It helps to relearn how to fully move the leg in the damaged area, as well as to return full function as soon as possible. The intensity of the exercises and duration are determined solely by the attending physician; a lack or excess of muscle load negatively affects recovery.
First aid
If you suspect a fracture of the ankle joint, it is recommended to follow the following algorithm to help the victim before the ambulance arrives or before going to the emergency room:
- Place your injured leg on an elevated surface. The surface on which the foot will be placed must be stable and level. This measure is intended to reduce blood flow to the injured area.
- It is necessary to fix the ankle without attempting to independently reposition the fragments and palpate it. A fixing bandage is applied to the foot and shin. Ideally, this is an overlapping bandage made of elastic bandage, but a long fabric 8-10 cm wide will do.
- Give the victim available analgesics to reduce pain from the injury. Pain disrupts the internal psychological balance, and the psychosomatic factor plays a significant role in recovery.
- Cold is applied to reduce swelling. This is not a mandatory measure, but if the swelling is intense, it is recommended to apply ice.
Diagnostics
When a patient is admitted to the hospital with a suspected fracture of the ankle joint, a whole range of diagnostic measures are carried out to clarify the nature of the injury and its location. The instruments used should help the doctor fully assess the current state of the body:
- First of all, an external examination is carried out, information is collected about the details of the injury. Doctors also perform palpation. The first stage of diagnosis provides a lot of information, based on which a decision is made on the tactics of subsequent examination. Attention is drawn to the presence of edema, hematomas and their size.
Attention! Palpation before examination by specialists is highly not recommended, as there is a possibility of aggravating the situation, which will become an obstacle to recovery.
- An X-ray examination will help visualize the damage, determine in which part it is localized and which structures are affected. The image can also show concomitant damage to blood vessels.
- If an x-ray does not provide a complete picture, then magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) will help to accurately diagnose. Here, injuries such as ligament ruptures, aggregate fractures of the leg and foot bones, and disruption of the integrity of blood vessels and neurons are visualized.
Consequences
And do not forget that a cracked ankle is not something to joke about, since the lack of proper treatment can lead to very disastrous consequences. For example, such as deforming arthrosis or restrictions on the mobile functions of the limb. In addition, a common result of such an injury is chronic pain. The situation will also be disappointing when the crack does not heal for a long time or has turned into a fracture with displaced fragments. In this case, surgery is necessary, otherwise angular deformity may occur.
But if your injury has healed and everything ended well, this does not mean that you can immediately put weight on your leg. The doctor will allow you to step on it little by little and only over time will it be possible to gradually increase the load.