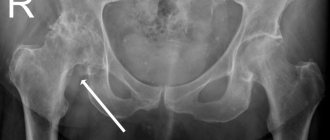
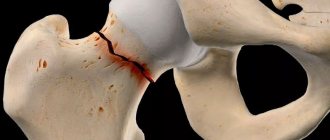
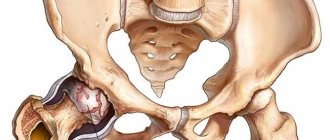
Arthrosis of the hip joint is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology, which is characterized by the destruction of hyaline cartilage. The disease develops gradually, accompanied by pain and decreased range of motion. In the absence of medical intervention at the initial stage of arthrosis, atrophy of the femoral muscles occurs after a few years. The damaged limb is shortened, and fusion of the joint space leads to partial or complete immobilization of the hip joint. The causes of the pathology are previous injuries, curvature of the spine, and systemic diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Arthrosis is usually detected in middle-aged and elderly patients. The diagnosis is made based on the results of instrumental studies - radiography, MRI, CT, arthroscopy. Treatment of pathology of 1st and 2nd severity is conservative. If ankylosis is detected or drug therapy is ineffective, surgery (arthrodesis, endoprosthetics) is performed.
The mechanism of pathology development
The hip joint is formed by two bones - the ilium and the femur. The lower part of the ilium is represented by its body, which participates in articulation with the femur, forming the upper part of the acetabulum. During movement, the glenoid fossa is motionless, and the femoral head moves freely. This “hinge” device of the hip joint allows it to bend, extend, rotate, and promotes abduction and adduction of the hip. The smooth, resilient, elastic hyaline cartilage lining the acetabulum and head of the femur ensures unhindered sliding of the articular structures. Its main functions are redistribution of loads during movement and prevention of rapid wear of bone tissue.
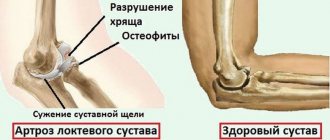
Under the influence of external or internal factors, the trophism of cartilage is disrupted. It does not have its own circulatory system - synovial fluid supplies the tissue with nutrients. With arthrosis, it thickens and becomes viscous. The resulting deficiency of nutrients provokes drying of the surface of the hyaline cartilage. It becomes covered with cracks, which leads to constant microtrauma of the tissue when flexing or extending the hip joint. The cartilage becomes thinner and loses its shock-absorbing properties. To “adapt” to the increase in pressure, the bones become deformed. And against the background of deteriorating metabolism in tissues, destructive and degenerative changes progress.
Prevention of hip diseases in women
Most often, according to statistics, coxarthrosis affects women after 40 years of age, so prevention of hip joint diseases is especially important for them. Experts give the following recommendations:
- watch your figure and avoid being overweight - this will help avoid stress on your hips;
- in supermarkets, do not carry a heavy basket, but use a trolley;
- wear comfortable shoes, try to wear high heels less often;
- walk down and up the stairs at least once a day - this will strengthen the muscles of the legs and thighs;
- take calcium and vitamin D complexes.
Prevention of hip diseases includes a set of measures - nutritional correction, exercise, exercise therapy, and timely diagnosis. It is important to follow the recommendations of specialists and not to neglect your health, because coxoarthrosis can lead to lameness and other serious complications.
Bibliography:
- https://artroz.guru/profilaktika-koksartroza-tazobedrennogo-sustava.html
- https://profilaktika-zabolevanij.ru/sistemy/oporno-dvigatelnyj-apparat/profilaktika-zabolevanij-tazobedrennogo-sustava/
Causes and provoking factors
Idiopathic or primary arthrosis develops without any reason. It is believed that the destruction of cartilage tissue occurs due to the natural aging of the body, a slowdown in recovery processes, a decrease in the production of collagen and other compounds necessary for the complete regeneration of the structures of the hip joint. Secondary arthrosis occurs against the background of a pathological condition already present in the body. The most common causes of secondary disease include:
- previous injuries - damage to the ligamentous-tendon apparatus, muscle ruptures, their complete separation from the bone base, fractures, dislocations;
- impaired articulation development, congenital dysplastic disorders;
- autoimmune pathologies - rheumatoid, reactive, psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- nonspecific inflammatory diseases, such as purulent arthritis;
- specific infections - gonorrhea, syphilis, brucellosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, encephalitis;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- degenerative-dystrophic pathologies - osteochondropathy of the femoral head, osteochondritis dissecans;
- hypermobility of the joints, caused by the production of “superextensible” collagen, provoking their excessive mobility, weakness of the ligaments.
Since the development of arthrosis can be caused by hemarthrosis (bleeding into the cavity of the hip joint), provoking factors include hematopoietic disorders. Prerequisites for the occurrence of the disease are excess weight, excessive physical activity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Its development is caused by improper organization of sports training and a deficiency in the diet of foods high in microelements, fat- and water-soluble vitamins. Postoperative arthrosis occurs several years after surgery, especially if it was accompanied by excision of a large amount of tissue. The trophism of hyaline cartilage is disrupted by frequent hypothermia, living in an environmentally unfavorable environment, or working with toxic substances.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint cannot be inherited. But in the presence of certain congenital characteristics (metabolic disorders, skeletal structure), the likelihood of its development increases significantly.
Prevention of arthrosis of the hip joint
To maintain joint health, one of the most important factors is a balanced diet. You need to eat less salt and sugar, fatty foods. Cereals, fermented milk, vegetables and fruits are useful. You need to drink clean water. This diet will help you adjust your weight and reduce stress on your joints.
You should also generally adjust your lifestyle. It is useful to walk, do exercises in the morning, and take the stairs instead of taking the elevator. When working sedentarily, you need to periodically take 5-minute breaks and get up to warm up.
Early diagnosis is of fundamental importance. Pain and limited mobility of the hip are symptoms that require going to the hospital. They will prescribe painkillers and orthopedic methods that will allow you to fully recover and prevent complications.
Symptoms
The leading symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint are pain when walking in the hip area, radiating to the groin and knee joint. A person suffers from stiffness of movement, stiffness, especially in the morning. To stabilize the joint, the patient begins to limp and his gait changes. Over time, due to muscle atrophy and joint deformation, the limb is noticeably shortened. Another characteristic sign of pathology is limited hip abduction. For example, difficulties arise when trying to sit on a stool with your legs apart.
Arthrosis of the first severity is characterized by periodic pain that occurs after intense physical activity. They are localized in the articulation area and disappear after a long rest.
With arthrosis of the second degree of the hip joint, the severity of the pain syndrome increases. Discomfortable sensations occur even at rest, spread to the thigh and groin, and intensify with lifting weights or increasing physical activity. To eliminate pain in the hip joint, a person begins to barely noticeably limp. There is a limitation of movements in the joint, especially during abduction and internal rotation of the hip.
Arthrosis of the third degree is characterized by constant severe pain that does not subside during the day and night. Difficulties arise when moving, so when walking a person is forced to use a cane or crutches. The hip joint is stiff, there is significant atrophy of the muscles of the buttocks, thighs, and legs. Due to the weakness of the abductor muscles of the femur, the pelvic bones are displaced in the frontal plane. To compensate for the shortening of the leg that has occurred, the patient bends towards the injured limb when moving. This provokes a strong shift in the center of gravity and an increase in loads on the joint. At this stage of arthrosis, severe ankylosis of the joint develops.
| Degrees | Radiographic signs |
| First | The changes are not pronounced. The joint spaces are moderately, unevenly narrowed, there is no destruction of the surface of the femur. Minor bone growths are observed on the outer or inner edge of the acetabulum |
| Second | The height of the joint space is significantly reduced due to its uneven fusion. The bony head of the femur is displaced upward, deformed, enlarged, and its contours become uneven. Bone spurs form on the surface of the inner and outer edges of the glenoid fossa |
| Third | Complete or partial fusion of the joint space is observed. The head of the femur is greatly expanded. Multiple bone growths are located on all surfaces of the acetabulum |
Contraindications
The following are strictly prohibited for this disease:
- static sports with a load on the hip joint: cycling, squatting, weightlifting;
- lifting weights (more than 3 kg);
- walking up the stairs (it is advisable to use the elevator);
- smoking (nicotine destroys body tissues, promotes the formation of blood clots that prevent proper blood circulation). This fact can significantly slow down the healing process and cause deterioration of the condition.
If you follow the doctor’s recommendations and complete the therapeutic course, arthrosis at the first stage of development is successfully cured without further relapses. Restrictions on diet and activity apply for a period of no more than 6 months (subject to diagnosis - complete recovery).
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the clinical manifestations of the pathology, anamnesis, the results of the patient’s external examination and instrumental studies. The most informative is radiography. With its help, the condition of the hip joint is assessed, the stage of its progression, the degree of damage to cartilage tissue, and in some cases the cause of development are established. If the cervical-diphyseal node is enlarged and the acetabulum is sloping and flattened, then with a high degree of probability dysplastic congenital changes in the articulation can be assumed. Perthes disease or juvenile epiphysiolysis is indicated by an abnormal shape of the hip bone. Radiography makes it possible to detect post-traumatic arthrosis, despite the absence of a history of previous trauma to the disease. Other diagnostic methods are also used:
- CT helps to detect proliferation of the edges of bone plates and formed osteophytes;
- MRI is performed to assess the condition of connective tissue structures and the degree of their involvement in the pathological process.
If necessary, the inner surface of the joint is examined using arthroscopic instruments. Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude gonarthrosis, lumbosacral or thoracic osteochondrosis. Pain due to arthrosis can be masked as clinical manifestations of radicular syndrome caused by pinched or inflammation of a nerve. It is usually possible to exclude neurogenic pathology using a number of tests. Arthrosis of the hip joint is necessarily differentiated from trochanteric bursitis of the hip joint, ankylosing spondylitis, and reactive arthritis. To exclude autoimmune pathologies, biochemical studies of blood and synovial fluid are performed.
Anton Epifanov about diagnostics:
Strengthening your knees
Knee Strengthening Exercises
If you are overweight, it is important to strengthen your knees. To do this, Elena Malysheva, speaking about strengthening the joints of the knees, suggests performing special exercises: lying on the floor, turning to one side. We bring our feet together and spread our legs at the knees.
Thanks to this exercise, the buttocks are strengthened, and they are directly responsible for the condition of the knees. Next, we place the jump rope under the thigh. The arm bends at the elbow and serves as a support for the body. Let's start skipping rope.
Half squats are also useful for knee problems. While sitting or lying down, you can rotate your leg at the knee area. But these exercises must be performed with caution. Avoid physical activities while standing, jumping and especially running!
Exercise increases blood flow. Therefore, little by little, but you need to start practicing. A massage will be very useful. You can do a vacuum massage using a can. You can buy a jar at any pharmacy. It costs up to 100 rubles.
Older people can wear a knee pad or an elastic bandage on the sore knee. The bandage will strengthen the joint and limit unnecessary movements.
To summarize, we can say that you need to take care of your health. In order not to trigger the disease, you need to listen to your body and contact a qualified specialist in a timely manner. This will prevent the extreme method of solving a knee problem - surgery. In order to familiarize yourself in detail with the recommendations of Professor Orletsky, you can watch the recording of the “Live Healthy” program about knee joints.
Tactics of drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s well-being. For this purpose, drugs of various clinical and pharmacological groups are used:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Indomethacin, Ketorolac. Injection solutions are used to relieve acute pain, and tablets, dragees, ointments, and gels help eliminate pain of mild or moderate severity;
- glucocorticosteroids - Triamcinolone, Diprospan, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Flosterone. They are used in the form of intra-articular blockades in combination with the anesthetics Novocaine, Lidocaine;
- muscle relaxants - Mydocalm, Baklosan, Sirdalud. Included in treatment regimens for spasms of skeletal muscles, pinching of sensitive nerve endings;
- drugs that improve blood circulation in the joint - Nicotinic acid, Eufillin, Pentoxifylline. Prescribed to patients to improve tissue trophism and prevent disease progression;
- chondroprotectors - Teraflex, Structum, Artra, Dona, Alflutop. Effective only at stages 1 and 2 of arthrosis.
Rubbing in ointments with a warming effect (Viprosal, Apizartron, Finalgon, Dikul balms) helps eliminate mild pain. The active ingredients of external agents are capsaicin, cinquefoil
, camphor, menthol. These substances are characterized by a locally irritating, distracting, analgesic effect. Compresses on the joints with Dimexide, bischofite, and medical bile will help you cope with puffiness and morning swelling of the thigh. Patients are recommended classic, acupressure or vacuum massage for coxarthrosis. An excellent prevention of further progression of arthrosis is daily physical therapy exercises.
Surgical intervention
If conservative therapy is ineffective or a pathology complicated by ankylosis is diagnosed, surgery is performed. It is impossible to restore cartilage tissue in a joint damaged by arthrosis without prosthetic surgery, but with the right approach to treatment, compliance with all medical prescriptions, maintaining a correct lifestyle, doing therapeutic exercises, regular massage courses, taking vitamins and proper nutrition, you can stop the process of damage and destruction of cartilage and hip joints.