Nature always expediently gives organisms one or another form of an organ as the most optimal for performing the complex of movements that are performed by a living organism. This also applies to the shape of a person’s foot. The human leg is a very specialized structure, consisting of 26 different bones, 33 joints, over 100 muscles, tendons and ligaments. And all these structures are somehow involved in the formation of the arch of the foot. The task of the arch of the foot is to perform a supporting function and distribute the body weight over the surface of the foot. The structure of the foot is flexible enough to allow a person to move smoothly, but at the same time strong enough to withstand heavy loads. Most people have a gap under the arch of their feet when they are standing. The arch of the foot, or the inside of the foot, is slightly raised off the ground. People with flat feet either have no arches at all or very low arches.
The normal foot has two arches - longitudinal (along the medial edge of the foot) and transverse (located under the bases of the toes). All types of flatfoot are divided into longitudinal flatfoot (decrease in the longitudinal arch of the foot) and transverse flatfoot (flattening of the transverse arch). The foot can thus increase in both width and length. With combined flatfoot, there is a decrease in both the transverse and longitudinal arch of the foot. The most common type is transverse flatfoot. Flat feet are a condition in which the longitudinal arch drops down and the entire sole touches the ground.
The feet of people with flat feet can twist to the inside; when standing and walking, the feet can stick outward as a result.
A significant proportion of people with flat feet do not experience pain and do not have any problems with their feet. However, some may experience leg pain, especially if there is associated ligament and muscle strain. Knee joints can also be a source of pain. If the ankles rotate inward due to flat feet, then the asymmetry can have a damaging effect on the feet, ankles, and knee joints. In some people, flat feet occur due to a congenital disorder of the development of the foot, while in others, flat feet occur as they age and develop involutional changes or after pregnancy.
Every day, people all over the world are born with flat feet . Many of them are quite active, play sports (running, football), and do hard work. So the question becomes how some people with flat feet feel great and lead active lives, while others experience discomfort and pain in their feet. First of all, it is necessary to understand the functioning of normal feet and feet with flat feet . During walking, the foot is usually aligned slightly so that it can absorb the load vector and distribute it across the supporting surface of the foot. A straightened or pronated foot is quite flexible. The arrangement of the foot bones essentially opens up the foot. Conversely, when the leg has a higher arch or is in a supinated position, the foot is locked and inactive and does not absorb the load well and adheres less tightly to the surface when the foot pronates.
Since flat feet are structurally weaker, this leads to chronic muscle tension as the muscles try to hold the legs in a stable position. For people who have always had flat feet, the muscles are likely very well adapted to normal levels of activity. However, when the load on the muscles or the intensity of the exercise increases, this can lead to pain. Decreased foot stability naturally increases displacement of the medial (inner) part of the foot.
When the leg flattens excessively, it can cause internal rotation of the tibia. Naturally, the disposition of the femur also occurs and the movement in the hip joint changes. So, ultimately, excessive or increased movement towards flattening the foot can lead to pain from the foot to the hip and even in the lower back.
Therefore, it is necessary to clearly determine whether the foot itself is the cause of leg rotation or whether there are other reasons. Just as a flat foot can lead to rotation of the lower extremity, rotation of the hip can also, in turn, lead to the appearance of a flattened foot. And only a thorough examination, including gait analysis, allows you to accurately make a diagnosis and determine treatment tactics.
Symptoms
Most often, the patient does not experience any sensations, only a certain disturbance in gait, which can be noted by others or the doctor. The main symptom is ankle pain, which may increase with exercise. There may also be swelling in the ankle area. Symptoms can vary and usually depend on the severity of flat feet. Some people have uneven distribution of body weight and the person may notice that the heel of the shoe wears out faster on one side than the other. The most common symptoms of flat feet are:
- Pain in the ankle area (inside), there may also be swelling there
- Pain in the foot area
- Pain in the arch of the foot
- Calf pain
- Knee pain
- Pain in the hip area.
- Back pain
- Patients with flat feet may also experience stiffness in one or both legs.
- One or both feet can be placed flat on the ground.
- Uneven shoe wear.
Prevention of flat feet in children
However, instead of wasting money, time, and most importantly nerves on getting rid of flat feet, a much better solution would be to eliminate the possibility of this disease in advance. Continuous implementation of preventive measures will help you with this. First, you need to make it a rule to undergo an annual examination by an orthopedist. The easiest way to prevent it is to undergo regular examination by an orthopedist. Another important step to preventing flat feet is choosing comfortable children's orthopedic shoes. Particular attention should be paid to the soles of shoes. It should be quite soft and flexible, and also be made of natural material. The child should feel as comfortable as possible in the shoes: the toes should be positioned freely, and the heel should be securely fixed with a hard heel. Avoid wearing heavily worn and worn shoes, as they have a negative impact on your feet. When you are outside the city in nature, do not be too lazy to walk barefoot more often, choosing mainly uneven surfaces such as sand, stones or small pebbles. To prevent flat feet, you can use special insoles. They reduce the load on the legs, and also help relieve pain when walking and contribute to the formation of the correct foot geometry.
A set of exercises to prevent flat feet
There are many special exercises designed to prevent flat feet. All of them are aimed at strengthening the muscles and ligaments located on the feet. After all, flat feet arise from the fact that the muscles of the foot become not strong enough to support it in an elevated position. Here is a set of simple but extremely useful exercises that will help you avoid flat feet if you perform them regularly.
The complex begins with a position sitting on a chair. In this position, perform the following elements:
- flexion and extension of toes;
- alternately lifting heels and toes off the floor;
- circular movements of the feet;
- pulling socks towards and away from you;
- the maximum possible spread of the heels to the sides without lifting the toes off the floor.
Causes
- Genetic determination.
- A weak arch may not be a problem while a person is sitting, but once they stand on their feet, they may fall.
- Injury
- Arthritis of the ankle joint of the foot
- Posterior tibial tendon rupture
- Pregnancy
- Diseases of the nervous system or muscles - such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spina bifida.
- Fusion of the tarsal bones can cause compaction and flat feet. Most often diagnosed in childhood.
- Diabetes
- Age-related changes. Long-term exercise (running, jumping, walking) can have negative consequences. One possible consequence may be flat feet. The tibialis posterior tendon can weaken after repeated microtears. The tibialis posterior tendon is the primary supporting structure of the arch of the foot. The tendon can become inflamed (tendinitis) after exercise or even rupture. Once the tendon is damaged, the arch of the foot may flatten.
The presence of flat feet in childhood is not a pathology, since the formation of the foot ends along with the end of the formation of the musculoskeletal system. In other words, the presence of flat feet in childhood does not mean at all that flat feet will persist in an adult. People with a low arch or no arch at all may not experience any problems until a certain time.
Flat foot test
You can determine if you or your child has flat feet using a fairly simple test. Take a sheet of paper and stand on it with your bare feet, after lubricating them with something greasy, such as oil. Make sure that your body weight is distributed evenly. If you have absolutely no problems with your feet, then you will see the following picture:
If you receive a print similar to the one shown below, consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will help you understand your problem and make the correct diagnosis.
Please note that in the absence of flat feet, the big toe should form one straight line with the heel. Patients who have flat feet often experience ingrown nails. Also, the presence of flat feet can be indicated by an irregularly shaped foot, as well as slightly curved toes. One of the consequences of flat feet is a protruding bone on the big toe. Flat feet lead to the appearance of various unpleasant symptoms such as “heel spurs” or calluses. This fact is worth taking note of for people with problem feet - perhaps the reason for your numerous calluses lies not in your shoes, but in the irregular shape of your foot. There is only one way to find out - by visiting an orthopedist. Remember that it is never too late to see an orthopedist, even if you are quite old.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the following signs of problem feet:
- wear and tear of your shoes on the inside;
- the wide dimensions of your feet do not allow you to fit into your favorite shoes;
- constant feeling of fatigue in the legs when walking;
- an unexpected feeling of discomfort when wearing high-heeled shoes;
- the appearance of swelling, pain or cramps in the legs.
If any of these signs are found in you or, more importantly, in your child, then seek help from a doctor immediately. Remember that flat feet are much easier to eliminate in childhood, when the skeleton has not yet completely ossified.
Diagnostics
People who have flat feet may not experience any symptoms and do not need to see a podiatrist. However, if there are certain signs, such as a visually flat foot, pain in the feet, ankles or lower extremities, a feeling of tension in the legs, heaviness in the legs, especially after exercise, then it is necessary to consult an orthopedic doctor.
Diagnosing flat feet is not difficult for a qualified doctor, who can make such a diagnosis based on an examination of the patient. The doctor will evaluate the person’s gait, the position of the foot to the surface, and evaluate the functional state of each leg.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe an x-ray, CT scan or MRI, especially if it is necessary to determine the genesis of flat feet. Podography also gives a good result, which allows you to assess the degree of flatfoot .
Why is childhood flatfoot dangerous?
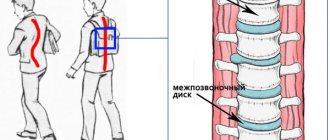
The most dangerous thing is the consequences of this disease, which are initially invisible to the parent’s eye. If the child's feet are positioned incorrectly, the child's posture changes, the shock absorption of the foot is disrupted, a load on the spine occurs, and the baby may develop scoliosis. Poor posture leads to diseases of the joints and spine (arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, bursitis, scoliosis, etc.). In addition to the fact that at school age such loads can cause pain in the joints, later all this will also affect the general health of the child, causing problems in the functioning of internal organs.
At the age of up to 5 years, this issue is dealt with by a neurologist, since this pathology in a child is associated with impaired muscle tone in the legs - this happens with muscle hypotension or hypertonicity. The problem of flat-valgus and flat-varus feet arises. This pathology is formed due to a violation of muscle tone. A pediatric neurologist treats these diseases.
After 5 years, this problem is solved jointly by a neurologist and an orthopedist, so in this case there are problems with the formation of the foot and the ligamentous apparatus.
Help your child stand strong on his feet!
Treatment
Some patients with flat feet adapt to changes in the arch of the foot and in such cases no treatment is required.
Foot pain that is caused by flat feet can be greatly minimized by wearing well-fitting shoes.
Ready-made orthopedic insoles or custom-made ones can significantly compensate for the lowering of the arch of the foot, and can reduce both the load on the foot and reduce disturbances in the biomechanics of movements.
Patients with tibialis posterior tendonitis may experience improvement by wearing orthotic inserts that can reduce stress on the tendon.
Wearing ankle orthoses can help patients with tendinitis reduce inflammation in the tendon.
Reducing the load on the foot also helps reduce discomfort in the foot.
In cases of tendon rupture or arthritis, a combination of NSAIDs and orthotics may be used, but if conservative treatment is not effective, surgical treatment may be required.
In the presence of congenital anomalies of the foot, surgical treatment may also be prescribed, especially if there is fusion of the bones of the foot.
Losing weight in case of obesity can reduce the load on the foot and significantly reduce pain.
As a rule, for flat feet caused by degenerative changes, surgical treatment is not required, but if there is severe pain, then surgical operations are possible - arthrodesis, removal of bone growths, changing the shape of the bone (osteotomy), cleansing the tendons from the membranes (synovectomy), plastic surgery tendons using autografts, reconstructive operations on bone tissue.
Medical Scientific and Practical Center for Vertebrology and Neuroorthopedics, Professor M.L. Kurganov
Flat feet today are a fairly common disease that often accompanies modern people due to their lifestyle. It is a deformation of the foot of varying degrees, which, in the absence of timely treatment, leads to excruciating pain in the legs, lower back and even head.
Flat feet is a rather insidious disease, as it can occur without obvious symptoms and at the same time greatly ruin life.
Indeed, there is hardly a person who has never complained about tired legs, especially if it was preceded by a long walk or other significant load. However, if the feeling of fatigue in your legs does not leave you for a long time and is regularly repeated, accompanied by pain, this is a reason to think about the need to visit an orthopedist.
The main symptoms of flat feet are as follows:
• legs get tired quickly when moving continuously or standing for a long time;
• at the end of the day, the legs feel leaden and swell noticeably;
• leg cramps often occur, especially in the morning;
• my back hurts regularly, especially my lower back.
Transverse flatfoot has the following characteristic symptoms:
• a bone that appears at the base of the thumb;
• expansion of the foot;
• the thumb is noticeably deviated outward, the second and third fingers are deformed.
Note that such signs do not necessarily indicate the presence of flat feet: some vascular and endocrine diseases manifest themselves in a similar way. Only an examination by an orthopedic surgeon will allow you to determine an accurate diagnosis.
Additional signs indicating a violation of the shape of the foot are uneven wearing of shoes (the inner edge is more worn), a visual increase in the width or length of the foot, as a result of which the purchase of shoes a size larger is required, and difficulties in wearing high heels.
Causes of flat feet
Human feet are a kind of shock absorbers (springs) when walking thanks to two types of arches - transverse and longitudinal. The transverse arch runs under the base of the toes, and the longitudinal arch runs on the inside along the edge of the foot. This structure avoids excessive stress on the spine and joints and ensures the proper functioning of the entire musculoskeletal system.
However, proper operation of the entire system is only possible if the arches of the feet are of sufficient height. If the height of the arch is below the required limit, the load on the musculoskeletal system increases noticeably, which can lead to the most serious consequences for the body.
Depending on the structure of which arch is disturbed, there are two main types of flat feet - transverse and longitudinal. Quite often, a patient has both types at the same time.
Stages of disease development
Flat feet do not occur suddenly; The process of disease development is quite long. It can be divided into three main stages.
1. The legs begin to hurt quite often, they get tired quickly, and a person’s posture noticeably deteriorates. The bones of the foot have not yet undergone a noticeable transformation; the arches retain the desired shape.
2. The arches of the feet begin to deform: their height decreases by 1.5-2.5 cm. The legs hurt more and more often and more severely, and not only the feet, but also the legs and ankles. The gait becomes noticeably heavier.
3. Changes in the foot become more and more noticeable. Even small loads lead to severe pain and swelling of the legs. The patient also feels discomfort in the lower back and headaches. If the disease has reached this stage, the consequences can be quite serious: the development of a herniated disc, scoliosis, osteochondrosis, arthrosis is possible.
As can be seen from the above, in order to avoid complications, as much attention as possible should be paid to the diagnosis of flat feet, because only competent and timely treatment will allow the patient to return to a full life. At the same time, it is advisable, but not necessary, to regularly visit an orthopedist: there are several simple ways to determine if you have flat feet right at home.
Causes of the disease
Some scientists believe that flat feet may occur due to a genetic predisposition. Be that as it may, the risk group clearly includes all people who have direct relatives with a similar disease.
Also, the development of flat feet is greatly facilitated by excess weight, pregnancy, professional sports or a profession in which you have to stand for a long time. The direct causes of flat feet include a number of diseases:
• rickets;
• osteoporosis;
• polio;
• dysfunction of the knee and hip joints;
• received injuries.
Flat feet most often occur in older people.
How to diagnose flat feet at home
This diagnosis is usually made by an orthopedic surgeon. But there are several ways to determine flat feet at home. Of course, if suspicions are confirmed, a visit to an orthopedist is still necessary. After all, the disease cannot be neglected, as this can lead to quite disastrous consequences.
The simplest and most accurate way to determine the presence of flat feet is as follows. You need to take a rich cream and apply it to the entire surface of the foot (both feet are lubricated at once). Then you need to stand with your feet on a white sheet of paper. You should stand straight, without leaning on anything: this is the only way the result will be correct. Fingerprints will remain on the paper, which will indicate the presence of the disease. For example, there you can see the size of the recess located on the inside of the foot, which should be at least half of its width.
If the notch is smaller or absent at all, this indicates the presence of flat feet. Instead of cream, vegetable oil or a weak solution of brilliant green can be used. In clinics, a similar test is used using a special device - a plantograph. It is a frame covered with polyethylene. A layer of ink is applied to it, on which a blank sheet is placed. Prints obtained this way are the most accurate.
It should be remembered that this method is only suitable for adults, since in children under 5 years of age the foot is not fully developed and has a protective fat layer. In this case, only a specialist can determine the presence of the disease.
The next method is also based on studying the foot print. It is necessary to draw a straight line between the center of the base of the big toe and the middle of the heel. Then you need to fix the distance between the center of the heel and the point located between the bases of the middle and index toes. If the narrowest place on the foot is located outside the boundaries of both lines or is within the boundaries of the second, there is no flatfoot. If the notch ends between the drawn lines, most likely you have first degree flat feet. If the studied contour extends beyond both lines, this indicates the second, and maybe third degree of transformation of the foot.
Another well-known method, which is often used by orthopedic doctors, is the Friland method. In this case, the height of the foot is multiplied by its length. The result should be at least 29-31. If the numbers are in the range of 27-29, you may have flat feet. A reading below 25 means pronounced flat feet. The operation of the device, the podometer, is based on the same method.
The degree of susceptibility to flat feet can be determined by the shape of the foot.
1. If the second toe is longer than the others and the foot is of average width, flat feet are unlikely to occur.
2. A wide foot in combination with the first toes of equal length indicates that the development of flat feet is extremely likely.
3. A narrow foot and long big toe indicate a risk of flat feet of approximately 50%.
Definition of flat feet in children
In the first two years, the baby does not have pronounced arches of the feet, since the baby’s weight is still small, and he experiences practically no stress on the feet. From the outside, their feet look completely flat, as they have a layer of fat. As soon as the child begins to walk with his feet, he develops normal arches. In order for the feet to form correctly, it is necessary to select comfortable, high-quality shoes for the child and regularly take him to an orthopedic doctor.
Parents should be wary if their child:
• steps with toes inward, that is, clubfoot; the correct position of the feet in children is parallel;
• when walking, the main load falls on the inner edges of the feet.
The presence of such signs should not go unnoticed: after all, only at a young age can flat feet be cured. The skeleton at this age has not yet ossified and can be easily adjusted. Statistics show that if you properly treat flat feet before the age of 6, you can avoid the severe consequences of the disease in adulthood.
The most accurate way to determine flat feet in children is an x-ray. The doctor takes a picture in different projections and determines the presence and degree of flat feet, and also prescribes treatment methods. X-rays should be used in all doubtful cases when an accurate diagnosis is required.
How to prevent flat feet
Prevention of the disease consists, first of all, of regular but moderate physical activity. The simplest and most effective exercise is alternating walking on your toes and heels, which you need to do every morning and every evening. Running in the morning several times a week is also a good prevention of flat feet. It is important not to get carried away with excessive physical activity, since its excess, as well as its deficiency, can lead to a dangerous illness.
A set of certain movements, however, can help not only prevent the disease, but also alleviate the symptoms of an existing disease. Regular barefoot walks on grass, sandy beaches, and pebbles are no less beneficial for your feet. The foot muscles are also well trained when swimming crawl, breaststroke and other styles that actively involve the legs.
An important factor influencing the occurrence of flat feet is the correct choice of shoes: uncomfortable lasts, narrow shoes or high heels when worn regularly can lead to foot disease.
Evening warm baths help improve blood circulation in the legs. They are also good for relieving tired legs. A weekly massage, which relaxes the muscles well, will not harm your feet.
In the initial stages, flat feet do not seem to us to be something serious, capable of limiting life activity and causing pain. It is important to remember that this is a serious disease, and if left untreated, it can cause a lot of problems. Therefore, flat feet should be identified as early as possible. Constant home monitoring can help you with this. Therefore, do not ignore the health of your feet and be sure to monitor your children’s gait
What are the types of flat feet?
There are several classifications of this disease of the musculoskeletal system. Doctors distinguish between congenital (anatomical) and acquired pathology. Based on the characteristics of foot deformation, the disease is divided into three types:
- longitudinal flatfoot, in which deformation of the longitudinal arch occurs. Almost the entire area of the sole touches the floor. Sometimes an increase in foot length is noted. Pathology is diagnosed in 20% of patients, more often in children;
- transverse flatfoot, which manifests itself as flattening of the transverse arch. Due to the development of this defect, deformation of the fingers occurs. Characteristic signs of transverse flatfoot are the formation of calluses, pain in the forefoot;
- longitudinal-transverse flatfoot, in which signs of both types of deformation appear;
- valgus flatfoot, which is more common in children. It manifests itself as a curvature of the axis of the foot: the heel and toes are turned outward, and the middle is turned inward.
All types of deformation, including longitudinal and transverse flatfoot, have degrees of development. This determines the treatment methods and the likelihood of full recovery.