More and more often, parents at doctor’s appointments hear a diagnosis: flat feet. Flat feet in children is a very common problem, and parents do not always pay due attention to it, considering it insignificant. In fact, flat feet that are not corrected in a timely manner can lead to many unpleasant consequences for the child in the future.
The foot of an adult has a shape that allows optimal distribution of body weight due to three arches (two longitudinal and one transverse). Its correct shape provides stable support, maintaining balance, shock absorption when walking and softening impacts when running and jumping.
Make an appointment Biketova Alexandra Viktorovna Osteopathic doctor Specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of pain syndromes in the cervical, thoracic, lumbar spine, chest, shoulder girdle and pelvic area, in the joints of the arms, legs, pain in the foot and heel area, numbness or swelling of the extremities, pain syndromes after operations and injuries of various ages, dysfunction of internal organs with and without pain syndrome. Consultation from 2000 rub.
A one-year-old child, as a rule, is not at risk of flat feet, because... The foot develops gradually and takes its natural correct shape by the age of three, and is finally formed closer to 6-8 years. In a one-year-old child, slight flat feet are physiological, since cartilage still predominates over bone tissue, and the shock-absorbing function is performed by a layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue on the soles. By about three years of age, the layer of subcutaneous fat is gradually replaced by ligaments and the formation of an arch occurs. However, sometimes by the age of one year it becomes clear that the child begins to develop longitudinal flat feet.
Flat feet is a deformation of the natural shape of the foot, in which its arches become flattened.
What is flat feet?
The shape of the arches depends on two components: passive and active. Passive arch stabilization – bone shape and ligament tension. The muscles actively hold the instep of the foot. The formation of a flat foot depends on disturbances of both active and passive factors.
How is a child's foot formed?
The child is born unable to walk. Most children take their first confident steps after 11 months. Before the period of walking, the child’s foot does not perform a supporting function and is a bone-fat pad. There is no talk of any arches before the start of walking.
If we look at the foot of any child under 2 years old on a plantoscope, we most likely will not see any arches. The bony rises are hidden from prying eyes by a thick layer of fat until about 4-5 years. Nevertheless, the legs perform their functions absolutely correctly and without visible arches.
The most active work on the formation of a healthy foot in children is done by the muscles. Even a “genetically good” child in the absence of physical activity is a candidate for the formation of flat feet. Therefore, the main task during the formation of arches in children (and this is up to 6 years of age) is the correct load on the feet.
How and when does flatfoot appear in children?
In orthopedics, there are two types of flat feet (based on origin). The so-called physiological flat foot is a natural stage in the development of any child under 6 years of age. At the same time, all joints have normal mobility, there is no pain, pronounced asymmetry of the “blockage” of the feet, or corns. It is believed that active intervention for physiological flat foot is inappropriate.
Pathological flat feet are caused by genetic abnormalities or severe neurological disorders. At the same time, the bone structure changes, the foot becomes rigid and inactive. The deformity is accompanied by pain, dysfunction of support and walking. With a pathological form, treatment is always needed - orthotics, physiotherapy, surgery.
It is controversial to maintain a flat foot after 6 years. Today, some scientists are inclined to believe that if flat feet in adults do not hurt, there is nothing to treat. However, other researchers insist on mandatory treatment for all deformities, since abnormalities in the shape of the feet affect all higher-lying parts.
Why is flatfoot 2nd and 3rd degree dangerous?
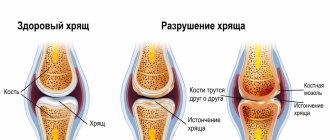
The first thing that is dangerous about 2nd degree flatfoot is the destruction of the entire musculoskeletal system. Each joint is an articulation of bones. Their heads inside the joint capsule are covered with a dense layer of synovial cartilage tissue. This is protection from abrasion and destruction under enormous pressure from shock absorption and the weight of your own body. But what happens when a person’s foot placement is disturbed:
- the condyles of the bones slide off their axis and begin to rest when walking not on those points that are reliably protected from destruction, but on others;
- rapid destruction of cartilage tissue occurs, which leads to early osteoarthritis and disability;
- the joint capsule is stretched, which entails instability of the joint and the appearance of habitual dislocations;
- Ligaments and tendons are deformed, muscles lose their functionality.
All these changes can lead to total destruction of the joints of the lower extremities at a fairly young age (25-30 years). In older people, flat feet ultimately lead to hip fractures and disability.
The most serious danger of 3rd degree flatfoot is the distortion of the pelvic bones, their twisting and destruction of the iliosacral joints. As a result, a person experiences severe pain in the lumbar and sacral areas. But an X-ray examination of the spinal column fails to identify pathological changes. This does not prevent many doctors in the city clinic from making an incorrect diagnosis of lumbosacral osteochondrosis and carrying out completely ineffective treatment, which is aimed solely at eliminating the symptoms and returning the person to work.
To avoid this fate, you need to look for an experienced orthopedist or vertebrologist. Using special diagnostic tests, he will be able to identify such pathologies and prescribe high-quality, comprehensive treatment.
Prevention and treatment of flat feet
Treatment of pathological flat feet is carried out in orthopedic hospitals. Children are prescribed plaster or plastic fixing bandages and reconstructive operations. Often several surgical interventions are required before the foot is completely formed.
If physiological flat feet or decreased arches persist after 6 years, active prevention of negative effects on the overlying joints is indicated. To ensure that the child’s foot is formed correctly, and the existing low arches do not affect the entire body, the following measures are useful:
- Activation of the muscles of the foot and lower leg. For normal muscle function, stimulation of the soles of the feet, the presence of uneven surfaces and exercise are necessary. The variable relief makes the muscles “think” and maintains their tone. Massage mats, balancing pillows, massage are useful.
- Wearing orthopedic insoles. These products stimulate muscles by simulating an uneven surface. The insole support supports the longitudinal arch and corrects the position of the heel. Custom insoles work even better because they allow you to correct the position of all parts of the foot.
- Correct orthopedic shoes. The heel of a shoe or sandal must be shape-resistant - sufficiently dense and at the same time elastic. A small arch support is desirable. The main thing is that the shoes do not restrict the foot and ankle joint. If there are no special indications, it is better to purchase shoes with a low top.
Medtechnika Orthosalon stores always stock the most comfortable, modern and effective insoles, orthopedic shoes and foot exercise equipment. Consultants are always ready to answer any questions and help in choosing the right product. Timely prevention significantly reduces the likelihood of flat feet in a child.
FormTotics
If all your knowledge on the topic boils down to the “truth” that “they don’t take you into the army with flat feet,” we have a lot of news for you.
What is dangerous about flat feet in a teenager and whether it can be corrected - we will figure it out together with an expert - a podiatrist (a doctor who specializes in the foot). But first, let's answer one question for ourselves... What surrounds modern children?
This is not an idle question; we are almost sure that most of us are raising our offspring in more or less civilized conditions (at least you have the Internet, since you are reading these lines!). This means that they spend the most important period of “barefoot childhood” (3-7 years) not barefoot at all, far from natural surfaces (pebble coast, forest paths, etc.). And in the conditions of the Central Russian zone, all children (even those who live outside the concrete metropolis) are almost constantly wearing shoes. Otherwise it's just cold, you know.
Every child is born flat-footed. But then he begins to walk, the leg muscles “turn on” and the arches of the feet gradually rise. For our ancestors, this was facilitated by running around fields and meadows with bumps and potholes. Modern children first stomp around in a playpen, then run on laminate, parquet, porcelain tiles and, at best, on a shag carpet. Does it promote proper arch formation? Unfortunately no.
So, the arches begin to form from the moment the baby begins to stand on his feet, and this process ends just in adolescence, closer to adulthood. There are three arches in total, and these are three “springs” that make walking comfortable. If they “sag” as they grow older, flat feet develop.
So how can you correct flat feet in a teenager? First, let's understand how to identify this problem.
Signs of flat feet in teenagers
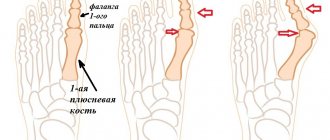
You can suspect an obvious problem before visiting a doctor. Pay attention to your child's shoes. If the sole wears unevenly and more strongly from the inner edge, this is an alarm signal.
You can also do a simple test yourself. Lubricate the child's feet with gouache or beet juice (vegetable oil will also work, but it is more difficult to wash off later). Prepare a blank sheet of paper and invite your child to stand on it. Then examine the resulting prints.
Is the foot imprinted almost entirely? This means that there is overpronation - flat feet. Is there a uniform taper towards the center in both prints? Great, the foot is working as it should.
However, expert diagnostics can only be carried out by a specialist - a podiatrist. Ideally, from the age of 7 until graduation, he should be visited annually for a preventive examination so as not to miss possible changes, since during this period the main growth and formation of the musculoskeletal system occurs, and problems tend to progress.
So, the doctor will examine the child using a special device - a podoscope (this device allows you to visually assess the position of the feet, the degree of flattening of the arches, overload zones, etc.) and make a verdict.
Causes of
flat feet in teenagers
· Sedentary lifestyle.
Modern schoolchildren prefer the virtual world behind gadget screens to active games. Weakness of the muscles and ligaments that support and strengthen the arches of the feet is one of the main causes of flat feet.
· Hypermobility of ligaments and joints.
Does your child demonstrate phenomenal flexibility? This could be a wake-up call. Typically, hypermobility first appears in adolescence, and more often in girls. Visually it looks like an excess of range of motion in the joints compared to peers. As a rule, it is associated with a hereditary collagen defect, which causes hyperextensibility and a decrease in the strength of ligaments and tendons. And, as a result, the ligaments that support the arch are also overstretched, and as a result, the foot becomes flattened.
· Wrong diet.
Excessive elasticity of the ligaments and weakening of the muscles of the arches of the feet can occur due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the teenager’s diet.
· Fast growth.
A schoolchild's foot sometimes grows at a rate of 1-2 sizes per year. Such active growth is reflected in the functional state of the musculoskeletal system. If muscles and ligaments, for example, do not keep up with the growth of bones, there is a systemic disruption of the biomechanics of the foot and subsequent deformation.
· Sports loads.
During school adolescence, many children attend sports clubs or even play sports professionally. Meanwhile, figure skating, basketball, acrobatics and other sports with shock loads on joints and ligaments lead to chronic microtraumas and deformations, including causing flat feet. Also harmful to the feet and the entire musculoskeletal system are sports with asymmetric loads: tennis, high jumping, javelin throwing.
· Overweight.
Excess weight has an adverse effect on the muscular-ligamentous system and is a problem that is increasingly being diagnosed in the new generation. Static load also causes the foot to flatten.
· Shoes.
Those who are especially susceptible to the most futuristic fashion influences are teenagers. They are open to experiments and are ready to wear the most uncomfortable shoes “in the name of the trend and its locomotive - the influencer.” Here are the legendary “ugly” sneakers with platform soles, which deprive the foot of the anatomical roll from heel to toe when stepping. And high heels, which young ladies try on for the first time at just 12+ years of age (the video of the Leningrad group caused another wave of fashion for those same shoes). A heel higher than 5 cm increases pressure on the forefoot, changes the biomechanics of its movement, which also provokes deformities. Meanwhile, doctors do not recommend long-term wearing of high heels for girls under 18-20 years old - the age at which the skeleton forms.
Another dangerous disadvantage of wearing heels in adolescence is the so-called contracture (shortening) of the Achilles tendons. When constantly walking “on your toes,” the tendon does not need to stretch in order to place your foot comfortably, as it would in shoes without heels.
However, sneakers and ballet shoes, beloved by the younger generation, provoke flat feet no less. In shoes with absolutely flat thin soles, a person walks down the street, literally beating his feet on the asphalt.
Specialists from the National Medical Research Center for Children's Health under the Russian Ministry of Health have been conducting research on the health of schoolchildren for 15 years. It turned out that by the 11th grade, 100% of children have some kind of health problem. Flat feet have become one of the most common disorders in boys.
What is the danger?
Flat feet are a systemic problem of the entire musculoskeletal system. Violation of the most important spring function of the foot leads to global trauma to the entire body. The consequences depend on the scale of the problem (doctors diagnose flat feet of degrees 1, 2 and 3). Undamped vibrations of the body during walking and running are transmitted higher to the lower leg, knee, hip joints, and spine. With age, this can lead to persistent pain in the legs and back, poor posture, destruction of joints, etc. Moreover, as a result of a global “distortion”, certain muscles, nerve endings, and blood vessels are pinched, causing pain syndromes and hypoxia in a variety of organs and parts of the body.
Is it possible to cure flat feet in a teenager?
So, we come to the question of how to treat flat feet in adolescents. It is worth noting that this age is the best time for foot correction. The skeleton, ligaments and muscles grow and respond well to any manipulation.
· Orthopedic insoles.
The gold standard for the prevention and treatment of such musculoskeletal problems is the wearing of individually molded orthopedic insoles (orthoses).
Orthoses made from modern elastic materials are designed to correct not only the position, but also the function of the foot. That is, they do not just mechanically support it, but at the same time stimulate the muscles when walking and running, forming and consolidating optimal movement in “muscle memory”. Important!
Serial instep supports from the pharmacy are more of an accessory than a medical device. The orthosis must be designed individually, taking into account the characteristics of each patient’s legs. · Physiotherapy.
Exercises for the legs should also be selected by a doctor. There is no universal complex, since in each case certain muscle groups are trained. However, there are a number of “moves” that are useful for every child, regardless of the severity of the problem, and they can be done at home. You can place pencils by the chair and ask your child to pick them up with their toes. Rolling a “spiky” rubber ball (often sold in pet stores) with your feet will also be useful.
· Massage.
Orthopedic mats have a good massage effect. Someone lays them almost all over the apartment (this is perhaps too much). Someone is by the bed - so there is a chance that the teenager will march along it in the morning as a wake-up exercise and before bed.
· Walking barefoot.
In Buddhist practices, walking barefoot along the rocky bottom of a stream was one of the stages of bodily training. Making a homemade “stream” is easy. Place sand, pebbles in a plastic container, and you can add non-thorny tree fruits like chestnuts and acorns. After an evening shower, stomping around for 15 minutes on such an improvised exercise machine is a pleasure and undoubted benefit.
· Physiotherapy.
Electrical muscle stimulation, ultrasound therapy, underwater massage - there are a lot of techniques, but the choice must be made by a specialist.
Flat feet can be corrected in children, so it is important to diagnose it in time and take action!
The article was published on December 13, 2019 on the website lisa.ru
A little about clubfoot
Finally, let’s dwell a little on congenital clubfoot. With congenital clubfoot, the child has a pronounced bean-shaped deformity of one or both feet with the presence of contractures. The causes of the changes are scar changes in the capsule, ligaments and joints of the foot, underdevelopment and shortening of the muscles and tendons of the lower leg. The disease is usually bilateral and is more common in boys. Pathology is easily detected in the maternity hospital. Such a disease cannot be left untreated! If a child begins to walk on such legs, the deformation of the damaged foot increases, the function of the entire leg is disrupted, “corns” appear on the foot and pain when walking. Support ability, gait and posture suffer, and difficulties arise with choosing shoes. Treatment should begin as early as possible, from the first days of the child’s life. Orthopedic treatment consists of gradually moving the feet out of an abnormal position using plaster casts and long-term fixation in a position of enhanced correction. At an early age, when the child’s muscles and ligaments are pliable and plastic, there is a high probability of complete elimination of the defect without surgical intervention. Treatment is carried out in combination with therapeutic exercises and massage. The prognosis of the disease is favorable. The sooner treatment is started, the faster the recovery will occur.
How to identify pathology?
Not only clinical signs help determine flat feet - there are also special methods by which the stage of development of the pathology is determined. Let's look at the main ones.
Plantography
The severity of the disease is determined by the prints of the feet, previously lubricated with a special substance, on paper. The weight of the entire body should rest on the legs.
Podometry
Allows you to determine the ratio (in percentage) between the height of the foot and its length.
There are other methods - clinical diagnostics, x-rays, etc. - but they can only be carried out in a hospital.
As a result, we note that for some reason flat feet are underestimated by many. People consider this disease not serious enough and do not pay due attention to it. But in reality, everything is not so, you yourself became convinced of this after reading the article. Therefore, if any of the described symptoms appear, you should immediately contact an orthopedist. Read how to treat dermatitis on the hands on our website.
Other symptoms of pathology
Let's consider the symptoms of flat foot not only in terms of the sensations that accompany the disease, but also from a slightly different angle.
- Shoes wear out faster, especially those with heels.
- A person has the feeling that his foot has increased in size (although, in principle, it is so). Because of this, you have to buy larger shoes (compared to the old ones, which you can no longer fit into).
- During physical activity, the feet begin to hurt.
- By evening, signs characteristic of pathology appear (swelling, cramps, “lead legs”).
- While walking, your limbs get tired quickly.
- Wearing high heels is becoming increasingly difficult.