HOW TO TREAT THRUST? USING DIFLUCAN®
After the first signs of the disease appear, consult a specialist. Thrush, or genital candidiasis, causes a lot of discomfort and requires complex treatment immediately after the first characteristic symptoms appear, since the advanced form of the disease significantly reduces the quality of life. In addition, the disease can cause complications in pregnant women (1).
Most infections caused by fungi are treatable, and one effective treatment for thrush is Diflucan 150 mg®.
Most fungal infections are treatable
In the therapeutic treatment of thrush, systemic drugs are often used. The active substance of Diflucan 150 mg® is fluconazole, which is quickly absorbed and, entering the bloodstream into organs and tissues, affects the lesions, destroying Candida fungi or suppressing their growth and reproduction.
For rare manifestations of thrush (no more than three times during the year), Diflucan 150 mg® is taken once. In case of relapses, a long course of treatment is required.
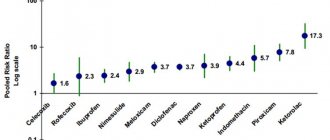
Diflucan 150 mg® works systemically in the treatment of thrush, affecting all foci of pathogenic Candida fungi. The effectiveness of Diflucan 150 mg® for the treatment of thrush has been proven in numerous studies involving 3,729 patients from 19 countries (3).
Indications for use
Diclofenac suppositories are used to relieve pain and prevent inflammatory processes in the presence of the following pathologies:
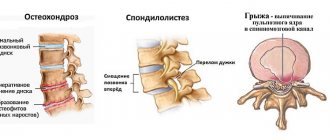
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- rheumatism;
- arthritis;
- spondyloarthritis;
- sciatica;
- migraine;
- lovemago;
- gout;
- algodismenorrhea;
- complications after injuries;
- complications after operations;
- ENT diseases (for example, laryngitis, otitis media).
Typically, the drug is taken in the form of tablets or ointments. But if oral administration is not possible (for example, in a weakened patient), the doctor prescribes rectal suppositories. This form of therapy has several advantages:
- the gastric mucosa is not damaged;
- the likelihood of developing muscle necrosis decreases;
- no suppuration forms at the injection site;
- more comfortable administration compared to injection.
Suppositories are used in combination treatment. For example, during the day the patient takes pills or receives an injection. At night, for a better therapeutic effect, suppositories are administered.
Suppositories are also used to treat prostatitis. In this case, the active substance does not enter the liver, but almost 100% goes to the affected prostate cells, which improves treatment results.
Another direction is in gynecology. Suppositories are placed in case of acute pain caused by inflammation of the ovaries or algomenorrhea. In this case, suppositories are inserted into the vagina, they dissolve quite quickly and actively affect the affected tissue.
Features of the drug
The active ingredient of the drug, fluconazole, inhibits the synthesis of sterols, which make up the structure of the cell walls of the Candida fungus. Diflucan 150 mg® is used to treat thrush of the genital organs, gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, skin, and candidal sepsis.
When taking Diflucan 150 mg® in capsule form, the active substance quickly enters the bloodstream. Concomitant use of the medicine with food does not reduce its effectiveness. When taken on an empty stomach, the peak concentration of the drug is observed after 30-90 minutes.
Diflucan 150 mg® penetrates into all liquid media of the human body: blood, intercellular, cerebrospinal and amniotic fluid, urine, sweat, saliva, sputum, vaginal secretions, breast milk. The drug is excreted in the urine, 80% of its concentration is excreted unchanged (4).
Contraindications and side effects
Suppositories and other forms of the drug are not used when the patient has certain contraindications:
- individual intolerance to diclofenac or auxiliary components;
- proctitis;
- severe disorders of the kidneys, liver, heart.
Taking suppositories has virtually no contraindications, since the medicine is administered externally, without entering the stomach and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, this form of the drug, along with ointments and gel, can be considered the safest. Suppositories have practically no side effects. If the dosage is observed, they do not pose a health threat.
How to use Diflucan® for thrush
The concentration and residence time of the drug in body fluids are influenced by the dosage and frequency of administration, and renal function. If you stop the course of treatment for chronic thrush with Diflucan 150 mg® without consulting your doctor, relapses of the disease are possible, because the concentration of the drug decreases sharply and the desired antifungal effect is not maintained.
The acute form of candidiasis of the female organs is treated with a single dose of the drug, dose - 150 mg.
If there is a tendency to relapse (more than 4 times a year), an appointment is prescribed according to a specific regimen.
Side effects
Diflucan 150 mg® has a favorable safety profile, possible adverse reactions:
- headache;
- fainting or seizures;
- changes in taste sensations;
- nausea, abdominal pain and flatulence;
- skin rashes;
- liver damage;
- allergic reactions;
- blood composition disorders.
Therefore, if you discover characteristic signs of the disease, do not rush to prescribe Diflucan 150 mg® against thrush without consulting a specialist! The dosage, frequency of administration and duration should be determined by the doctor after studying all objective data.
The effectiveness and safety of Diflucan 150 mg® have been well studied, and the possibility of using the drug for treatment in children and the elderly has been confirmed (4).
Diclofenac rectal suppositories. 100 mg package No. 10
Trade name: Diclofenac International nonproprietary name: Diclofenac Brief characteristics of the dosage form White or white with a yellowish tint, cylindrical-conical suppositories. The cut is allowed to have an airy and porous core and a funnel-shaped depression.
Composition of the drug One suppository contains: active substance: diclofenac sodium 50 mg or 100 mg; excipients: cetyl alcohol, semi-synthetic glycerides - sufficient quantity to obtain a suppository weighing 2 g.
Pharmacotherapeutic group Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Derivatives of acetic acid. Indications for use Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatic arthritis, rheumatoid, psoriatic, juvenile chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, gouty arthritis); bursitis, tendovaginitis; lumbago, sciatica, ossalgia, arthralgia, radiculitis; rheumatic soft tissue damage; Pain syndrome: headache (including migraine) and toothache, neuralgia, myalgia, renal and biliary colic, in cancer, post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation. Gynecological diseases: primary algodismenorrhea, inflammatory processes in the pelvis, including adnexitis. Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs with severe pain syndrome (as part of complex therapy): pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media. Feverish syndrome in acute respiratory diseases (colds) and influenza.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to diclofenac or other components of the drug; intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs in combination (complete or incomplete) with bronchial asthma, polyps of the nose and paranasal sinuses (including a history); hematopoiesis disorder of unknown etiology; gastric and duodenal ulcers in the acute phase; inflammatory and erosive-ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract in the acute phase; active gastrointestinal bleeding, incl. rectal; severe liver and heart failure; active liver disease, severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min); confirmed hyperkalemia; proctitis, hemorrhoids in the acute stage, age up to 16 years; pregnancy (for suppositories); lactation period.
Precautions Use with caution if there is a history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, or the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection; history of liver disease, hepatic porphyria, chronic renal failure; bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, obstructive respiratory diseases; arterial hypertension, chronic heart failure, coronary heart disease, significant reduction in circulating blood volume; immediately immediately after surgery; for cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial diseases; in elderly patients (including those receiving diuretics, weakened patients and those with low body weight), with indications of a history of allergic reactions (urticaria, Quincke's edema, etc.), alcoholism, severe somatic diseases. Simultaneous use with ethanol (alcohol) increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. When carrying out long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor liver function, peripheral blood patterns, and stool analysis for occult blood. If side effects occur, stop taking the drug. To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the minimum effective dose should be used for the shortest possible short course.
Interaction with other drugs When used together, it increases the plasma concentration of lithium and digoxin. Reduces the effect of diuretics; against the background of potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases. When taking anticoagulants (including warfarin), antiplatelet drugs (including acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel) and thrombolytic drugs (including alteplase, streptokinase), the risk of developing bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract increases simultaneously. Increases the toxicity of methotrexate by increasing plasma concentrations. Plasma concentrations of diclofenac are reduced with simultaneous use of acetylsalicylic acid. When used together with other NSAIDs and glucocorticoid drugs (including prednisolone), it increases the likelihood of side effects (gastrointestinal bleeding). Reduces the effect of hypoglycemic, antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs. Combined use with paracetamol, cyclosporine and gold preparations increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic effects. Co-administration with colchicine and corticotropin increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (including citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline) increase the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Medicines that block tubular secretion (including verapamil, nifedipine, diltiazem) increase the plasma concentration of diclofenac, thereby increasing its effectiveness and toxicity. Antibacterial agents, quinolone derivatives increase the risk of developing seizures.
Features of use Use in pediatrics: the drug can be prescribed from 16 years of age. Pregnancy and lactation: during pregnancy and lactation, the use of the drug in the form of suppositories is contraindicated. Impact on human behavior, ability to drive a car or machinery: during the treatment period, the speed of mental and motor reactions may decrease, so it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and operating potentially dangerous mechanisms that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Directions for use and dosage: Rectal. Adults and children over 16 years of age: 50 mg 2 times a day or 100 mg 1 time a day. In mild cases and with long-term therapy, the daily dose is 50-100 mg per day. The maximum daily dose is 150 mg. The duration of the course of therapy is determined individually. For a migraine attack: 100 mg at the first sign of an attack, if necessary, the dose can be increased to 150 mg. Method of using suppositories. Suppositories must be inserted into the rectum as deeply as possible, preferably after cleansing the intestines. Suppositories should not be cut into pieces, since such a change in the storage conditions of the drug can lead to disruption of the distribution of the active substance.
Overdose Symptoms: headache, dizziness, tinnitus, lethargy, convulsions; epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract; increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, hepatotoxic effect, respiratory depression, coma. Treatment: symptomatic therapy. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective (due to the significant connection with proteins and intensive metabolism).
Skipping the next dose of the drug If you miss the next dose of the drug, you should not use a double dose; you must continue treatment with the drug at the recommended dosage.
Side effects Local reactions: local irritation, mucous discharge mixed with blood, pain during defecation; local allergic reactions; With long-term use, systemic reactions are possible: From the digestive tract: pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia; increased aminotransferase activity; rarely - gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting blood, melena, diarrhea mixed with blood), stomach and intestinal ulcers, accompanied or not accompanied by bleeding or perforation; hepatitis, jaundice, liver dysfunction; in some cases - aphthous stomatitis, glossitis, esophagitis, the occurrence of diaphragm-like strictures in the intestine, disorders of the lower intestines, such as nonspecific hemorrhagic colitis, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, constipation, pancreatitis, fulminant hepatitis, proctitis, exacerbation of hemorrhoids. From the nervous system: sometimes - headache, dizziness; rarely - drowsiness; in some cases - sensory disturbances, including paresthesia, memory impairment, tremor, convulsions, anxiety, cerebrovascular disorders, disorientation, insomnia, irritability, depression, anxiety, nightmares, mental disorders, aseptic meningitis. From the senses: in some cases - visual impairment (blurred visual perception, diplopia), hearing impairment, tinnitus, impaired taste. From the skin: skin rash; rarely - urticaria; in some cases - bullous rashes, erythema multiforme, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome (acute toxic epidermal necrolysis), erythroderma (exfoliative dermatitis), itching, hair loss, photosensitivity; purpura, including allergic. From the urinary system: very rarely - acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis. From the hematopoietic system: in some cases thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic and aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis. Allergic reactions: rarely - severe bronchospasm, systemic anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including hypotension and shock; angioedema (including the face). From the cardiovascular system: in some cases - palpitations, chest pain, arterial hypertension, vasculitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction. From the respiratory system: rarely - bronchial asthma (including shortness of breath); very rarely - pneumonitis. Other: edema, hyperkalemia.
Conditions and shelf life List B. Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 15-25C.
Shelf life: 3 years. Do not use the medicine after the expiration date indicated on the package. Keep out of the reach of children. Dispensing conditions: by prescription. Packaging Suppositories containing 100 mg of diclofenac, 5 suppositories each in a blister pack made of PVC/PE film. 2 blister packs each along with instructions for use in a cardboard pack. Suppositories containing 100 mg of diclofenac, 6 suppositories each in a blister pack made of PVC/PE film. 1 blister pack along with instructions for use in a cardboard pack. Suppositories containing 50 mg of diclofenac, 6 suppositories each in a blister pack made of PVC/PE film. 1 blister pack along with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Contraindications
You should not take Diflucan 150 mg® if you have thrush:
- if there is increased sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- simultaneously with taking certain medications to regulate heart rate;
- pregnant and lactating women.
There are also a number of other contraindications. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will decide on the advisability of taking the drug.
Bibliography:
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis: clinical picture, diagnosis, principles of therapy. V.N. Prilepskaya, G.R. Bayramova, M.: Geotar-Media, 2010, p. 80; https://www.rmj.ru/articles/ginekologiya/Vulyvovaginalynyy_kandidoz_sovremennyy_vzglyad_na_problemu/
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015(June 5);64(RR-03):1-137. available on June 29, 2017 at https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/candidiasis.html
- Sobel, Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet 2007, 369: 1961-1971.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug Diflucan® P NO 13546\02
- Source of the article: https://www.diflucan.ru/molochnitsa/lechenie