Our clinic is engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mWe have solid experience in diagnosing and treating autoimmune diseases. We use effective diagnostic tools, this helps save your time and budget for treatment.tion. The clinic is open seven days a week.
- MRI and CT scan of bones and joints
- X-ray in rheumatology
- Osteodensitometry. Densitometry
- Electromyography in rheumatology. ENMG diagnosis of polymyositis, polymyalgia, tunnel syndromes, polyneuritis
- Electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (Echo-CG) in rheumatology
- Ultrasound in rheumatology. Ultrasound of joints
MRI and CT scan of bones and joints
Modern CT and MR imaging sees what is invisible to X-rays. It allows you to obtain images of bones, cartilage, blood vessels and soft tissues in the form of sections and volumetric reconstructions. To make an appointment for MRI and CT (X-ray computed tomography), please contact the clinic reception.
We recommend taking with you to the examination the results of previously performed MRI studies, x-rays, extracts: this can make the examination more informative.
On MRI and CT, the following are distinguishable and assessable:
- inflammation,
- swelling (inflammatory and traumatic),
- tears of meniscus, cartilage and ligaments,
- arthrosis,
- tumors
- intervertebral disc herniation.
CT scan (CT) of joint bones is an X-ray computed tomography scan of the musculoskeletal system. X-rays, passing through the patient's body, hit sensors, the data from which is subjected to computer processing. Bones, joints and their traumatic changes are better visible on X-ray CT. You can get a three-dimensional image. If necessary, a radiopaque contrast agent can be injected intravenously to contrast the blood vessels.
Three-dimensional CT reconstruction of the chest bones
MRI – magnetic resonance imaging. To form an image, magnetic resonance of the atomic nuclei of certain elements contained in the human body is used. MRI scanners use a magnetic field rather than x-rays .
Using various MRI processing programs and contrast agents, you can obtain a clear image and evaluate the condition:
- brain and spinal cord,
- joints (knee, hip, shoulder, etc.),
- muscles,
- soft tissue organs.
MRI scan of the knee joint
Preparing for magnetic resonance imaging
No special preparation is required to successfully perform an MRI of the hip joint. You must take with you a doctor's referral, as well as all medical documents and the results of previous instrumental studies.
If an MRI of the hip is performed with contrast, you should stop eating and drinking 6 hours before the examination. The doctor must be sure that the patient does not have renal failure and is not pregnant, so you should take a blood test in advance to check your kidney function and get a gynecologist’s opinion.
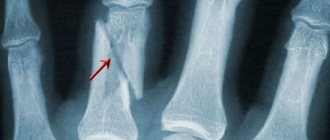
X-ray in rheumatology
X-ray examination of joints is the “gold standard” in rheumatology. Over more than 100 years of X-ray diagnostics, vast experience has been accumulated in the interpretation of X-ray images in rheumatology. Modern X-ray machines are able to obtain high-quality images with minimal X-ray power. We recommend that you take the minimum number of photographs from which you can obtain the maximum amount of information.
How to do an x-ray. How to reduce the number of shots? We recommend that you first obtain the opinion of a rheumatologist. The condition of the joints of the fingers and sacrum can tell a lot about the condition of the entire osteoarticular system . Therefore, in rheumatology, X-rays of the arms (hands), legs (feet) and pelvis are widely practiced. X-rays are poorly blocked by soft tissues, so cartilage, ligaments, and muscles are poorly visible on X-rays and it is better to examine them using other methods, for example, ultrasound of joints.
The structure of bones and joints changes rather slowly during the course of the disease and during treatment. Therefore, there is usually no point in imaging the same joints more than once a year. The exception is cases of acute inflammation in the joint or injury.
Before taking an x-ray, you should consult your doctor about what exactly to examine and in what projection.
How often can x-rays be taken? How many pictures can you take without harming your health? Quite a bit of. The safe number of images in one day depends on the area and thickness of the area being examined, on the type of device, and can reach 20. In any case, you can rest assured: the radiologist calculates and records the x-ray dose during the examination and in no case should it exceed the safe one threshold.
Decoding the results obtained
The obtained ultrasound values of the hip joints in children are taken as the norm, and the development of the hip joint occurs in accordance with age if the echogenicity of the femur and acetabulum is increased. On the oscilloscope screen they are visualized as white spots, and the femoral head and hyaline cartilage tissue look like dark, slightly blurred areas. The older the child, the more pronounced the contrasting outlines of the hip joint are due to the formed foci of ossification. The deciphering of the obtained values is carried out by a diagnostician who measures the angles obtained after drawing linear segments on the photographs. When connecting the lower part of the small ischial muscle to the ilium, only straight lines should be obtained, and the hyaline cartilaginous structures with the acetabulum should be curved. When lines intersect in such projections, alpha and beta angles are formed, measured by a diagnostician using the Graph method. The norm is characterized by the following digital parameters:
- an alpha angle of more than 60°, formed by bends and horizontal straight lines, indicates the correct formation and hardening of the surfaces of the acetabulum;
- a beta angle of less than 55° indicates the degree of development of the cartilaginous zones in the acetabulum and is normal.
Alpha angles with values of 39-40° are considered deviations from the norm during ultrasound of the hip joints. Such parameters of a diagnostic study indicate the presence of a subluxated joint in a child. When the alpha angle is less than 43°, children are diagnosed with hip dysplasia. Beta angles in these diseases are almost always greater than 77°.
In adult patients, the increased echogenicity of the acetabular labrum, the fibrous arrangement of the ligaments of the synovial capsule, and the lack of visualization of the synovial membrane are taken as the norm for the structure of the hip joint. The normal distance from the femoral neck to the articular capsule is 0.6-0.9 cm. The main task of the doctor when examining adults is to carry out differential diagnosis, which makes it possible to separate intra-articular pathology from extra-articular one. This helps the doctor choose treatment tactics and the best medications. What intra-articular pathologies are detected by ultrasound:
- the presence of effusion in the joint cavity, or synovitis. A thickened joint capsule indicates accumulation of foreign fluid. The thickness of this structural element is compared with a similar one in a healthy joint. If the difference is more than 0.2 cm, then the synovial joint capsule is not functioning properly. The resulting images measure the length of the line connecting the joint capsule and the femoral neck. Values above 1 cm allow us to establish developed synovitis;
- the presence of foreign fragments in the synovial fluid. This pathological condition is usually preceded by fractures, avulsions of particles of cartilage or bone. The cause of the appearance of tiny foreign bodies is osteoarthritis, accompanied by an acute or chronic inflammatory process. Foreign particles penetrate the joint capsule and are visualized on the resulting images in the form of an intra-articular mobile hyperechoic structure;
- formation of a false joint. With delayed fusion of fragments, irregular extraneous joints are formed. Their formation is provoked by surgical reposition of bone fragments with the help of various fixing structures for closed fractures of the femur, the complication of which was suppuration and osteomyelitis. Ultrasound of the hip joint reveals false joints. Signs of their formation are intermittent outlines of bone structures with uneven calluses. Areas of inflammation and swelling of nearby soft tissues are also well visualized.
Ultrasonography is prescribed to detect necrotic changes in the femoral head, a pathology that most often affects men. The disease progresses quickly and severely, causing decreased ability to work and disability. An ultrasound scan of the hip joint allows you to identify pathology at the initial stage and begin treatment immediately. With necrosis, the symptoms are dominated by pain, atrophic muscle damage, limited range of motion and gait disturbance. When deciphering the results of an ultrasound, the disease is indicated by a violation of the symmetry of the contours of the joint, narrowing of the joint space, and uneven outlines of the head.
Osteodensitometry. Densitometry
Bone densitometry is a procedure for measuring bone density. There are two main methods of osteodensitometry:
- ultrasonic,
- x-ray
Osteodensitometry (densitometry) allows you to reliably assess the condition of bone tissue. Densitometry is an absolutely painless procedure.
The result of osteodensitometry is displayed in the form of a visual graph
We recommend osteodensitometry for diagnosing osteoporosis . X-ray osteodensitometry is a highly effective study because sees the slightest changes in bone density.
The density of the studied bones is assessed in a numerical format, so during the treatment we can always check:
- Are we doing enough for the patient?
- bone density increases or decreases.
We recommend consulting with your doctor if you suffer from arthritis or excess weight. This may affect the results of the study.
Flaws
This research method in orthopedic practice is used to determine the main sonographic indicators of the hip joints, identify structural changes provoked by the development of arthrosis and arthritis, and study the dynamics of sonographic criteria against the background of conservative treatment and surgical interventions. Its main problems:
- requirement of a certain accuracy of measurements;
- low quality of the resulting images;
- inaccurate installation of sensors in standard ultrasonic positions, as a reason for low repeatability of results.
Ultrasound images are characterized by specific distortions, interference and artifacts, which are closely related to the characteristics of ultrasonic wave propagation in biological tissues. The inaccuracy of images is influenced by the characteristics of the ultrasonic sensor, the difficulty of obtaining a standard position, and the psychophysical state of the human visual organs. An in-depth analysis of the conditions for studying the hip joint and the use of modern equipment that allows the implementation of the latest techniques for digital processing and quantitative assessment of images helps to gradually solve all the problems of ultrasonography.
Electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (Echo-CG) in rheumatology
There is a well-known medical saying: “rheumatism licks the joints but bites the heart.” If you suspect rheumatic diseases, we will definitely suggest that you check the structure and function of the heart. We largely rely on Echo-CG data when prescribing treatment. Your doctor may recommend performing both an ECG and an Echo-CG; These studies do not replace, but complement each other well. Section of our website about inflammatory heart diseases
Watch our video about diagnosing the heart, blood vessels and external respiration function
Electrocardiography (ECG) helps to assess disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart, recognize disturbances in the rhythm and conduction of electrical impulses, and indirectly judge the condition of the heart muscle.
The condition of the heart valves and heart muscle is most easily examined using ultrasound - Echocardiography (Echo-CG). An echocardiograph (ECHO-CG) sees heart defects and inflammatory changes (carditis, pericarditis).
Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart). The operation of the valves is visible: the valves open and close
Contractions of the heart muscle occur at the command of a special system of nerves - the conduction system of the heart. Electrical impulses passing from the conduction system to the heart muscle cause it to contract rhythmically and pump blood.
Benefits of diagnostics
Let's look at several reasons for the popularity of magnetic resonance imaging among doctors and patients:
- High quality images, which can be used to diagnose even the smallest disorders and pathological processes.
- During magnetic resonance imaging, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort.
- Magnetic fields do not harm the body, unlike x-rays. For this reason, the number of MRI sessions is not limited.
- There are very few contraindications to the procedure.
- MRI can be done at any age. However, such diagnostics are not recommended for children, since it is difficult for the baby to lie still.
- Possibility of obtaining images and a doctor’s report in literally 1.5-2 hours.
Do you still think that it is impossible to cure your joints?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against inflammation of cartilage tissue is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about inpatient treatment? This is understandable, because joint pain is a very dangerous symptom, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can result in limited mobility. Suspicious crunching, stiffness after a night's rest, the skin around the problem area is stretched, swelling in the sore spot... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
(function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-267561-2', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-267561-2', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks '); var m5c7780e466284 = document.createElement('script'); m5c7780e466284.src='https://www.sustavbolit.ru/show/?' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '= 7397&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + document.title +'&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000); function f5c7780e466284() { if(!self.medtizer) { self.medtizer = 7397; document.body.appendChild(m5c7780e466284); } else { setTimeout('f5c7780e466284()',200); } } f5c7780e466284(); window.RESOURCE_O1B2L3 = 'kalinom.ru';EtoSustav.ru » All about joints » Procedures for joint diseases
Ultrasound examination after endoprosthetics
Endoprosthetics is the replacement of a hip joint with an artificial one, which consists of metal. In this regard, patients who have undergone such surgery cannot undergo MRI, which was the main diagnostic method before surgery. It is for such patients that ultrasound is the only method of postoperative examination.
The doctor may order an ultrasound examination in the postoperative period if the following symptoms are present:
- temperature;
- pain;
- limited mobility;
- discharge from the wound;
- shortening of the limb;
- inability to lean on the leg.
Postoperative ultrasound examination can reveal the following complications:
- hematoma;
- infection;
- intra-articular effusion (fluid accumulation in the joint cavity);
- abscess.
This type of study is the most informative in identifying postoperative inflammation, as it shows soft tissue around the joint.
What an ultrasound protocol may contain
Based on the results of the study, the patient is given an ultrasound protocol and a photograph so that the doctor can additionally view the images and draw his own conclusions. The ultrasound protocol received by the patient may contain the following points:
- Contours of the head and neck of the femur: deformed, not deformed.
- Fluid content in the cervical-capsular space: yes, no
- Contours of the greater trochanters: smooth, not smooth.
- The thickness of the anterior muscle group, indicated in mm.
- Echogenicity of the anterior muscle group: increased, not increased.
- Epiphysis: flattened, not flattened.
All these points are accompanied by comments. If everything is in order in the organ, then the doctor makes a note that no pathological changes were found.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/_67OH4zsoAc