Author
Feshchenko Svetlana Yurievna
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Endocrinologist
until October 31
Prevention of fractures: diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis with a 20% discount More details All promotions
Densitometry
(another name
for osteodensitometry
) is an x-ray examination that allows you to determine the mineral density of bone tissue.
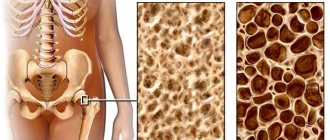
As osteoporosis develops, bone density decreases, bones become less elastic and strong, and the risk of fractures increases. Densitometry can detect bone degradation in the early stages, whereas conventional radiography cannot detect bone loss of less than 25-30%.
An important advantage of densitometry is the low level of radiation - 10 times less than with radiography.
When is densitometry recommended?
Indications for densitometry are:
- age over 50 years;
- for women – the onset of menopause;
- endocrine and rheumatic diseases;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- underweight;
- long history of smoking.
A fracture may be a consequence of bone tissue degradation. Therefore, in the case of a fracture, densitometry is highly desirable. Early treatment will reduce the risk of future fractures.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → If the bones are fragile. Osteoporosis: diagnosis, treatment, prevention
How to restore bone density? When should you undergo densitometry? A septic specialist answered these and other questions from readers during a direct line in the press center.
How to restore bone density? When should you undergo densitometry? These and other questions from readers were answered during a direct line in the press center by the chief freelance rheumatologist of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, Associate Professor of the Department of Cardiology and Internal Medicine of the Belarusian State Medical University, Candidate of Medical Sciences Natalya MARTUSEVICH.
- Diagnosis: “osteopenia, osteoporosis of the lumbosacral vertebra.” The conclusion says: “DHA-2,4.” What it is? Are calcium supplements really deposited in the kidneys? Should Colecalciferol be taken continuously? Svetlana Vladimirovna, Minsk
— When performing densitometry, the bone mineral density (BMD) is assessed. Absolute BMD values (in g/cm²) have no clinical significance. The examination results are assessed using two parameters: T-criterion and Z-criterion. T-criterion - the ratio of the obtained value of bone density to the average (norm) indicator. It is the T-criterion that is used to diagnose osteoporosis. Z-score is the ratio of bone density to the age norm. This criterion is used to judge whether the patient’s BMD corresponds to his age. If the Z-score is less than expected (for example, less than -2.0), the reason for the decrease or delay in achieving optimal BMD should be sought among factors such as diseases or poor lifestyle. WHO proposed diagnosing osteoporosis and osteopenia in postmenopausal women using the T-criterion at any part of the skeleton.
Your T-score is -2.4, which indicates the presence of osteopenia.
There is currently no evidence base regarding the effect/lack of effect of drugs containing calcium on the risk of stone formation. The risk of developing urolithiasis increases in the following cases: with the development of hypo- or hypercalcemia (which is more significant for people taking calcium and vitamin D supplements), as well as in the presence of other, no less significant risk factors - urodynamic disorders, urinary tract infections, etc. The use of drugs with colecalciferols in Belarus is indicated from November to April, in other months, taking into account the increase in solar activity, you can take a break. The duration of treatment is long, for years. MEANINGS OF NORM AND PATHOLOGY
| T-test | Diagnosis |
| > -1,0 | norm |
| -1.0 to -2.5 | osteopenia |
| -2.5 or less | osteoporosis |
| less than -2.5 and in the presence of one or more fractures | severe osteoporosis |
- I was diagnosed with osteoporosis L-1-4 of the lower part, osteopenia of the necks and subpocket parts of the femurs, coxarthrosis on both legs of the 1st degree. I have been taking alendronic acid and calcium for a year now. Do I need to replace alendronic acid with something? Is it necessary to take omeprazole in parallel with it to protect the stomach and can it be combined with chondroprotectors? Tamara Nikolaevna Ladieva, Shklov
— Alendronic acid (a representative of the group of bisphosphonates) in combination with calcium and vitamin D preparations is an effective regimen for the treatment of osteoporosis, requiring long-term use. The question of the advisability of continuing treatment and its correction is decided by the doctor, as a rule, after assessing the effectiveness of treatment - based on the degree of increase in BMD according to the results of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (densitometry). The use of omeprazole in short short courses is possible in case of symptoms of damage to the stomach (esophagus), which are determined by the doctor. The basis of prevention for such changes is following the recommendations for taking alendronic acid with the obligatory stay in an upright position after using it. Long-term (months) use of omeprazole is not recommended, given its effect on long-term use on BMD (decrease). The use of chondroprotectors and alendronic acid in joint courses is possible.
- I am 70 years old. The diagnosis was “osteoporosis of the lower spine and both hip bones, coxorthrosis of the 2nd degree”, established 8 years ago. Treatment was carried out repeatedly, with no success. Osteoporosis below the age norm (corticosteroid). I take calcium supplements. Do I need them? If yes, how long should I take them? How to restore bone density? Svetlana Mashegirova
— To choose the right tactics for your treatment, you need to make sure that you have osteoporosis. To do this, it is necessary to assess the initial state of the BMD using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (densitometry). The referral for this study, if indicated, is carried out by a doctor. If there are changes on the radiograph characteristic of osteoporosis (vertebral fractures), a significant decrease in height, densitometry is not necessary to make a diagnosis and select the correct treatment. The effectiveness of osteoporosis treatment is determined by the doctor based on the degree of increase in BMD over the year using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Taking calcium and vitamin D supplements when taking glucocorticoid hormones is mandatory, as it reduces the risk of bone loss that develops while taking hormonal medications. In some cases, taking calcium and vitamin D supplements may not be enough, then additional medications are included in the treatment regimen (determined by the doctor).
- The instructions for calcium supplements indicate that when taking them for a long time, it is necessary to monitor the calcium and creatinine levels in the blood. How often should it be checked? Which doctor should be consulted if these indicators deviate from the norm?
- What food is most effective to take calcium supplements with?
- Do patients with osteoporosis and a disability group have the right to receive bisphosphonates, free of charge or at least with reduced payment?
- Can patients from the Minsk region undergo free densitometry if indicated (for example, with steroid osteoporosis, after treatment with bisphosphonates, over the age of 60 years with pain and fractures)? The local therapist replies that densitometry can only be done for a fee, regardless of the indications and categories of citizens.
Oksana Valerievna Azanovich, ROOBRZ “Road to Life”
- — The prophylactic dose of calcium, which is usually used (1000 mg/day), does not require monitoring of creatinine and calcium levels in the blood. If the patient has hypo- or hypercalcemia, the general practitioner determines a list of examinations to clarify the cause of the identified changes.
- It is optimal to take calcium supplements after meals.
- There is a list of diseases for which patients receive certain drugs free of charge, but osteoporosis is not included in it. At the same time, alendronic acid is included in the list of vital drugs. People with a disability group can receive alendronic acid with certain benefits, but not for free. Zoledronic acid is administered only in a hospital setting.
- Yes, they can with the direction of a therapist if there are indications. Densitometry is performed at the Minsk Regional Clinical Hospital.
'Arguments and Facts' in Belarus No. 06 , February 07, 2017
Share
Preparation and time of the study:
Densitometry of the lumbar spine does not require any preliminary preparation. The procedure itself is completely painless. Study time – 2-3 minutes.
Eat as usual, but stop taking calcium supplements at least 24 hours before your test. Wear loose, comfortable clothing without metal fasteners, belts or buttons.
If you have recently had a barium test or computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast agent or radioisotope scan, tell your doctor; You may have to wait 7-10 days before doing the test.
If there is any chance that you are pregnant, tell your doctor.
Dose load : 0.03 mSv
BONE DENSITOMETRY IS A NON-INVASIVE AND ABSOLUTELY PAINLESS EXAMINATION, REMINDING US ALL OF THE FAMILIAR RADIOGRAPHY.
A pacemaker is not a contraindication to standard densitometry.
Contraindications for the “whole body” are: pregnancy, lactation, endoprostheses, pacemaker.
Contraindications for performing densitometry of the lumbar spine:
- the presence of fractures of the lumbar vertebral bodies (these vertebrae are excluded from the study), as well as the presence of metal structures after operations on the lumbar vertebrae
- pronounced degenerative-dystrophic changes (osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine)
- undergoing an X-ray examination using a contrast agent (barium suspension or water-soluble contrast agent) less than 10 days before densitometry.
- presence of pregnancy
Computer diagnostic methods
Computer densitometry methods allow not only to measure mineral density, but also to obtain a three-dimensional image of the structures of the outer and cancellous layers of bone. This helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and also provides data necessary for surgical interventions.
The computed tomography (CT) method is based on layer-by-layer scanning of bone tissue using thin beams of X-ray radiation. The radiation dose for CT is slightly higher than for X-ray bone densitometry. This examination is not applicable for pregnant women, but for others it can be repeated once every six months. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the effect of electromagnetic waves on atomic nuclei. This method allows you to visualize the structure of bone tissue. Unlike CT, the MRI method is harmless and has no restrictions on its use, except in cases where the patient has metal implants in the body. MRI can be used to diagnose pregnant women.
Ultrasonography
Patients who are prescribed ultrasound densitometry are interested in what it is. This examination is performed using a special ultrasound machine that generates waves with a frequency of 20–1000 kHz. The device analyzes the propagation speed and broadband attenuation of ultrasound as it passes through bone tissue.
Ultrasonic waves cause microvibrations of bone tissue, which depend on its mechanical and structural properties. By measuring the parameters of these vibrations, it is possible to assess the condition of the surface and internal structures of bones and joints. The device uses a special program that compares the data obtained with standard indicators for different age categories. Ultrasound examinations are harmless, they can be used without restrictions, including for examination at any stage of pregnancy.
Features of densitometry
The examination has several varieties, differing in technique, and the most accurate among them is dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (can be found under the simplified name “X-ray densitometry”). This is exactly the procedure that is carried out in our clinic. Its effectiveness is so high that it allows you to identify the slightest deviations from the norm.
In any case, this procedure is relatively quick (5-10 to 30 minutes) and painless. But regardless of what kind of densitometry will be performed, where you decide to do it, before the examination you need to follow a few simple rules.
How is the densitometry procedure performed?
Those who are undergoing a densitometric examination need to know how bone densitometry is performed and prepare for the fact that they will have to remain completely still for some time, otherwise the pictures may be blurry. Depending on the chosen diagnostic method, the procedure can be carried out differently, but in general it goes like this:
- The patient is placed on a flat surface, upholstered with soft material, and asked to take a certain position. The spine examination is usually performed in the supine position, with the lower legs placed on an elevation so that the lumbar region is in contact with the table.
- The radiation source is usually located under the table, and the sensor is located above the patient's body. They move synchronously along the area under study and transmit the received data to the computer.
- During densitometry of the hip joint, the foot is fixed in a holder, which rotates the femur into the desired position.
- If an examination of the bones of an arm or leg is performed, the limb is placed inside the cavity of a special apparatus.
The procedure does not cause pain or discomfort, its duration ranges from half an hour (examination of the spine and hip joints) to 5–10 minutes (examination of the limb). At the end of the procedure, the orthopedist determines the bone density and issues a printout with the results.
Research methodology:
Before densitometry, the patient reports his height and weight. It is necessary to remove clothing with metal elements (buttons, buckles, fasteners). During densitometry, the patient is on a special table in a supine position, the legs are bent at the hip and knee joints and placed on a special cube. The area of 4 lumbar vertebrae (from the 1st to the 4th) is scanned with X-rays, and a special sensor measures the degree of absorption of passing rays, on the basis of which a graph is constructed. If it is not possible to measure all four vertebrae, three or two vertebrae can be used. A vertebra with anatomical changes may be excluded from analysis if it is clearly pathological and cannot be interpreted within the system, or if the difference between the analyzed vertebra and the adjacent one is more than 1.0SD. Densitometry calculates the mineral density of bone tissue of the vertebral bodies.
Decoding the results
The data obtained are assessed according to two criteria - T and Z. The T-criterion shows how the patient’s bone density indicators differ from the norms for young people of the same sex. A value less than -2.5 indicates osteoporosis with a high risk of fractures. The Z-score characterizes bone density in comparison with norms for people of suitable age. If this indicator is negative, then bone density is below age norms.
Now that we know what densitometry is and how it is performed, all that remains is to choose the right clinic for diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis. The accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment depend on the level of equipment used, as well as on the qualifications and experience of doctors.
Our clinic is equipped with the latest densitometry equipment and employs the best specialists in Moscow. We use the most accurate diagnostic programs and effective treatment protocols, which allow us to detect osteoporosis at the initial stage and successfully treat it.
Types of densitometric studies
Most often, densitometry of the pelvis, hip joints and spine is performed, but according to indications, examination of the limbs, jaws, and teeth may be prescribed. Depending on the devices used, the following types of densitometry are distinguished:
- X-ray;
- ultrasonic;
- computer
The latter is divided into MRI and CT (magnetic resonance and computed tomography). For each patient, the doctor selects the optimal research method, taking into account contraindications.
In our clinic you can undergo diagnostics and treatment of the spine and joints. We use the latest equipment, which allows us to accurately determine densitometric parameters in one procedure and obtain a three-dimensional image of the vertebrae and hip joints to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the most effective therapy.
Contraindications to the procedure
There are no absolute contraindications to densitometry. There are only some restrictions. At any stage of pregnancy, it is prohibited to use methods using x-ray radiation - x-ray densitometry and CT. During this period, only the use of ultrasound densitometry and MRI is allowed.
Densitometry is also impossible if the patient, due to pain or other reasons, is unable to take the position required for the examination and maintain it during the entire procedure.