home
/
Branches and centers
/
Back Pain Treatment Center
/
What is spondylosis deformans? Spondyloarthrosis? Spondylolisthesis?
Branches and centers
Treatment methods
Diagnostic methods
Diseases and symptoms
These questions may arise in a patient's mind after a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the spine is performed. These terms are often used in the MRI report. Are these conditions independent diseases and why are they dangerous?
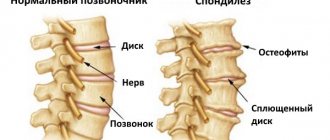
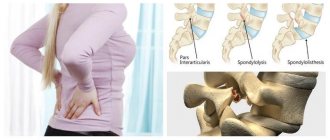
Spondylosis deformans
usually accompanies spinal osteochondrosis and is manifested by calcification of the edges of the intervertebral discs and the formation of bone outgrowths (osteophytes) along the edges of the vertebral bodies. This is the age-related process of “aging” of the spinal column. For many years it occurs without symptoms. Progression leads to limited mobility and periodic pain in the neck, interscapular region and lower back. Large osteophytes put pressure on the nerve fibers and vessels of the spinal column, which is manifested by “lumbago” in the back, girdle pain in the chest, dizziness and headache.
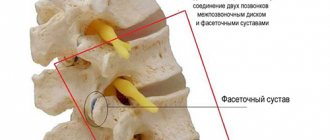
Spondyloarthrosis
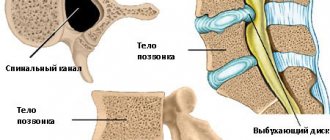
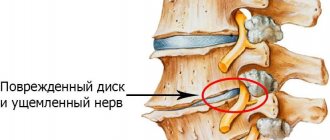
is a chronic inflammation of the small “facet” joints of the spine. A characteristic manifestation is back pain during active physical activity: bending, straightening and rotating the body. Spondyloarthrosis is often accompanied by thickening (hypertrophy) of the yellow ligaments between the vertebrae. Hypertrophy of the yellow ligaments and arthrosis of the “facet” joint leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramen. Symptoms of compression of the spinal nerve root occur (as with a herniated disc): pain radiating to the arm, leg, a feeling of “pins and needles”, decreased sensitivity and strength of the fingers and toes.
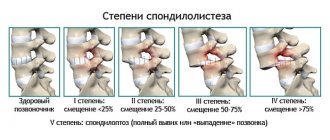
Spondylolisthesis
- displacement (slipping) of a vertebra relative to the underlying vertebra. The main reason: the inability of the spinal ligaments to hold adjacent vertebrae on top of each other (spinal motion segment instability). Spondylolisthesis can be the result of trauma or damage to the spine due to heavy physical or sports activities. Congenital listhesis is formed due to dysplasia (disorder of vertebral development) in childhood; age-related, involutive against the background of progression of osteoporosis, osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernias. There are anterior (antelisthesis), posterior (retrolisthesis) and lateral displacement. The patient experiences acute pain in the back when bending slightly, for example, “back jamming” when bending over the sink while washing. Other characteristic symptoms: decreased strength and sensitivity in the legs, are associated with compression of the roots and spinal cord with severe spondylolisthesis. When examined, there may be a “step” or a depression at the site of displacement of the vertebra. Displacement of the vertebrae leads to deformation of the spinal column, narrowing of the spinal canal and requires mandatory consultation with a vertebrologist or orthopedist.
The main methods for diagnosing spondylosis and spondylolisthesis are radiography of the spine, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). Osteoporosis is diagnosed using ultrasound and x-ray densitometry, determining the level of calcium and vitamin D3 in the blood. Electromyography (EMG) will assess the conduction and degree of compression of the roots and nerves of the limbs.
Treatment of Spondylosis and Spondyloarthrosis in Samara
Treatment is aimed at reducing pain in the spine, relaxing the back muscles, and as a result, increasing the range of active movements. Complex therapy includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and chondroprotectors. In order to improve blood flow in the vertebral artery basin and facilitate venous outflow from the spine, mesoinjection therapy is used. If osteoporosis is detected, the doctor will prescribe vitamin D3 and calcium supplements, as well as bone tissue formation stimulants.
To quickly relieve pain, it is important to prescribe high-tech hardware techniques. The use of shock wave therapy is aimed at reducing muscle spasm and inflammation of the facet joints, improving blood supply to the spine and restoring the bone structure of damaged vertebrae. Peripheral magnetic stimulation “evens out” muscle tone at the epicenter of pain, stimulates blood circulation and conduction along the peripheral nerves of the back and limbs. Another method of magnetic stimulation is also actively used on the Multimag magnetotherapeutic complex. Its action helps restore damaged spinal joints and reduce inflammation in them, soothes and relaxes the back muscles, and stimulates the functions of the brain and spinal cord. To improve the trophism of the nerves and musculoskeletal system of the spinal column, Khivamat therapy is prescribed. Electrostatic impulses create deeply penetrating vibrations in the tissues, which leads to effective pain relief and reduction of inflammation in the joints of the spine, improving lymphatic and venous drainage of the back tissues.
In the treatment of spondylolisthesis, in addition to medication and physiotherapeutic methods, orthopedic corsets are used to fix the spine and limit instability between the vertebrae. If the displacement of the vertebrae increases and neurological symptoms appear (decreased strength and sensitivity in the legs, urinary incontinence, changes in gait), surgical treatment is indicated: immobilization of 2-3 adjacent vertebrae (spinal fusion).
It is important to note that all 3 pathological processes (spondylosis, spondyloathrosis, spondylolisthesis) develop very slowly. Initially, they do not have characteristic symptoms, manifesting only periodic pain in the back and neck during physical activity. Often, diagnosis is carried out after the appearance of symptoms from the spinal cord and a violation of the musculoskeletal function of the spine. It is necessary not to miss the first “calls” of the disease, consult a neurologist-vertebrologist and orthopedist in a timely manner and conduct a spinal examination. At the initial stages, these pathologies can be effectively treated using physiotherapeutic techniques, physical therapy and posture correction.
Shock wave therapy: mechanisms of therapeutic action
A shock wave is a sound pulse emitted in a short period of time (1 microsecond) and having a high pressure (3-20 MPa). As a result of short-term exposure to the tissues of the human body, the following changes develop in the latter:
- capillaries expand, blood supply improves;
- pain is relieved due to the effect on nerve receptors;
- due to the production of certain enzymes, the penetration of drugs into cells is improved;
- a new vascular network is formed in the area of impact of shock waves;
- osteophytes are destroyed, their fragments are excreted along with lymph and blood;
- areas of fibrosis soften.
Due to the impact of shock waves on the tissues of the spinal column, pain is reduced and spinal mobility is restored.
Rice. 4. Shock wave treatment for spondylopathies
Read also
Cervicobrachialgia
Cervicobrachialgia is a condition caused by compression of the nerve structures related to the spinal nerves C5, C6, C7 and C8, which mainly causes neck pain and pain in one or both upper limbs…
Read More
Spondylosis of the cervical spine
It just so happens that patients very often associate any pain in the back or neck with the presence of a herniated disc, and with nothing more. That's understandable! Scrolling through your news feed on Instagram you will definitely come across an advertisement...
More details
Pathological kyphosis
Our spine, contrary to popular belief, is not straight. And he should not strive for directness, but quite the opposite. It has 4 physiological curves - 2 lordosis and 2 kyphosis, which make it much...
More details
Thoracalgia
Thoracalgia is pain localized in the chest, the intensity of which varies from dull, aching to sharp, sharp pain. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the neck, lower jaw, back, one...
More details
Scoliosis and posture disorders
Unfortunately, parents, in the overwhelming majority of cases, do not want to notice the problem of their child’s curved back and correct it in a timely manner. The reasons for this are varied. Beginning…
More details
What is more dangerous: hernia or spondyloarthrosis?
All patients ask a logical question: what is more dangerous – a hernia or spondyloarthrosis? The answer cannot be clear-cut. Both conditions are equally dangerous for human health. But in terms of the prognosis of the treatment, everything depends on the stage. If an intervertebral hernia can be treated successfully using manual therapy methods at almost any stage, regardless of its size and location, then with spondyloarthrosis everything is different.
This disease, in principle, can be treated conservatively only if at least remnants of the cartilaginous synovial layer on the heads of the bones inside the joint are preserved. If all the cartilage has already been destroyed, then nothing can be done. The patient will have to come to terms with the fact that inevitably his spine in the segment where the affected joints are located will lose its flexibility and mobility.
As spondyloarthrosis develops, the bone heads will fuse together. First, ankylosis will develop, then complete contracture. Using manual therapy methods, it is possible to cure a large intervertebral hernia, provided that it is not sequestered. But spondyloarthrosis can be cured using manual therapy methods only at the 1st and 2nd stages. When moving to the 3rd stage of development of spondyloarthrosis, a chiropractor can only alleviate the patient’s suffering, improve his quality of life, and delay the moment when the spinal column begins to completely lose its flexibility and mobility.
Spinal hernia and spondyloarthrosis give a characteristic clinical picture - it includes the following symptoms:
- pain in the affected area (if it is a herniated disc L5-S1, then the pain is localized in the lower back and sacrum);
- spread of pain along the affected radicular nerve (with a lumbar hernia, this may radiate along the leg or anterior abdominal wall);
- numbness of certain parts of the body;
- decreased muscle strength;
- decreased intensity of tendon reflexes;
- limited mobility;
- excessive tension of the muscle fiber in the lesion of the intervertebral disc and joint.
If such clinical signs appear, you should immediately consult a vertebrologist or neurologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe examinations. They begin with an X-ray of the affected part of the spinal column. Based on this result, it is possible to exclude the possibility of cracks and fractures and the development of osteophytes. An experienced doctor will see a decrease in the height of the intervertebral spaces and destruction of the joint. To clarify the diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct an MRI examination.
Causes
This disease is not as rare as it seems at first glance. Basically, every third elderly person suffers from it. In younger people, it occurs only after reaching the age of over thirty years. However, we can safely say that spondyloarthrosis is diagnosed less often in them, and those who are diagnosed with it are more likely to be the exception rather than the rule.
To study Compression fracture of the spine in children
As a rule, the main cause of spondyloarthrosis is osteochondrosis. There are other reasons too.
Table No. 1. Causes of the disease in different age categories of people.
| Young people | Aged people |
| Initially incorrect development of the spine. Spondylolysis. Various types of injuries received during sports or during work. Microtraumas that have not been treated. Incorrect posture. | Metabolic disorders. Providing a strong load on the spine (as a rule, this applies to people over fifty years of age). Long-term work at a computer in a sitting position. |
There is another reason that is common in both categories of people – flat feet. It directly affects a person's gait. If you have this disease, a person suffers greatly, since a large load is placed on the spine.
Disease prevention
Spondyloarthrosis is a functional disorder, therefore, to prevent its development in risk groups, it is necessary to regularly conduct a medical examination. It will allow timely detection of vertebral destruction and take the necessary measures.
In addition, the following recommendations should be taken into account:
- Maintaining optimal weight through optimal exercise and balanced nutrition.
- Refusal of excessive physical activity (sports, professional, household).
- Timely treatment of emerging inflammatory diseases.
- Regular walks in the fresh air.
- A balanced diet enriched with vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
- Properly selected bedding (pillow, mattress).
- Avoid injury or constant mechanical impact on the spine.
- Wearing orthopedic shoes or using special insoles.
- Constantly monitor your posture, which will ensure normal blood circulation in the back.
To study Ankylosing spondylitis - diagnosis and treatment
If you have a sedentary lifestyle or work in an office, it is recommended to take breaks from time to time and do simple exercises. They will help you warm up and eliminate the possibility of stagnant processes in the body.
Spondyloarthrosis is a dangerous pathology that is treated comprehensively. Drugs and various physiotherapy techniques are prescribed individually, depending on whether the patient has contraindications to certain groups of medications.
Symptoms
Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine is characterized by several clinical manifestations:
- Pain syndrome. As the inflammatory process develops, severe pain occurs in the affected segment of the vertebral part. The initial stage of the disease is not accompanied by significant discomfort and practically does not attract the patient’s attention. This is one of the reasons for delaying seeing a doctor.
- At stages 1 and 2, the manifestations of pathology are not so strong as to limit mobility. There is only increased fatigue of the back after a long walk. At stages 3 and 4, functionality is reduced to a minimum. Due to pain and a feeling of stiffness in the back, the patient loses the ability to self-care.
- Dizziness, problems with the vestibular system.
- Headache of varying nature and intensity.
- Paresthesia is an imaginary sensation of insects moving around the body; the patient feels as if goosebumps are moving across his skin. This causes psychological discomfort.
There is unusual weakness in the arms. An attempt to lean forward or to the sides is accompanied by acute pain and the need to change the position of the body.
General information
Spondyloarthrosis is chronic and first affects cartilage tissue, after which it spreads to the bones. Gradually, osteophytes (bone growths) form, which can cause severe pain and deformation of the vertebrae. Destroyed intervertebral joints, in turn, provoke problems with blood vessels and nerve endings. The result is dysfunction of internal organs (heart, lungs and gastrointestinal tract).
Gradually, spondyloarthrosis can damage the entire spinal column, but this usually takes several decades. Cartilage tissue does not immediately lose its elasticity, and in most cases this occurs due to an acute disruption of its nutrition. Over time, it becomes thinner, cracks appear, and the joint tissue becomes inflamed.
The growth of bone tissue is considered a natural response of the body to destabilization of the intervertebral joint. But this happens unevenly, so small tubercles, antennae and spines appear. Such processes are called osteophytes. They are the ones who limit the mobility of the ridge. Characteristic changes occur not only in bones, but also in muscles. The patient feels this as a spasm, which leads to the development of intercostal neuralgia.
Diagnostics
The presence of the disease can be detected through the following types of research:
- Questioning, inspection. The specialist learns important information from the patient’s medical history – previous pathologies, injuries; features of work.
- Laboratory analysis of blood and urine. An increase in the level of leukocytes is detected in the media, which indicates the presence of an active inflammatory process.
- X-ray examination.
- MRI, CT - complex radiation imaging methods are aimed at determining the spectrum of the lesion and the stage of the disease.
Other diagnostic procedures depend on the characteristics of the disease and associated disorders.
Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine is a serious disease. It involves laboratory and hardware diagnostics. The patient’s task is not to interrupt the therapeutic course at the first signs of improvement. Positive dynamics are not yet a sign of complete elimination of inflammation.