A tendon is a formation of connective tissue, part of the structure of striated muscles that ensure their attachment to bones. Tendon rupture occurs in the area where it transitions into muscle or attaches to bone tissue. The latter case is also characterized by separation of the adjacent bone or muscle.
The cause of rupture of the Achilles or other tendons is its excessive stretching by a spasmodically contracted muscle. But there are also cases when direct trauma becomes the determining factor.
You can undergo treatment for a tendon rupture in the leg or arm at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. Our specialists will make every effort to ensure that recovery occurs as quickly as possible, and you can lead your normal lifestyle again.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Clinical manifestations of tendon ruptures
One of the most common injuries is a rupture of the Achilles tendon at the heel. Often there is also a rupture of the tendons of the shoulder joint, a separation of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris muscle from the patella or the triceps brachii muscle from the elbow. Often people come to our clinic for treatment of an injury such as a rupture of the extensor tendon of the finger.
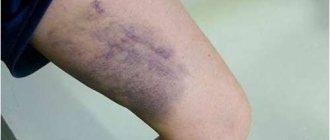
The symptoms of injury directly depend on which tendon is injured and the degree of damage. Thus, the symptoms of an Achilles tendon rupture can be expressed in mild pain and slight swelling of the ankle in grade 1 or in severe pain and swelling of the joint.
In general, the symptoms of ruptures are as follows:
- displacement of the muscle belly;
- defect in the tendon;
- loss of muscle function;
- limitation of mobility.
Clinical picture
How does it manifest?
In each patient, rupture of the tendons of the finger or other areas of the leg manifests itself differently, which is related to the extent of the damage. If the damage is mild, the patient may not pay much attention to the stretched tendon. Pathology comes in 3 stages, which are shown in the table:
| Degree | Nature of damage | Peculiarities |
| I | Partial tear | The leg hurts slightly in the damaged area only when walking or exercising |
| II | The stretched tendon constantly hurts and swells | |
| Partial loss of motor function of a finger or toe | ||
| III | Complete break | Muscle contraction |
| Sensation of popping in the sore spot when it ruptures | ||
| Sharp pain and blue discoloration in the affected area |
It is quite difficult to treat the last degree of deviation, in which the gap does not heal for a long time. Often it is necessary to have surgery.
Characteristic symptoms of a tendon rupture in the leg
A tendon rupture in the leg area manifests itself with various pathological signs that are difficult to ignore. The clinical picture of the pathology is as follows:
An increase in body temperature after injury indicates a rupture.
Pain syndrome, which is especially disturbing when moving the affected leg.- Impaired motor function, the patient is unable to flex/extend the limb.
- High body temperature.
- Blueness of the skin and swelling in the area where the damaged tendons are located.
- An altered external contour of the movable joint, which is localized near the area of the rupture.
- Clicking and crunching when trying to move the leg.
- Stinging sensations and numbness in the affected area.
Types of tendon ruptures
Damage to the tendons of the fingers and hand - appears when working in factories and factories during emergencies. Rarely, injury occurs during cooking (cutting meat with a heavy knife). There is a loss of flexion and extension function of the fingers. Treatment is carried out only in the hospital. This includes PST of the affected area and the application of a primary tendon suture (metal, nylon, nylon). The treatment method depends on the severity of the damage. Treatment should begin no later than 12 hours after the injury. First, the wound is cleaned and then sutured. In severe cases, a tendon graft is used to restore functionality.
Damage to the Achilles tendon - often occurs during work in industrial enterprises and has a closed and open type. Often, tissue destruction occurs in athletes asymptomatically, after which a decrease in mobility and weakness in the legs gradually appears. With a complete rupture, mobility disappears by 100%, and touching the affected area causes acute pain. Conservative therapy is carried out using immobilization with a plaster cast in the first 48 hours after injury. For old injuries, Achilles tendon plastic surgery is performed using a graft. Rehabilitation takes 3 months and includes physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
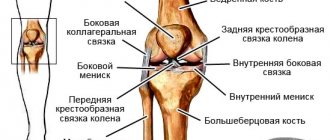
Damage to the patellar ligament is accompanied by the separation of a small part of the bone plate from the tibia. It occurs due to strong flexion of the knee joint with a tense quadriceps femoris muscle. Often the disorders are asymptomatic, after which the person experiences acute pain and decreased mobility. Treatment is surgical and involves joining the ends of the ligament with mattress sutures. Next, a cast is applied for a month, after which the recovery period begins with exercise therapy, massage, ultrasound, as well as taking antibiotics and painkillers.
Damage to the biceps tendon is a rare pathology that occurs due to sudden movement in the shoulder joint when lifting heavy weights. If a person has previously experienced weakening of muscle, cartilage and bone tissue, then the likelihood of injury increases. A slight swelling appears on the front of the shoulder. To restore tissue, an operation is used, during which the tendon is sutured using mattress sutures and drainage is performed. After this, the arm is immobilized for 21 days, and physiotherapy is prescribed.
Damage to the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle - appears due to strong physical exertion without prior warm-up and during falls. Aged athletes with degenerative changes in tissues are more prone to injury. The main symptom is acute pain when straightening the leg (decreased mobility). If the gap is complete, then immobilization is carried out for 6-7 weeks. Additionally, an operation is performed to stitch the tissues and speed up the recovery process. After this period, treatment begins, which includes ultrasound, exercise therapy, and massage.
How to treat?
In each case, the treatment of tendon ruptures is different, depending on the stage of the disorder and clinical manifestations. If there is a tear, conservative measures can be used. In this case, you need to wrap your leg with an elastic bandage, which will limit the activity of the limb. Wear the bandage for 3-5 days. It is also recommended to use medications:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- medications with analgesic effects;
- drugs that increase the outflow of venous blood - “Troxevasin”.
If the tear is 2nd degree, then the bandage is worn for 2 weeks, while the limb is kept above the level of the heart for the first day. In especially severe cases, surgical intervention is used, during which the torn tendon is sutured. Often, patients with stage 3 lesions are given a cast on the affected leg. This treatment is long-term and sometimes lasts more than 30 days. After the operation, the patient will have a long period of rehabilitation, during which medications are used and therapeutic exercises are performed to develop the joints of the lower limb.
To prevent re-rupture, you should carefully select your shoes, and women should avoid wearing high heels. It is recommended to perform light exercises daily, which involves doing shallow squats on your toes. It is also important to limit physical activity and not overload the moving joints and tendons of the legs.
Treatment of tendon rupture
Treatment for tendon ruptures directly depends on which tendon is damaged. Thus, injuries to the tendons of the hand are treated by puncturing a suture. Surgical intervention in this case is aimed at restoring the tendon bed, which eliminates the possibility of scar formation. In addition, the damaged limb is immobilized with a plaster cast, and antibiotics and analgesics are prescribed.
To restore the Achilles tendon, conservative treatment with plaster fixation for six weeks is possible. If this does not give the desired effect, surgical intervention is performed, which is aimed at connecting the ends of the tendon by applying a suture. If the injury is old, our specialists resort to plastic surgery using a graft. In addition, analgesics and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Diagnostic manipulations
If you notice symptoms of a tendon rupture, you should contact a doctor, who will immediately examine the sore leg and interview the patient. It is important to find out under what circumstances the injury occurred. Additionally, it is required to undergo instrumental examinations:
MRI is the most reliable and accurate diagnostic method.
Computed tomography. The method confirms the preliminary diagnosis and monitors the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.- MRI. The most informative diagnostic method, which determines the localization of pathology and the number of torn fibers.
- X-ray. A complication is detected in the form of a dislocation or fracture of the leg bones.
- Ultrasound examination. It is an auxiliary diagnostic method.
Prevention
To avoid tendon rupture, follow safety precautions when working in production or when preparing food.
In more than 80% of cases, injury occurs due to carelessness and haste. When doing intense sports, pay special attention to warming up. Use warming ointments and do warm-up sets before performing the exercise to avoid serious injury. If you are overweight, you need to normalize your diet and add moderate physical activity. Often, increased body weight places high stress on the joints, increasing the likelihood of injury.
We do not recommend self-medication, as it can lead to serious consequences.
What is the reason for the gap?
In women, the injury often occurs when walking quickly in high heels.
An injury in which a person ruptures a tendon can occur at any time. Mostly, the pathology is diagnosed with mechanical damage to the foot or other part of the leg. The main causes of tendon rupture:
- Squats while lifting a heavy object. Often such damage is observed in weightlifters who lift barbells. To prevent rupture, you should warm up the muscles for a long time.
- Falls that result in a person landing incorrectly on their foot and tearing a tendon.
- Sudden movements in which the foot cannot withstand the load.
- Intense physical training.
- Uncomfortable shoes.
- Congenital tendon weakness.
- Anomalies in the structure of the legs, as a result of which the load is unevenly distributed.
- Deviations of the musculoskeletal system.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues, lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 2 300 |
| MRI of soft tissues (one anatomical region) | 6 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Why surgery is needed
Ligamentous injuries accompanied by tendon rupture are among the most severe.
Tendons consist of a special tissue formed from tenocytes, cells that do not have the ability to regenerate. Therefore, if they rupture, the problem can be corrected without losing the functionality of the ligamentous apparatus only through surgical intervention. In this case, it makes no sense to apply a fixing bandage or plaster. At the same time, timely contact with a traumatologist is important. Over time, the tendon endings at the rupture sites thicken, join the adjacent tissues, and 2–3 months after the injury, they are very difficult to isolate and connect to each other. That is, the sooner you see a doctor, the higher the chances of restoring full functionality of the limb.
What to do if you are injured
First of all, you should immediately contact the SANMEDEXPERT clinic, where they will take an X-ray, conduct an examination and make an accurate diagnosis. After providing first aid, the doctors at our clinic will ensure the acceleration of the regeneration process by increasing the speed of blood circulation, using special equipment that allows you to warm up the damaged tissue, not the skin.
You should put stress on an injured tendon or ligament only after consulting a doctor, otherwise you risk getting re-injured, which will cause the development of a chronic form of inflammation. Don't self-medicate! Contact the SANMEDEXPERT clinic for qualified medical help!
2. Reasons
If the injury is not penetrating, open (cut, stab, mine-explosive, gunshot, etc.), then tendon rupture is caused by exceeding the limit of mechanical strength of collagen fibers along any axis or plane. This can be a static overload, for example, when trying to hold back an unbearable weight that has begun to tilt or slide, or a dynamic, sharp, sudden load, in the form of a jerk or turn. Examples include falls on a slippery road, unsuccessfully performed pirouettes in dancing, legs that “turned up” on an uneven surface, various reckless jumps (not taking into account distance, body weight and level of training), etc. Often, complete or partial tendon rupture is accompanied by severe complicated fractures. It should be repeated that the elasticity of tendon fibers is small: they can stretch no more than 10% of the longitudinal length. The risk factor for such an injury is constant microdamage under loads that do not reach a critical value, but, nevertheless, gradually reduce this threshold due to residual, residual degenerative changes.
Visit our Microsurgery page
Types of forearm injuries
- 1st degree. During such injuries, no bleeding occurs. Sometimes puffiness and swelling are observed. With a microtear, the integrity of the tendon and ligament tissues is preserved.
- 2nd degree. It is also called an incomplete rupture. The cross section is not completely damaged. Sometimes bleeding and swelling are observed. The patient has difficulty moving the affected joint and there is pain.
- 3rd degree. There is a complete rupture of the ligaments and tendons of the forearm. Patients complain of severe pain.
Causes and mechanism of rupture
A rupture of the distal biceps tendon is usually traumatic in nature. This injury occurs predominantly in men, as they are more likely to lift heavy objects and undergo intense physical activity.
In older people, a rupture of the head of the biceps tendon can occur for no apparent reason. This is due to age-related changes in the tendons and the consequences of microtraumas that have occurred throughout life. But the pathology often occurs in young, active men 35-40 years old. Predisposing factors are tendinitis resulting from constant microtrauma.
Professional sports and some activities that place constant stress on the biceps muscle over time make the anatomical structures vulnerable, and they rupture even with moderate force.
The injury usually occurs during sudden lifting of weight, as well as during sudden forced extension of the elbow joint. The tendon most often ruptures in the area of attachment to the scapula, the glenohumeral joint, or near the intertubercular groove.
Anatomy of the flexor tendons
Flexor tendons are divided into superficial and deep. The superficial flexor tendons are attached to the middle phalanges, and the deep flexor tendons are attached to the distal (ungual) phalanges. All tendons are located in channels in which they slide. When the muscles contract, the tendons pull the corresponding phalanges and the fingers bend. These muscles are located on the forearm.
The tendons on the back of the hand and forearm are known as extensor tendons.
The flexor tendons are held in the canals by annular ligaments. This ensures smooth bending without tension on the skin.
Damaged tendons in the forearm, wrist, palm or finger are characterized by an inability to bend.
Tendons can be damaged very easily due to the fact that they are located very close to the surface of the skin. And a fairly shallow wound to the hand will most likely result in damage to the flexor tendons.
Tendons are constantly under tension from their muscles. If the tendon is damaged, the contracted muscle pulls the proximal end (which is closer to the forearm). The damaged ends diverge far from each other, which makes it impossible for them to heal independently.
It is very important to suture the ends of the tendon in the first few days after the injury, otherwise the changes in the sheaths and tendons themselves will be irreversible and a two-stage repair will be required, which can take from 4 to 6 months of treatment.
Since the nerves and blood vessels in the hand and forearm are located next to the tendons, a shallow wound can damage them. Damage to the nerve will result in numbness on one or both sides of the finger, but damage to both digital arteries will lead to more serious consequences - severe ischemia of the finger (lack of blood supply), which can cause necrosis of the finger. This requires, of course, immediate surgery - revascularization of the finger (stitching of blood vessels).
Preparation, diagnostics
Diagnosing a tendon rupture is not difficult. Because it is accompanied by movement disorders characteristic of one or another muscle lesion. To visualize the site of damage and determine the degree of its severity, the following is prescribed:
- radiography in different projections;
- CT or MRI with layer-by-layer tissue scanning;
- Ultrasound;
- arthroscopy.
Before applying a tendon suture, you will need to take blood and urine tests and consult with an anesthesiologist.
How is tendon repair performed?
Applying a tendon suture is the simplest, safest and most effective (provided that the operation is performed by an experienced doctor) way to restore damage. Basic requirements for a tendon suture:
- the seam should be as simple as possible;
- when applying a suture, it is necessary to use as little suture material as possible;
- the suture should not disrupt the tendon blood supply;
- the seam should reliably fasten the ends of the tendons, without the possibility of them breaking apart.
There are different methods for applying a tendon suture, depending on the location of the rupture, the general condition of the adjacent tissues, for example, the suture according to Cuneo, Rozov, etc. Depending on the time of application, the following types of sutures are distinguished:
- primary - applied in the first hours after the injury;
- secondary (early and late) - applied several weeks after injury.
The doctor isolates the ends of the tendons at the site of the rupture, tightens them, suturing them in a way that will ensure the maximum result in this situation. In addition, during the intervention, the traumatologist restores not only the tendon, but also its sheath. After manipulation, a sterile bandage is applied to the wound. The operation is performed under local, epidural or general anesthesia.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
1.General information
In anatomy, a tendon is the terminal “attachment” of the striated muscle to the bone that must rotate (bend or straighten) in the joint under mechanical tension of this muscle. The structure of a tendon can be likened to the structure of a rope: the direction of muscle fibers is continued by fibers from connective tissue (collagen), forming a dense, rigid bundle. Elasticity is not required in this case - the underlying muscle tissue is sufficiently extensible and elastic - since the natural purpose of the tendon is different: to provide the most reliable and durable mechanical connection with the associated bone. Along the tendon there is a blood supply vascular network. The shape of the tendon usually follows the geometry of the muscle: broad muscles, as a rule, end in a lamellar “attachment”, and elongated muscles end in an oblong one.
A tendon rupture or tear is one of the most serious injuries. Most often this happens in sports, and especially in professional sports, where training and competitive loads have long exceeded the level that nature defines for humans as natural and even extreme (the human body is capable of withstanding much more than what we have to face in everyday modern life, but there is a limit to everything, even hidden resources). However, traumatologists have to observe similar injuries received at home, at work, and in road accidents.
Subcutaneous is any closed, i.e. not associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin, rupture of a tendon - be it the Achilles tendon, the extensor tendon of the finger or any other.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!