A sprained foot ligament is a partial or complete disruption of its integrity as a result of injury. At the time of injury, severe, acute pain occurs, and subsequently inflammatory edema and hematoma form. For mild sprains, conservative treatment methods are used - applying ointments and gels, performing physical procedures, wearing orthopedic devices. And patients with serious ligament injuries are prepared for surgery.
What are the causes of sprains?
“Sprain” is a common term in everyday life, but it misinterprets ligament damage. These strong connective tissue cords are inelastic. When exposed to loads exceeding the strength limits of the ligaments, their fibers rupture rather than stretch. The mechanisms of foot injury are different:
- rotational gap. The cause of damage to the ligaments is a sharp turn of the foot inward while simultaneously moving the leg and body forward. Such injuries are quite common when walking on slippery or uneven surfaces, and also occur while jogging;
- tucking. At the moment of unnatural rotation of the foot, tension occurs in the ligaments, which, against the background of imbalance, provokes their rupture. External connective tissue cords, which are exposed to increased loads, are more often damaged.
Joint hypermobility, wearing high-heeled shoes, previous ankle injuries, excessive physical activity, and excess weight predispose to sprains. Inflammatory or destructive-degenerative processes in the foot, the causes of which are arthritis, arthrosis, tendovaginitis, and synovitis, can provoke injury.
First aid and what to do if you sprain your foot
If you have a sprained foot, remove your shoes and socks. Do not squeeze your swollen leg. Place a soft pillow, mat or cloth under the injured joint.
The leg should be in an elevated position. Additionally, the injury site should be immobilized with a splint or elastic bandage. The patient should not experience discomfort. Cold compresses are recommended. You can buy a cold compress at the pharmacy that prevents hematomas and swelling.
If you have a sprained foot, you will need to place something under your foot to keep it elevated.
It is important to pay attention to sore toes and blue nails. This symptom indicates poor circulation in the limb. You should call an ambulance or go to an emergency room. During transportation, it is important to immobilize the limb and keep it in an elevated position.
It is strictly forbidden to stretch muscles and ligaments. In this case, the pain will increase and the healing process will slow down. In the case of a large tear or sprain, it is important to immediately apply a splint or tight bandage to the injured area.
Symptoms of injury
The leading symptoms of a foot sprain are pain, limited mobility, swelling and bruising. They do not appear immediately, but gradually. At first, a sharp pain is felt, which intensifies when trying to lean on the foot. Gradually its severity decreases, but after a few hours inflammatory edema forms. It compresses sensitive nerve endings, causing constant pain in the foot. After the swelling resolves, an extensive dark purple hematoma forms, which persists for a week. Blood cells released from damaged vessels slowly disintegrate. Therefore, the color of the bruise also changes - it becomes greenish-yellow.
Light stretch
Mild damage is characterized by ruptures of a small number of fibers. Pain occurs only at the moment of injury, and then its intensity quickly decreases. After a few hours, a slight swelling forms in the area of the ligaments, and if a hematoma forms, it is mild. The victim feels pain when placing weight on the foot, but can move without any restrictions.
Medium stretch
This diagnosis is made to the victim when about 50% of the fibers are torn. Clinically, foot damage is manifested by acute pain, which intensifies when trying to take a step. A person can move independently, limping for a short distance. After about 5 hours, the foot swells, further limiting mobility. And after a few days, an extensive bruise appears at the site of the swelling.
Severe sprain
Damage of high severity - rupture of most of the fibers or their complete separation from the bone base. When injured, not only piercing pain occurs, but a crunching sound is also clearly heard. It resembles the sound that occurs when breaking a dry thick stick. The pain subsides slightly, intensifies with the formation of swelling throughout the entire foot, and sometimes on the lower part of the ankle. The resulting hematoma is also not localized at the site of the torn ligaments, but spreads to the heel and lateral surfaces of the foot. The victim is unable to put weight on his leg due to pain and loss of stability of the foot.
Big toe ligament injuries
With injuries to the first metatarsophalangeal joint or big toe, pain and swelling may initially be relatively mild, but during the first 24 hours they usually intensify, and the next day the athlete comes to training already limping.
In order to choose the most optimal treatment tactics and one way or another assess its prognosis, doctors use a special classification.
Grade 1 injuries are characterized by overstretching of the capsule and ligaments of the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Patients complain of pain along the plantar and inner surface of the first toe, swelling is minimal, and there are no hemorrhages (bruises).
Movement in the joint is slightly limited, and athletes usually retain the ability to put weight on the foot and continue training, although with some pain.
Grade 2 injuries are characterized by partial rupture of the capsule and ligaments of the first finger.
The pain is more intense, swelling and hemorrhages are pronounced. Painful sensations and defensive reactions lead to some limitation of movements in the joint.
Athletes complain of moderate pain and lameness. They cannot train at a normal level.
Grade 3 injuries are complete ruptures leading to severe pain, swelling and hemorrhage.
Locally, there is severe tenderness along both the plantar and dorsal surfaces of the big toe and the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Third degree damage leads to rupture of the plantar plate. In many cases, this type of injury is characterized by dislocation of the big toe at the first metatarsophalangeal joint, followed by spontaneous reduction.
A pronounced restriction of movement in the joint almost always develops. Athletes in such situations cannot load the inner surface of the foot and, of course, cannot continue training.
X-ray of the foot in a direct projection of a professional football player with signs of pronounced migration of the sesamoid bones.
Chronic damage to the ligaments of the first metatarsophalangeal joint is a consequence of acute injury, which at one time was missed or did not receive due attention from both doctors and the athlete himself.
This condition is characterized by long-lasting pain in the metatarsophalangeal joint and contracture of the big toe.
Due to the lack of plantar stabilizers of the joint, dorsal subluxation of the big toe develops.
Against the background of scar changes in the first metatarsophalangeal joint, hallux rigidus can form, manifested by a pronounced limitation of the mobility of the big toe.
In cases of severe injuries to the ligaments of the first finger, standard radiography is performed to exclude possible bone injuries, be it avulsions of the joint capsule with bone fragments, fractures of the sesamoid bones, dehiscence or migration of the sesamoid bones.
We consider MRI as the most informative method for visualizing ligamentous and osteochondral injuries.
MRI allows one to clearly see all types of injuries and more accurately localize possible ligament and capsule ruptures and plan surgical intervention.
MRI for severe damage to the ligaments of the first finger. A, MRI shows signs of ligament rupture and displacement of the sesamoid bone. B, MRI shows evidence of complete rupture of the medial collateral ligament while maintaining the integrity of the similar lateral ligament.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of moderate and severe ligament damage may mask periarticular and intra-articular fractures. Therefore, radiography is performed to exclude damage to bone structures. This study is also informative in case of complete separation of the ligament from the bone base. In the area of their attachment, a freely lying separate fragment is clearly visualized. Such a thin plate is part of the bone, torn off with the fibers of the connective tissue cord.
MRI and CT are performed to determine the severity of the injury, exclude damage to cartilage tissue, and assess the condition of the blood vessels. Arthroscopy is usually used when it is difficult to make a definitive diagnosis.
X-ray of the foot.
Causes
The main etiological factors are sprain or strain due to excessive load on the ligamentous apparatus of the joint, which causes stretching or rupture of the ligaments. Overstrain occurs due to repeated microtrauma of soft tissue structures, disrupting local capillary microcirculation with changes in the structure of the fibers. The problem is accompanied by infiltration (penetration) of fluids and cellular elements into the tissue.
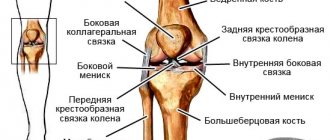
| Mechanism of ankle ligament injury. Scheme |
Sign up for treatment
Partial ruptures of connective fibers occur due to improper foot position, household and sports injuries. About 20% of people whose activities require standing for a long time complain of relapses. Among athletes, the number of joint injuries reaches 50%.
- When the sole is tucked towards itself, the talo-tibial soft tissue structures are affected.
- Eversion often results in a sprain or fracture in the medial malleolus or head of the fibula below the knee.
- Rolling up the outside of the foot injures the lateral group, which restrains excessive supination of the ankle.
- When the leg is fixed and the center of gravity is shifted forward at the moment of flexion of the lower leg, the Achilles tendon suffers.
Occasionally repeated injuries disrupt the stability of the joints, ultimately leading to wear and tear of the bone tissue.
In addition to traumatic causes, there are also degenerative ones that arise due to physiological changes. With age, due to low collagen production, the structural density and elasticity of the fibers decrease. Microtraumas and infections, deforming loads lead to inflammation and the appearance of growths on the bones - osteophytes.
Based only on the symptoms of an ankle sprain, it is impossible to make a conclusion about the patient’s condition. A differential diagnosis is needed to exclude dislocation and intra-articular fracture. In the absence of certain informative measures that determine the degree of rupture and the lesion, it is easy to make a mistake in choosing a treatment method.
Diagnostics
Before treatment for a sprained ankle begins, the patient is sent for an x-ray. Pictures in two projections with an extended and bent lower limb help to form a clinical picture. To assess the stability of the talofibial fibers, the traumatologist performs a test in parallel. One hand creates resistance when moving the ankle, the other holds the heel and moves it forward. To determine problems of the fibula, avulsion fractures of the metatarsal and talus bones, more informative diagnostics are used.
Ultrasound examination
Using high-frequency waves, specialists detect areas involved in the pathological process. On the monitor you can see signs of an ankle sprain:
- Thickening of the ligament, loss of echogenicity in the fatty tissue - the ability to reflect acoustic sound over a certain period of time.
- With partial injury, a hematoma and swollen tissue are clearly visible.
- When a complete rupture occurs, fluid is present in the tendon sheath. In this case, there are disturbances in the movement of the fibers, their intermittency is visible. There is a lot of effusion in the synovial capsule.
- With an old injury, damaged connective tissue and fibrous areas are visible.
If an ankle sprain does not go away for a long time, soft tissues are additionally scanned. This allows you to determine the condition of the fibrous capsule, blood vessels, bone surfaces, and the volume of effusion.
Magnetic resonance scanning
It is prescribed when it is not possible to differentiate the pathology by other methods. It shows:
- condition of the tendons after a sprain in the ankle joint:
- fractures;
- bleeding in the joint (hemarthrosis);
- inflammation;
- arthrosis destructive-dystrophic changes;
- purulent infections and other pathologies.
First aid
Often timely and correctly provided first aid allows you to avoid surgical intervention. Rapid relief of inflammatory swelling prevents injury to soft tissues, compression of nerve endings, and damage to small blood vessels.
| Stages of first aid to the victim | Correct provision of first aid |
| Immobilization | The victim should be placed on a hard surface, with the leg raised so that the foot is slightly higher than the chest. To do this, place a bolster or pillow under your ankle. |
| Joint fixation | To immobilize the foot, it is necessary to make a splint from available materials. If you don’t have the skills, you can fix your leg up to the knee with an elastic bandage or a special compression bandage |
| Cold compresses | Immediately after injuring the ligaments, cold should be applied to the foot: apply a plastic bag with ice cubes, wrapped in thick cloth, for 10 minutes. The procedure must be repeated every hour. If there is no ice, then a piece of frozen meat or a bag of mixed vegetables will do. |
| Taking medications | To eliminate pain, it is necessary to give the victim a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) tablet, for example, Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac |
Splint for fixing the foot and ankle.
Sprain treatment
After first aid is provided, the victim must be taken to the emergency room. Therapeutic tactics depend on the severity of the injury. If most of the ligament fibers are torn, surgical intervention is indicated. In all other cases, treatment is carried out at home.
Medication
To eliminate acute pain, intramuscular administration of NSAIDs (Movalis, Ortofen, Ketorolac) is practiced. But more often, to improve the well-being of the victim, it is enough to use tablets Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Celecoxib.
The pain persists for a week. But they are quite weakly expressed, so you can get rid of them with the help of NSAIDs for local application to the foot. These are gels and ointments: Fastum, Voltaren, Artrosilen, Dolgit.
To quickly resolve hematomas, external agents with venoprotective activity are used - Lyoton, Troxevasin, Troxerutin, Heparin.
Physiotherapy and massage
Physiotherapeutic methods for treating sprains are used during the rehabilitation phase to reduce the recovery time for damaged ligaments. The patient is prescribed 5-10 sessions of magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF therapy, and shock wave therapy. Applications with paraffin and ozokerite, electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis with B vitamins, chondroprotectors, and solutions of calcium salts are also used.
Electrophoresis for the foot.
Massage procedures can be started only after complete fusion of the torn ligaments. The most therapeutically effective are classic, acupressure, and vacuum massage.
Exercise therapy
A few weeks after the foot injury, the patient is recommended to begin physical therapy exercises, but only if the integrity of the ligaments is completely restored. The following exercises are most effective for such injuries:
- walking on the outside of the foot;
- rolling round objects, such as water bottles, with the sole;
- rotational movements of the foot;
- gripping with toes and holding small objects;
- rolling from heels to toes and back.
In the warm season, it is useful to walk on grass, sand, large and small pebbles. For home workouts, you can use special massage mats that imitate natural surfaces.
Surgical intervention
The reasons for surgery are fresh complete ruptures and instability of the joint after conservative therapy. The surgeon sews the ligaments together, and for old (more than 2 months) injuries, performs plastic surgery. In the latter case, the defect in the connective tissue cords is replaced with synthetic material or part of the tendon.
Traditional methods
It is not advisable to use folk remedies in the treatment of sprains. The ingredients of some of them can slightly ease the pain, but are not able to restore the integrity of the ligaments. Therefore, surgical intervention (plasty) is often indicated specifically for patients who have practiced treatment with folk remedies for such injuries.
Degrees of severity and characteristic symptoms
Torn foot ligaments are common in people who are actively involved in sports. This type of pathology is characterized by several degrees of severity:
- First degree. The pathology is accompanied by moderate pain. This degree is characterized by rupture of several fibers of the ligament.
- Second step. The patient experiences moderate pain. This person becomes incapacitated for a long time. There is severe swelling at the site of the twist.
- Third degree. Twisted ligaments are manifested by the rupture of most of the fibers. The patient experiences severe pain and instability in the joint.
It is impossible for a person to distinguish between a sprain and muscle damage. The severity depends on the choice of treatment method. In the foot, not only the ligamentous fibers are torn, but also the capillaries surrounding them.
The following characteristic symptoms can be identified:
- Increasing pain (worsens in the evening);
- formation of hematomas;
- impaired mobility of the injured limb;
- swelling at the site of a ruptured or dislocated ligament.
Swelling may be visually noticeable or detected by palpation. To understand the difference between a cut and a sprain, it is important to know that these injuries vary in how painful they are. When a tear occurs, the ability to move the damaged area slows down.
Complications of a sprain
Even after competent conservative or surgical treatment, fibrous foci are formed in certain areas of the ligaments, devoid of any functional activity. This leads to weakening of connective tissue structures. In the future, such injuries can cause frequent dislocations, and sometimes flat feet. In the absence of medical intervention, ligament ruptures predispose to the development of arthritis and arthrosis in the foot.
Sprain or rupture of ligaments: how to determine?
Joint ligaments are a kind of association of individual connective tissue fibers. They are designed to connect the bone elements of a particular joint, strengthen it and restrain the range of motion in the joint.
Among ligament injuries, the most common are their rupture and sprain. How does a ligament tear or sprain manifest? How can you tell if a ligament rupture or sprain occurs after a joint injury?
Ligament sprain is a pathological condition that is characterized by tearing of its individual fibers, but while maintaining the continuity of the organ in anatomical terms. The reasons for this condition may be different. It occurs with sudden and strong movements that are not characteristic of a particular joint.
Ligament rupture is a traumatic condition that occurs as a result of a complete violation of its integrity due to transverse separation of connective tissue fibers. The causes of ligament rupture are the same as for sprains, but the force that acts on the joint is much greater.
At first glance, it is impossible to understand the difference between a ligament rupture and a sprain. There is no clear difference between these pathological conditions. In both cases, the integrity of the fibers is damaged. There is one exception: in case of stretching it is partial, and in case of rupture it is complete.