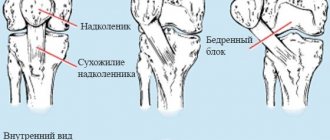
Why does my knee hurt?
The knee joint is one of the most resilient in our body. However, degenerative processes often begin in it. They occur, for example, due to a genetic predisposition - in those whose relatives have already been treated for osteoarthritis. For many, pain occurs due to external factors - poor lifestyle, bad habits, injuries.
Knee pain during extension often appears after intense physical activity. It progresses especially in older age, when the cartilage tissue wears out on its own. The most common causes that lead to pain during extension are:
- intense running;
- prolonged carrying of heavy objects;
- previous injuries;
- bacterial infections;
- age-related changes;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor circulation due to lack of movement;
- degenerative-dystrophic changes in arthrosis;
- deficiency of synovial fluid in the body;
- pinched nerve fibers.
Whatever the cause of pain during extension, knee pads will never hurt
Osteopathic doctors, representatives of alternative medicine, have their own view of knee pain:
Pain in the knee joint: treatment at the Yusupov Hospital
The main goals for the treatment of pain in the knee joint, which the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic set for themselves, are the following:
- eliminate swelling;
- relieve the patient from discomfort;
- restore the functions of the knee joint;
- prevent new attacks.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics are used to relieve pain. The use of warming and distracting ointments, as well as restorative drugs, is effective.
In the remission stage, patients are prescribed the use of physiotherapeutic techniques, massages, and therapeutic exercises.
In the absence of effectiveness from conservative therapy, specialists, taking into account all the pros and cons, consider the advisability of surgical treatment.
In addition, there are a number of traditional medicine that help reduce pain, but their use must first be discussed with specialists who monitor the progress of treatment aimed at eliminating pain in the knee joint. How to treat this pathology should only be decided by an experienced, highly qualified doctor who is familiar with the patient’s research results, the individual characteristics of his body and many other important nuances.
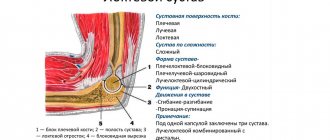
What happens when the knee extends
When we perform habitual flexion-extension movements, a huge number of structures are involved - bones, muscles, cartilage, nerve endings, synovial fluid, etc. If the knee cartilage has an integral, undamaged structure, a person does not even notice these movements. If the surface of the cartilage is destroyed, during extension the nerve endings are affected - pain and discomfort appear.
If there is not enough synovial fluid in the body, the cartilage quickly wears out because there is no lubrication between them. Damaged areas form on the surface - the joint ceases to function normally, and every extension movement causes pain.
You can partially replenish collagen reserves, which takes part in the synthesis of synovial fluid, from food products - meat and fish by-products, jellied meat. But this is usually not enough. To restore the functionality of the joint, it is better to insert the Noltrex synovial fluid prosthesis into it and stop the friction.
Does it hurt to straighten your knee? Avoid self-medication with jellied meat and gelatin
Symptoms of knee damage
There are symptoms that clearly indicate serious problems and the need to see a doctor:
- There is absolutely no mobility in the knee joint.
- Painful sensations prevent you from transferring weight to the affected leg.
- The skin in the area of the knee joint is severely hyperemic to the point of hematoma formation, the knee is swollen.
- Flexion and extension movements cause severe pain.
- Noises or clicking noises are heard in the knee while moving.
- At rest and when walking, periodic muscle spasms, numbness, weakness, and tingling are felt.
These symptoms not only cause inconvenience and constant discomfort to a person, but can also indicate sprains, microtears and tears of the ligamentous apparatus or muscles.
What diseases can cause pain in the knee when extending?
Sometimes this symptom occurs from fatigue, after active physical activity. But sometimes it accompanies serious pathologies, depending on which the nature of the pain changes:
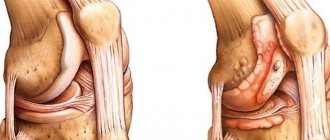
- Osteoarthritis – pain is constant and severe, intensifies with movement. If gonarthrosis is not treated, it can lead to disability.
- Arthritis - pain develops gradually, subsides in the morning and becomes more active at night. The disease is chronic inflammatory in nature. It differs from arthrosis in the presence of inflammation.
- Bursitis is intense pain, accompanied by stiffness of the knee joint. Inflammation of the knee bursa is also dangerous.
- Synovitis is a dull and aching pain that intensifies with flexion and extension. The cause is a pathological accumulation of synovial fluid in the joint.
- Osteochondrosis is a sharp pain, accompanied by pain in the back, neck, and other parts of the spine. The disease is accompanied by damage to the spine and intervertebral discs, but is also dangerous for the knees.
- Osteoporosis – the pain can be aching and dull, as well as sharp. The reason is pathological fragility of bones.
- Scoliosis is always combined with back pain due to the curvature of the spine.
Knee pain occurs due to problems with the spine
Arthritis of the knee joint
A distinctive feature of arthritis is discomfort at rest, and its weakening during movement. If arthritis continues to progress, the processes of deformation of the articular surfaces and destruction of cartilage tissue begin. At this stage, acute pain appears when the joint is extended, and redness of the skin in the knee area is noted due to inflammatory processes.
Arthritis is not limited only to local symptoms; the disease also affects other systems and organs:
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- hyperthermia with signs of intoxication;
- genitourinary system disorders, skin rashes and other symptoms.
In some cases, arthritis is aggravated by exposure to atmospheric conditions.
How to treat knee pain during extension
If your knee hurts during straightening movements, first of all, limit your activity and avoid strenuous exercise until the cause is determined. Pay attention to the shoes you wear. Perhaps your feet are tired from too high a heel or platform, and replacing the pair with a new one, with preventative orthopedic insoles, will correct the situation.
If the cause is not so obvious, consult a specialist and undergo diagnostics to determine the cause of the pain. The treatment regimen will be different in each case. For example, for arthrosis, you will be recommended painkillers, physiotherapy, and intra-articular injections to replenish the deficiency of synovial fluid. If the cause is another disease, you will be referred to a specialized specialist who will adjust the prescriptions. In any case, do not ignore this symptom, otherwise you risk losing the most important thing - the joy of free movements!
Signs of tendonitis
Tendinitis is an inflammatory lesion of the ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint. The disease belongs to the category of occupational pathologies among athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor.
Knee tendinitis develops for two reasons:
- Degenerative – impaired elasticity of ligaments due to age-related changes, metabolic disorders.
- Mechanical – constant overloads lead to gradual thinning of the tendons, and subsequently to rupture of the ligaments.
In the initial stage of tendinitis, the patient complains of mild pain after physical activity, the pain worsens both with extension and flexion of the joint.
When visiting a doctor, tendonitis is diagnosed using the following methods:
- when palpating the knee joint and pressing on the hole from the outside, the pain worsens - the disease spreads into the deep tendons;
- the patient, in a sitting position, tries to straighten the leg, and the doctor applies pressure, preventing extension - painful sensations are characteristic of partial damage to the tendons.
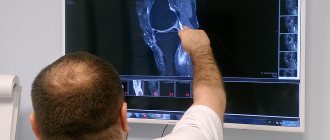
Diagnosis of pathologies using radiography, ultrasound and MRI of the knee
If the described remedies do not help, pain appears more and more often and is supplemented by accompanying symptoms, you must urgently contact an orthopedic traumatologist. If necessary, he will recommend involving other highly specialized specialists in diagnostic procedures: a surgeon, rheumatologist, oncologist or neurologist. Maple MRI is rarely used as a primary method, since mechanical damage to the area is easily detected using traditional hardware procedures (X-ray and ultrasound).
If the cause of pain is not a previous injury, but an internal disease, it is necessary to differentiate the pathology from similar articular anomalies. Classical methods are not able to cope with explaining the root cause of inflammatory processes or the appearance of tumor formations. If a pathological object was detected, diagnosticians could not clearly determine how aggressive the cells were embedded in adjacent tissues. Using tomographic research methods, this problem is solved in a short period of time.
MRI of the knee provides numerous images of the internal structures of the area being studied, in which both dense bone fibers and soft tissue formations are clearly visible. The possibility of multiple magnification allows you to examine blood and nerve channels, detect foci of infection, degenerative disorders, find the primary tumor and metastases spreading from it. The technique allows you to obtain maximum information in a short time, when the timeliness of therapy plays an important role.
Why and how does pain appear when walking on the inside of the knee, how to deal with it
The healthiest people are periodically susceptible to pain in the knee area. There are a large number of causes of pathology. And diseases manifest themselves in a variety of ways. Let's talk about this today.
Symptoms
If the disease affects the knees, the following signs can be observed:
- there is severe pain in the limb. It is difficult to walk and squat. When the situation worsens, pathology can be felt even at rest;
- the knee swells, a change in appearance is visible, which leads over time to a modification of the gait;
- in the morning it is difficult to bend and straighten the leg at the knee;
- While walking, a crunching sound is heard and pain is felt that does not go away even at night.
Causes
Pain is often felt when walking for a number of reasons:
- Ligaments are damaged. At the time of injury, a person may hear a crunching or loud click, which is replaced by acute pain in the area of the inside of the knee.
- Damage to the tendons, manifested by inflammation and irritation. A person feels pain in the knee while moving. If the tendons are completely torn, the ability to walk is lost. The situation can only be corrected by surgical intervention.
- If the meniscus is damaged, the leg swells several hours after the injury. Pain in the leg is also felt not only at the moment of movement, but also at rest.
- Joint pain
can also occur with periarthritis of the knee joint. The pathology is especially pronounced if a person changes position, squats or sits quietly. - If a Baker's cyst, otherwise called a popliteal hernia, develops, the inside of the knee hurts. A person feels his joint ache. A tumor is observed, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
- In septic arthritis, pain in the kneecap is felt due to infection of the joint. A swollen leg indicates pathology; it is difficult to bend it. The limb takes on a reddish tint. If purulent (septic) arthritis develops, the person feels severe chills and the temperature rises greatly.
- With rheumatoid arthritis, a person feels discomfort in the knee area, movements are constrained, and the knee joints are deformed. The disease manifests itself in the morning. You can observe it on the right and left knee.
- With the development of bursitis, an inflammatory process develops in the area where the synovial fluid is located, which leads to a pathological process expressed by severe pain.
The most common causes leading to painful sensations were listed. There are a number of other pathologies. Only a doctor can determine the nature of development after examining the patient.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your knees hurt, you should not self-medicate. To prevent the situation from worsening, contact a medical facility at the first signs of illness.
To determine the nature of the sensations, you should consult a rheumatologist. He will send you for a series of studies, which will determine whether osteoporosis, fibromyalgia, or osteoarthritis is developing.
It is also recommended to consult a traumatologist. The pathology is treated by a physiotherapist who prescribes therapeutic exercises. In some cases, a course of massage performed by a chiropractor will significantly ease the condition of the joints.
Diagnostics
The doctor examines the affected limb. At the same time, the specialist interviews the patient, collecting reliable data about the history of the development of the pathology. Based on this, a primary diagnosis is made.
To confirm the assumption, the doctor prescribes a whole range of different studies. Patients undergo a general blood and urine test and a biochemical blood test.
Diagnosis of the development of the disease will help:
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination;
- angiography prescribed by a phlebologist;
- full computer diagnostics.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes a puncture. Based on the diagnostic data, the subsequent treatment method is carried out.
Eliminating diseases with medicines
Treatment of the knee joint should be carried out only after diagnosing the disease. The doctor selects an individual scheme of therapeutic procedures:
- When treating minor injuries, the use of Diclofenac, Dicloberl, Movalis, analgesics, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants and vitamin complexes is prescribed. Complex injuries are eliminated through surgery.
- A damaged meniscus is treated in combination, using medications along with physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage and endoprosthetics.
- The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics, antibiotics, chondroprotectors, B vitamins, and muscle relaxants is prescribed if sprains and tendinitis are diagnosed. To quickly resolve the pathology, it is necessary to apply a tight bandage.
- If arthritis, arthrosis and a number of other diseases develop, intramuscular injections, pills, and a multivitamin complex are prescribed.
In each situation, a different treatment method is prescribed. The drugs are used in combination.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of various pathological situations, try not to fall, hit or injure your knees.
You should not gain excessive weight. At the first signs of infectious diseases, begin treatment. Lead a healthy lifestyle. If the recommendations are followed, knees will not bother a person until old age. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Evaluation of treatment effectiveness using MRI of the knee
After the reconstructive manipulations have been carried out, it is recommended to carry out preventive diagnostics, which allows us to assess the correctness of the therapy or surgical intervention. Screening evaluates the rate of tissue regeneration and the absence of recurrent processes. The study is available in specialized clinics that provide consultations in every district of the city.
The pages of the “Unified Recording Center” service provide a complete list of tomography medical organizations. Choose a service, compare ratings of institutions, location addresses and prices for procedures, mark the best offers and sign up for an examination. When registering, each portal guest receives a guaranteed discount on the selected type of hardware scanning.
Causes of pain seen on MRI of the knee
There are temporary pathological conditions, manifested in episodic joint pain, and permanent ones, indicating the development of a disease. Temporary discomfort may occur due to improper distribution of physical activity, mild to moderate injuries, a reaction to weather changes, or minor sprains of ligaments or tendons.
Chronic pain requires an urgent MRI. A knee that constantly bothers you indicates a pathology that can manifest itself as persistent discomfort or a painful syndrome that appears after walking, running, bending and straightening the legs, or squats. So, if unpleasant sensations arose after the first run, then most often this is evidence of muscle overstrain. But if the pain repeats after each race, this is a signal of meniscus damage, dislocation of the cup, rupture of ligamentous fibers or the appearance of an intervertebral hernia, which is also visualized on MRI. The knee suffers from this anomaly due to pinching of the nerve passing through the damaged vertebra.
When walking, the joint may hurt due to poor circulation or wearing uncomfortable shoes. Pain in the popliteal space occurs after an “unsuccessful” lifting of heavy objects or an injury that is not noticeable at first glance. If you experience an aching sensation when trying to sit down, go up or down stairs, this indicates the initial stage of development of arthritis or arthrosis, Schlatter's disease, or microscopic fiber sprains resulting from improper exercise.
Pain on the inside requiring an MRI of the knee
Internal pain may be accompanied by an upward change in local tissue temperature, redness of the skin, visible swelling and bruising. Caused by the following pathologies:
- arthritis;
- experience of trauma, recent or old;
- the same daily exhausting overloads;
- bone infection;
- cystic formations in the joint structure;
- osteochondritis, clearly visible on MRI of the knee.
As a result of incorrect load distribution, deformation of the “hinged” section occurs. The tissues lose their safe interaction, rub against each other, and the main pressure falls on the inside of the joint.
Types of knee injuries
Lower extremity injuries are the most common cause of knee pain. Sharp pain with blocking of joint movement indicates a partial or complete tear of the meniscus. The blockage is explained by the fact that part of the damaged meniscus enters the joint space, jamming it.
Symptoms of a meniscus tear are:
- edema and hemarthrosis;
- upon palpation below the patella, the pain worsens;
- Functionality tests by rotation and extension.
Violation of the integrity of the ligaments can also cause joint blockage. The following characteristic signs are noted:
- extension or collapse of the knee;
- deviation of the joint inward or outward;
- pain when moving.
When the ligaments are torn, the knee joint is not secured and upon examination, free mobility appears, as in a joint dislocation.
What to do if the disease is not detected on MRI images of the knee?
If the patient cannot accurately determine the intensity with which he feels pain, and the treating specialist does not observe concomitant pathological signs of known diseases, it can be assumed that the phenomenon is temporary. If the pain appears as a result of fatigue and working on your feet for a long time, it is enough to lie down for a while and increase the rest period. The absence of pain after such a break indicates the absence of the disease.
To speed up the recovery time of joints after a load or stress, you can use some folk recommendations or use an anti-inflammatory drug in the form of an ointment or gel. Herbal compresses mixed with St. John's wort, hop cones and sweet clover have proven themselves well. Sea buckthorn oil or aloe juice mixed with honey works well for inflammation.
Treatment of diseases detected on MRI of the knee
After scanning and identifying the problem, a plan for subsequent restoration of the articular area is developed. So, if the cause of pain is a severe bruise, but destruction or cracking of bone or cartilage fibers has not occurred, prolonged rest and cold compresses on the affected area are required. It is important to immobilize your leg for a while.
If, during a diagnostic MRI screening of the knee, inflammations occurring in various tissues of the articular system are detected, drug therapy is prescribed. Most often, medications are used in the form of external ointments or gels. Accompanying treatment is wearing a pressure bandage if bursitis was previously diagnosed. In some cases, internal administration of antiseptic agents is required, introduced into the source of infection through a puncture of a syringe.
Specific joint diseases are treated with targeted drug therapy. If tissue destruction is severe, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. At the remission stage, physiotherapeutic warming, massages, and courses of therapeutic exercises are traditionally used.